Blockchain in Intellectual Property: Definitive Guide 2026

Managing copyrights and patents has always been complex and time-consuming. Now, blockchain in intellectual property is transforming how creators and businesses protect and monetize their innovations. This MOR Software’s guide explores how blockchain streamlines ownership verification, automates licensing, and strengthens global IP protection, helping organizations prepare for a more transparent and secure digital future.
What Is Blockchain In Intellectual Property (IP)?
In 2021, fake and pirated products were worth around USD 467 billion, making up about 2.3% of global imports. This huge number shows how serious the problem is and why strong IP protection is important.
Blockchain in intellectual property refers to using distributed ledger technology to manage and protect creative assets like patents, copyrights, trademarks, industrial designs, and trade secrets. It provides a transparent, time-stamped system for recording and validating ownership, helping creators and businesses secure their innovations from misuse or duplication.
At its core, this technology builds a decentralized ledger that permanently stores data across multiple nodes, making it nearly impossible to alter or counterfeit. Each transaction related to intellectual property, whether a new registration, ownership transfer, or license agreement, is recorded as a verifiable block. This system ensures authenticity, traceability, and proof of origin for creative works.
The blockchain role in tokenizing intellectual property is also gaining attention. Through tokenization, digital tokens can represent ownership or licensing rights to IP assets, enabling easier transfers, fractional ownership, and automated royalty payments through smart contracts. Analysts from BCG and ADDX estimate that asset tokenization could be worth around US$16.1 trillion by 2030, which would equal about 10% of the world’s GDP. This shows how big the opportunity for IP tokenization might become in the near future.
This innovation simplifies IP transactions while maintaining legal integrity.
In short, blockchain introduces a trustworthy, tamper-proof foundation for protecting and commercializing intellectual property in the digital era, empowering creators, companies, and legal entities to manage rights with greater security and transparency.
How Does A Blockchain In Intellectual Property Platform Work?
Before explaining how a blockchain in intellectual property platform operates, it’s useful to understand who takes part in the system and what roles they play.
Key Users:
- Patent Creators: Individuals who produce original work, researchers, designers, writers, or inventors, seeking to secure and prove authorship.
- Patent Consumers: Businesses or individuals interested in licensing, purchasing, or investing in creative assets.
- IP Management Entities: Organizations that monitor, verify, and enforce intellectual property rights on behalf of creators and rights holders.
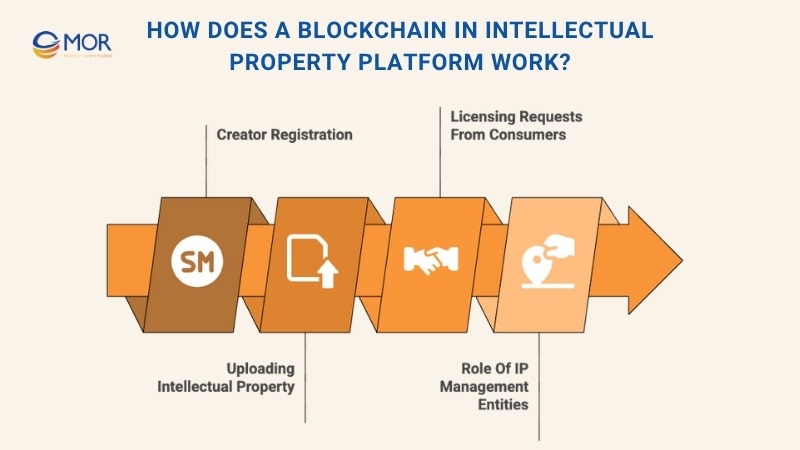
Step 1: Creator Registration
Creators begin by signing up on the platform to establish ownership of their work. During registration, they provide verified details such as:
- Full name
- Address
- Contact information
- Designation or professional title
Each record is securely stored on the distributed ledger, ensuring authenticity and data protection. Because the information cannot be altered once added, creators can prove the originality of their work at any time. This immutable record enhances trust between all parties and strengthens the foundation for future transactions and licensing within the system.
Step 2: Uploading Intellectual Property To The Blockchain
After registration, creators upload their intellectual property data to the blockchain network. Each entry includes key details such as:
- Creator’s name
- Current owner
- Title of the work
- Relevant keywords
- Abstract or description
- Classification type
Once uploaded, the system encrypts and timestamps every record to maintain authenticity. This setup guarantees auditability and traceability, making it nearly impossible to duplicate or alter the information. The entry becomes a permanent reference point within the network, visible to authorized participants for verification and validation of ownership. This process also supports blockchain for patents, ensuring creators retain transparent proof of their rights from the moment of submission.
Step 3: Licensing Requests From Consumers
Consumers who want to access or license a creator’s work must register and verify their identity within the blockchain in intellectual property platform. Once verified, they can submit requests directly to the creator through the system.
Before granting access, the platform automatically generates a smart contract outlining usage terms, payment conditions, and licensing duration. Token-based transactions are often used to automate these payments securely. After both parties agree, a non-disclosure agreement (NDA) is digitally signed alongside the contract, ensuring legal protection and transparent execution. This process streamlines licensing while maintaining compliance and trust across the network.
Step 4: Role Of IP Management Entities
Once transactions are recorded, disputes or clarifications may occur, such as:
- Unauthorized distribution or misuse of protected material
- Questions about original authorship
- Ownership or transfer disagreements
- Defensive publications or prior art claims
In such situations, creators or consumers can contact IP management authorities or legal professionals directly within the blockchain network. These entities review immutable, time-stamped records to verify authenticity, ownership, and originality of the intellectual property. The transparent audit trail helps resolve conflicts quickly without manual documentation.
With this framework in place, blockchain in intellectual property platforms demonstrate how governance and verification can be handled efficiently in a decentralized ecosystem, paving the way for wider adoption across industries.
Benefits Of Blockchain In Intellectual Property For Businesses
Traditional intellectual property systems rely heavily on centralized databases that are often slow, fragmented, and open to human error. In contrast, blockchain in intellectual property introduces a tamper-proof record of every transaction, verified and timestamped across a distributed ledger. This means:
- Proof of ownership and creation can be verified instantly.
- Every transfer, licensing action, or update remains permanently auditable.
- Any stakeholder can confirm authenticity and ownership within seconds.
Smarter IP Management And Licensing
Blockchain simplifies the complex process of managing and licensing creative assets.
- Smart contracts automate licensing and royalty payments, activating instantly when agreed terms are met.
- Digital registries accelerate registration and allow for global management without borders.
- Through tokenization, creators can represent IP assets as digital tokens, making transfers and licensing transparent and frictionless.
These innovations highlight how blockchain applications in intellectual property protection are reshaping traditional workflows, giving tech companies faster, safer, and more transparent control over their IP assets.
Cost And Time Efficiency
Managing intellectual property traditionally involves layers of documentation and intermediaries. Blockchain reduces these barriers by:
- Cutting out middlemen and redundant checks
- Minimizing paperwork and administrative delays
- Allowing disputes to be resolved quickly with immutable, timestamped data
Through replacing manual verification with automation, businesses save both time and cost while strengthening trust across every stage of their IP lifecycle.
Blockchain Applications In Intellectual Property Protection
Blockchain in intellectual property is redefining how ownership, authenticity, and licensing are handled across industries. It gives creators and enterprises a transparent way to secure their patents, trademarks, and digital assets without relying on centralized registries. Combining automation and cryptographic validation, blockchain technology future in intellectual property protection is moving from theory to real-world adoption. Below are key use cases showing how it works in practice.
Proof Of Ownership
Recording an innovation or creative work on the blockchain instantly establishes verifiable ownership. Each entry is timestamped and encrypted, providing a permanent link between the creator and the asset. Unlike traditional systems that depend on paper records or government-led databases, this decentralized structure guarantees that the record cannot be altered or forged.
The same principle applies to blockchain for patents, where digital proof of authorship helps distinguish original inventions from duplicates and strengthens legal claims when ownership is challenged.
Decentralized IP Marketplace
A blockchain in intellectual property platform can host a decentralized marketplace where creators, investors, and companies trade or license IP rights without intermediaries. This digital ecosystem promotes transparency, efficiency, and fair compensation for all participants.
The system typically includes three main components:
- IP Registries: A shared digital ledger where ownership details and creative works are permanently recorded.
- IP Exchange: A blockchain-based mechanism for verifying and transferring IP rights securely between parties.
- IP Payments: Smart contracts manage and release royalty payments automatically once licensing or sales conditions are fulfilled.
Together, these elements create a trusted environment for global collaboration, giving creators new opportunities to monetize innovation while maintaining full control over their intellectual assets.
Evidence Of IP Rights Usage
Tracking how intellectual property is used across regions often requires extensive documentation and oversight. A blockchain in intellectual property system simplifies this process by logging every interaction with an asset in real time.
Each time a trademark, patent, or copyrighted material is used commercially, the network automatically records the event and timestamps it. These immutable logs serve as digital evidence, proving active use and ownership continuity. This approach not only helps organizations comply with legal standards but also prevents misuse or unauthorized exploitation of their creative assets.
Version Control For Evolving IP Assets
Creative works and patents often go through multiple revisions as they mature. A blockchain in intellectual property platform maintains a transparent record of every modification, ensuring that each version is securely linked to the previous one.
Every update is logged with a distinct digital signature and timestamp, forming an unbroken chain of development. This structure prevents tampering, accidental overwrites, or data loss while giving creators a detailed version history of their intellectual assets. It ensures complete visibility into how an invention or creative work has evolved over time.
Verification Of Unregistered IP Rights
Not all creators register their intellectual property immediately, yet ownership still needs protection. Through blockchain in intellectual property, creators can record a timestamped proof of authorship even before official registration.
Each record stores essential metadata, including creator identity and creation date, forming verifiable evidence of originality. When these blockchain records are later reviewed by an IP office or collective rights organization, they can serve as strong legal support in disputes or licensing negotiations.
This approach ensures transparency and early protection for unregistered works, showing how blockchain technology future in intellectual property protection will continue to reinforce trust, authenticity, and fairness across creative and technical sectors.
A Creator’s Guide To Blockchain In Intellectual Property Rights
Many creators still view blockchain in intellectual property as something complex or highly technical, but the reality is becoming much simpler. Modern platforms now make it easy for artists, writers, developers, and inventors to register and manage their creations securely on the blockchain. These systems provide automated protection, transparent ownership records, and flexible tools for monetization, all without requiring deep technical knowledge.
How To Earn From Your Work Using Blockchain
This is where ip crypto opens up exciting opportunities. By integrating micropayments into blockchain-registered intellectual property, creators can earn revenue each time their work is accessed or licensed. For instance, whenever someone downloads a design, streams a song, or uses a photo, a small amount of digital currency can be transferred instantly to the creator’s wallet.
This automated income model reduces intermediaries and ensures that creators receive fair compensation in real time. It’s a direct, transparent way to monetize creative assets while maintaining full control over how and where their work is used.
Practical Ways Blockchain Protects Creators
With growing digital exposure, creators need stronger control over how their work is shared, sold, and credited. The following real-world uses of blockchain in intellectual property show how this technology empowers creators to protect, monetize, and manage their content with transparency and confidence.
1. Establish A Digital IP Marketplace
A blockchain in intellectual property platform can host a global marketplace where creators upload their music, designs, software, or any digital content with verified ownership. These decentralized spaces allow creators to showcase and license their work directly to buyers or investors, eliminating intermediaries and reducing fees. By connecting creators and licensees securely, blockchain encourages a fair and open creative economy where rights and payments are fully transparent.
2. Version Control For Creative Assets
Blockchain platforms designed for intellectual property management act like a digital archive for every edit or update. Each modification, whether it’s a code revision or an artwork enhancement, is permanently logged with a timestamp. This makes it easy to track development over time and provides indisputable evidence against plagiarism or false ownership claims.
3. Protection For Unregistered Works
Even without formal registration, creators can still safeguard their work. When a file is added to a blockchain-based IP platform, it’s automatically timestamped and verified. This record proves authorship and originality, supporting future ownership claims if disputes arise. For many independent creators, this process offers affordable and reliable early protection without legal complexity.
4. Blockchain As A Shield Against Digital Piracy
Unauthorized distribution has long been a nightmare for creators. With blockchain in intellectual property, every creative work receives a verifiable proof of ownership that’s recorded permanently. This record allows creators to identify authentic versions of their work and take action against piracy quickly. By linking each asset to an immutable blockchain record, creators gain strong legal backing to combat counterfeit copies and unauthorized uploads online.
5. Automated Royalties For Creators
Smart contracts embedded in blockchain platforms simplify royalty management. These digital agreements automatically release payments whenever a registered work is used, streamed, or downloaded. Every transaction is transparent, traceable, and instant. Whether it’s a song played on a streaming service or a design licensed to a brand, the creator receives funds directly, removing intermediaries and payment delays. It’s a fair, automated system that keeps creators in control of their income.
6. The Future Of Digital Ownership With NFTs
NFTs, powered by blockchain, give creators a way to assign verified ownership to digital assets like music, artwork, videos, and in-game collectibles. Each NFT acts as a unique certificate of authenticity, proving originality and enabling creators to sell limited editions of their work. This modern approach merges creative freedom with secure digital ownership, expanding how value is created and exchanged online.
7. Enforcing Creative Rights And Fair Terms
Blockchain in intellectual property platforms make fair licensing automatic. With smart contracts, creators can define how others use their work, such as permitting personal use but restricting commercial exploitation. These self-executing contracts enforce terms instantly, ensuring fair compensation and compliance without legal intervention. It’s a reliable way to safeguard creative rights while maintaining transparency in every transaction.
Countries Adopting Blockchain In Intellectual Property Protection
The adoption of blockchain in intellectual property is gaining traction as governments and organizations explore ways to modernize copyright management. Although still developing, several regions have already begun testing or implementing blockchain-based IP systems to improve transparency, efficiency, and security.
The United States
The U.S. Copyright Office is studying how blockchain can simplify copyright registration and improve public access to ownership data. According to an official report, the agency is also reviewing how NFTs can help creators verify authorship, automate licensing, and strengthen copyright claims beyond traditional registration systems.
China
China has taken a proactive approach by launching a national blockchain intellectual property platform through the Copyright Society of China. This initiative, introduced in 2021, focuses on lowering costs and boosting the efficiency of digital rights protection. It enables creators to track and manage their content ownership across multiple online platforms.
European Union
The European Commission introduced the Blockchain Regulatory Sandbox in early 2023 to encourage experimentation and knowledge sharing among regulators, innovators, and industry experts. The program helps participants test blockchain solutions in intellectual property, ensuring that legal and compliance frameworks keep pace with technological progress.
India
India’s National Informatics Centre has integrated blockchain into its digital document infrastructure, hosting millions of verifiable records across sectors such as education, property, and pharmaceuticals. The same framework is being extended to protect creative works and establish verifiable authorship, paving the way for broader blockchain adoption in IP protection.
Global Companies Applying Blockchain In Intellectual Property
Several leading corporations have already integrated blockchain in intellectual property systems to strengthen transparency, prevent counterfeiting, and ensure fair compensation for creators. These initiatives show how the technology is being used across industries, from tech to entertainment, to protect innovation and maintain trust.
IBM
IBM applies blockchain to track product origin, ownership, and movement across complex supply chains. This solution helps confirm authenticity, reduce fraud, and protect the intellectual property linked to goods and components. Its patent blockchain framework supports data-driven insights that help businesses build more resilient and traceable operations.
Samsung
Samsung is developing blockchain patents and tools for managing digital rights across its platforms. The company’s blockchain ecosystem enables secure distribution of copyrighted content and allows developers to integrate decentralized applications through the Samsung Blockchain Wallet. This initiative helps creators safeguard their content while participating in a trusted digital marketplace.
BASF
BASF began adopting blockchain technology in 2018 to monitor and document its research and material innovation processes. By recording every stage of product development, the company protects the intellectual property behind its R&D while improving transparency across supply chains and collaborations.
Sony Music Entertainment
Sony is testing blockchain with AWS to ensure artists receive fair and timely royalties. Its pilot projects use blockchain-ledger tracking to verify music streaming data, automate payments, and prevent disputes over usage reporting. The result is a more transparent and accurate digital rights management model.
Pfizer
Pfizer is exploring blockchain through the Clinical Supply Blockchain Working Group, aiming to enhance experimental drug tracking and intellectual property management. This initiative focuses on securing research data and improving visibility across the clinical trial supply chain, strengthening the integrity of pharmaceutical innovation.
Common Challenges In Blockchain-Based IP Systems
Despite the growing success of blockchain in intellectual property, its implementation still faces several hurdles that companies and regulators must address to achieve broader adoption.
Scalability Barriers
Public blockchains, while secure, often struggle with high fees and slower transaction speeds when handling large volumes of IP data. These limitations make it difficult to scale efficiently for global copyright and patent systems. Emerging solutions such as private or hybrid blockchains, as well as Layer 2 frameworks, can improve performance, but they may compromise interoperability and decentralization in the process.
Legal And Regulatory Gaps
Global IP regulations have yet to fully align with blockchain technology. Key challenges include:
- Whether blockchain records are legally admissible in intellectual property disputes
- How courts interpret and enforce smart contract obligations
- The lack of harmonized rules for cross-border licensing and recognition of blockchain-based IP ownership
These uncertainties show that blockchain and IP law must evolve together to support widespread legal adoption.
Technical Skill Requirements
Deploying blockchain IP solutions demands specialized technical expertise. Teams must know how to integrate blockchain networks, safeguard sensitive data, and defend systems against emerging cyber threats. Building these solutions securely is not a plug-and-play process, it requires coordination between developers, cybersecurity experts, and legal advisors to maintain compliance and protect intellectual assets effectively.
How MOR Software Helps Protect Businesses’ IP Rights
Protecting intellectual property is central to every project we deliver. At MOR Software, we treat clients’ ideas, data, and code as business-critical assets that demand confidentiality and security from start to finish. Our approach combines trusted processes, clear ownership policies, and modern technology to keep IP safe.
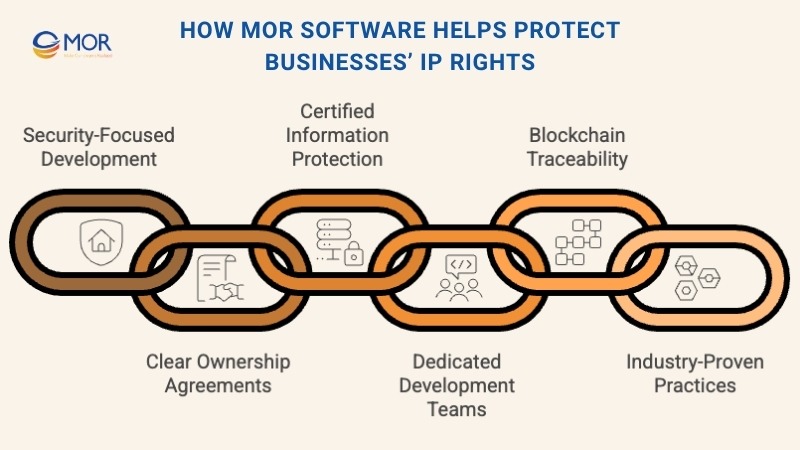
- Security-Focused Development: Every product is built with strict security controls, encryption, and code reviews to prevent leaks and unauthorized access.
- Clear Ownership Agreements: Clients retain full rights to all source code, documentation, and digital assets under legally binding IP clauses.
- Certified Information Protection: With ISO 27001 and ISO 9001 certifications, we maintain global standards for data security and quality management.
- Dedicated Development Teams: Offshore teams work under NDAs in isolated, access-controlled environments to protect sensitive business information.
- Blockchain Traceability: Our R&D efforts apply blockchain technology to create timestamped proof of authorship, licensing, and IP transfers.
- Industry-Proven Practices: From healthcare to fintech, our 850+ global projects follow strict compliance and privacy requirements.
MOR Software builds lasting partnerships based on trust, transparency, and protection. We don’t just create software, we safeguard the innovation that drives your business forward.
FAQs: Blockchain In Intellectual Property
1. How can blockchain be used in intellectual property?
Blockchain creates an unchangeable, time-stamped record that proves when and by whom an idea or asset was created. This helps creators verify ownership of inventions, designs, or written works while preventing disputes over originality.
2. What is an IP blockchain?
An IP blockchain is a decentralized network where intellectual property rights, like patents, trademarks, and copyrights, are securely stored, managed, and transferred. It allows creators to register and track their assets digitally without relying on centralized authorities.
3. How does blockchain help prevent IP theft?
Blockchain provides transparent records that can’t be modified or deleted. Each transaction or ownership change is recorded permanently, making it easier to detect unauthorized use or duplication of creative or patented work.
4. Can blockchain replace traditional IP registration systems?
Not yet. Blockchain complements existing IP systems by offering verifiable proof of ownership and faster verification. However, formal IP registration with government offices is still required for full legal protection.
5. Is Bitcoin considered intellectual property?
The Bitcoin protocol itself isn’t patented, but the Bitcoin name and logo are protected trademarks in several jurisdictions. The technology behind Bitcoin is open source, yet related brand identities can still fall under IP protection.
6. What are the main types of intellectual property?
Intellectual property protection typically covers four main categories: copyrights, trademarks, patents, and trade secrets. Each safeguards different forms of creative or technical innovation.
7. Can blockchain verify ownership of digital art or NFTs?
Yes. Blockchain’s immutable records verify who owns a piece of digital art, when it was created, and every time it changes hands. This transparency has made it the foundation of NFT-based ownership models.
8. How do smart contracts support IP licensing?
Smart contracts automate licensing terms by releasing usage rights or payments once specific conditions are met. This reduces disputes, speeds up royalties, and ensures fair compensation for creators.
9. Is blockchain suitable for small creators and startups?
Absolutely. Blockchain-based IP tools let small creators register their work instantly at low cost, giving them a secure timestamped record without needing large legal resources.
10. What challenges exist in applying blockchain to IP management?
The biggest hurdles are regulatory uncertainty, lack of global standardization, and technical complexity. While blockchain strengthens IP verification, international laws still need to evolve to recognize its full legal validity.
Conclusion
As industries continue to innovate, protecting intellectual property has never been more important. Blockchain in intellectual property gives businesses and creators a transparent, secure way to manage ownership and licensing. With proven expertise across 850+ global projects, MOR Software helps organizations apply cutting-edge technology to protect, verify, and monetize their ideas. Ready to secure your digital assets with confidence? Contact us today to start building a safer foundation for your IP future.
Rate this article
0
over 5.0 based on 0 reviews
Your rating on this news:
Name
*Email
*Write your comment
*Send your comment
1