AI in Payroll: The Complete Business Guide for 2026

Payroll teams are under pressure from manual work, rising compliance risk, and growing cost complexity. Many know automation is needed but are unsure where to start or what actually works. In this guide, MOR Software will break down AI in payroll in a clear, practical way, showing how modern businesses can apply it to processing, management, and long-term planning in 2026 without unnecessary complexity.
What Is AI In Payroll?
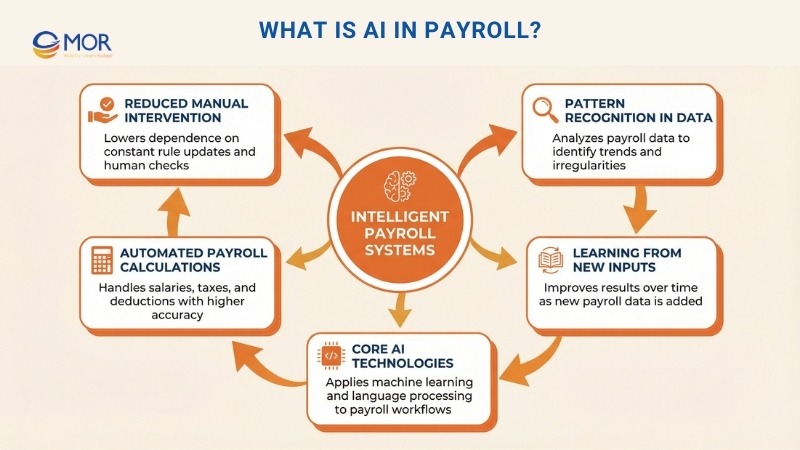
Artificial Intelligence refers to systems that can perform tasks usually handled by people, including reasoning, learning, and problem solving. In simple terms, artificial intelligence payroll solutions rely on methods like machine learning, natural language processing, and visual recognition to study data, identify patterns, and reach decisions. These technologies allow systems to improve their outputs over time as new data becomes available, without needing constant rule updates.
What Is AI In Payroll?
Within payroll environments, advanced payroll automation applies these capabilities to handle complex and time-sensitive activities, including salary calculations, tax withholdings, and statutory checks. Through AI in payroll processing, payroll platforms work faster and with fewer mistakes while reducing manual effort. This change shifts payroll away from a purely reactive task toward a structured, data-guided operation that supports better planning and control.
How AI In Payroll Is Reshaping Daily Payroll Operations
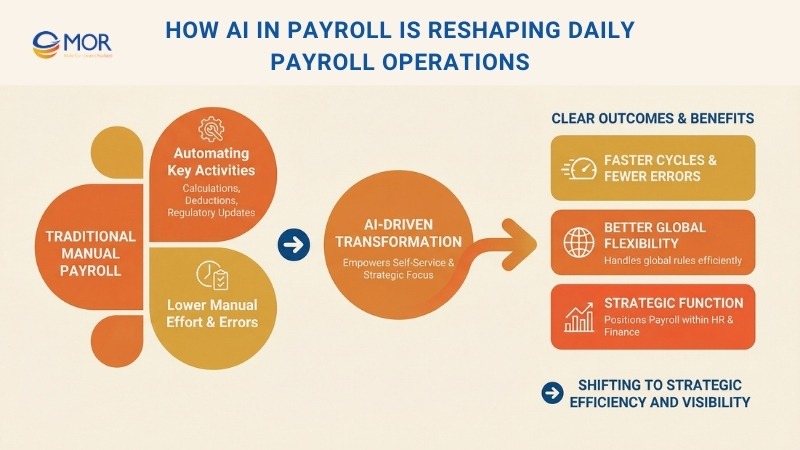
AI in payroll is changing how payroll teams handle everyday work by automating key activities like calculations, deductions, and regulatory updates, which lowers manual effort and limits human mistakes. As a result, teams gain more time to focus on higher-value work, including financial planning and compliance supervision. It also supports employee self-service tools, which increases visibility and builds confidence in payroll results.
How AI In Payroll Is Reshaping Daily Payroll Operations
Many organizations are already seeing clear outcomes, including faster payroll cycles, fewer errors, and better flexibility when dealing with global rules. This shift improves day-to-day efficiency and positions payroll as a more strategic function within HR and finance teams.
Adoption Trends And Market Signals Around AI In Payroll
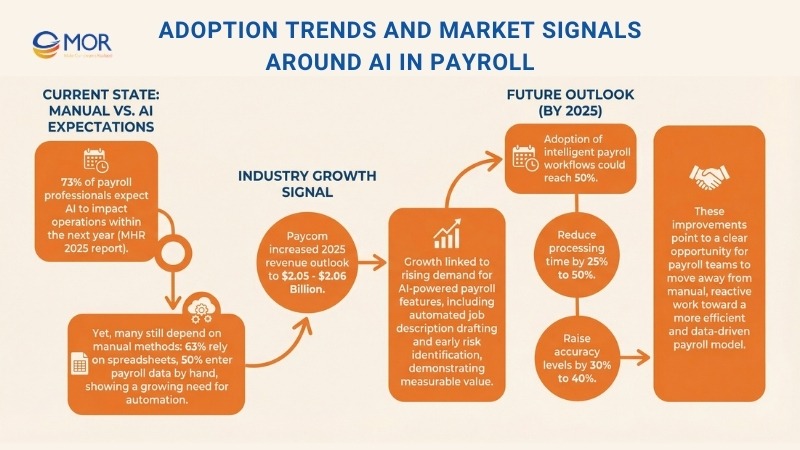
Adoption of AI in payroll continues to rise, with 73% of payroll professionals expecting it to affect their operations in a meaningful way within the next year, based on MHR’s 2025 report. Even so, many teams still depend on manual methods, as 63% rely on spreadsheets and 50% enter payroll data by hand, which shows a growing need for automation.
Adoption Trends And Market Signals Around AI In Payroll
From an industry perspective, Paycom, a well-known payroll vendor, increased its 2025 revenue outlook to between $2.05 and $2.06 billion, linking this growth to rising demand for its AI-powered payroll features. These tools support tasks like automated job description drafting and early identification of employees at risk, which highlights how payroll AI delivers measurable value across payroll and workforce operations.
Looking forward, global estimates suggest that adoption of intelligent payroll workflows could reach 50% by 2025, enabling organizations to reduce processing time by 25% to 50% and raise accuracy levels by 30% to 40%. These improvements point to a clear opportunity for payroll teams to move away from manual, reactive work toward a more efficient and data-driven payroll model.
Key Applications Of AI In Payroll
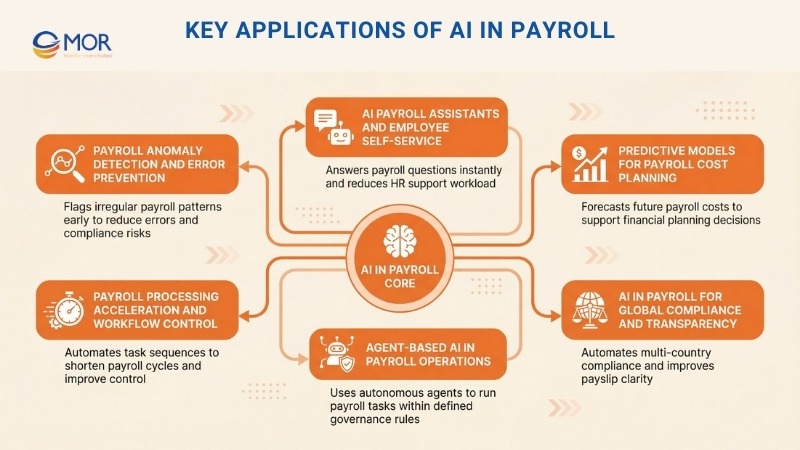
This section outlines how AI in payroll supports practical use cases that improve accuracy, control, and daily execution. Each application shows how intelligent systems now handle tasks that once required heavy manual review.
Key Applications Of AI In Payroll
1. Payroll Anomaly Detection And Error Prevention
AI-driven systems significantly improve payroll accuracy by identifying irregular patterns, including duplicate records, missing work hours, or incorrect pay codes, before payroll is finalized. Machine learning models study historical data patterns and flag unusual behavior through statistical limits and cluster-based outlier analysis. These solutions connect with time tracking tools, HRIS platforms, and pay policy data to detect issues early and with consistency.
These tools reduce the manual burden on payroll teams, since staff no longer need to perform full reconciliations for every cycle and instead receive clear alerts for exception review. Error rates that previously ranged from 1% to 8% in manual environments drop sharply when this solution is applied. This strengthens compliance, improves employee confidence, and supports reliable payroll operations at scale.
Deployment challenges include maintaining transparency in how models flag issues to avoid bias, protecting sensitive payroll data, and setting thresholds that limit false alerts. Human review still plays an important role in interpreting flagged cases within real-world context. In practice, AI in payroll shifts error handling from after-the-fact correction to early prevention.
Real-World Example:
Deloitte shared that a multinational organization using AI-driven anomaly detection lowered payroll error rates by 42% and reduced payroll processing time by 33%. These results came from embedding machine learning models directly into the payroll validation workflow.
2. Payroll Processing Acceleration And Workflow Control
AI improves payroll speed by automating task sequences such as calculations, approvals, and batch execution, which reduces manual handovers between teams. Intelligent process automation coordinates each workflow stage through event triggers and rule-based routing. This approach results in shorter payroll cycles and fewer operational slowdowns.
It also refines task order, which limits delays caused by dependencies like timesheet checks or tax updates. These platforms study past workflow issues and adjust routing in real time to increase overall throughput. Payroll teams see lower overtime demands and quicker completion using fewer internal resources.
Integration with legacy platforms and managing organizational change remain common challenges during rollout. Careful workflow design is needed to preserve compliance standards and maintain clear audit trails. When applied correctly, this approach turns traditional payroll execution into a more responsive and real-time operation.
Real-World Example:
Ignite HCM states that organizations using AI-supported payroll workflows achieve payroll runs that are up to 65% faster and lower process costs by around 30%. Their approach improves approval routing and exception handling across payroll cycles.
3. AI Payroll Assistants And Employee Self-Service
AI-powered chatbots allow employees to handle payroll questions related to deductions, benefits, and pay schedules without waiting for HR support. Using natural language processing, these assistants understand intent and pull answers from payroll systems or internal knowledge bases. This self-service approach lowers the volume of HR requests and shortens response times.
More advanced assistants manage location-specific questions, tailor replies to individual employees, and pass complex cases to human staff when needed. Connection with HRIS platforms and payroll tools keeps information current and accurate. Employees receive a reliable support experience that remains available at all times.
Data protection, response accuracy, and clear escalation rules are essential for successful rollout. These assistants need regular updates to stay aligned with policy or regulatory changes. When implemented properly, AI for payroll reduces support tickets and raises employee satisfaction.
Real-World Example:
EY and Microsoft created an AI-based payroll assistant to handle employee questions across multinational organizations, delivering consistent guidance across different compliance regions. The solution lowered HR inquiry volumes by up to 40% and improved resolution speed.
4. Agent-Based AI In Payroll Operations
Agent-based platforms allow intelligent agents to complete payroll tasks on their own while staying within defined policies. These agents validate payroll data, run payments, apply limits, and send alerts without direct human input. They connect with enterprise systems like HRMS platforms and finance applications, which supports coordinated payroll execution.
Processes that once depended on manual actions, including tax recalculations or benefit adjustments, are now managed automatically through agent-driven workflows. Human review still plays a role when agents raise exceptions or request approvals. This balance maintains speed while keeping governance and oversight intact across advanced payroll automation.
Strong governance, clear traceability, and detailed audit logs are required to keep autonomous payroll activity compliant. Responsible use of these agents depends on clear rules that define their authority and limits. When deployed with care, generative AI in payroll raises productivity without weakening accountability.
Real-World Example:
Workday’s Illuminate platform, released in 2024, uses AI agents to manage payroll-related tasks like compliance checks and document generation. The company reported a 52% improvement in accounts payable efficiency and a 49% increase in HR task automation.
5. Predictive Models For Payroll Cost Planning
AI models review historical payroll records to estimate future salary expenses, tax obligations, and labor costs with strong precision. Techniques like time series analysis and regression help detect seasonal patterns, hiring changes, and overtime increases. This supports stronger cash flow planning and more informed financial decisions.
With access to predictive insights, finance teams can prepare for workforce cost growth, bonus periods, or overtime peaks before they happen. These forecasts adapt to specific teams, regions, or pay structures as needed. This approach shifts payroll from a basic expense function to a more strategic planning tool within AI in payroll management.
Forecast quality relies on accurate input data and well-adjusted models, especially in organizations with complex staffing structures. Regular validation remains necessary to prevent cost estimates that are too high or too low. When applied correctly, AI in payroll processing supports proactive financial leadership.
Real-World Example:
Organizations using OpenLedger’s AI-based payroll forecasting tools reported a 15% to 20% improvement in labor cost forecast accuracy during Q4 2024. This improvement helped HR and finance teams align planning efforts more closely.
6. AI In Payroll For Global Compliance And Transparency
AI automates compliance checks across different regions through ongoing updates to tax rules, labor regulations, and location-specific requirements. These systems support accurate tax deductions, benefits handling, and country-level reporting without manual tracking. They also create clear, easy-to-read payslips that explain deductions and benefits in a way employees can understand.
Managing cross-border payroll becomes simpler as these platforms monitor legal changes and adjust payroll logic in real time. Employees gain clearer insight into how their pay is calculated, which builds trust and lowers the number of payroll questions. This approach helps organizations manage global payroll operations more smoothly.
Successful deployment depends on correct localization, legal review, and accurate language handling. These platforms also need to meet GDPR and other data protection standards when operating across borders. With the right controls in place, this approach makes global compliance more scalable and efficient.
Real-World Example:
Neeyamo’s global payroll platform applies AI to automate compliance checks and produce localized payslips for staff in more than 150 countries. Clients reported shorter payroll cycles and lower legal risk during 2024.
Business Benefits Of Using AI In Payroll
AI in payroll delivers clear value across payroll operations by addressing long-standing inefficiencies and reducing risk exposure. From automating repetitive work to strengthening compliance and improving pay visibility, these benefits help payroll teams become more strategic and responsive.
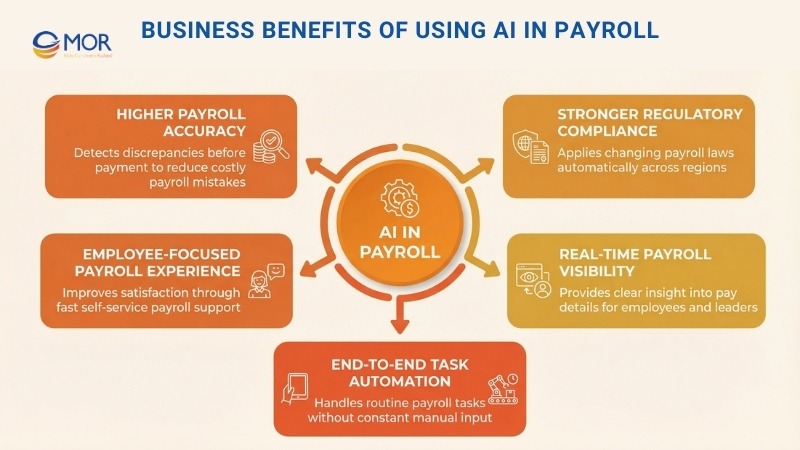
Business Benefits Of Using AI In Payroll
1. Higher Payroll Accuracy
AI increases payroll accuracy by detecting data anomalies before payments are finalized. It flags issues like duplicate records, incorrect work hours, or wrongly classified deductions that often slip through manual reviews. This reduces expensive payroll mistakes and limits the need for corrections after processing when using AI for payroll.
Real-time detection of discrepancies also helps organizations avoid compliance breaches. Automated controls reduce the risk of underpayments or overpayments that can harm employee trust and result in penalties. This forward-looking approach makes payroll more dependable and ready for audits through AI in payroll management.
2. Stronger Regulatory Compliance
Payroll rules differ across countries, regions, and employee categories. AI solutions monitor legal updates in real time and apply rule changes across payroll systems automatically. This helps payroll teams stay compliant even when managing complex, multi-location payroll structures through AI in payroll.
Using AI to support compliance lowers overall risk and reduces dependence on frequent external audits or legal advice. It also simplifies tax reporting and benefits administration by keeping calculations aligned with current laws. This brings greater confidence and flexibility to daily payroll operations.
3. Real-Time Payroll Visibility
AI supports real-time review of gross-to-net pay details, which helps employees and managers clearly see each part of a paycheck. This covers bonuses, deductions, benefits, and currency adjustments in international payroll settings. Greater transparency builds trust and lowers the number of payroll questions through AI in payroll.
For HR and finance leaders, this level of visibility improves forecasting accuracy and workforce planning. Instead of relying on reports after payroll closes, leaders can view live summaries and emerging patterns. This responsiveness strengthens planning quality and financial control.
4. End-To-End Task Automation
AI manages routine payroll activities like timesheet checks, payroll scheduling, and benefits updates without constant manual input. This lowers reliance on human data entry and reduces the chance of mistakes during busy payroll periods. Automated workflows speed up processing and keep payroll data consistent across connected systems.
When routine work is handled automatically, payroll teams gain time to focus on higher-value tasks. These may include reviewing pay models, examining labor expenses, or supporting workforce policy decisions. This shift helps build a more engaged and forward-looking payroll function with AI for payroll.
5. Employee-Focused Payroll Experience
AI chatbots provide employees with quick and accurate answers to common payroll questions. This cuts down support tickets and removes delays for simple requests. Faster responses improve overall satisfaction with payroll services through advanced payroll automation and connected AI HR software.
Self-service features also allow staff to update personal details or retrieve payroll documents without HR support. This reduces administrative effort and gives employees more control over their information. Over time, these tools create a smoother and more user-friendly payroll experience,
How To Roll Out AI In Payroll Successfully
Rolling out AI in payroll goes beyond adding new technology. It requires changes in how teams operate, make decisions, and deliver payroll outcomes. Success depends on a clear plan that balances data preparation, tool choice, and employee involvement.
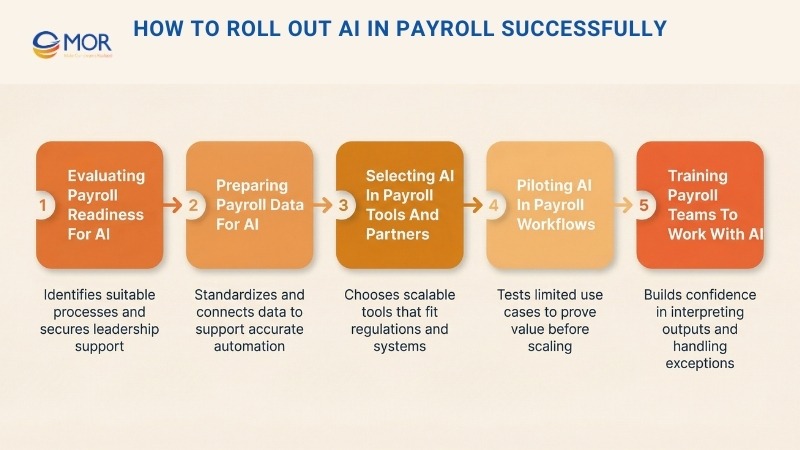
How To Roll Out AI In Payroll Successfully
Step 1: Evaluating Payroll Readiness For AI
Before introducing this solution, organizations need to review their current operations and identify existing challenges. This starts with spotting repetitive and time-heavy activities, including manual data entry, compliance monitoring, or handling common employee questions. These tasks are well suited for early adoption of how to use AI in payroll because gains are fast, visible, and carry low risk.
Leadership support matters as much as choosing the right processes. Moving toward AI in payroll management often changes how teams work and requires confidence in automated decisions. Without strong backing from leaders and acceptance from payroll staff, even well-designed solutions may fail to deliver long-term results.
Step 2: Preparing Payroll Data For AI
Accurate and consistent data forms the foundation of effective payroll automation. Systems need to capture and standardize details like working hours, benefits information, tax rules, and employee categories. When data is structured and current, generative AI in payroll can identify errors, recognize patterns, and run calculations with greater reliability.
Bringing data together across HR, finance, and payroll systems improves overall visibility and coordination. Clear data governance also plays a critical role, with defined rules for access, updates, and validation helping protect data quality and compliance. A solid data foundation allows it to operate more intelligently and scale as business needs grow.
Step 3: Selecting AI In Payroll Tools And Partners
Selecting tools for AI in payroll is a strategic choice, not only a technical one. Organizations should evaluate solutions that match operational requirements and local regulations, while allowing room to scale over time. Strong compatibility with current systems helps reduce disruption and shortens deployment timelines when adopting AI payroll software.
Vendor transparency is just as important during this stage. Payroll teams need clarity on how data is processed, stored, and updated, especially around security and compliance obligations. A reliable partner provides ongoing support, training resources, and clear documentation to support long-term use of payroll AI.
Step 4: Piloting AI In Payroll Workflows
Early adoption should begin with limited payroll areas where risk is controlled and benefits are easy to observe. Testing the system within compliance checks or payroll forecasting helps deliver quick results and reveal process gaps before wider use. These focused trials help confirm the practical value of this solution under real operating conditions.
During the pilot stage, teams should track performance and collect feedback from users. When improvements appear in speed, accuracy, or employee experience, it becomes easier to justify broader rollout. Once results are proven and workflows refined, scaling it can move forward with confidence and clarity.
Step 5: Training Payroll Teams To Work With AI
Payroll teams need proper guidance and ongoing support to work confidently with AI-powered payroll systems. Training should help staff interpret system outputs, handle exceptions, and feel comfortable relying on automated workflows. When users understand how decisions are made, adoption of AI in payroll becomes more stable and long lasting.
Close cooperation between payroll professionals and technical specialists is also important. These systems perform best when they support human review rather than replace it. A skilled and confident team encourages consistent use and helps organizations gain lasting value.
Challenges When Deploying AI In Payroll
Despite the strong potential of AI in payroll, many organizations face notable obstacles during implementation. Recent surveys show that 43% of companies encounter at least one major challenge when adopting payroll AI solutions. These issues go beyond technology alone and often involve ethical risks, system integration limits, and changing regulatory demands.
Many businesses underestimate how complex these challenges can be, especially when moving away from long-standing legacy payroll systems. The most effective rollouts usually rely on cross-functional teams that combine payroll expertise, data knowledge, IT security skills, and compliance oversight, rather than placing responsibility only on HR or finance teams.
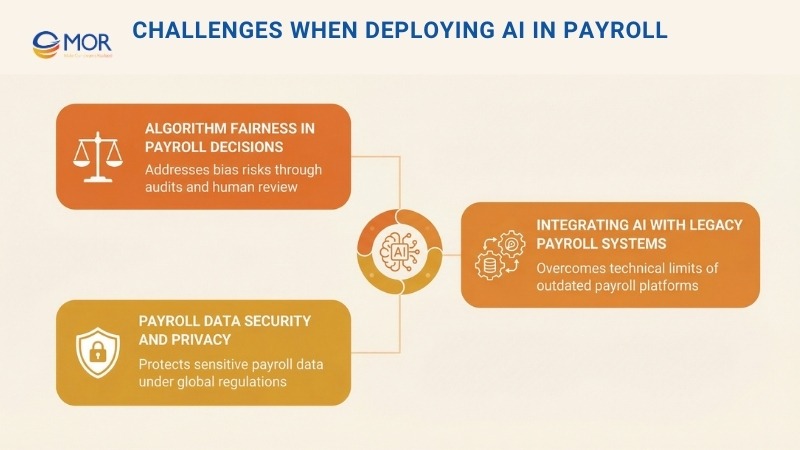
Challenges When Deploying AI In Payroll
1. Algorithm Fairness In Payroll Decisions
AI systems may unintentionally reinforce existing bias when they are trained on historical pay data that reflects past inequality. For instance, if earlier records show that male employees received quicker promotions or higher salary increases, the system may treat those patterns as indicators of performance instead of recognizing them as possible bias within AI in payroll decisions.
Organizations respond to this risk by using bias detection tools that review AI models before they go live. These tools examine how raises, bonuses, and promotions are allocated across different demographic groups to uncover patterns that lack a clear explanation. When bias indicators appear, human reviewers step in to reassess decisions and adjust the underlying logic.
Many organizations now mandate routine algorithm audits carried out by independent specialists. These audits use synthetic data that reflects a wide range of employee profiles to test system behavior. The goal is to confirm that recommendations remain consistent across gender, age, race, and other protected attributes, with findings recorded to support transparency and compliance.
2. Integrating AI With Legacy Payroll Systems
Many organizations still rely on payroll systems built decades ago, often using outdated programming languages and closed designs that do not connect easily with modern tools. A 2024 survey showed that 67% of companies view legacy compatibility as the main barrier to adopting AI in payroll, and many integration efforts exceed original time and budget plans by 40% to 60%.
The difficulty grows when businesses operate several payroll systems across regions or departments. A global manufacturer, for example, may run one HRIS in North America, a different platform in Europe, and another in Asia. Each system uses different data formats, calculation logic, and compliance rules that must be aligned before intelligent payroll processing can work correctly.
Organizations must decide whether to fully replace older platforms or build middleware that links them with newer AI capabilities. Both options involve major investment. Full replacement often costs three to five times more at the start, but it can reduce long-term maintenance work and lower integration complexity over time.
3. Payroll Data Security And Privacy
Payroll platforms store highly sensitive information, including social security numbers, bank details, salary records, and personal identifiers. Systems that use AI in payroll must apply strict security controls that meet fast-changing global regulations, including GDPR in Europe, CCPA in California, and LGPD in Brazil.
Remote and hybrid work models have increased security risks, since payroll data is now accessed from many locations and devices. Organizations need end-to-end encryption for data at rest and in transit, with careful protection of API connections that link payroll systems with other platforms.
Multi-factor authentication is now common for payroll access, yet many organizations are moving toward more advanced methods like continuous authentication that tracks user behavior. These approaches can spot unusual activity, including unexpected login times, location changes, or abnormal data access, which may signal compromised accounts or internal threats.
Real-World Case Studies Of Using AI In Payroll
After reviewing the main use cases of AI in payroll, it is important to see how these technologies work in real business settings. The following examples show practical, data-backed implementations of payroll AI across different types of organizations.
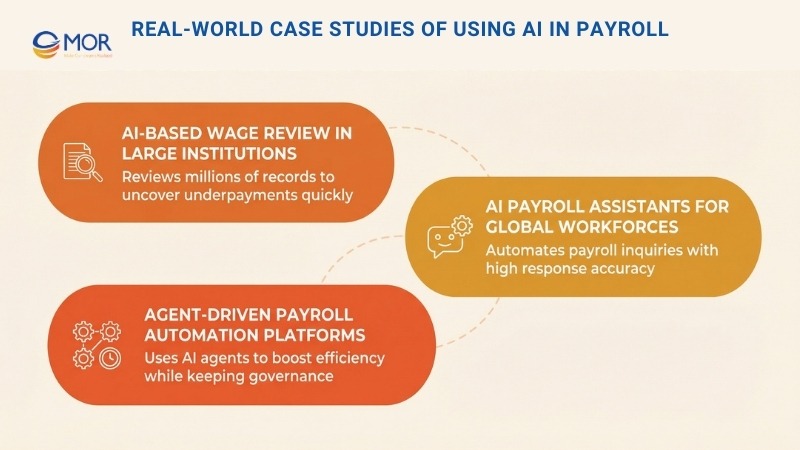
Real-World Case Studies Of Using AI In Payroll
1. AI-Based Wage Review In Large Institutions
Deloitte implemented an AI-powered solution at a large university in Australia to review more than 3.2 million timesheets and payslips. The system examined handwritten and scanned records to uncover wage underpayments affecting over 15,000 casual staff members. This replaced months of manual checking with a faster, scalable, and more accurate payroll review process.
The platform identified inconsistencies through pattern analysis and comparison with historical wage records. This helped the university find issues quickly and take corrective action without delay. The project improved payroll transparency and lowered both legal exposure and reputational risk through effective use of AI in payroll management.
2. AI Payroll Assistants For Global Workforces
EY worked with Microsoft to introduce an AI chatbot powered by Azure OpenAI to manage payroll questions across global teams. The chatbot reached a 93% accuracy rate on first responses and now handles more than half of employee payroll requests. It connects with HR platforms to deliver real-time and personalized answers.
This assistant eased pressure on HR teams by automating responses to common payroll questions. It also provided consistent support across regions and languages, which improved response speed and employee satisfaction.
3. Agent-Driven Payroll Automation Platforms
Workday launched Illuminate AI Agents, supported by a centralized Agent System of Record, to handle activities across payroll, finance, and HR. These agents independently carried out tasks like compliance verification and document preparation without manual triggers. Organizations reported a 49% gain in financial planning efficiency and a 52% increase in accounts payable processing speed.
The platform kept strong control in place, with every agent action tracked and aligned with internal policies. Routine work shifted to the system, which allowed teams to concentrate on exceptions and higher-level planning. This example shows how agent-driven payroll AI can increase productivity while maintaining governance and oversight.
The Future Direction Of AI In Payroll
AI in payroll is set to change how payroll functions operate over the coming years. Instead of supporting isolated tasks, intelligent systems are expected to manage full workflows from start to finish. Organizations now face a clear choice about how they prepare for this shift, since decisions made today will shape long-term readiness in the future of payroll.
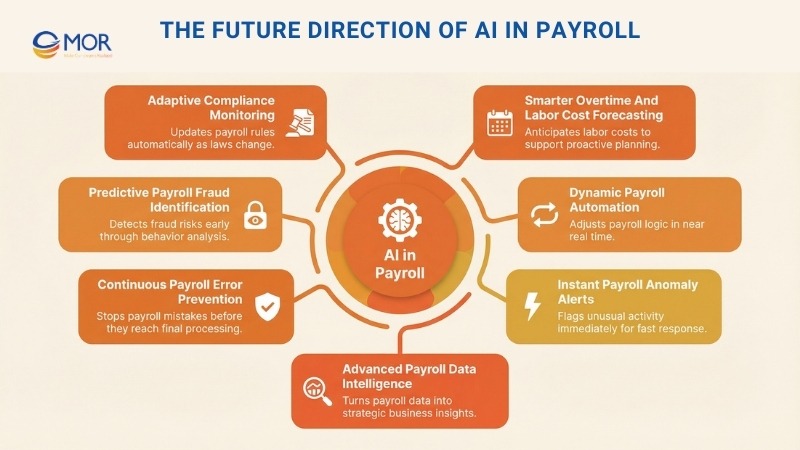
The Future Direction Of AI In Payroll
Continuous Payroll Error Prevention
AI is reshaping payroll from a routine obligation into a process driven by precision and control. Instead of correcting mistakes after payroll closes, intelligent systems detect issues early and prevent errors from moving forward. This approach reshapes workflows, maintains accuracy, and allows teams to focus on higher-level responsibilities while strengthening trust and efficiency across operations.
Predictive Payroll Fraud Identification
Predictive AI makes it possible to identify payroll fraud risks before losses occur. These systems examine behavioral patterns and transaction data to uncover unusual activity and notify teams of potential issues. This forward-looking model shifts payroll security away from reaction and toward prevention, helping protect financial integrity and maintain confidence in AI in payroll management systems.
Adaptive Compliance Monitoring
Adaptive compliance monitoring supports payroll systems that adjust automatically as regulations change. These platforms update rules as new laws take effect, which lowers the risk of penalties and removes the need for constant manual checks. This approach turns compliance into a built-in part of payroll operations, improving confidence and efficiency.
Smarter Overtime And Labor Cost Forecasting
Advanced forecasting tools allow organizations to estimate overtime costs with greater accuracy. Through pattern and trend analysis, these systems anticipate overtime spending and help teams plan staffing and budgets more effectively. This capability supports proactive financial decisions and strengthens long-term planning.
Dynamic Payroll Automation
Dynamic automation allows payroll systems to adjust quickly as business needs change. These platforms update employee records, tax rules, and compliance settings in near real time without constant manual input. This approach maintains accuracy and consistency while reducing routine workload, which allows teams to concentrate on higher-level priorities.
Instant Payroll Anomaly Alerts
Real-time alerting makes it possible to detect payroll issues as soon as they appear. Systems flag unusual activity immediately, which helps organizations respond to errors or potential fraud without delay. This proactive setup improves accuracy and strengthens trust, turning payroll into a more secure and transparent operation.
Advanced Payroll Data Intelligence
AI-driven analysis helps payroll data reveal patterns that are easy to miss with manual review. These tools examine trends to highlight cost-saving opportunities and areas for process improvement. This capability shifts payroll from routine administration to a strategic resource, giving teams clearer insights and better decision support.
MOR Software - Your Trusted Partner For AI In Payroll
MOR Software helps organizations apply AI in payroll with a clear focus on accuracy, compliance, and long-term scalability. Our teams work closely with HR and finance stakeholders to turn complex payroll operations into structured, automated systems that teams can trust.
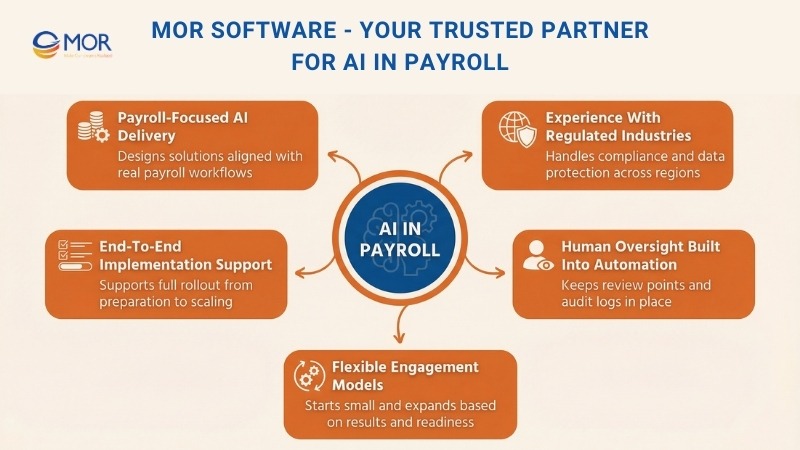
MOR Software - Your Trusted Partner For AI In Payroll
- Payroll-focused AI delivery: We design payroll AI solutions around real payroll workflows, not generic automation ideas. This keeps calculations, validations, and approval flows aligned with how payroll actually runs.
- Experience with regulated industries: Our engineers understand data protection rules, audit requirements, and regional compliance needs. This is critical when payroll data moves across countries or jurisdictions.
- End-to-end implementation support: From data preparation and system integration to pilot testing and scaling, we support the full rollout journey from start to finish.
- Human oversight built into automation: We build systems that support payroll teams rather than replace them. Clear alerts, review steps, and audit logs remain part of daily operations.
- Flexible engagement models: Teams can begin with focused use cases and expand over time based on results and internal readiness.
If you are planning to introduce AI for payroll or improve an existing setup, we can help you move faster with fewer risks.
Contact us to discuss your payroll goals and see how we can support your roadmap.
Conclusion
AI in payroll is quickly becoming a practical requirement as organizations face higher accuracy demands, tighter compliance, and growing workforce complexity. Teams that prepare early gain better control over costs, transparency, and long-term operations. Moving forward with the right partner reduces risk and shortens the learning curve. If you are reviewing your payroll strategy or planning next steps, contact us to explore how MOR Software can support a clear and scalable direction.
Rate this article
0
over 5.0 based on 0 reviews
Your rating on this news:
Name
*Email
*Write your comment
*Send your comment
1