Blockchain for Supply Chain: Real-World Success Stories

Supply chains are under pressure to be faster, cleaner, and more transparent than ever before. That’s where blockchain for supply chain comes in, helping businesses gain real-time visibility, traceability, and trust across every transaction. This MOR Software’s guide explores how leading companies are using blockchain to fix long-standing supply chain challenges and what that means for the future of global trade.
What Is Blockchain For Supply Chain Management?
Blockchain for supply chain introduces a decentralized and secure way to manage data flow between suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and retailers. In blockchain for supply chain management, every transaction is recorded on a shared, immutable ledger that promotes transparency and trust across all participants. Each verified transaction is added as a block, forming a traceable record of exchanges within the network. Since no single party controls the ledger, any unauthorized attempt to alter data is easily detected, keeping records accurate and tamper-proof.
The use of blockchain technology for supply chain helps organizations minimize fraud, cut paperwork, and gain real-time visibility of product movement. This visibility extends from raw material sourcing to final delivery, making it easier to detect bottlenecks and verify authenticity. Businesses can monitor every step of the process with confidence, knowing that all records are verified and auditable.
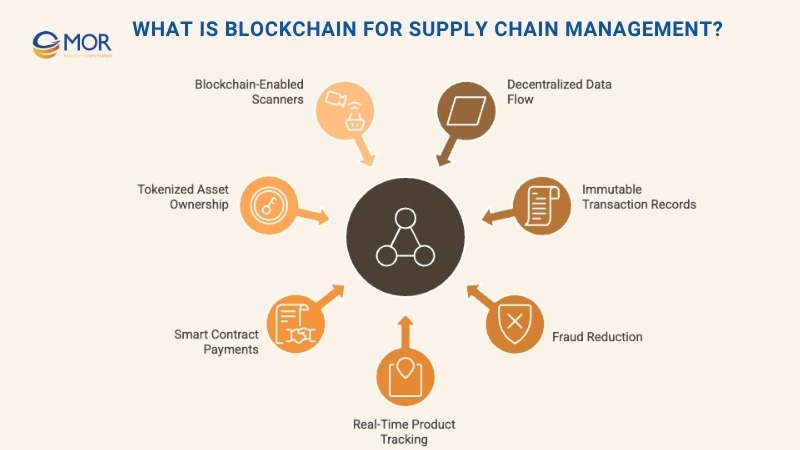
For supply chain management, blockchain offers several practical benefits that enhance both security and collaboration:
- It allows businesses to confirm product authenticity, track goods from origin to shelf, and ensure storage conditions comply with quality standards.
- Shared, validated data gives every stakeholder access to the same information, eliminating misinformation and reducing errors.
- Smart contracts automate payments when delivery terms are met, ensuring smooth cash flow and stronger partner relationships.
An emerging concept tied to blockchain for supply chain is tokenized assets, where ownership of physical or digital goods is represented by digital tokens on a blockchain. These tokens serve as certificates of authenticity for assets like real estate, gems, or intellectual property.
Some companies now employ blockchain-enabled scanners to read barcodes, QR codes, or RFID tags. The collected data is automatically written to the blockchain, ensuring full visibility of an item’s journey from factory to customer. This integration strengthens supply chain management by improving traceability and reliability at every stage.
Blockchain For Supply Chain Operations
At its core, blockchain for supply chain works as a decentralized digital ledger that records and verifies every transaction without relying on a central authority. Originally introduced in 2008 to power Bitcoin, blockchain has evolved into a trusted data structure that links information in sequential, unchangeable blocks. Each transaction added to the chain is validated by network participants, making it transparent, tamper-proof, and auditable at all times.
When combined with supply chain management, blockchain enables companies to operate within a unified, secure, and often cloud-based network. Every stakeholder, from manufacturers and logistics providers to carriers and brokers, can access real-time data, track goods, and confirm the integrity of operations on one shared platform. This structure strengthens coordination across logistics and supports automated settlements through smart contracts with minimal disruption to existing systems.
The integration of blockchain technology for supply chain ensures that every shipment, transaction, and document is verified and synchronized, reducing risks of fraud or data loss. It builds a continuous and tamper-resistant audit trail that improves accountability and simplifies compliance. With these capabilities, blockchain for scm helps businesses protect sensitive trade data and streamline end-to-end logistics.
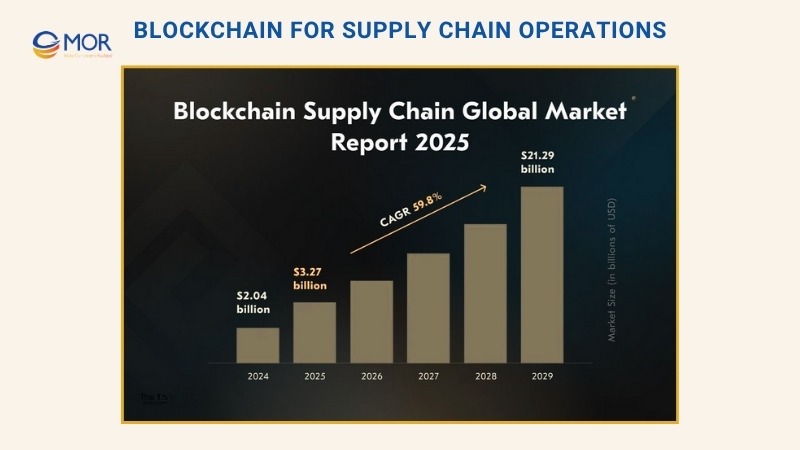
As adoption rises globally, the blockchain for supply chain market continues to expand at a remarkable pace. Analysts estimate its value to reach around $3.27 billion in 2025 and project it to climb to nearly $21.29 billion by 2029, reflecting a compound annual growth rate of about 59.8%. These figures highlight how this technology is reshaping modern logistics and driving smarter, more transparent operations.
Why Businesses Operate With Blockchain For Supply Chain
Recent studies show that over 43% of organizations still face difficulties in exchanging data with logistics partners, revealing a strong need for greater visibility and collaboration. The adoption of blockchain for supply chain gives companies the transparency they need while cutting unnecessary costs. Removing intermediaries and reducing paperwork, businesses can accelerate operations from procurement to delivery and returns. The technology not only saves money but also simplifies complex workflows and improves accountability across every step of production.
The advantages go far beyond cost savings. When implemented strategically, blockchain for supply chain management enhances transparency, traceability, efficiency, and security across global networks.
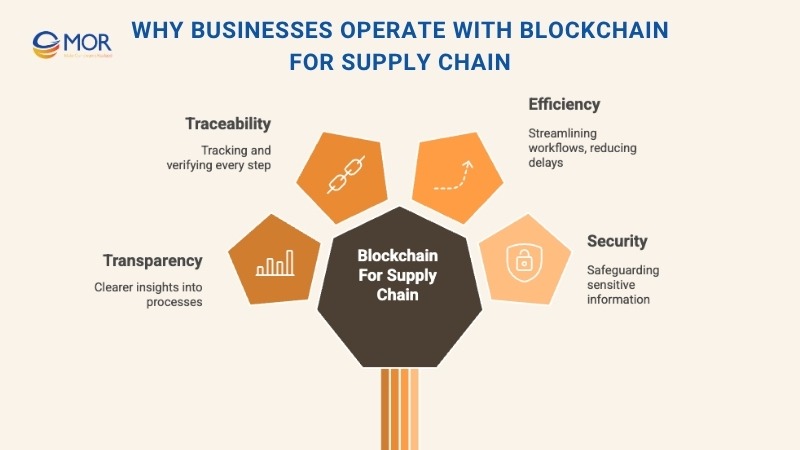
Enhanced Transparency
With the integration of blockchain and smart tracking tools, companies gain end-to-end visibility of goods in motion. Through IoT devices and RFID sensors, temperature, humidity, and location data are recorded and stored on the blockchain, ensuring all details remain verifiable and accurate. This improved visibility strengthens blockchain for supply chain transparency, allowing data to flow seamlessly into logistics management and analytical systems in real time. The combination of distributed ledgers and logistics blockchain solutions gives every stakeholder the same, trusted version of truth.
Improved Traceability
In modern supply chain management, traceability means knowing where each product originates and how it moves across the network. With decentralized ledgers, businesses can monitor real-time product data such as source, quality, certifications, and transport conditions. This approach strengthens authenticity checks and reduces counterfeiting. As demand for transparent tracking grows, the blockchain for supply chain traceability market continues to expand, helping companies create responsible, data-driven operations.
Increased Efficiency
One of the most noticeable benefits of blockchain for supply chain is the automation it brings. Smart contracts automatically execute tasks like compliance verification, order approval, or payments upon delivery, minimizing human involvement. The improved visibility also helps companies detect irregularities early, saving time and resources. As a result, firms can manage workflows faster and comply with regulations more effectively, boosting overall productivity.
Stronger Security
Every record stored on the blockchain is encrypted and immutable, protecting sensitive information from tampering or unauthorized access. This high level of security builds trust among partners and customers. Integrating blockchain for supply chain, businesses can verify every transaction independently and maintain transparent audit trails. Smart contracts further reduce fraud and human error by automating invoice settlements and creating a secure payment ecosystem.
What are the benefits of blockchain for supply chain? Altogether, these strengths highlight: transparency, reliability, efficiency, and safety, forming a new foundation for global trade integrity.
Real-World Applications Of Blockchain For Supply Chain (2025)
Over the past five years, blockchain for supply chain has shifted from pilot programs to real-world success. The technology now underpins some of the most innovative projects in logistics, trade, and production. Businesses are moving beyond experimentation to practical, large-scale use, proving that distributed ledgers can solve long-standing inefficiencies in global supply networks.
The industry’s growing adoption of blockchain for supply chain transparency in 2025 shows just how far the technology has come. From luxury goods to food safety and energy management, companies are implementing blockchain to trace assets, automate transactions, and strengthen trust among stakeholders. The following examples demonstrate how organizations are already using this technology to bring lasting change.
Product Authentication And Luxury Goods
Luxury brands face a persistent problem with counterfeit products, which cost the industry billions each year. To address this, many have turned to blockchain for supply chain systems to protect authenticity and ensure consumer trust.
- The Aura Consortium uses blockchain to certify the origin and authenticity of handbags for global names like Louis Vuitton and Prada.
- Breitling provides digital passports for each of its watches, allowing owners to verify provenance instantly.
- De Beers applies blockchain to track diamonds from mine to retail, creating full transparency for buyers and sellers.
Each product is assigned a digital identity on the blockchain, enabling verification with a simple scan. Customers can view detailed information about where and how their item was made, stored, and sold. This approach represents a powerful blockchain in supply chain case study, showing how technology improves trust and traceability.
Linking digital records with physical goods, blockchain for supply chain eliminates doubts about authenticity, strengthens brand protection, and builds lasting confidence among consumers and supply partners alike.
Automotive Supplier Payments
Beyond tracking materials and verifying authenticity, blockchain for supply chain is changing how automotive manufacturers handle payments across their global supplier networks. With decentralized systems, companies can send funds securely and instantly, avoiding long delays caused by intermediaries or traditional bank transfers. Payments occur directly between buyer and supplier, taking only a few minutes instead of several days through conventional clearing processes.
This approach also reduces transaction fees and simplifies cross-border settlements. One real-world blockchain for supply chain finance example comes from the Australian car manufacturer Tomcar, which uses Bitcoin to pay suppliers in Israel and Taiwan. While their contracts still follow standard commercial terms, blockchain enables faster transfers and noticeable cost savings.
However, Tomcar also takes precautions to minimize risk. Since many governments treat cryptocurrency as a capital asset, price fluctuations between purchase and use may trigger taxable events. For instance, if Bitcoin’s value rises while held in the company’s account, converting it to local currency could generate a capital gain subject to tax.
Another notable case is Tesla, which uses blockchain to ensure that its raw materials come from sustainable and verified sources. This practice reinforces how blockchain for supply chain not only supports global financial efficiency but also strengthens ethical and environmental accountability throughout the automotive industry.
Blockchain And Internet Of Things (IoT)
The integration of blockchain for supply chain and IoT in supply chain is creating smarter, more automated systems across industries, especially in automotive. Through connecting blockchain networks with IoT sensors, manufacturers and service providers can manage vehicles, payments, and logistics in real time without manual intervention.
One emerging use case involves smart contracts handling driverless car rentals. The contract automatically verifies payment and monitors the rental period. If the payment is missed or the term expires, it can lock the vehicle remotely and instruct it to return to the rental company’s facility. This shows how blockchain and IoT together can manage physical assets efficiently and securely.
A standout example is BMW’s Vehicle Digital Passport, a live demonstration of how blockchain for supply chain innovation supports transparency. Every car receives a permanent digital identity that logs its entire lifecycle, from manufacturing and mileage to maintenance, insurance, and resale. Through BMW’s subscription program Access by BMW, smart contracts validate payments while the vehicle’s IoT systems activate access.
When a subscription ends or a payment fails, the system automatically disables access, ensuring clear accountability between the company, customer, and service providers. This combination of blockchain and IoT strengthens data accuracy, automates compliance, and enhances customer trust, paving the way for smarter and more reliable automotive ecosystems.
Food And Meat Traceability
Food safety remains one of the most powerful real-world use cases of blockchain for supply chain. Recording every step of production, processing, and distribution on a distributed ledger, companies gain full visibility into the movement of food products. This continuous record creates an unbroken chain of custody, ensuring transparency, accountability, and rapid response during recalls.
Retail giant Walmart is a strong example of blockchain for supply chain innovation in the food industry. Its system can trace any package of pork in China back through every stage of production, from the farm and processing plants to cold storage and transportation. With this setup, Walmart can identify the origin, movement, and storage conditions of each product, as well as its expiration date. In case of contamination or recall, affected batches can be located within seconds.
Similarly, Starbucks uses blockchain in its Bean-to-Cup initiative, tracking coffee beans from farms to cafés. Every bean’s journey, from sourcing and roasting to brewing, is recorded, giving customers detailed insight into quality and origin.
These examples highlight how blockchain for supply chain ensures safety, trust, and authenticity across food networks. Adopting transparent digital ledgers, brands can strengthen compliance, improve quality control, and reinforce consumer confidence in what they eat and drink.
Transparency In The Tea Industry
Blockchain isn’t limited to luxury goods or high-end assets. It’s also transforming how everyday commodities are sourced and verified. The global tea trade, for instance, is turning to blockchain for supply chain solutions to fight counterfeiting and guarantee authenticity from plantation to cup.
Tea is one of the most consumed beverages in the world, yet its supply chain often faces issues with imitation products. Lower-quality tea is frequently mislabeled and sold as premium varieties from renowned regions like Darjeeling. These counterfeit practices not only hurt farmers and brands but also mislead millions of consumers who value authenticity and sustainability.
To address this, Unilever has implemented blockchain for supply chain transparency across its African tea plantations. Integrating blockchain into existing tracking systems, the company now verifies the origin, quality, and sustainability of each batch faster and more efficiently than before. This initiative, known as Trado, is a collaboration between Unilever, Sainsbury’s, and the University of Cambridge’s Institute for Sustainability Leadership. Farmers who participate are financially rewarded for providing accurate data, creating both transparency and social impact.
The success of Trado has inspired other regions to follow suit. In India, the Coffee Board of India uses blockchain to trace coffee production, with over 30,000 farmers already enrolled. Encouraged by its success, the Tea Board of India plans to introduce a similar end-to-end traceability system.
Through projects like these, blockchain for supply chain is building trust, improving accountability, and bringing greater visibility to industries that touch our daily lives, one cup at a time.
Renewable Energy And Micro-Grids
The flexibility of blockchain for supply chain extends well beyond traditional industries like retail or manufacturing. In recent years, the energy sector has become one of the most innovative adopters, using blockchain to change how electricity is produced, shared, and consumed. These projects demonstrate how decentralized systems can empower communities to trade energy directly and operate more sustainably.
Blockchain’s transparency and automation allow even small-scale producers to participate in the energy market. Through smart contracts, households with solar panels can sell excess electricity to nearby homes without relying on large utility companies. This decentralized model reduces costs and promotes cleaner power distribution.
A strong example of this application is The Transactive Grid, which uses blockchain to monitor and redistribute renewable energy within local micro-grids. The system automates buying and selling through smart contracts built on the Ethereum platform, cutting both expenses and carbon emissions.
Another notable case is Brooklyn Energy, a community project that enables residents to sell surplus solar energy directly to their neighbors using blockchain technology. This initiative shows how blockchain for supply chain principles, like traceability, trust, and peer-to-peer transactions, can support sustainable energy ecosystems while lowering dependency on centralized grids.
These advancements prove that blockchain’s potential reaches far beyond product tracking, helping create smarter, greener, and more independent communities worldwide.
Smart Contract Automation
Automation is one of the strongest advantages of blockchain for supply chain, and smart contracts are at the heart of this transformation. In the past, RFID tags were the standard for tracking products. Today, companies rely on a combination of modern tools, QR codes, NFC chips, IoT sensors, GPS trackers, and Bluetooth beacons, to create a seamless and transparent monitoring system.
These connected devices feed real-time data into blockchain networks, enabling instant verification and action. A leading example comes from DHL, which uses smart pallets equipped with IoT sensors across its global network. These pallets monitor not only their exact location but also key environmental factors like temperature, humidity, and potential impact during transit.
When any reading falls outside safe limits, smart contracts automatically issue alerts to responsible parties. This process ensures that all stakeholders, from warehouse operators to end customers, have full visibility into the shipment’s condition. Automating alerts, documentation, and reporting, blockchain for supply chain significantly reduces damage, improves delivery accuracy, and strengthens overall accountability.
The result is a more responsive and data-driven logistics ecosystem, where every action is traceable, secure, and executed in real time without manual intervention.
Cold Chain Monitoring
Certain industries depend on precise environmental control to protect sensitive goods like food, pharmaceuticals, and medical supplies. Maintaining consistent conditions throughout the distribution process is critical, and blockchain for supply chain has become an essential tool for achieving that reliability.
In shared storage and logistics networks, IoT sensors attached to products monitor temperature, humidity, vibration, and other environmental factors. These readings are instantly uploaded to the blockchain, creating an immutable record that all partners can access. If the temperature or humidity drifts beyond safe limits, alerts are triggered in real time, allowing immediate action. This level of visibility helps companies maintain product quality, reduce waste, and prevent costly recalls.
A prominent example comes from Moderna, which used blockchain during COVID-19 vaccine distribution to ensure doses stayed within strict temperature requirements of around -70°C. The system offered full traceability across every stage of transport and storage, providing blockchain for supply chain transparency that safeguarded both data and product integrity.
When issues arise, smart contracts can automatically initiate corrective actions, such as adjusting storage conditions, updating expiry dates, or flagging products as unfit. These mechanisms reinforce compliance and accountability without manual oversight.
From vaccine tracking to luxury goods authentication, these diverse use cases highlight how blockchain for supply chain strengthens trust, data accuracy, and operational efficiency across industries worldwide.
Challenges And Limitations Of Blockchain For Supply Chain
Although blockchain for supply chain brings transparency and efficiency to logistics, businesses still face a series of practical challenges when adopting it. Understanding these limitations is crucial for organizations aiming to deploy blockchain solutions effectively and sustainably.
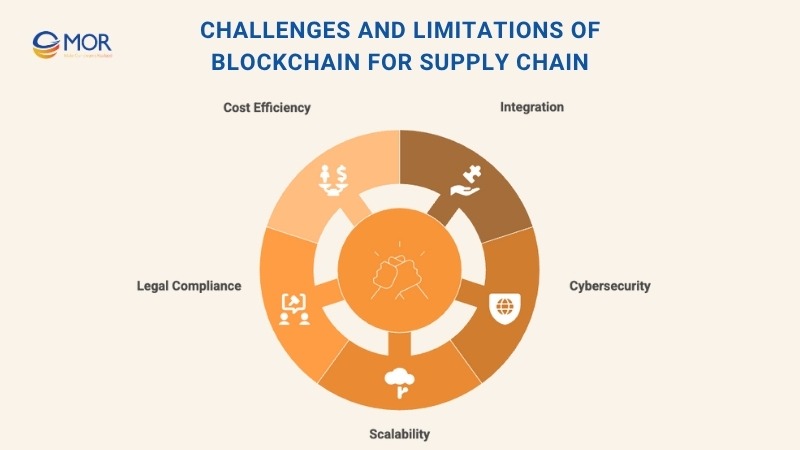
Integration With Existing Systems
Integrating blockchain with current enterprise infrastructure remains one of the toughest barriers. Many companies rely on legacy ERP or logistics systems that were never designed to connect with decentralized platforms. Aligning these older technologies with blockchain requires both time and specialized expertise. Without a proper transition plan, synchronization errors and workflow disruptions can occur. For this reason, businesses investing in blockchain for supply chain need a clear integration roadmap, ensuring smooth data exchange between old and new systems.
Cybersecurity And Data Privacy
While blockchain’s distributed nature makes it resistant to tampering, it doesn’t eliminate all security risks. Cybercriminals can still target network endpoints or exploit vulnerabilities in connected applications. Furthermore, because data on a blockchain is transparent and permanent, sensitive business information could be exposed if privacy controls aren’t implemented correctly. Strong cybersecurity measures, encryption, access control, and identity verification, remain essential. Protecting digital assets must go hand in hand with maintaining blockchain for supply chain transparency, especially when multiple parties share data.
Scalability
As adoption expands, scalability becomes a growing concern. Current blockchain infrastructures can struggle with high transaction volumes, leading to slower processing times and increased energy consumption. This issue is particularly relevant when networks involve thousands of supply partners. Upgrading protocols or using hybrid systems may be necessary to keep performance stable. Addressing these scalability limits is critical for enterprises that plan to manage global logistics through blockchain for supply chain platforms.
Legal And Regulatory Uncertainty
The legal framework for blockchain use still varies widely across regions. Since no universal standard governs data sharing, taxation, or digital transactions, companies face uncertainty about compliance and liability. For international operations, this inconsistency can complicate cross-border agreements. Businesses must stay alert to evolving laws that could influence how blockchain for supply chain systems are deployed or monitored.
Cost And Resource Constraints
Implementing blockchain requires considerable investment in development, infrastructure, and specialized talent. Setting up private or consortium-based networks also adds long-term maintenance costs. Moreover, the shortage of skilled blockchain developers drives up project budgets. While the potential return on investment is high, companies must balance expected gains against the total cost of ownership. Adopting blockchain for supply chain should therefore involve detailed cost–benefit analysis and a realistic scaling plan.
Despite these hurdles, businesses that address integration, security, scalability, regulation, and cost strategically can unlock blockchain’s full potential and build more transparent, resilient, and data-driven supply chains.
Best Practices For Implementing Blockchain For Supply Chain
While blockchain for supply chain presents certain challenges, many organizations have achieved success by following well-structured implementation strategies. Applying the right practices helps businesses manage risks, enhance security, and unlock long-term value from blockchain adoption. Below are six proven steps that companies can take to ensure a successful rollout.
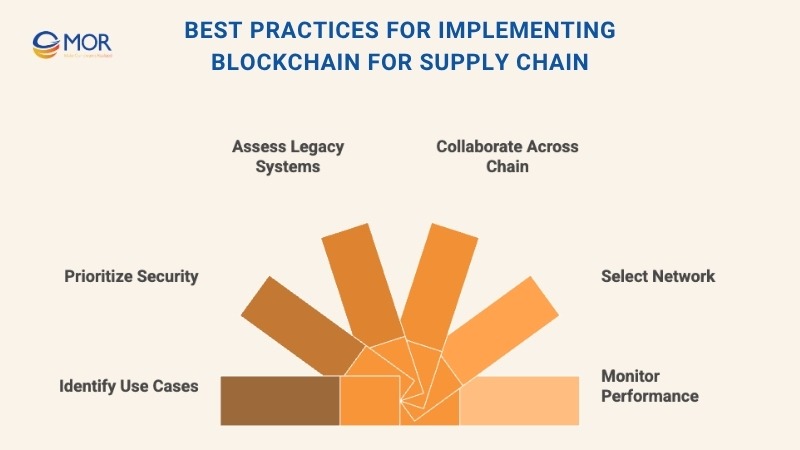
1. Identify The Right Use Cases
The first step is to determine where blockchain can bring the greatest value. Focus on areas where transparency, traceability, or automation directly improve outcomes, such as fraud prevention, inventory visibility, or sustainability reporting. Choosing the right projects ensures measurable results and reduces unnecessary complexity. When evaluating opportunities, consider both benefits and potential costs to avoid overextension. Strategic planning is key to identifying the best blockchain for supply chain operations.
2. Prioritize Security And Data Integrity
Security must be at the forefront of every blockchain initiative. As networks often handle confidential trade and shipment data, companies should apply robust encryption, authentication systems, and access controls. Regular security audits are also essential to detect vulnerabilities early. When building blockchain for supply chain, protecting sensitive data through encryption and user verification maintains trust and compliance across all participants.
3. Assess Impact On Legacy Systems
Before integration, businesses need to analyze how blockchain will interact with their existing ERP or logistics systems. Many supply networks still depend on legacy technology that requires modification to connect with decentralized platforms. Conducting a technical assessment ensures compatibility and minimizes disruptions during deployment. This step also helps align blockchain’s real-time data capabilities with current workflow structures.
4. Collaborate Across The Supply Chain
Blockchain for supply chain thrives on collaboration. Its benefits, transparency, traceability, and efficiency, can only be realized when all partners share data consistently. Building trust through open communication, pilot testing, and shared governance ensures smoother adoption. Collaboration also helps tackle common challenges like data standardization, compliance, and security concerns.
5. Select A Suitable Blockchain Network
Choosing the right blockchain infrastructure can determine the success or failure of implementation. Businesses should evaluate factors like transaction speed, scalability, security, and interoperability before committing. Public, private, or consortium-based networks each have distinct advantages depending on business goals. Selecting the most compatible solution ensures the system delivers long-term value and reliability.
6. Continuously Monitor Performance
Post-deployment monitoring ensures that the blockchain system remains efficient and secure. Tracking performance metrics helps detect operational issues early and measure progress against business goals. Continuous optimization, such as updating smart contracts or refining integration layers, keeps performance stable and value consistent over time.
When following these best practices, enterprises can implement blockchain for supply chain more effectively. Partnering with experienced technology providers ensures technical precision and smooth execution, allowing businesses to fully capitalize on blockchain’s ability to drive transparency, security, and operational excellence.
Future Outlook: The Next Era Of Blockchain For Supply Chain
The evolution of blockchain for supply chain is far from over. What began as an experimental technology is now driving large-scale transformation in global trade, logistics, and manufacturing. Over the next few years, blockchain’s role will deepen as it integrates with advanced technologies and reshapes how businesses track, trade, and verify goods worldwide.
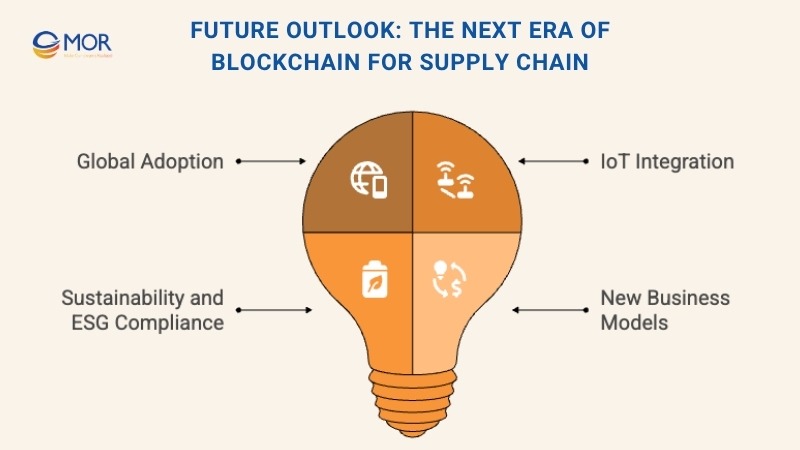
Greater Global Adoption
As awareness of blockchain’s advantages continues to grow, adoption is expected to accelerate across industries. More organizations are recognizing the value of decentralized, transparent operations that enhance trust and efficiency. Governments and enterprises alike are investing in solutions that connect suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors through unified digital networks. This expansion will create a more resilient and collaborative global ecosystem powered by blockchain for supply chain.
Deeper IoT Integration
The connection between blockchain and IoT is set to strengthen further. Smart sensors, GPS trackers, and IoT devices already collect massive amounts of data across logistics networks. When linked with blockchain, this information becomes immutable and verifiable, improving both visibility and accuracy. Enhanced automation from IoT will allow businesses to optimize inventory, monitor environmental conditions, and prevent fraud. This seamless integration of blockchain for supply chains and international trade ensures that every transaction and shipment can be validated in real time.
Sustainability And ESG Compliance
Sustainability is quickly becoming a global standard rather than an option. With new ESG regulations, like Europe’s Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive, companies will soon be required to provide verified data on environmental and ethical practices. Blockchain enables this by offering transparent records of product origins, fair trade certification, and carbon tracking. The use of blockchain for supply chain helps prevent greenwashing by giving regulators, partners, and consumers a clear view of every sustainability claim.
New Business Models Emerging
As innovation continues, new digital-first business models will emerge around traceability and accountability. Platforms such as IBM’s Food Trust demonstrate how blockchain can verify food safety, quality, and origin in seconds. Producers, distributors, and retailers can quickly identify contaminated batches, improving public safety and reducing waste. These systems highlight how blockchain for supply chain fosters collaboration and real-time visibility while encouraging smarter, safer trade practices.
Looking ahead, the future of blockchain for supply chain promises broader adoption, deeper technological integration, and stronger sustainability standards. Together, these shifts will redefine how global industries operate, making trade networks more transparent, secure, and connected than ever before.
MOR Software – Delivering Blockchain For Supply Chain Solutions
At MOR Software, we help businesses transform their supply chain operations through customized blockchain solutions. Our team combines deep technical expertise with industry knowledge to build systems that enhance transparency, automation, and trust across every stage of the supply chain.
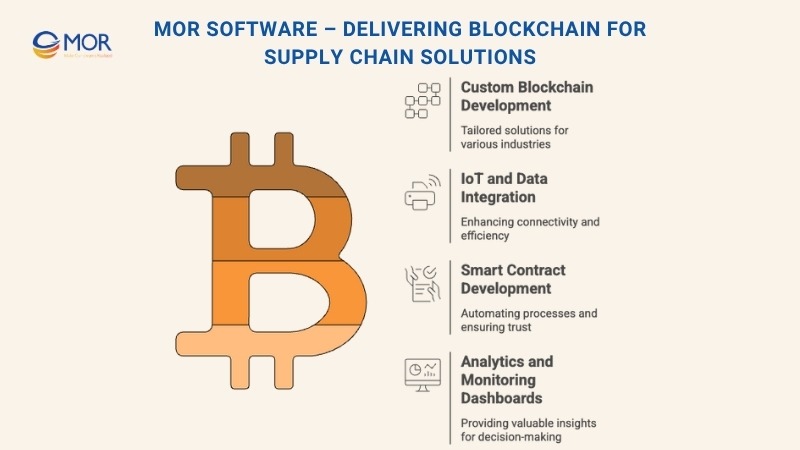
Our blockchain development services include:
- Custom Blockchain Development: We build tailored blockchain architectures using leading technologies like Hyperledger, Ethereum, and Polygon to match each client’s specific operational model.
- IoT and Data Integration: We connect IoT sensors, logistics data, and production records to blockchain networks, enabling real-time traceability and data integrity.
- Smart Contract Development: We design and deploy smart contracts that automate payments, track product authenticity, and manage digital certificates with precision and security.
- Analytics and Monitoring Dashboards: We implement data visualization dashboards that provide stakeholders with real-time insights into logistics performance and supply chain health.
Blockchain is reshaping how businesses track, verify, and manage global supply chains. At MOR Software, we turn that innovation into practical value by creating scalable, secure, and transparent systems tailored to your business needs. Our goal is simple: to help you build smarter, more connected operations powered by trust and real-time data.
Ready to transform your supply chain with blockchain?
Contact us to start your digital transformation journey with MOR Software.
Conclusion
Blockchain is no longer just a trend, it’s the foundation of transparent, traceable, and efficient supply chains. Integrating blockchain for supply chain, businesses gain visibility, security, and trust across every transaction. With MOR Software’s expertise, you can turn complex logistics into a streamlined, data-driven ecosystem. Let’s build your next-generation supply chain together. Contact MOR Software today to start your blockchain transformation journey.
Rate this article
0
over 5.0 based on 0 reviews
Your rating on this news:
Name
*Email
*Write your comment
*Send your comment
1