Blockchain Interoperability: Ultimate Guide for Enterprises 2025

As blockchain networks continue to expand, the need for seamless blockchain interoperability has become more urgent than ever. Many enterprises struggle with isolated systems that limit data exchange, increase costs, and slow innovation.In this MOR Software‘s guide, we explore how interoperability blockchain solutions are transforming enterprises in 2025, driving connectivity and growth.
What Is Interoperability In Blockchain?
Blockchain interoperability is the capability of different blockchain networks to connect, share data, and exchange value without friction. In simple terms, it allows separate systems to talk to each other instead of working in isolation. Without this link, most blockchains remain closed environments, each running its own set of rules, assets, and users with no direct bridge for communication. This function is central to the interoperability crypto list, which continues to expand as new projects aim to build more connected blockchain ecosystems.
What Is Interoperability In Blockchain?
Interoperability matters because it unlocks blockchain’s broader purpose: collaboration. It lets assets and information flow across chains, supporting multi-network applications and integrated financial systems. This connection transforms blockchains from isolated platforms into a unified ecosystem where transactions, smart contracts, and digital assets can operate together.
Analysts now expect tokenized assets alone to approach about 2 trillion dollars in market value by 2030. This shows why seamless operation across networks is becoming so important.
Key Terms In Blockchain Interoperability
Before exploring how blockchain interoperability works, it’s important to understand a few core terms that define how different blockchains communicate, share data, and exchange assets across networks. These concepts form the foundation for every interoperability framework.
Key Terms In Blockchain Interoperability
- Cross-chain: This term describes how separate blockchain networks can connect, exchange data, and move digital assets between one another. A cross-chain mechanism acts as a bridge, allowing transactions like sending Bitcoin from its native chain to Ethereum without leaving the blockchain environment. To see the scale of these bridges in everyday use, Wrapped Bitcoin on Ethereum sits at roughly 127,000 tokens in circulation with a market capitalization of around 14.3 billion dollars.
- Multi-chain: This refers to an ecosystem or application that operates across several blockchain networks at once. Each network plays a different role, one might process transactions faster, while another ensures strong security and immutability. Working together, they create a balanced system that blends speed with reliability.
- Interoperable blockchains: These are blockchains intentionally built to communicate and collaborate with other networks. Well-known examples include Polkadot and Cosmos, which use their core architecture to support shared communication layers, letting decentralized systems exchange data and assets efficiently across multiple platforms.
How Does Blockchain Interoperability Work?
Let’s say you hold 1 Bitcoin (BTC) and want to use it within an Ethereum-based DeFi app. In a disconnected blockchain setup, you’d have to sell your BTC for Ether (ETH) through a centralized exchange. That means paying fees, waiting for confirmation, and losing some of your asset’s value in the process.
With blockchain interoperability, that step isn’t necessary. You can simply convert your BTC into Wrapped Bitcoin (WBTC), a token pegged 1:1 to Bitcoin but built on the Ethereum network. This wrapped asset gives you the same value as BTC while being compatible with Ethereum’s DeFi ecosystem, allowing faster and cheaper transactions.
At its core, blockchain interoperability depends on a mix of interoperability protocols, smart contracts, and network bridges that enable smooth data and asset exchange between different chains. These technologies work together to link separate systems, letting users move digital assets freely and securely across platforms.
How Does Blockchain Interoperability Work?
Technical Mechanisms And Protocols
The foundation of blockchain interoperability lies in the technical systems and blockchain interoperability protocols that let different blockchains communicate under shared rules. These define how data or assets move, get verified, and are recorded across multiple networks, ensuring transactions remain transparent and secure.
Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC) Protocols
Interoperability blockchain relies on IBC protocols to enable direct exchanges of data and value between networks. A good example is Cosmos, which uses its IBC framework to let connected blockchains interact safely within a unified ecosystem.
Atomic Swaps
Atomic swaps make it possible for users to trade cryptocurrencies across chains without relying on intermediaries. Using cryptographic safeguards, these swaps ensure that either both sides of the exchange succeed or neither does, preventing fraud or partial completion.
Hashed Timelock Contracts (HTLCs)
HTLCs are specialized smart contracts that support secure cross-chain transactions. They employ hash functions and time-based conditions to ensure trades occur as intended within a set timeframe, maintaining trust between independent networks.
Smart Contracts And Bridges
Both smart contracts and blockchain bridges are vital components that make blockchain interoperability practical and efficient across different ecosystems. They automate complex transactions and create the pathways that let data and assets move securely between networks.
Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are self-executing agreements written directly in code. Once the preset conditions are met, they trigger actions automatically, eliminating intermediaries. In an interoperability blockchain setup, these contracts allow decentralized applications to coordinate actions across multiple networks, ensuring trust and consistency.
Blockchain Bridges
Blockchain bridges, often known as cross chain protocol systems, connect two or more blockchains so assets and data can flow freely between them. They can work through pegged tokens, where one chain mirrors the value of another, or through cross-chain oracles that deliver validation data between independent networks, keeping every transaction transparent and verifiable.
Consensus And Validation Across Chains
Maintaining trust in blockchain interoperability depends on strong consensus and validation methods that work across networks. These systems confirm that every transaction and data exchange remains accurate and tamper-proof, no matter which blockchain it occurs on.
Cross-Chain Consensus Mechanisms
Cross-chain consensus mechanisms align multiple blockchains to agree on the same transaction outcomes. A well-known example is Polkadot, which uses a central relay chain to coordinate consensus among its parachains, keeping all network states synchronized and verifiable.
Validation Nodes
Validation nodes act as gatekeepers in interoperable blockchains, operating across several networks to authenticate and approve transactions. In ecosystems like Cosmos, validators share a common security framework, reducing the risk of fraud and ensuring consistency throughout the blockchain interoperability market.
Security And Trust Models
Strong security and trust frameworks are critical to keeping blockchain interoperability networks reliable and tamper-proof. Each model focuses on safeguarding transactions and data while preventing fraud or unauthorized interference across multiple blockchains.
Shared Security Models
In shared security models, several blockchains rely on a unified security layer. Polkadot’s relay chain is a prime example, protecting its connected parachains under one security structure. This design ensures that a vulnerability in one network doesn’t compromise others, maintaining overall system stability.
Decentralized Trust Models
Decentralized trust models distribute control among independent participants to eliminate single points of failure. Using decentralized oracles and multi-signature wallets helps establish trust between networks by requiring consensus from multiple parties before confirming transactions.
Cryptographic Techniques
Modern blockchain interoperability solutions employ cryptographic tools like zero-knowledge proofs and multi-party computation to secure cross-chain operations. These methods keep transaction data private and verifiable without depending on centralized authorities, building a stronger layer of protection for interconnected blockchains.
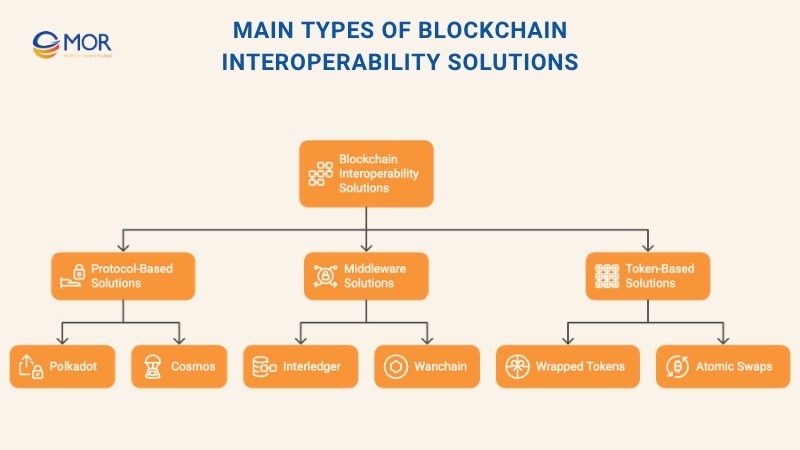
Main Types Of Blockchain Interoperability Solutions
Different approaches have emerged to make blockchain interoperability practical across industries. The following solution types highlight how protocols, middleware, and token-based systems each enable seamless data and asset exchange between networks.
Main Types Of Blockchain Interoperability Solutions
Protocol-Based Solutions
Protocol-based blockchain interoperability solutions focus on developing standardized communication systems that let different blockchains connect and share data effortlessly. These blockchain interoperability protocols are often embedded directly into a blockchain’s structure, making communication automatic and consistent across networks.
One of the best-known examples is Polkadot (DOT), a project designed to unite multiple blockchains under one network.
Polkadot (DOT)
Polkadot connects various blockchains through a central relay chain that ensures smooth data and asset transfer between them. Its architecture includes:
- Relay Chain: The main coordination hub that links all connected blockchains, known as parachains, and manages communication and transaction validation.
- Parachains: Independent blockchains that operate alongside the relay chain, benefiting from shared security while maintaining their own governance and rules.
- Bridges: Dedicated links that connect Polkadot with external blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum, widening the scope of interoperable blockchains.
Polkadot’s shared security layer protects every connected chain while maintaining flexibility. This design makes it one of the most trusted systems for enabling efficient blockchain interoperability across diverse networks.
Cosmos (ATOM)
Cosmos (ATOM) was built to form an “Internet of Blockchains,” allowing independent networks to connect and operate together without central control. Its goal is to make blockchain interoperability simpler, faster, and more decentralized.
The Cosmos ecosystem is powered by three main components:
- Tendermint Core: A high-speed consensus engine that secures transactions and maintains synchronization across blockchains.
- Cosmos SDK: A modular toolkit that helps developers build custom blockchains suited to different use cases, from finance to gaming.
- Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC) Protocol: A universal standard for transferring data and digital assets between networks within the Cosmos ecosystem.
Through its IBC protocol, Cosmos creates a reliable pathway for independent blockchains to exchange information and value, strengthening connectivity and scalability across the entire blockchain interoperability market.
Middleware Solutions
Middleware solutions act as bridges between blockchain platforms, helping them exchange data and assets without modifying their underlying structure. This approach makes them easier to adopt within existing systems while still delivering the benefits of blockchain interoperability.
Interledger
Interledger is a value transfer protocol that links different payment systems and ledgers, including blockchains, into one interoperable framework.
Key features include:
- Ledger-Agnostic Design: Interledger works independently of any single blockchain, making it compatible with traditional financial systems and digital ledgers alike.
- Connectors: These serve as intermediaries, safely routing transactions between ledgers to ensure secure and reliable value exchange.
- Payment Pointers: Unique identifiers that simplify payment routing across diverse systems and ledgers.
Through its flexible design, Interledger enables smooth cross-ledger communication, improving collaboration between blockchain networks and conventional finance systems.
Wanchain
Wanchain provides decentralized infrastructure that supports cross-chain asset transfers and applications for the growing DeFi sector.
Key components include:
- Cross-Chain Bridges: Connect Wanchain with blockchains like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Eos to enable direct asset transfers.
- Locked Account Mechanism: Combines smart contracts and multi-party computation to secure transactions across networks.
- Universal Multi-Chain Bridges: Allow interaction with several blockchains at once, expanding network connectivity and flexibility.
By integrating these technologies, Wanchain strengthens liquidity and network collaboration within the blockchain interoperability protocol ecosystem, enabling digital assets to move freely between diverse chains.
Token-Based Solutions
Token-based blockchain interoperability solutions use digital tokens to represent assets across different networks, allowing users to transfer and trade seamlessly. These systems depend on smart contracts and cryptographic safeguards to guarantee transparency, accuracy, and security throughout every transaction.
Wrapped Tokens
Wrapped tokens mirror the value of an asset from one blockchain while making it usable on another. This design lets users enjoy the advantages of multiple ecosystems, such as Ethereum’s smart contract functionality combined with Bitcoin’s value stability.
Key characteristics include:
- 1:1 Backing: Each wrapped token maintains equal value with its original asset, preserving trust and liquidity.
- Smart Contracts: Handle token issuance and redemption automatically, ensuring reliable and secure processes.
- Cross-Network Interoperability: Let users move non-native assets across blockchains, expanding functionality and creating new DeFi opportunities.
Popular examples include Wrapped Bitcoin (WBTC) on Ethereum and Wrapped Ether (WETH), both widely used in decentralized applications. These assets play a key role in linking isolated blockchain economies into one connected ecosystem.
Atomic Swaps
Atomic swaps are peer-to-peer exchanges that let users trade cryptocurrencies directly across different blockchains, removing the need for intermediaries. This method boosts liquidity and supports trustless trading across ecosystems.
Key characteristics include:
- Hashed Time-Locked Contracts (HTLCs): Provide transactional security by ensuring both sides of a trade complete their commitments or cancel safely.
- Cross-Chain Compatibility: Enable direct swaps between assets like Bitcoin and Litecoin without using centralized exchanges.
- Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs): Many DEXs rely on atomic swaps, automated market makers, and smart order systems to power efficient, transparent, and secure interoperability blockchain trading environments.
Comparison Of Blockchain Interoperability Solutions
The table below highlights how major blockchain interoperability solutions differ in their structure, use cases, and adoption levels:
Feature | Polkadot (DOT) | Cosmos (ATOM) | Interledger | Wanchain | Wrapped Tokens | Atomic Swaps |
| Capabilities | Cross-chain transfers with shared security | Direct cross-chain communication | Cross-ledger value transfer | Cross-chain asset movement | Asset representation through tokens | Peer-to-peer crypto exchanges |
| Adoption | High | High | Medium | Medium | High | Medium |
| Use Cases | DeFi, IoT, gaming ecosystems | DeFi networks, interoperability hubs | Payment and settlement systems | DeFi applications, cross-chain finance | DeFi, digital asset tokenization | DEXs and decentralized trading |
| Limitations | Governance and technical complexity | Scalability and adoption hurdles | Limited blockchain compatibility | Integration and security concerns | Reliance on original asset value | Complex implementation process |
Each approach contributes differently to the blockchain interoperability problem, showing how innovation continues to connect fragmented blockchain systems into a more unified digital ecosystem.
Key Benefits Of Blockchain Interoperability
Blockchain interoperability delivers a range of advantages that make decentralized systems more connected, efficient, and practical for real-world use. These benefits support both technical innovation and broader adoption across industries.
Key Benefits Of Blockchain Interoperability
1. Cost Efficiency
When blockchains can communicate directly, there’s no need to build and maintain separate, isolated systems. Shared data and resource exchange help reduce infrastructure costs, simplify integration, and eliminate repetitive development efforts. This creates leaner operations and faster project deployment across multiple chains.
The global policy push reflects this priority too, with the G20’s targets calling for average retail cross-border payment costs to drop to about 1% and no corridor above 3% by the end of 2027. This is a goal that interoperability helps enable.
2. Liquidity
Cross-chain connectivity improves liquidity by allowing assets to move freely between ecosystems. For example, tokens like Wrapped Bitcoin (WBTC) can operate on Ethereum and other DeFi networks, expanding their reach and functionality. The result is a more active, liquid marketplace for digital assets across the blockchain interoperability market.
3. Better User Experience
Interoperable blockchains make it easier for users to manage assets across different platforms from a single access point. Instead of switching between separate wallets or apps, users can interact with multiple decentralized applications through unified interfaces, saving time and improving accessibility.
Even in traditional payments, the shift toward connected networks is clear. India, Malaysia, Thailand, Singapore, and the Philippines are building an instant cross-border retail platform expected to serve a combined market of roughly 1.7 billion people by 2026.
4. New Business Models
Interconnected networks allow businesses to combine the advantages of different blockchains into unique solutions. A company might integrate Bitcoin’s security layer with Ethereum’s smart contract flexibility, or blend multiple ecosystems to create cross-industry services, expanding what’s possible through blockchain interoperability solutions.
Challenges And Limitations Of Blockchain Interoperability
While blockchain interoperability offers major progress toward connected digital ecosystems, it also introduces technical and structural hurdles that must be solved before global adoption can occur.
Challenges And Limitations Of Blockchain Interoperability
1. Technical Complexity
Building seamless communication between independent blockchains is no simple task. It requires sophisticated design, advanced blockchain interoperability protocols, and deep technical expertise. Maintaining compatibility, managing data formats, and ensuring system stability demand continuous updates and careful coordination across networks.
2. Security Risks
When multiple blockchains link together, the entire system becomes as strong as its weakest chain. A flaw or breach in one network can expose others to risk. Protecting cross-chain transactions, validating data integrity, and preventing fraud or cyberattacks remain ongoing priorities for any interoperability framework.
3. Regulatory Concerns
Varying national laws and compliance standards complicate interoperability efforts. Some regions may impose strict requirements on digital asset transfers or data sharing. To operate safely, interoperability blockchain solutions must balance innovation with adherence to evolving global regulations.
4. Scalability Bottlenecks
As the number of interconnected blockchains grows, so does the flow of cross-chain activity. High transaction volumes can slow performance and increase costs. Overcoming these scalability issues calls for more efficient consensus models and next-generation infrastructure capable of handling the expanding blockchain interoperability challenges.
Real-World Applications Of Blockchain Interoperability
Blockchain interoperability is reshaping how industries exchange data and value. By connecting separate blockchain systems, it opens pathways for smoother collaboration, transparency, and innovation across multiple sectors. Below are some of the most promising applications driving this transformation.
Real-World Applications Of Blockchain Interoperability
DeFi And Cross-Chain Asset Transfers
Modern DeFi platforms depend heavily on asset mobility across different chains. Through atomic swaps and wrapped tokens, interoperability blockchain technology enables users to lend, borrow, or trade assets without switching ecosystems. This flexibility boosts liquidity and supports a new generation of decentralized financial products.
In 2023, security across the DeFi sector showed progress, as the total value stolen from hacks dropped by roughly 63.7% compared to the previous year. This decline points to stronger infrastructure and more reliable security practices as cross-chain activity continues to grow.
Supply Chain And Logistics
In global supply chains, interoperable blockchains allow partners to share verified information in real time. Manufacturers, suppliers, and retailers can trace goods at every step, cutting inefficiencies and reducing fraud. The result is a more transparent and coordinated logistics network.
More broadly, digital trade facilitation is estimated to reduce trade costs by up to 25%. This shows the economic impact of interoperable data flows and standardized networks across borders.
Healthcare And Data Sharing
Blockchain interoperability enables medical providers to exchange patient data securely and instantly. Hospitals, clinics, and labs can access the same verified information, ensuring accurate diagnoses and continuity of care while preserving privacy.
Interoperable Digital Identity Solutions
Digital identity systems built on blockchain interoperability solutions let users carry one secure identity across multiple platforms. Projects like Worldcoin are paving the way for unified identity management, allowing people to verify themselves on one network and access services across others, without repeatedly recreating profiles or exposing private data.
The global need is significant, with roughly 850 million people still lacking official identification, making portable, verifiable identity a pivotal building block for access to services.
Enterprise Implementation Strategies For Blockchain Interoperability
Enterprises aiming to harness blockchain interoperability must build a clear roadmap that connects technical design with business outcomes. This requires balancing innovation with compliance, scalability, and integration efficiency, especially when legacy systems are involved.
Enterprise Implementation Strategies For Blockchain Interoperability
Evaluating Business And Technical Needs
Successful implementation starts with a deep understanding of your organization’s goals and existing infrastructure. Identify where blockchain interoperability solutions can create the most value, whether by streamlining transactions, improving transparency in supply chains, or enabling secure data sharing between partners.
When selecting a blockchain interoperability protocol, consider operational scale and regional focus. U.S.-based enterprises, for instance, may need to prioritize compliance and data governance, while global companies might favor faster settlement speeds and cost-effective multi-chain operations.
Technical readiness also matters. Some interoperability frameworks demand specialized skills and advanced resources, while others integrate smoothly with modern API-based systems. Companies already using cloud-native or modular architectures typically achieve faster, lower-cost rollouts than those reliant on legacy technologies.
By clearly defining both technical and business requirements upfront, enterprises can build a sustainable foundation for interoperability blockchain adoption, ensuring that new systems align seamlessly with existing operations and deliver measurable long-term impact.
Integrating Blockchain With Existing Systems
Integrating blockchain interoperability into enterprise infrastructure demands precise planning and synchronization. Most organizations today operate hybrid setups that mix cloud services, on-premises databases, and long-standing legacy systems, all of which must work smoothly with new blockchain layers.
API gateways often act as the central link between internal systems and blockchain networks. They facilitate data flow and communication, while enterprise service buses can convert blockchain data into formats compatible with older applications. Thorough API design, testing, and validation are essential for accurate data mapping and transformation across systems.
Real-time consistency is another hurdle. Many enterprises adopt event-driven architectures with message queues to manage data synchronization and reduce the risk of discrepancies between on-chain and off-chain systems.
Performance tuning also plays a major role. While blockchain frameworks may support fast transaction speeds, traditional databases or middleware might lag behind. Using caching mechanisms and asynchronous processing can help maintain throughput without costly infrastructure overhauls.
Lastly, strong monitoring tools are critical. Traditional tracking systems rarely provide visibility into decentralized operations, so specialized solutions designed for interoperable blockchains are necessary. These tools help ensure reliable performance, compliance, and transparency across every cross-chain transaction.
Strengthening Compliance And Security
Any blockchain interoperability framework must align with strict regulatory and security standards to ensure trust across connected networks. This includes compliance with KYC (Know Your Customer), AML (Anti-Money Laundering), and data residency regulations that govern how information is verified, processed, and stored.
Because different blockchains use varying identity and verification methods, enterprises often need unified compliance layers that can validate transactions across all systems in real time. Data residency laws also add complexity, some protocols can localize data processing, while others may require dedicated regional infrastructure, which can raise operational costs.
Maintaining robust access control is vital. Enterprises should implement centralized permission management, automated audit trails, and intelligent reporting tools to simplify regulatory documentation. These capabilities help create a transparent and auditable environment across blockchain interoperability solutions.
Security remains the backbone of any enterprise-grade system. Multi-signature wallets, hardware security modules, and advanced key management protocols are essential safeguards against unauthorized access and potential breaches. Though these measures demand investment, they provide the resilience and assurance enterprises need to operate safely within interoperability blockchain ecosystems.
Future Trends In Blockchain Interoperability
Blockchain interoperability is entering a new phase, redefining how enterprises build cross-chain strategies and digital infrastructures. Recent advancements reflect not only technical innovation but also the growing need for connected, compliant, and scalable systems that support global business operations.

Future Trends In Blockchain Interoperability
2023–2025 Developments
The rapid rise of asset tokenization is one of the main forces behind expanding interoperability demand. Financial institutions are increasingly tokenizing assets such as real estate, commodities, and securities across different blockchains. To do this effectively, they rely on interoperable blockchains that can move tokenized assets between networks without disrupting regulatory compliance.
Another emerging focus is Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) tracking. Businesses are adopting blockchain interoperability solutions to unify sustainability data across supply chains, carbon markets, and social responsibility initiatives. This helps companies generate reliable ESG insights and automate sustainability reporting through integrated dashboards.
In the U.S., growing interest in Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) programs, like the ongoing digital dollar discussions, has accelerated enterprise blockchain adoption. Many organizations are already assessing how to integrate their systems with future CBDCs while maintaining interoperability with current payment infrastructure.
Meanwhile, Layer 2 scaling solutions are improving transaction speed and lowering costs, making cross-chain operations more practical for large-scale enterprises. These developments are also inspiring new blockchain interoperability standards that strengthen performance and security.
Finally, AI is becoming a key player. AI-driven interoperability blockchain tools now help businesses forecast congestion, optimize routing, and select the most efficient protocols. Combined with clearer regulations and early state-level compliance frameworks, these innovations are giving enterprises the confidence to invest in scalable, interconnected blockchain ecosystems.
Long-Term Enterprise Outlook
As blockchain interoperability technology advances, enterprises can expect smoother, more natural integration of blockchain networks into everyday operations. The next generation of interoperability tools will prioritize user experience, making multi-chain interactions as simple and intuitive as navigating a traditional business platform.
Ongoing progress in standardization will play a crucial role. The development of unified blockchain interoperability protocols is expected to cut down on costly custom integrations and boost reliability across networks, giving businesses a consistent foundation for multi-chain collaboration.
Financial innovation is another major outcome. As interoperability matures, organizations will be able to explore cross-chain arbitrage, optimize treasury operations, and access wider liquidity pools. Consulting partners like Phoenix Strategy Group are already supporting enterprises in building financial strategies that take advantage of these emerging opportunities.
Automation will also redefine enterprise operations. Intelligent routing systems and predictive analytics will streamline cross-chain transactions, while real-time compliance tools will strengthen transparency and reduce operational risks.
Greater competition among blockchain interoperability solutions is expected to drive cost efficiency, with flexible pricing and pay-per-use models making adoption more affordable for businesses of any scale.
The merging of traditional finance and blockchain ecosystems marks the next major leap. As enterprises connect legacy platforms with blockchain infrastructure, the need for scalable and secure interoperability frameworks will grow. These advancements will enable organizations to operate confidently in a hybrid digital economy, one where traditional systems and decentralized networks function side by side.
Partner With MOR Software For Blockchain Interoperability Solutions
MOR Software develops enterprise-grade blockchain systems built to connect, scale, and deliver measurable business value. We go beyond theory, turning blockchain interoperability into real-world performance across industries.
Partner With MOR Software For Blockchain Interoperability Solutions
Comprehensive Development Expertise
We manage the full lifecycle from consulting to deployment. Our engineers design smart contracts, cross-chain integrations, and API frameworks that link multiple blockchain networks into a unified ecosystem.
Secure And Compliant Architecture
All projects follow ISO 9001:2015 and ISO 27001:2013 standards. Our solutions align with international regulations like KYC, AML, and data residency laws to protect business operations and maintain user trust.
Tailored Blockchain Strategy
Every business has unique processes and legacy systems. We customize blockchain interoperability frameworks to match your infrastructure, ensuring seamless integration with existing ERPs, CRMs, and data platforms.
Global Delivery Capability
With development centers in Vietnam, Japan, and across Asia, MOR combines technical depth with cross-border experience. This structure allows us to deliver scalable blockchain systems that meet regional and global demands.
Proven Success Across Industries
From healthcare and logistics to finance and manufacturing, we’ve built blockchain solutions that connect ecosystems, automate transactions, and enhance transparency for clients worldwide.
Conclusion
As businesses move toward more connected digital ecosystems, blockchain interoperability is becoming a defining factor in enterprise growth and efficiency. It bridges data silos, drives innovation, and enables secure collaboration across networks. With its global expertise and proven delivery record, MOR Software helps enterprises unlock the full potential of interoperable blockchain systems. Ready to transform your operations? Contact us today to start building your connected future.
MOR SOFTWARE
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What does blockchain interoperability mean?
Blockchain interoperability describes how different blockchain systems can connect and share information or value with one another. It enables smooth communication between independent networks, allowing assets or data to move freely. This function is essential for expanding blockchain’s real-world applications and supporting collaboration across platforms.
What is an example of cross-chain interoperability?
Projects like Celer Network make it possible to send payments across different blockchains instantly. These systems allow assets to move between chains as easily as traditional bank transfers, helping to create a unified and more connected blockchain environment.
Which blockchain project focuses on interoperability?
Cosmos is widely recognized for advancing interoperability. Often referred to as the “Internet of Blockchains,” Cosmos enables independent blockchains to operate together through shared protocols while maintaining their individual sovereignty.
How big is the blockchain interoperability market?
The global blockchain interoperability market was valued at around USD 12.1 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 19.6 billion by 2032, with a steady annual growth rate of 5.5%. This reflects the growing demand for cross-chain communication and collaboration in blockchain ecosystems.
What is an example of interoperability in the real world?
A real-world example is the integration of cross-chain payment solutions that let users transfer digital assets between Ethereum and Bitcoin networks without intermediaries. This mirrors how different banks connect through payment gateways to allow instant money transfers.
What is a blockchain bridge?
A blockchain bridge enables the movement of digital assets and information between two separate blockchain ecosystems. These bridges can be centralized, decentralized, or hybrid, and typically transfer assets using either wrapped tokens or liquidity pools.
What are the challenges of blockchain interoperability?
Blockchain interoperability still faces technical and structural hurdles. Many blockchains cannot yet communicate across entirely different networks, and ensuring security during cross-chain transfers remains complex. Standardized communication protocols are still evolving, which slows widespread adoption.
Is Ethereum interoperable?
Ethereum supports interoperability through tools like the Geth Ethereum client and REST APIs that facilitate transactions between Ethereum-based systems and external blockchains. This allows developers to connect Ethereum smart contracts with other blockchain environments efficiently.
Which blockchain project focused on interoperability?
Ethereum 2.0, now known as the Ethereum Consensus Layer, is enhancing interoperability by implementing shared standards and communication protocols. It also supports the creation of decentralized applications that can function across multiple networks.
How does blockchain interoperability work?
Blockchain interoperability works through specialized protocols, smart contracts, and bridges that allow separate blockchains to exchange information or digital assets. These mechanisms synchronize data between networks while maintaining the security and decentralization of each system.
Which is a benefit of interoperability in crypto?
Interoperability provides a smoother experience for users and developers. It allows access to multiple blockchains from a single interface, reducing the need to switch platforms. This convenience promotes broader adoption and more integrated decentralized applications.
Rate this article
0
over 5.0 based on 0 reviews
Your rating on this news:
Name
*Email
*Write your comment
*Send your comment
1