Blockchain in Finance: The Ultimate 2025 Guide with Use Cases
The financial world is changing fast, and blockchain in finance is leading that shift. As banks and fintech firms look for safer, faster, and more transparent systems, blockchain is proving to be more than a trend, it’s becoming a foundation for global finance. This MOR Software’s guide explores how blockchain is transforming financial services, from blockchain in trade finance to asset tokenization, digital payments, and beyond.
What Is Blockchain In Finance?
Blockchain in finance is the application of distributed ledger technology to securely record, verify, and store financial transactions across multiple systems. Rather than depending on a single authority, such as a bank, this model allows peer-to-peer exchanges where every transaction is encrypted, time-stamped, and permanently linked within a connected chain of data blocks.
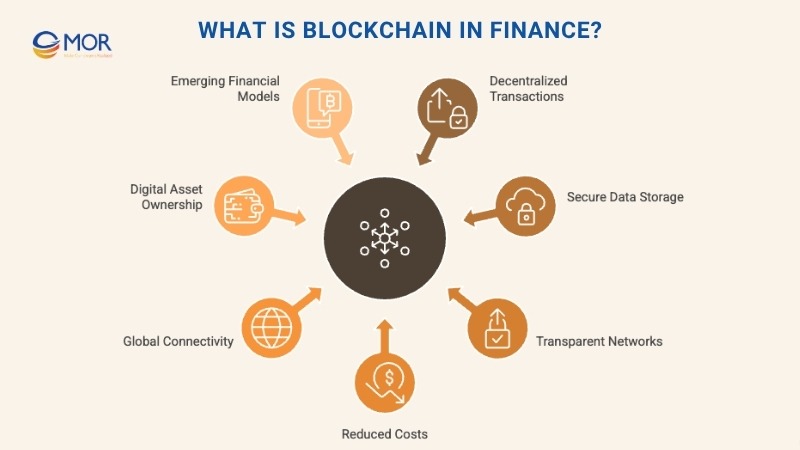
What Is Blockchain In Finance?
This decentralized setup eliminates opportunities for tampering, strengthens transparency, and builds trust across financial participants. Within the blockchain in finance industry, institutions rely on this technology to improve processes in cross-border payments, securities trading, lending, and asset management. Through removing middlemen, blockchain helps lower operational costs and accelerates settlement times.
Beyond transaction efficiency, blockchain technology in finance powers new concepts like decentralized finance (DeFi) and asset tokenization, giving users greater ownership and liquidity over digital assets. Even as issues like regulation and scalability remain, blockchain in finance continues to redefine how money moves, how data is validated, and how financial networks connect globally. This progress signals the start of a faster, safer, and more transparent digital economy.
What Are The Benefits Of Blockchain In Finance?
The blockchain in finance model introduces greater openness, inclusion, and reliability to global financial systems. Platforms like Ethereum enable faster and more cost-effective operations, shared standards, and secure data management across business networks. Issuing digital securities with shorter turnaround times and lower unit costs, blockchain allows for greater customization and market accessibility. This flexibility benefits both investors and issuers by expanding investment opportunities, cutting operational costs, and minimizing counterparty risk. Over the past several years, enterprise adoption of blockchain in banking and finance has proven its tangible value through several key advantages.
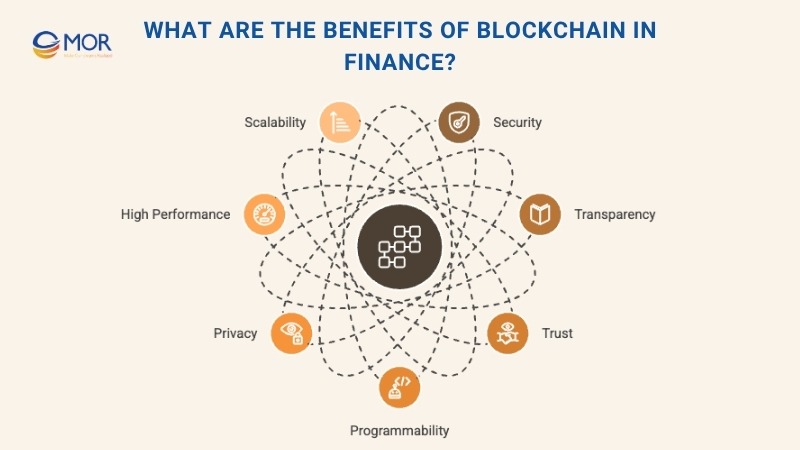
What Are The Benefits Of Blockchain In Finance?
- Security: The decentralized consensus model removes single points of failure, protecting against fraud and eliminating the need for intermediaries. Smart code design also helps prevent unauthorized data manipulation or tampering.
- Transparency: Shared protocols and mutual standards create a unified system of record, ensuring consistent visibility across all participants.
- Trust: With an immutable ledger, organizations can collaborate and verify data without relying on external validation.
- Programmability: Smart contracts automatically execute predefined business logic, improving both accuracy and operational speed.
- Privacy: Advanced permission settings allow selective data sharing, improving confidentiality while maintaining accountability.
- High Performance: Private and hybrid blockchains can handle hundreds of transactions per second while maintaining reliability during peak activity.
- Scalability: Interoperability between private and public chains supports global reach and long-term resilience.
According to Jupiter Research, blockchain in finance research paper findings estimate that blockchain could help banks save as much as $27 billion annually on cross-border settlements by 2030, cutting transaction expenses by over 11%. This shift highlights the growing importance of blockchain in financial operations as institutions continue to adopt it for long-term efficiency and cost savings.
Top 10 Use Cases Of Blockchain In Finance That Shows Results
A 2022 report by FTI Consulting titled The State of Blockchain Technology and Digital Assets in Financial Services revealed a clear trend: most financial leaders now view blockchain in finance as a top strategic investment. Over 85% of executives expressed optimism about the technology’s long-term influence on their operations, signaling a major shift toward blockchain-based systems.
Further supporting this view, Global Industry Analysts’ 2023 FinTech Blockchain: Global Strategic Business Report projected the market’s expansion from $1.4 billion in 2022 to an impressive $43.1 billion by 2030. This growth underscores how rapidly the blockchain in trade finance and broader fintech ecosystems are scaling to meet industry needs.
As more financial institutions adopt the technology, new possibilities continue to emerge. From faster settlements to transparent asset management, blockchain applications in finance are redefining traditional models while supporting fresh financial products and services. Below are ten proven use cases that reflect the growing strength and measurable results of blockchain’s real-world adoption.

Top 10 Use Cases Of Blockchain In Finance That Shows Results
1. Faster, More Affordable Financial Transactions
With its ability to process immutable transactions almost instantly, blockchain in finance delivers a faster, safer, and more scalable way to manage core financial activities. Payments, transfers, peer-to-peer settlements, and even blockchain in trade finance operations all benefit from this real-time transparency.
Because blockchain removes middlemen like clearinghouses and transfer agents, it cuts processing costs and minimizes human error. The system’s near-tamper-proof nature also makes it harder for fraud to occur, while encrypted validation ensures every transaction remains traceable and verifiable.
In addition, how blockchain enhances transparency in finance is transforming institutional trust. Shared records give all parties equal access to transaction data, reducing disputes and improving accountability. The use of verified digital identities further strengthens data security and participant validation, creating a safer financial environment overall.
Unlike traditional payment systems that rely on multiple intermediaries, blockchain streamlines reconciliation, clearing, and settlement into a single, automated process. This shift helps institutions save time, cut costs, and eliminate paperwork-heavy steps like document verification and insurance form handling, paving the way for faster, cleaner, and more reliable transactions.
2. Collateral Management
Blockchain in finance is transforming how organizations manage collateral, track assets, and verify ownership across global networks. Using a shared ledger, lenders can record and monitor collateralized assets in real time, removing delays and data inconsistencies found in traditional systems.
For instance, when a corporate borrower secures a loan with several assets, blockchain allows the lending institution to instantly verify, value, and update the collateral data without relying on intermediaries. This transparency minimizes errors and prevents double pledging, helping both lenders and clients maintain accurate financial records.
Beyond lending, blockchain supports commodity tracking and trading across supply chains. Each transaction creates a permanent record that follows the asset from origin to delivery, allowing companies to confirm authenticity and location at every step. For insurers, this traceability helps identify when and where damage or loss occurred, improving claim accuracy and reducing fraud.
As financial operations expand digitally, integrating blockchain into collateral management offers a more reliable, transparent, and efficient approach to asset supervision.
3. Stablecoins
One of the most impactful innovations in blockchain in finance is the development of stablecoins, cryptocurrencies built to hold consistent value. Unlike traditional crypto assets that swing sharply in price, stablecoins are backed by stable reserves such as fiat currencies, commodities, or financial instruments, ensuring reliability for trading, payments, and asset storage.
This stability gives institutions a trusted bridge between digital and traditional finance. It enables seamless cross-border payments and settlements with lower costs and faster processing, combining blockchain transparency with real-world dependability.
As adoption continues to rise, stablecoins are proving to be a vital part of the crypto block chain ecosystem. As Paul Brody, EY’s Global Blockchain Leader, explained, “Stablecoins bring the liquidity and speed of crypto with the dependability of traditional money, creating a digital asset built for everyday use.”
4. Asset Tokenization
A major advancement in blockchain in finance is the tokenization of real-world assets, which makes it possible to divide ownership into smaller, tradable digital units. This allows investors to buy, sell, or exchange fractional shares of valuable assets such as real estate, commodities, or private equity with greater liquidity and transparency.
Tokenization removes traditional barriers to investment and opens access to markets that were once limited to large institutions. It also allows asset owners to use their tokenized holdings as collateral, making capital more flexible and accessible.
As Lata Varghese, Managing Director of Digital Assets and Blockchain Solutions at Protiviti, stated, “You can tokenize anything of real-world value, from real estate to private equity.” Major banks, including Bank of America, now view tokenization as a leading driver of digital asset adoption, shaping a more inclusive and efficient financial ecosystem.
5. Virtual Economy And Digital Rewards
In the expanding virtual economy, blockchain in finance plays a crucial role in enabling secure and traceable transactions across metaverse environments. As digital spaces evolve, blockchain provides the infrastructure needed for transparent asset exchanges, ownership verification, and value transfer in real time.
Through blockchain-based platforms, organizations can create participation and reward systems using digital tokens. These tokens can be earned by users who attend virtual events, interact with digital stores, or engage in branded experiences. Similar to loyalty or cashback programs, these rewards can later be traded, redeemed, or even exchanged for other digital assets.
This approach not only drives engagement but also builds trust in virtual economies. Connecting virtual and real-world value systems, blockchain is helping businesses explore new financial models that merge entertainment, commerce, and digital ownership, cementing its place as a foundation for the next phase of online economies and analyze blockchain innovation.
6. Crypto Staking
Blockchain in finance has introduced new ways for investors to earn passive income through crypto staking. In this model, holders of digital assets commit a portion of their cryptocurrency to help maintain and secure blockchain networks. Locking these assets for a set period, participants contribute to transaction validation and the creation of new data blocks.
When validators approve legitimate transactions, they receive additional tokens as rewards, effectively earning yield similar to interest in traditional finance. However, if fraudulent transactions are confirmed, stakers risk losing part or all of their locked assets. This structure promotes integrity and accountability across decentralized systems.
While staking continues to grow as a source of income and liquidity for crypto holders, regulatory uncertainty still surrounds its long-term role in financial markets. Questions about its classification as a security persist, but it remains a defining innovation in the ongoing evolution of blockchain technology in finance and decentralized investment models.
7. Invoice Factoring
Blockchain in finance is reshaping invoice factoring, giving businesses a faster and more reliable way to access short-term funding. Traditionally, companies borrow against unpaid invoices to generate immediate cash flow, but verifying those accounts receivable often requires extensive documentation and third-party validation, slowing the process.
Integrating blockchain, these transactions become transparent, traceable, and nearly fraud-proof. Every invoice is time-stamped and securely recorded on a decentralized ledger, allowing lenders to verify authenticity in real time. This reduces administrative overhead and eliminates disputes over invoice ownership or value.
With blockchain automation, invoice factoring turns into a more accessible and efficient financing option for both lenders and borrowers. The transparency and security built into decentralized systems not only speed up funding but also strengthen trust between all parties involved, showcasing another practical use of blockchain applications in finance for real-world business needs.
8. B2B Network Collaboration
A growing application of blockchain in banking and finance is its ability to strengthen collaboration across business networks. By creating a shared, trustworthy infrastructure, blockchain enables companies to extend ERP capabilities such as inventory tracking, invoicing, and financial settlement beyond their own internal systems.
Everest Group describes these systems as Network Resource Planners (NRPs): “a blockchain-based software system that helps manage data and processes across multiple stakeholders in a business network.” With NRPs, organizations can synchronize data, streamline workflows, and deliver smoother, more unified customer experiences across partners and suppliers.
As Ronak Doshi noted, “We’re seeing that there is a way for enterprises to come together to solve customer issues and create a better customer experience. The only way to bring them all together is with a foundational infrastructure. Blockchain fits beautifully in this.” This collaborative model shows how blockchain is redefining how institutions connect, communicate, and transact securely in the digital economy.
9. Internal Data Management
While blockchain in finance is best known for building trust between institutions, many banks and financial firms are now adopting it internally to strengthen data integrity and compliance. Creating a single, tamper-proof ledger shared across departments, blockchain ensures consistent, accurate information flows throughout the organization.
Financial institutions use blockchain to manage intracompany transactions, transferring financial data securely between internal ledgers. This improves visibility into liquidity, capital flow, and reconciliation. It also supports strict regulatory demands by maintaining a transparent audit trail for every data update.
Some banks are applying blockchain to streamline Know Your Customer (KYC) processes, ensuring client records remain consistent and current across systems. In large organizations where customer data may reside in dozens of databases, this unified approach prevents discrepancies and reduces risks tied to outdated or duplicated information.
Blockchain’s immutable record-keeping also supports data lineage tracking, allowing institutions to trace each data point from origin to end use. This capability strengthens both internal governance and external regulatory trust, reinforcing blockchain in finance industry adoption as a foundation for secure data management and accountability.
10. Moving Toward A Cashless Economy
As global finance shifts toward digitalization, blockchain in finance is emerging as the foundation for replacing physical money with digital assets. A distributed ledger provides the transparency, traceability, and security needed to support this transition while eliminating inefficiencies tied to paper bills and coins.
Financial institutions are showing strong interest in blockchain-based payment systems because they reduce transaction friction, enhance visibility, and curb financial fraud. Automating validation and settlement, blockchain enables faster payments with lower costs and fewer intermediaries, strengthening confidence in digital money systems.
The momentum is already visible across the blockchain in finance industry. Deloitte’s 2022 survey found that 85% of businesses expect digital currency payments to become standard within five years, and an equal percentage foresee suppliers accepting stablecoins and cryptocurrencies. Meanwhile, 64% of organizations reported strong customer interest in using digital payments, especially among younger users.
These trends suggest that the path to a fully cashless economy is accelerating. With blockchain as its backbone, the global financial ecosystem is steadily evolving toward faster, safer, and more transparent digital transactions.
What Are The Challenges Of Blockchain In Finance?
While blockchain in finance brings major advantages to banking and investment systems, several barriers still limit its full-scale adoption. These challenges must be addressed for blockchain to reach enterprise maturity and deliver consistent long-term value.
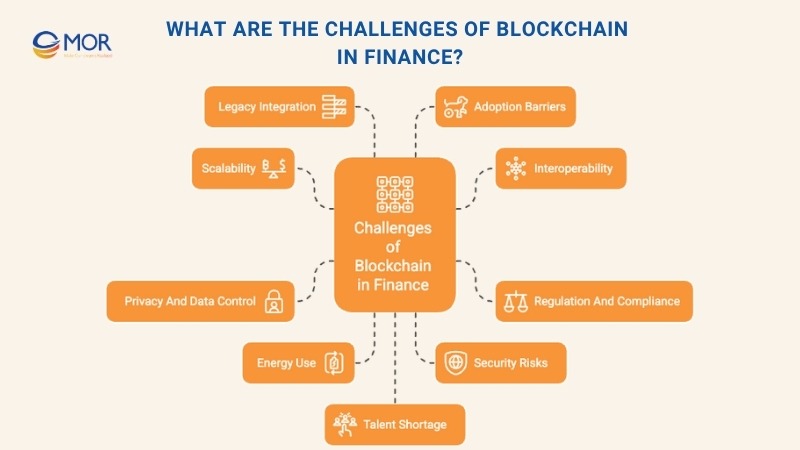
What Are The Challenges Of Blockchain In Finance?
- Scalability: As transaction volumes rise, many blockchain networks struggle with congestion and slower processing speeds. Financial systems require high throughput and minimal latency, making scalability a key technical hurdle.
- Interoperability: Limited compatibility between different blockchain frameworks creates fragmented systems. Without shared standards, data exchange and communication across financial networks become difficult, slowing integration within the blockchain in finance industry.
- Regulation and Compliance: The fast-changing blockchain landscape lacks a clear, global legal structure. Financial institutions often face uncertainty when aligning with local or cross-border regulations, especially around digital assets and smart contracts.
- Privacy and Data Control: Public blockchains are inherently transparent, which can expose sensitive financial information. Private and permissioned ledgers address this but may reduce the level of decentralization.
- Energy Use: Some consensus mechanisms, such as proof-of-work, consume high amounts of power. Newer systems using proof-of-stake or hybrid models are addressing these environmental concerns while maintaining network security.
- Security Risks: Although blockchain’s encryption enhances safety, vulnerabilities remain. Attacks like the 51% takeover can allow manipulation if one party gains majority control, highlighting the need for stronger governance models.
- Legacy Integration: Connecting blockchain with existing IT systems requires complex restructuring. Financial firms must redesign workflows and data pipelines to make distributed ledgers compatible with legacy platforms.
- Adoption Barriers: Organizational resistance remains common. Many firms hesitate to invest in blockchain due to cost, technical complexity, or disruption to existing operations.
- Talent Shortage: A lack of blockchain-skilled professionals slows implementation. Building and maintaining advanced blockchain for trading and finance systems demand expertise that’s still in limited supply.
Overcoming these challenges will be essential for blockchain’s long-term success in transforming how global finance operates.
How To Build The Future Of Blockchain In Finance
As the financial world continues to adopt digital innovation, blockchain in finance is evolving from experimentation to real-world transformation. Building its future requires combining automation, transparency, and decentralization into practical, scalable solutions. Below are five key approaches shaping that future.
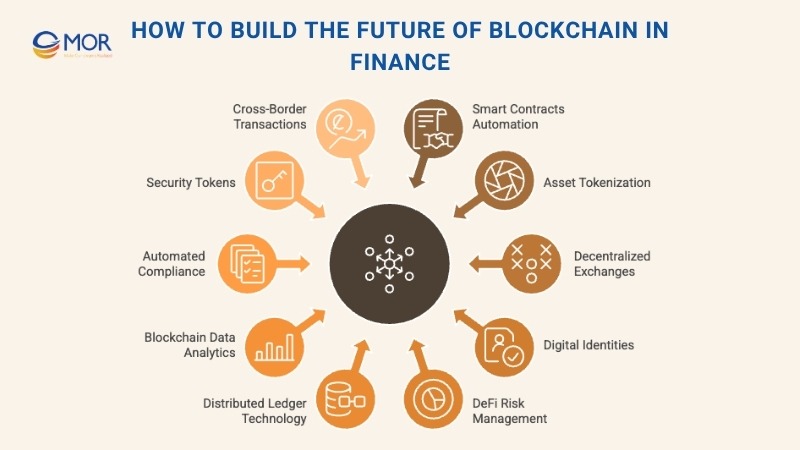
How To Build The Future Of Blockchain In Finance
1. Smart Contracts for Payment Automation
Smart contracts enable self-executing agreements that trigger payments automatically once conditions are met. Replacing manual paperwork, they cut operational costs and reduce processing time. These digital agreements are already streamlining loan approvals, insurance claims, and settlement workflows. Over time, this same automation will help drive sustainability efforts and transparent climate finance systems.
2. Tokenization to Transform Asset Ownership
Through blockchain technology in finance, real-world assets like real estate or equities can be represented as digital tokens. Tokenization lowers the cost of asset transfers, ensures traceable ownership, and opens access to previously illiquid markets. It’s a step toward a borderless economy where assets can be traded securely and instantly.
3. Decentralized Exchanges for Global Trading
Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) eliminate the need for intermediaries, allowing direct peer-to-peer trading of digital assets. This structure improves market liquidity, reduces trading fees, and strengthens privacy. With the global rise of blockchain for trading, institutions are exploring DEXs as a transparent alternative to centralized exchanges.
4. Digital Identities for Secure Verification
Blockchain-based digital identity systems simplify Know Your Customer (KYC) verification. These solutions let individuals control their personal data while giving banks tamper-proof access to verified information. The result is faster onboarding, fewer compliance risks, and a major step forward in preventing fraud.
5. DeFi Tools for Smarter Risk Management
Decentralized finance solutions, including stablecoins, staking, and liquidity pools, enable financial institutions to diversify portfolios and manage risk more efficiently. Using these tools, banks can maintain exposure to growth opportunities while minimizing volatility, paving the way for a more stable and inclusive blockchain in finance research paper future.
6. Distributed Ledger Technology for Transparency and Traceability
Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) forms the foundation of blockchain in finance, providing a permanent and verifiable record of all transactions. Removing the need for intermediaries, it strengthens accountability and reduces the risk of manipulation or data loss. This transparency is especially valuable for detecting fraud, preventing money laundering, and ensuring compliance with financial reporting standards.
7. Blockchain-Based Data Analytics for Risk Prediction
Integrating advanced analytics with blockchain infrastructure enables financial institutions to connect secure data sources and uncover deeper insights. Using AI-driven predictive analysis, firms can identify irregularities, detect potential risks, and forecast market behavior with greater accuracy. This combination of blockchain integrity and data intelligence enhances trust in financial forecasting and decision-making.
8. Automated Compliance Through Smart Rules
Embedding regulatory policies into smart, rules-based blockchain systems helps financial organizations stay compliant with evolving laws. These automated mechanisms verify transactions against legal requirements in real time, minimizing manual paperwork and reducing administrative costs. It’s a major step toward operational efficiency in the blockchain in finance industry.
9. Security Tokens for Safer Investment Access
Security tokens provide a compliant and transparent way for investors to participate in regulated markets. Representing ownership digitally, they simplify issuance, track investor rights, and ensure alignment with local regulations. These blockchain-enabled assets combine security with accessibility, opening new opportunities for institutional and retail investors alike.
10. Blockchain for Cross-Border Transactions
Blockchain in finance continues to revolutionize international payments by removing the friction of traditional banking channels. Transactions that once took days can now settle in seconds with lower fees and complete transparency. Through smart, decentralized systems, cross-border payments are becoming faster, safer, and more reliable, offering a true glimpse into the connected future of global finance.
MOR Software: Trusted Partner For Enterprise Blockchain In Finance
MOR Software delivers end-to-end blockchain in finance solutions tailored for real business results. We help financial institutions and enterprises move from theory to deployment with secure, scalable, and regulatory-ready systems.
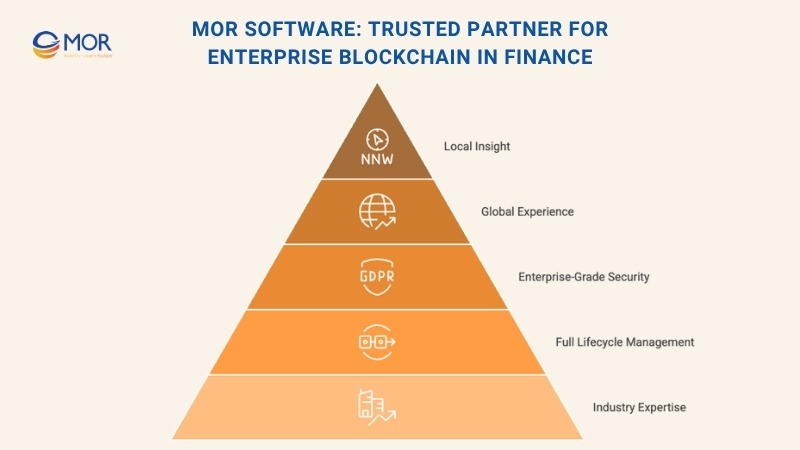
MOR Software: Trusted Partner For Enterprise Blockchain In Finance
Our approach combines technical expertise, domain knowledge, and agile development to ensure every blockchain project delivers measurable impact.
- Proven Industry Expertise: We’ve built blockchain solutions for sectors like banking, healthcare, and fintech, ensuring compliance, transparency, and data security at every stage.
- Full Development Lifecycle: From consultation and smart contract design to integration and long-term maintenance, we manage the complete blockchain implementation journey.
- Enterprise-Grade Security: All our blockchain in finance projects comply with ISO 9001:2015 and ISO 27001:2013 standards to safeguard transactions and customer data.
Global Experience, Local Insight: With offices across Vietnam and Japan, MOR Software bridges global best practices with local market understanding to deliver solutions that truly work.
Conclusion
The rise of blockchain in finance marks a turning point for global financial systems. From automation and transparency to faster cross-border payments, blockchain is redefining how institutions operate and build trust. As adoption grows, those who act early will gain the strongest advantage. Partner with MOR Software to turn blockchain potential into business value. Contact us today to build secure, future-ready blockchain solutions for your enterprise.
MOR SOFTWARE
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a blockchain in finance?
Blockchain in finance refers to a distributed digital ledger that records transactions securely and transparently across a shared network. It eliminates the need for intermediaries, allowing financial institutions to track assets, verify data, and manage transactions through a single, reliable system.
Is blockchain the future of finance?
Blockchain is becoming a foundation for modern financial infrastructure. It streamlines operations like payments, settlements, and trading while enhancing security and transparency. Many financial organizations see it as the next step toward faster, more cost-efficient, and trustworthy global finance systems.
How does JP Morgan use blockchain?
JP Morgan applies blockchain through its Onyx platform, which supports instant cross-border payments, tokenized deposits, and smart contracts. This approach helps the bank reduce transaction time, lower operational costs, and improve liquidity management.
What is the role of blockchain in modern finance?
Blockchain plays a key role in improving transaction speed, security, and data integrity. It enables smart contracts that execute automatically when conditions are met, reducing manual errors and increasing transparency across financial processes.
How to implement blockchain in finance?
Businesses can integrate blockchain without building new systems from scratch. Many adopt existing blockchain networks to write smart contracts, automate recordkeeping, and securely manage data. Implementation often starts with small-scale pilots before expanding to core financial operations.
Are any banks using blockchain?
Yes. Leading banks like JP Morgan, Goldman Sachs, and Santander already use blockchain for cross-border payments, asset tokenization, and foreign exchange. These efforts demonstrate how blockchain can enhance speed and reduce transaction costs across banking operations.
Why don’t banks use blockchain?
Some banks remain cautious due to challenges like scalability, regulatory uncertainty, and legacy system integration. However, many early adopters have already found practical ways to overcome these issues through hybrid models and compliance-focused blockchain frameworks.
How can blockchain revolutionize the finance industry?
Blockchain has the power to modernize finance by reducing settlement delays, minimizing fraud, and strengthening KYC and AML compliance. It ensures real-time data validation, improving efficiency in areas like lending, trading, and payments.
What is the future of blockchain in finance?
Blockchain will continue to transform how institutions handle compliance, security, and transparency. It can help reduce financial crimes, enhance data governance, and promote safer, more efficient digital financial ecosystems worldwide.
How blockchain will replace banks?
In a central bank digital currency (CBDC) system, blockchain could allow direct interaction between central banks and consumers. This shift might reduce the role of commercial banks in managing deposits or creating money, especially for routine digital transactions.
Will blockchain change the future of financial systems?
Yes. Blockchain is reshaping financial systems by improving risk management, transaction accuracy, and overall trust. Many institutions are already using it to power smart contracts, automate settlements, and open new revenue streams through digital finance innovation.
Rate this article
0
over 5.0 based on 0 reviews
Your rating on this news:
Name
*Email
*Write your comment
*Send your comment
1