CRM Terminology: 200+ Terms Glossary Every User Need to Know

Understanding CRM terminology is essential for businesses to maximize the value of their customer relationship management systems. This MOR Software’s guide will walk you through key CRM terms, helping you communicate effectively, streamline processes, and get the most out of your CRM investment.
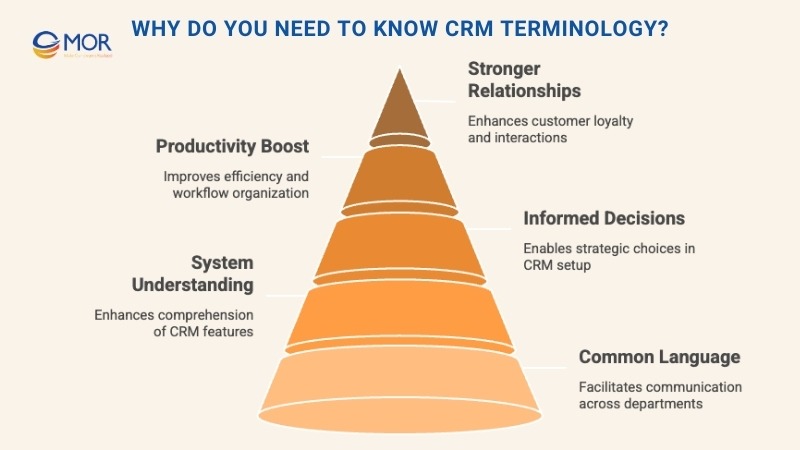
Why Do You Need To Know CRM Terminology?
Grasping CRM terminology is like learning the shared language of customer relationship management. Whether you work in sales, marketing, support, or operations, it gives you the vocabulary to connect with colleagues, follow industry developments, and use your CRM system with confidence.
When you understand CRM terms, you can communicate clearly, collaborate more effectively, and make informed choices about system setup, customisation, and ongoing use. This understanding helps you tap into a CRM’s features, apply its functions to real business needs, and improve customer interactions.
The result is better relationship management, higher productivity, and stronger customer satisfaction.
It also makes discussions with Salesforce CRM terminology experts, vendors, and IT teams far smoother. From implementation to troubleshooting, you can explain needs and interpret advice without confusion.
These words aren’t empty jargon. They represent key processes that shape growth. For example:
- Knowing the difference between a ‘lead’ and an ‘opportunity’ helps keep your sales pipeline organised.
- Understanding ‘customer segmentation’ lets you target marketing with precision.
- Valuing ‘customer retention’ motivates you to raise service standards and strengthen loyalty.
CRM Terminology Basics: The 10 Terms You Should Know First
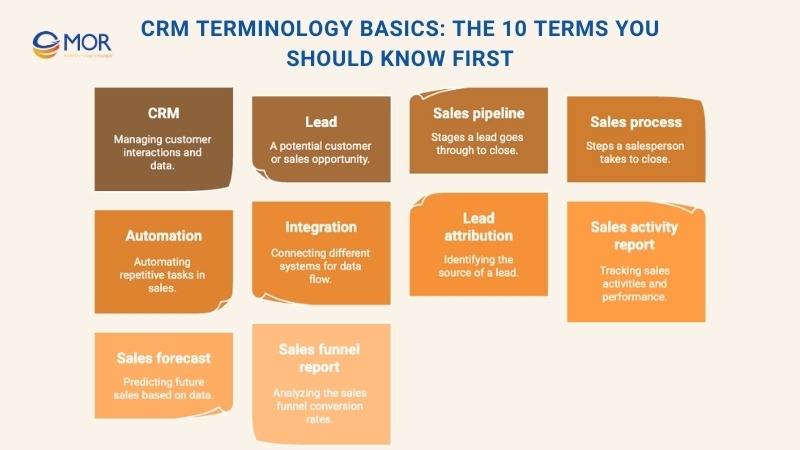
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
Customer relationship management (CRM) is a business strategy aimed at understanding and improving how you interact with prospects and customers. It relies on CRM software to collect, organise, and analyse customer data, helping deliver better experiences and increasing customer lifetime value.
Lead
A lead is an individual or organisation showing interest in your products or services, added to your CRM at the start of the sales pipeline. Leads can be unqualified at first or marked as qualified by sales and marketing teams. They remain leads until they either drop out of the process or make a purchase, becoming customers.
Sales Pipeline
A sales pipeline maps out the stages leads pass through on their way to conversion and the actions your team takes to guide them there. It gives a clear view of opportunities, highlighting what’s working and where improvements are needed. Multiple pipelines can be set up in a CRM for different offerings or workflows.
Sales Process
The sales process is your company’s step-by-step method for moving prospects through the pipeline to a successful close. It details the activities your team should follow, from nurturing leads to finalising deals. A CRM supports this by mapping and automating tasks to keep the process consistent and efficient.
Automation
Automation uses technology to handle repetitive sales, marketing, and customer service tasks without manual input. With automation tools in your CRM, teams save time and focus on building relationships. Actions can be triggered by specific events, such as sending a follow-up email when a lead fills out a form.
Integration
An integration connects your CRM to other applications, enabling smooth data sharing. Modern systems, including those with salesforce CRM terminology features, support native, one-click, or third-party integrations. These connections extend CRM capabilities and simplify workflows.
Lead Attribution
Lead attribution identifies which marketing channels generate your leads. With this feature in a CRM, you can track where high-quality leads originate and decide which channels deserve more attention to improve marketing results.
Sales Activity Report
A sales activity report summarises the actions your sales team takes over a set period. It can include calls, emails, meetings, and follow-ups. Logged manually or automatically, these reports help managers monitor performance and customer engagement.
Sales Forecast
A sales forecast predicts future revenue based on past performance, trends, and other factors. Your CRM can generate these reports, helping you manage resources, plan activities, and make informed strategic decisions.
Sales Funnel Report
A sales funnel report shows how deals are progressing through the pipeline and where bottlenecks may exist. It provides data like conversion rates, average deal size, and total value per stage, helping improve pipeline health and accuracy in predictions.
Essential CRM Terminology Every User Must Know
CRM Terminology: 123 To D
123: Terms That Start With Digits
360-degree customer view
A 360-degree customer view is a complete picture of everything you know about your customers, made possible with the right CRM glossary tools. Often mentioned by sales and marketing teams, this view covers all touchpoints, communications, campaigns, and experiences that shape how customers perceive and interact with your brand.
A: Terms That Start With “A”
Account
In CRM definitions, accounts are companies or organisations your business interacts with in some way. Customer accounts are those you sell to, while supplier accounts are those you buy from. Each account record in your CRM includes details like contact info, payment terms, communications, and related documents.
Account management software
This software goes beyond storing contact information. It tracks every interaction and transaction with accounts and linked individuals, ensuring you always have up-to-date context for decision-making. It’s one of the core capabilities in any modern CRM system.
Account settings
Account settings in your CRM let you tailor your interface to fit your preferences. You can control how company and contact information appears, arrange activity history, and manage related data for easier navigation and organisation.
Action
An action is any step taken by your team or system to advance a task in a workflow or pipeline. Automated workflows in your CRM trigger actions such as logging calls, sending emails, or updating contact records based on set conditions.
Activity
Activities cover any action tied to leads, contacts, or accounts, such as emails, calls, or meetings. You can log these manually or have them recorded automatically when triggered, then track them in an activity report.
Ad-hoc reporting
Ad-hoc reporting lets you create one-off reports to extract specific information not covered by regular reporting schedules. With built-in business intelligence tools, a CRM can generate targeted insights into sales, marketing, or service performance when you need them.
Administrator
An administrator has full access to all CRM functions and settings. They manage user roles, control access, configure system options, and ensure everything runs smoothly.
Alert
Alerts are notifications triggered by certain actions or events in the CRM. They help teams respond quickly to important changes, whether it’s a new lead or an urgent customer issue.
Analytics
CRM analytics analyse data to uncover trends, performance metrics, and customer behaviour patterns. This supports better decision-making, from refining marketing campaigns to improving customer service.
API
An API (application programming interface) allows your CRM to connect and share data with other software. APIs make it possible to integrate tools into your tech stack, ensuring smooth data flow between systems.
Artificial intelligence (AI)
AI in CRM automates intelligent tasks, from summarising account activity to drafting emails. It replaces manual work that would require human reasoning, speeding up operations and improving accuracy.
Assignment rule
Assignment rules automatically distribute leads or contacts to the right team members based on predefined conditions. They can be configured for direct assignment or through a fair round-robin approach.
Audit log
An audit log records specific user actions within the CRM, like logins, list exports, or mass updates, helping maintain accountability and security.
Authentication token
This secure digital key grants API access while protecting sensitive business and customer data during system-to-system communication.
Autoresponder
An autoresponder sends follow-up emails based on rules or schedules, helping maintain ongoing engagement with leads and customers.
Automation
Automation uses technology to execute routine sales, marketing, or service tasks without manual effort. It increases team efficiency and frees staff to focus on relationship building and conversions.
B: Terms That Start With “B”
BANT
BANT is a qualification method your sales team applies when assessing prospects early in the pipeline. The acronym stands for Budget, Authority, Need, and Timing. By checking these four factors, sales teams can determine whether a lead is worth pursuing, ensuring efforts focus on those most likely to convert.
Board view
Board view is a pipeline layout option in many CRM terminologies that displays leads and deals in a Kanban-style format. This setup allows users to move cards between stages, customize the card details, and quickly assess the status of opportunities. It’s a visual way to keep the pipeline organised and transparent.
Bulk email
Bulk email enables you to send a single message to a large group of recipients simultaneously. Many CRMs include this feature, allowing targeted campaigns to segmented lists or general announcements to all customers. Pre-designed templates help create professional and engaging bulk messages quickly.
Business card scanner
A business card scanner captures contact details directly from a physical card using a mobile device. The CRM automatically creates a contact or lead record from the scanned data, often saving an image of the card as an attachment. This tool speeds up data entry and ensures accuracy.
Business intelligence (BI)
Business intelligence in CRM definitions refers to a suite of tools for analysing and interpreting customer and sales data. BI features often combine analytics, data mining, and visual dashboards, giving decision-makers a clear view of trends, opportunities, and performance.
C: Terms That Start With “C”
Calendar sync
Calendar sync is the process of linking your email platform’s calendar with your CRM terminology system. This integration centralises meetings, appointments, and events, making it easier to schedule and manage directly from the CRM or email platform.
Campaign
A campaign is a planned set of promotional activities with a specific goal, such as launching a product or driving sales. Marketing teams often segment audiences and run targeted email sequences using CRM tools to execute campaigns effectively.
Campaign management
Campaign management is the process of planning, running, and analysing marketing campaigns. It involves setting objectives, executing strategies, and reviewing results to improve future initiatives.
Case
A case, sometimes called a ticket or inquiry, is any customer-reported issue or request related to an account. CRMs track cases through support workflows to ensure timely resolution.
Case escalation
Case escalation is a predefined process that routes unresolved or urgent cases to higher-level teams. This ensures issues are addressed quickly, improving the customer experience.
CHAMP
CHAMP is a lead qualification framework focusing on Challenges, Authority, Money, and Prioritisation. Unlike BANT, it begins by addressing the prospect’s main challenges before budget considerations.
Changelog
A changelog records all updates or actions taken within a CRM contact or account timeline, making it easy to track engagement history.
Channel
Channels are the communication paths used internally or externally. Internal channels allow secure information sharing between employees, while external channels like email and social media connect brands to customers.
Chart view
Chart view is a pipeline layout option that displays leads visually in chart format, helping teams assess performance at a glance.
Click-through rate (CTR)
CTR measures the percentage of people who click a link or call-to-action within a campaign. It’s calculated by dividing clicks by total impressions or emails sent.
Click-to-call
Click-to-call enables users to place calls directly from the CRM using integrated telephony tools, making outreach faster and more efficient.
Closed sale
A closed sale refers to a completed deal, whether won or lost, marking the end of that sales cycle.
Cloud-based CRM
A cloud-based CRM is hosted online, giving teams access from any internet-enabled device. It supports remote work and reduces dependency on local infrastructure.
Connected form
A connected form is an online form integrated with a CRM to automatically create records for people, companies, or leads based on submitted information.
Contact
A contact is a person or company stored in your CRM. Detailed profiles include interaction history, notes, and other relevant data.
Contact role
Contact roles define a person’s position or responsibility in relation to an account, lead, or case, such as administrator or decision-maker.
Contact management
Contact management is the organisation and tracking of contact records in a CRM, including sorting, filtering, and sharing across teams.
Contract management
Contract management oversees agreements with customers, suppliers, or partners. CRMs can integrate with contract tools to track lifecycles, renewals, and updates.
Conversion rate
Conversion rate is the percentage of leads that become customers, calculated by dividing deals won by total leads within a set timeframe.
Converted lead
A converted lead is a prospect whose status has changed in the CRM to indicate qualification and the creation of a formal account record.
CPQ
CPQ stands for Configure, Price, Quote. It’s a process sales reps use to customise offers, calculate prices, and generate proposals for customers.
CRM analytical reporting
This involves generating reports from CRM data to find trends in customer behaviour, demographics, and sales, guiding strategic decisions.
CRM software
CRM software is a platform for managing relationships, interactions, and data related to prospects and customers. It stores accounts, communications, and transactions in one place.
CSV file
A CSV (comma-separated values) file is a common format for importing or exporting CRM data, easily created in spreadsheets or text editors.
Customer database
A customer database contains all stored details about your clients, such as contact information, purchase history, and preferences, centralised in the CRM.
Customer experience (CX)
CX is the overall impression a customer has after interacting with your brand, shaped by service, communication, and product quality.
Customer experience management (CXM/CEM)
CXM/CEM is the strategic oversight of all customer touchpoints, using tools like CRM to improve satisfaction and loyalty.
Customer journey
The customer journey covers every step a customer takes from first awareness to post-purchase interactions, guiding process improvements.
Customer relationship management (CRM)
CRM is the practice of managing and improving interactions with prospects and customers using technology to organise and analyse data.
Customer self-service (CSS)
CSS tools let customers solve issues independently, often through portals, FAQs, or knowledge bases integrated with CRM systems.
Customer service and support (CS&S) automation
This refers to systems that automate support tasks, such as ticket handling and complaint resolution, for faster responses.
Customer success management
Customer success management focuses on helping customers achieve goals post-sale through ongoing engagement and tailored solutions.
Custom field
Custom fields are additional data fields in your CRM tailored to store company-specific information for better filtering and reporting.
D: Terms That Start With “D”
Dashboard
A CRM dashboard is a visual hub displaying essential metrics and data in real time. It offers an at-a-glance view of sales performance, trends, and other KPIs. By customising the dashboard layout, teams can prioritise the figures most relevant to their goals, enabling quicker, data-driven decisions.
Data enrichment
Data enrichment is the process of adding valuable details to existing contact, company, or lead records in your CRM glossary. This could include a company’s background, a contact’s social media activity, or past purchasing behaviour. Enriched data helps sales, marketing, and service teams better understand and engage with their audience.
Data import
Data import refers to bringing existing contact and account information into your CRM system during setup or migration. The most common method is uploading a CSV file, though many CRMs also support importing from address books, email marketing tools, or other CRM platforms. Some providers offer concierge-style import assistance to ensure accuracy.
Data security
Data security in a CRM involves implementing protective measures to safeguard customer and business information. This includes encryption, secure access controls, and compliance with data privacy regulations. Strong data security builds trust and protects against breaches or cyberattacks.
Dead lead
A dead lead is a prospect who has opted out of the buying process or shown no further interest. Once marked as dead, sales teams typically stop pursuing them to focus on higher-potential opportunities.
Deal
A deal is a sales opportunity tied to a lead in your CRM pipeline, carrying a specific monetary value. Sales teams work to advance deals through the pipeline stages until they close. Tracking deals in the CRM helps with forecasting and hitting revenue targets.
Demand generation
Demand generation is a marketing approach designed to spark interest and awareness for your brand, products, or services among audiences who may not yet know about them. These campaigns aim to create market demand, filling the top of the sales funnel with new prospects.
CRM Terminology: E To I
E: Terms That Start With “E”
Email automation
Email automation is the practice of sending pre-designed emails to leads or customers without manual effort, triggered by specific actions or events in your CRM terminology.
These triggers might include completing a sales call, moving a lead to a new stage, or signing up for a webinar. Automation ensures timely communication while reducing repetitive tasks.
Email drip sequences
An email drip sequence is a planned set of emails sent to a targeted audience over a scheduled period. Within a CRM, these sequences guide recipients toward a desired action, such as booking a demo or making a purchase. Campaigns can be set to pause for a contact once they respond or complete the intended action.
Email marketing
Email marketing covers all strategies and activities involving sending messages to your audience to drive engagement or conversion. This can range from personalised follow-up emails to large-scale campaigns promoting offers or resources.
Many modern CRMs provide built-in email marketing tools for better campaign management and audience targeting.
Email marketing migration
Email marketing migration is the process of moving campaign data, templates, and contact lists from an external email platform into your CRM’s built-in email system. This creates a more unified approach, letting you manage campaigns, track engagement, and segment contacts directly from the CRM.
Email sync
Email sync links your CRM with your email service to automatically update and log messages, contacts, and calendar events. This integration keeps all communications visible in one place, giving teams a full history of interactions and improving collaboration.
Email template
An email template is a reusable format designed for consistent and branded communication. Templates in salesforce CRM terminology tools help teams quickly create professional newsletters, outreach messages, and updates without starting from scratch each time.
Email writing assistant
An email writing assistant uses AI within the CRM to help craft impactful, clear, and engaging emails. It can suggest phrasing, correct grammar, and tailor tone to suit the audience, saving time for sales, marketing, and support teams.
Escalation
Escalation refers to transferring a customer issue from the initial support team to a higher-level or specialised team for resolution. Well-structured escalation processes within a CRM improve issue resolution speed, enhance customer satisfaction, and minimise operational strain.
F: Terms That Start With “F”
First touch
First touch marks the moment a potential customer first interacts with your brand. This could happen through a website visit, clicking a social media post, seeing a paid ad, or landing on a dedicated campaign page.
Each of these touchpoints is designed to spark curiosity and prompt further engagement, guiding the prospect into your conversion funnel.
Funnel velocity
Funnel velocity measures how quickly a lead moves from one stage of your sales pipeline to the next. A fast funnel velocity means leads are progressing efficiently, while a slow velocity signals potential bottlenecks.
Tracking funnel velocity in your CRM terminology setup can help pinpoint areas that need attention to improve sales cycle speed.
H: Terms That Start With “H”
Health score
A health score evaluates the strength and stability of your company’s relationship with a customer. CRMs can calculate health scores based on engagement levels, satisfaction ratings, and account activity. This metric helps teams prioritise outreach to accounts showing lower scores, supporting retention and upselling strategies.
Hot lead
A hot lead is a prospect showing strong buying intent for your product or service. Sales reps can tag leads as hot manually or set up automation rules in the CRM to assign this status when specific actions occur. These triggers are often based on behaviours that match patterns from previous customers who converted.
I: Terms That Start With “I”
Integration
An integration links your CRM platform with another software application, enabling seamless data exchange between the two systems. This connection allows information to flow automatically, reducing manual entry and improving accuracy.
Modern CRM solutions provide various integration options, including built-in native integrations, one-click setups, and connections through third-party tools like Zapier. By implementing integrations in your CRM terminology toolkit, you can extend system capabilities, automate workflows, and create a more connected and efficient business environment.
CRM Terminology: J To N
J: Terms That Start With “J”
Junk lead
A junk lead is a prospect that fails to meet your business’s baseline criteria for a qualified lead. Even if there’s initial interest in your product or service, factors like being outside your target region or not matching your customer profile mean they’re unlikely to convert.
In most CRM terminology setups, junk leads are filtered out early to avoid wasting sales team resources, ensuring focus stays on higher-quality opportunities.
K: Terms That Start With “K”
Knowledge base
A knowledge base is a centralised online repository containing helpful resources for customers, prospects, and internal teams. Accessible anytime, it typically lives on the company’s website and includes guides, setup instructions, troubleshooting steps, and FAQs.
By integrating a knowledge base into your CRM glossary of tools, you can strengthen self-service support, allowing customers to find solutions without needing direct assistance from your service team.
L: Terms That Start With “L”
Last touch
Last touch refers to the final interaction a prospect or lead has with your business before converting into a customer. This interaction could be an email exchange, a phone conversation, a website visit, or an in-person meeting.
Marketers track last touch points to identify the specific action or engagement that ultimately influenced the purchase decision.
Lead
A lead is an individual or organisation showing interest in your products or services and entered into your CRM system at the start of the sales pipeline.
Leads can be unqualified when first captured or later qualified by sales and marketing teams as genuine prospects. They remain leads until they either disengage from the process or make a purchase and become customers.
Lead advancement
Lead advancement is the practice of moving a lead through different stages of the sales pipeline, from initial contact to closing the deal.
This progression depends on factors such as qualification level and engagement. A strong lead advancement plan can improve conversion rates and shorten the sales cycle.
Lead assignment
Lead assignment is the allocation of incoming leads to specific sales representatives or teams based on predefined rules. This process ensures timely follow-ups, balanced workloads, and more personalised engagement.
Well-structured lead assignment processes can positively influence conversion outcomes.
Lead attribution
Lead attribution is the method of identifying which marketing channel or campaign generated a specific lead.
CRMs equipped with lead attribution features help you pinpoint the most effective lead sources so you can optimize marketing spend and strengthen lead generation efforts.
Lead confidence
Lead confidence is a metric used to predict the likelihood of a lead becoming a paying customer. It’s determined by factors such as product fit, engagement frequency, and buying signals. High-confidence leads are prioritised by sales teams for targeted follow-up.
Lead conversion process
The lead conversion process includes all actions taken to transform a lead into a customer. This might involve lead nurturing via personalised emails, scheduled calls, targeted content, and in-person meetings, along with moving the lead through the defined pipeline stages.
Lead conversion rate
Lead conversion rate measures the percentage of leads that turn into customers during a specific timeframe. It’s a key performance indicator for evaluating the success of your sales and marketing strategies. Higher conversion rates often reflect an effective sales process and strong campaign targeting.
Lead generation
Lead generation is the process of identifying, attracting, and capturing potential customers’ contact information. This often involves marketing activities designed to create awareness and interest, with captured data stored in your CRM for nurturing.
Some CRM tools, such as ProspectorIQ, provide access to extensive databases to find suitable leads.
Lead management
Lead management is the end-to-end handling of leads, from initial capture to conversion. It requires collaboration between sales and marketing teams and includes organisation, scoring, prioritisation, and consistent nurturing to guide leads toward purchase.
Lead qualification
Lead qualification determines whether a prospect meets the set criteria to become a viable customer. Factors such as budget, authority, need, and timeline (BANT) are often evaluated to filter out unsuitable leads and focus resources on high-potential ones.
Lead-to-cash
Lead-to-cash describes the process from acquiring a lead to completing the sale. When a lead becomes a customer and generates revenue for the business, it marks the lead-to-cash point in the sales cycle.
List view
List view in a CRM displays leads in a straightforward list format. This layout makes it easier to sort, filter, and manage contact records, particularly for pipelines containing a large number of leads.
M: Terms That Start With “M”
Machine learning
Machine learning is a branch of artificial intelligence (AI) that enables systems to adapt and improve automatically through experience, without being explicitly reprogrammed.
These systems rely on algorithms to process data, recognise trends, forecast outcomes, and decide on the next actions. Many modern CRM platforms incorporate AI capabilities powered by machine learning to streamline workflows, provide predictive insights, and increase overall efficiency.
Map view
Map view is a pipeline display feature in a CRM that shows leads based on their geographic location. This layout is particularly useful for territory-based sales teams, as it helps them identify lead distribution and plan strategic outreach.
For field sales representatives, map view is an effective tool for route planning, enabling more efficient travel and better scheduling of in-person visits.
Marketing-accepted lead (MAL)
A marketing-accepted lead (MAL) is a prospect identified by the marketing team as fitting the company’s target customer profile. This determination is usually based on demographic and geographic criteria, as well as demonstrated interest in the company’s offerings.
MALs are passed on to the sales team for further qualification and potential conversion.
Marketing automation
Marketing automation involves using software tools, often integrated with a CRM, to streamline and automate recurring marketing tasks. By reducing manual work, marketing automation boosts productivity, improves lead nurturing, and increases engagement.
Common uses include running targeted email campaigns, scoring leads, segmenting audiences, personalising content, and generating forecasts.
Marketing funnel
The marketing funnel represents the stages a prospect goes through, from brand awareness to making a purchase. Typically visualised as a funnel shape, it outlines each phase of the buyer’s journey, allowing businesses to monitor progress, identify bottlenecks, refine strategies, and measure conversion performance.
Marketing-qualified lead (MQL)
A marketing-qualified lead (MQL) is a prospect flagged by the marketing team as having a high likelihood of becoming a customer. This classification is based on set qualification criteria, such as engagement level or expressed interest.
MQLs are handed off to the sales team, who conduct their own vetting process to confirm suitability before further pursuit.
Meeting scheduler
A meeting scheduler is a CRM feature that allows users to arrange appointments and meetings directly from the platform. Often integrated with calendar services, it helps align schedules, manage availability, and minimise back-and-forth communication.
This tool ensures booking processes are quicker, more organised, and better coordinated across teams.
N: Terms That Start With “N”
Natural language processing (NLP)
Natural language processing, or NLP, is a branch of machine learning within the broader field of artificial intelligence (AI). It focuses on enabling machines to interpret, analyse, and understand human language, both written and spoken.
In CRM platforms, NLP can be used to process and summarise communications such as meeting transcripts, voice notes, and customer messages, helping teams quickly extract relevant insights and improve response quality.
New leads report
A new leads report is a CRM-generated document that lists all leads captured during a specific period.
This report offers valuable data on the volume and sources of incoming leads, enabling teams to evaluate the effectiveness of marketing initiatives and sales outreach. By reviewing this report, businesses can fine-tune their strategies for better lead acquisition.
Notification
A notification is a system alert within a CRM that signals important customer or prospect-related events. Examples include updates to assigned tasks, responses from contacts, or significant changes in lead status.
Notifications ensure timely action by keeping team members informed, reducing the risk of missed opportunities or delayed follow-ups.
CRM Terminology: O To S
O: Terms That Start With “O”
Onboarding
Onboarding refers to the process of introducing new users to a CRM system and ensuring they can use it effectively. This stage often includes structured training sessions, user guides, and other resources designed to help team members become familiar with the platform’s features.
A well-executed onboarding program helps your team gain confidence in using the CRM, allowing them to fully harness its capabilities for daily operations.
Opportunity
An opportunity is any potential sale or deal, whether it involves an existing client or a brand-new lead. Once identified, the opportunity is tracked within the CRM from its entry into the sales pipeline through to its conclusion.
Managing opportunities in a centralised system makes it easier to monitor progress, assign responsibilities, and align team efforts toward closing the deal.
Opportunity management
Opportunity management encompasses all the tasks and strategies used to oversee potential deals in your pipeline. This involves tracking interactions, updating deal stages, and prioritising high-value prospects.
By using CRM tools to automate parts of the process, sales teams can focus their time on the most important actions needed to move opportunities toward a successful close.
P: Terms That Start With “P”
Performance tracking
Performance tracking is the process of measuring and reviewing the results of your sales and marketing activities. Using your CRM’s analytics and reporting features, you can monitor key performance metrics to evaluate how well your strategies are working.
Regularly assessing these figures helps pinpoint areas for improvement, guides decision-making, and ensures the team stays aligned with company objectives.
Personal email sequence
A personal email sequence is a set of pre-written email templates sent in a scheduled order, with each message customized for the individual recipient. These sequences aim to strengthen relationships with leads and customers, increasing engagement, conversions, and loyalty.
Automating personal email sequences ensures consistent communication while saving time for your sales and marketing teams.
Pipeline distribution
Pipeline distribution refers to assigning leads to the most appropriate sales pipeline based on predetermined criteria. Advanced CRM platforms allow multiple pipelines to accommodate different products, services, or sales processes.
Distributing leads effectively keeps workloads balanced and ensures each lead is handled promptly and appropriately.
Pipeline management
Pipeline management involves tracking and guiding leads as they move through each stage of your sales process. This responsibility often falls to sales representatives, who nurture leads toward conversion by completing necessary follow-ups and actions.
Proper pipeline management helps improve efficiency, reduce missed opportunities, and increase sales success rates.
Post-sale
Post-sale refers to the activities and support provided to customers after a purchase is complete. These efforts focus on building long-term relationships through retention strategies, customer satisfaction initiatives, and upselling opportunities.
A strong post-sale process boosts customer lifetime value and encourages repeat business.
Predictive analytics
Predictive analytics uses artificial intelligence and machine learning to assess both current and historical data. By analyzing patterns and trends, predictive analytics can forecast potential outcomes and business opportunities.
This approach allows companies to plan proactively, minimize risks, and refine their sales and marketing strategies.
Probability to close
Probability to close is a percentage-based estimate of how likely a lead is to convert into a customer. This figure typically increases as the lead advances through the sales pipeline.
Tracking probability to close helps sales teams prioritize opportunities and create more accurate revenue forecasts.
Prospect
A prospect is an individual or business that matches your ideal customer profile and is considered worth targeting by your sales or marketing team. Prospects have not yet shown active interest in your offering, so initial outreach and qualification are necessary before they can be added as leads in the CRM.
Prospecting
Prospecting is the process of finding and connecting with potential customers to create new sales opportunities. It involves research, outreach via cold emails or calls, and initial engagement to determine fit and interest.
Effective prospecting ensures your sales pipeline stays active and full of high-quality leads. Some CRMs, such as Nutshell, include prospecting tools to help locate and engage the right potential clients.
R: Terms That Begin With “R”
Raw lead
A raw lead is an individual or organization that has interacted with your brand but has not yet been evaluated by the sales or marketing team. The interaction might come from activities like downloading a gated resource, filling out a form on a landing page, or signing up for a webinar.
At this stage, the lead’s potential fit as a customer is still unknown and requires qualification before entering the main sales process.
Relationship intelligence
Relationship intelligence refers to the insights generated from analyzing the relationship data stored in your CRM system. These insights offer sales, marketing, and customer service teams valuable details about past interactions, engagement history, and the overall strength of relationships with prospects and existing clients.
Using this data, teams can make informed decisions to strengthen customer connections and improve outreach strategies.
Remarket lead
A remarket lead is a contact identified through sales or marketing campaigns that did not initially meet the criteria for a qualified lead but may have potential in the future. These leads remain on marketing lists to receive retargeting efforts, email campaigns, and nurturing activities.
The goal is to keep them engaged until they are ready to enter the sales pipeline or are deemed no longer viable.
Reminder
A reminder is an automated notification generated by your CRM system to alert team members of key upcoming actions, such as scheduled meetings, follow-up calls, or pending tasks.
By setting up customized reminders, teams ensure important steps in the sales process are handled promptly, reducing the risk of missed opportunities and keeping operations on track.
Reply rate
Reply rate measures the percentage of recipients who respond to an email communication sent from your CRM, whether it’s a personal message, bulk campaign, newsletter, or broadcast.
Tracking this metric helps assess the effectiveness of email strategies, with higher reply rates indicating stronger engagement and more compelling messaging.
Roles
Roles within a CRM determine what each user can access and the actions they are allowed to perform, based on permissions set by the CRM administrator.
Typically, these permissions align with job responsibilities, ensuring each team member has the right tools while protecting sensitive company and customer information. Clearly defined roles support data security and efficient workflow management.
S: Terms That Begin With “S”
Sales-accepted lead (SAL)
A sales-accepted lead (SAL) is a marketing-qualified lead (MQL) that has been reviewed and approved by the sales team as ready for direct engagement.
These leads have already passed the marketing team’s qualification process and meet the agreed-upon criteria for active pursuit by sales representatives.
Sales activity report
A sales activity report is a record of sales-related actions over a defined time period. Generated within a CRM system, it tracks activities such as calls, emails, meetings, and follow-ups. These entries may be logged manually or automatically, giving managers a clear view of team efforts and customer interactions.
Sales automation
Sales automation involves using CRM tools to handle repetitive sales tasks automatically, boosting efficiency and freeing up time for high-value activities. Common automated actions include moving leads between pipeline stages, sending email sequences, generating reports, and forecasting sales performance.
Sales forecast
A sales forecast estimates future sales and projected revenue, helping teams plan and allocate resources effectively. CRMs generate these reports using historical sales data, market trends, and current pipeline information to support informed decision-making and goal setting.
Sales funnel
A sales funnel visually represents the flow of leads through different stages of the sales cycle. Wider at the top and narrower toward the bottom, it reflects the natural drop-off of prospects over time. Tracking the funnel helps identify where leads stall and where process improvements are needed.
Sales funnel report
A sales funnel report breaks down the status of deals across each funnel stage, showing metrics like total deal value, average deal size, and conversion rates. This report allows sales managers to pinpoint bottlenecks, assess funnel health, and forecast revenue more accurately.
Sales performance management (SPM)
Sales performance management (SPM) is the practice of tracking, guiding, and improving sales team performance. It includes monitoring quotas, incentives, training programs, and forecasts to ensure team output aligns with business objectives and revenue goals.
Sales pipeline
A sales pipeline outlines the journey of leads from initial contact to conversion. It gives a visual overview of opportunities at each stage, enabling sales teams to prioritize efforts, manage workload, and identify areas where the process can be improved.
Sales process
The sales process is the structured series of steps sales reps follow to move prospects toward a purchase. With CRM integration, these steps can be mapped, tracked, and automated to ensure consistency, efficiency, and better overall results.
Sales-qualified lead (SQL)
A sales-qualified lead (SQL) is a prospect determined by the sales team to be ready for in-depth engagement. SQLs have shown strong buying intent and match the company’s ideal customer profile, making them high-priority opportunities for conversion.
Sales quota
A sales quota is a set revenue or unit sales target for a sales rep or team over a specific timeframe. Quotas drive performance by providing measurable goals, and meeting or exceeding them can lead to bonuses, incentives, or recognition.
Sales-ready lead (SRL)
A sales-ready lead (SRL) is a marketing-qualified contact that has the authority, budget, and need to make a purchasing decision. These leads are prepared for direct sales conversations and are likely to move quickly through the pipeline.
Sales report
A sales report compiles data on sales activities, deal progress, and revenue performance. These reports offer valuable insights into team achievements and challenges, allowing managers to make informed adjustments to strategy and resource allocation.
Sales stage
Sales stages are the defined steps a lead moves through within the pipeline, from first contact to closing. CRMs allow customization of these stages to reflect each company’s process, making it easier to track progress and forecast outcomes.
Sales velocity
Sales velocity measures how quickly deals progress from one pipeline stage to the next. Higher velocity indicates a faster sales cycle, while slower movement may point to process inefficiencies or bottlenecks that need attention.
Self-service portal (SSP)
A self-service portal (SSP) is an online hub where customers can access information and tools to address their needs without contacting support. Common features include knowledge bases, FAQs, and account management tools that improve customer convenience and reduce support team workload.
Single sign-on (SSO)
Single sign-on (SSO) lets users access multiple applications, including their CRM, with a single login. This improves security, reduces password fatigue, and simplifies access to the systems employees use daily.
Snapshot
A snapshot is a quick, visual summary of key CRM metrics, offering an instant overview of sales and marketing performance. It allows users to check the current status without navigating multiple reports.
Suspect
A suspect is a potential customer identified as a possible fit for your products or services but who has not yet engaged. These early-stage contacts require outreach to determine if they have genuine interest and can be developed into qualified leads.
CRM Terminology: T To W
T: Terms That Begin With “T”
Task
A task in a CRM is a defined activity assigned to a specific user, complete with a deadline and relevant instructions.
Tasks often include additional notes or requirements, enabling managers to monitor progress and ensure clarity in execution. By assigning tasks within the CRM, teams can prioritize their daily responsibilities, stay accountable, and maintain a consistent workflow.
Timeline
A timeline is a chronological log within a contact’s CRM profile, detailing every interaction between your team and a lead, customer, or company account. This running history gives all authorized users a clear view of past communications and relationship developments.
With this data, sales, marketing, and service teams can tailor their approach for more personalized and effective engagement.
Timeline summarization
Timeline summarization condenses a detailed CRM interaction history into a concise list of major highlights and important actions. This function provides a quick-reference snapshot of the most relevant events without requiring users to read through lengthy records. It helps teams save time and quickly prepare for follow-ups or meetings.
Transactional reporting
Transactional reporting delivers a detailed account of individual transactions between your company and customers. Reports typically include deal amounts, key participants, agreements, and related documentation. These insights help track sales performance and assess financial trends to guide strategic planning.
Transcription
Transcription is the process of converting spoken words into written form. Sales, marketing, and support teams can use CRM-integrated AI tools to transcribe meetings, calls, and voice notes.
Some CRMs, such as Nutshell, even allow one-click transcription of virtual meetings like Zoom calls. This creates searchable written records for easy reference and analysis.
V: Terms That Begin With “V”
Voice of the customer (VoC)
Voice of the customer (VoC) refers to gathering and analyzing customer opinions, expectations, and preferences. Data can be collected through surveys, interviews, reviews, and social media monitoring.
VoC insights, both direct and indirect. help businesses refine products, services, and support strategies to improve satisfaction and loyalty.
Voice transcription
Voice transcription is the automated process of converting audio speech into text. Advanced CRM platforms offer voice-to-text tools that make note-taking faster and more accurate. By storing transcriptions within customer accounts, teams can use CRM search functions to locate and review key details instantly.
W: Terms That Begin With “W”
Warm leads
Warm leads are potential customers who have demonstrated interest in your offerings but have not yet committed to a purchase. They usually appear further along in the sales funnel and are more likely to buy than cold leads. Nurturing warm leads can yield higher conversion rates and shorter sales cycles.
Web form
A web form is an online form placed on a company’s website to capture visitor information. Collected data is often fed directly into the CRM, enabling automated lead creation and follow-up. Web forms help streamline lead generation and support better audience segmentation.
Workflow
A workflow is a structured series of steps required to complete a specific business process. These steps may be executed in sequence or in parallel, depending on operational needs. Well-organized workflows boost productivity and ensure consistency in output.
Workflow automation
Workflow automation uses integrated tools and CRM features to trigger specific actions when certain conditions are met. It can apply to sales, marketing, customer service, and operational processes. By automating repetitive tasks, workflow automation improves efficiency, reduces errors, and helps teams focus on higher-value work.
Conclusion
Mastering CRM terminology equips your team with the knowledge needed to communicate clearly, optimize workflows, and fully utilize your CRM system’s capabilities. You can improve collaboration, boost productivity, and deliver better customer experiences when understanding these concepts. If you are ready to implement or enhance your CRM for maximum efficiency, contact MOR Software. We can help you design and integrate a solution tailored to your business goals.
Rate this article
0
over 5.0 based on 0 reviews
Your rating on this news:
Name
*Email
*Write your comment
*Send your comment
1