HRIS Integration: The Ultimate Guide for HR Leaders 2026 Edition

Effective HRIS integration helps HR leaders cut manual work, eliminate errors, and build connected systems for payroll, recruiting, and employee data. Yet fragmented tools still create challenges for many companies. This MOR Software’s guide explores HRIS integrations in 2025, covering common use cases, benefits, challenges, and strategies to build scalable, future-ready solutions.
What Is An HRIS Integration?
An HRIS integration links a Human Resource Information System with another software application so data can flow smoothly between them. This connection allows information to be stored, shared, and updated in real time. In most cases, integrations rely on application programming interfaces (APIs), which are sets of rules that let different programs communicate effectively.
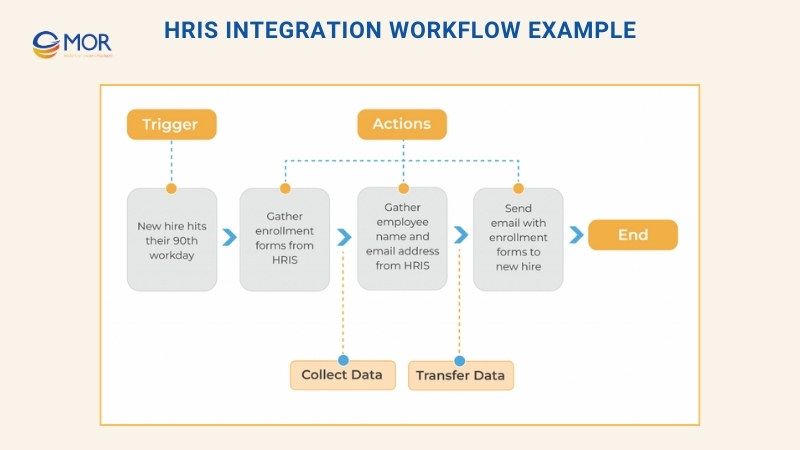
So how does this integration workflow operate?
At the core, an HRIS integration follows a system of triggers and actions. A trigger signals when to pull or send data, and the action tells the connected system how to use that information. These exchanges can happen between internal company tools or external platforms, depending on the process being automated.
Take this scenario: new hires qualify for benefits 90 days after joining. You want their enrollment forms emailed automatically on that date. Since an HRIS rarely includes built-in email functions, the workflow would need an HRIS integration platform that connects the HRIS with your company’s email service. The trigger here is the employee’s 90th workday, and the action is sending the enrollment forms to the employee’s inbox.
The trigger-and-action workflow in an integration might look like this:
This simple use case highlights how integrations work on a small scale. Yet, more advanced connections can build an integrated HRIS system that manages multiple HR processes at once, automates repetitive tasks, and gives HR leaders the time to focus on larger strategic goals.
>>> Discover more topics on MOR Blog right now!
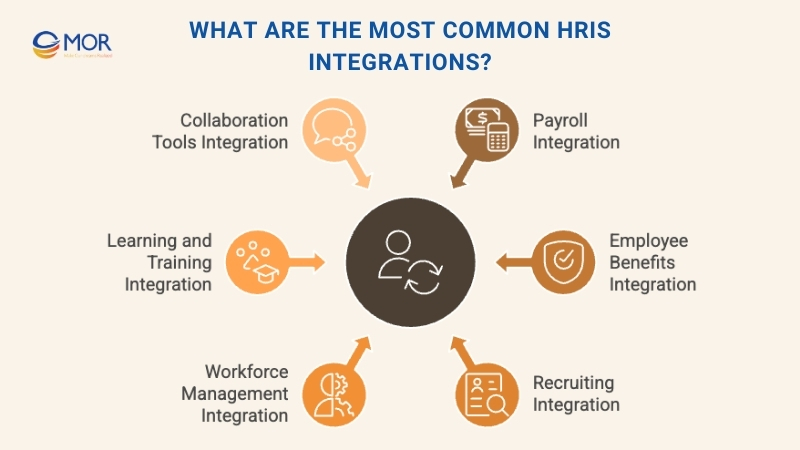
What Are The Most Common HRIS Integrations?
Most HRIS integrations usually fit into these main categories:
- Payroll management system integration
- Employee benefits integration
- Recruiting and talent acquisition
- Workforce management connections
- Learning and training systems
- Collaboration and productivity integrations
Each of these areas directly connects to HR processes. Still, businesses may also consider integrations that extend beyond HR. For example, many enterprises link their HRIS with an enterprise resource planning (ERP) solution to enable company-wide data sharing and improve operational flow.
Other useful options include accounting systems, HR risk management platforms, project management tools, and software tailored to specific industries. With the right integrations in place, organizations reduce repetitive data entry, build stronger HR software integrations, and extend the overall value of their HRIS.
Payroll Integration
A HRIS integration for payroll allows businesses to manage salary and compensation tasks without heavy manual work. If the HRIS in use does not include payroll features, it can be connected to a third-party system that takes care of this function.
Common payroll integration setups include:
- Moving payroll details into company financial accounts
- Pulling new hire pay information directly from recruitment software
- Delivering payroll data to an outsourced payroll provider
With the right setup, payroll functions can also connect seamlessly with talent management workflows, giving organizations a single system to manage both employee data and compensation. This approach supports teams across regions and ensures consistency for a diverse workforce.
Since payroll depends on key HR data like personal details, pay rates, tax IDs, and timesheets, accurate data flow between systems is critical. Smooth HRMS payroll software integrations reduce errors from manual entry and keep payments consistent for the entire workforce.
Employee Benefits Integration
When an HRIS integration does not include built-in benefits management, companies often connect it with third-party tools. Without this link, human resource development teams would need to manually handle employee enrollments, updates, and cancellations, which increases both effort and risk of error.
Typical benefits-related integrations cover:
- Insurance carrier platforms
- ACA compliance tracking solutions
- COBRA management tools
A well-known example is UKG’s EverythingBenefits, a system that works alongside HR platforms to deliver benefits enrollment, ongoing management, and COBRA support. It also connects with hundreds of insurance carriers, giving HR staff one central hub instead of negotiating with multiple provider systems.
This type of setup transforms a basic HRIS into a more complete human resource integrated system, saving time and improving accuracy in benefits administration.
Recruiting And Talent Acquisition
Unlike a full human resources management system (HRMS), a standard HRIS typically does not include recruitment tools such as an applicant tracking system (ATS). To fill this gap, companies often rely on HRIS integration with dedicated recruitment solutions.
Common integrations in this area include:
- Job posting platforms
- Interview scheduling software
- Tools for reference checks, background checks, or pre-employment testing
- AI-powered solutions for candidate ranking and selection
These connections simplify hiring by linking multiple sourcing channels and generating detailed reports that combine data from both the HRIS and recruitment applications.
For instance, TriNet Zenefits does not have a built-in ATS. Instead, it integrates with JazzHR to add applicant tracking features to its base plan.
Through this setup, employers can post job openings, review resumes, and issue offer letters directly from the Zenefits system. This kind of integration makes recruitment faster and helps teams build a more effective HR connect between hiring processes and employee data.
Workforce Management Connections
Workforce management HRIS integrations support companies in managing and retaining employees after they are hired. Typical functions included in these connections are:
- Time tracking and absence monitoring
- Employee enterprise scheduling tools
- Performance management systems
- Employee engagement platforms
Bringing these tools into the HRIS helps eliminate the need to operate across disconnected systems. Instead, everyday tasks like shift scheduling or vacation requests happen in one place, creating a smoother employee experience. At the same time, managers gain a clearer picture of workforce health and overall satisfaction levels.
As an example, linking an HRIS with an engagement and performance solution like Lattice makes it possible to run reviews and monitor progress against individual goals. When tied through HR software integrations, performance data flows back into employee records automatically. This not only supports better retention strategies but also keeps HR data accurate and up to date.
Learning And Training Systems
Connecting a learning management system (LMS) with your HR platform through HRIS integration gives HR teams visibility into completed courses and employee progress. These insights make it easier to monitor professional growth, spot training gaps, and address skill shortages across the organization.
For instance, BambooHR integrates directly with TalentLMS to streamline onboarding. As soon as a new hire is added into BambooHR, the system can automatically assign tailored training courses from TalentLMS. Features such as local language support and gamified learning elements further improve the employee experience, making training both practical and engaging.
With this type of setup, professional development data flows directly into the HRIS, helping HR leaders align workforce skills with company goals while strengthening overall HR connections between learning and career growth.
Collaboration And Productivity Integrations
Bringing collaboration and productivity platforms into your HR system through HRIS integration helps reduce the time spent on repetitive administrative work. The most common types of connections include:
- Calendar applications
- Team collaboration software
- Document management systems
- Communication tools
For example, syncing your HRIS with a calendar tool makes it easier to schedule interviews or manage employee review cycles. Integrating with services like Adobe, Google Workspace, or Microsoft 365 allows HR teams to draft policies, share documents, and collect e-signatures securely.
Communication platforms such as Gmail, Slack, or Microsoft Teams are also popular choices. They make it simple to distribute company updates, notify staff about new paystubs, or gather employee feedback. Adopting these HRIS integrations creates a more connected workplace, improves information flow, and strengthens productivity across the HR department.
This approach also shows how closely tied HR has become to the everyday digital tools that power modern organizations, aligning with the need for what are the best HRIS-integrated messaging tools for frontline employees.
Key Benefits Of HRIS Integrations
Implementing an HRIS integration delivers clear advantages, from saving time and resources to improving the overall experience for both providers and employers.
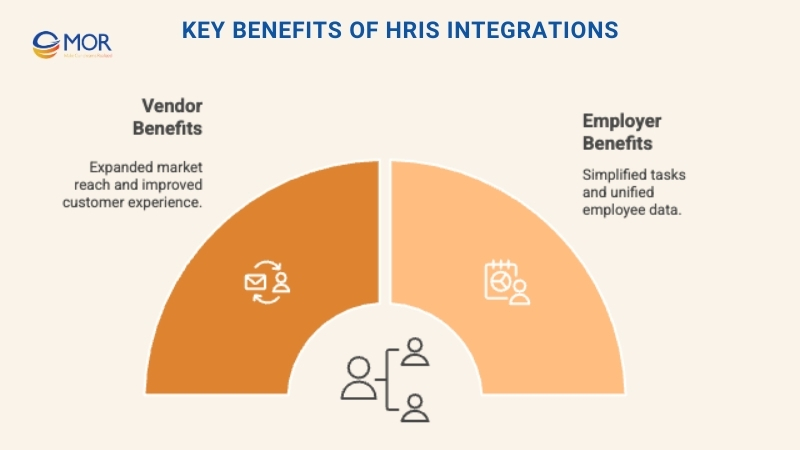
For Software Vendors And Service Providers
Vendors benefit directly from building stronger connections between their products and HR systems. The following advantages show why HRIS integrations have become a priority for SaaS providers:
- Expanded market reach: The depth of available integrations strongly influences SaaS purchasing decisions. According to industry data, nearly all HR admins view direct connections with employment systems like HRIS as essential. Supporting a wider range of HRIS integrations allows vendors to serve more businesses and shorten sales cycles. Using unified APIs can also simplify development and speed up the integration roadmap.
- Stronger customer experience: Automated synchronization between applications reduces manual work. For instance, when a new employee joins, the system can automatically enroll them in onboarding or benefit programs. This seamless process improves satisfaction and strengthens long-term engagement with the product.
- Improved compliance and accuracy: Continuous syncing between an application and the HRIS ensures that critical employee or company data stays up to date. With this setup, important details are less likely to be missed, helping maintain compliance standards and building reliable HR connections across systems.
For Employers
Employers see equally important gains from HRIS integration, particularly in daily HR operations. These benefits highlight how integration creates efficiency while improving the employee experience:
- Simplified HR tasks: Automating routine processes through an HRIS integration reduces administrative workload, allowing HR teams to focus on more strategic goals.
- Greater accuracy in records: With information entered once in the HRIS and synced to other connected systems, errors from duplicate entry or missed updates are far less common. This ensures payroll, benefits, and compliance data stay reliable.
- Unified employee data: Linking the HRIS with commonly used platforms creates a single source of truth for all employment details. This integration eliminates silos and gives leaders clearer visibility into workforce trends.
- Better employee experience: An integrated HRIS system allows staff to manage their information in one place. From checking pay details to updating benefits, employees no longer need to switch between multiple tools, creating a smoother overall experience.
How To Build HRIS Integrations?
The best way to create an HRIS integration depends on factors like how many systems need to be connected, the specific goals of integration, scalability requirements, engineering resources, and overall budget. SaaS providers often choose among several common methods when implementing HRIS integrations.
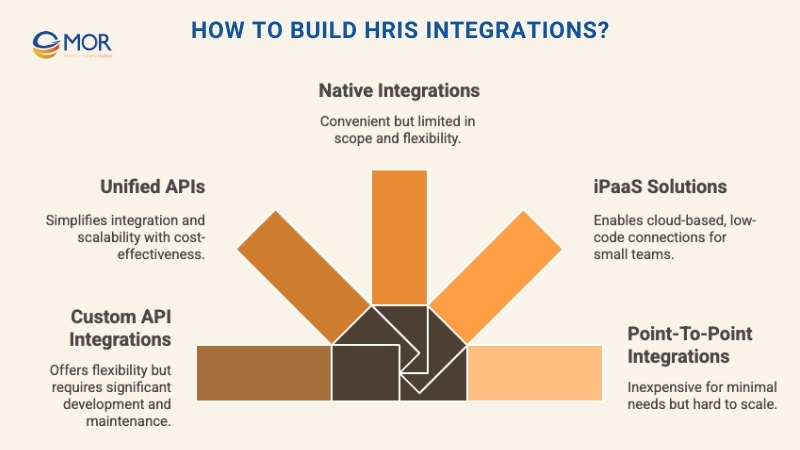
Custom API Integrations
APIs, or application programming interfaces, act as the bridge for transferring data between different applications. Building custom APIs allows businesses to design workflows that trigger and automate specific HR processes. This approach provides flexibility and the ability to tailor the end-user experience.
That said, custom API connections come with challenges. Each HRIS integration demands a fair amount of development effort and collaboration with vendors, which can make scaling difficult. On top of that, when an HRIS provider updates or changes its API, the integration must be updated as well, adding ongoing complexity and maintenance needs.
Unified APIs
To address the need for scalable connections, new solutions such as unified APIs have emerged. These tools bring together the APIs of multiple applications within a single category, allowing developers to link with several platforms at once. By standardizing data into a common format, unified APIs also make it easier for teams to manage and utilize information consistently.
Take Finch’s unified employment API as an example. With one setup, it enables integration with over 200 HRIS and payroll providers. Instead of managing dozens of separate connections, developers only maintain a single link, making this one of the fastest and most cost-effective ways to expand HRIS integrations. For many vendors, this approach represents a practical and scalable HRIS integration platform.
Native Integrations
Some HRIS providers build direct partnerships with other vendors to deliver ready-made integrations. These native options can be convenient, but they are often limited in scope and may come with extra charges. Service quality can also vary, leaving customers with fewer choices and less flexibility compared to other HRIS integration methods.
iPaaS Solutions
Integration platform as a service (iPaaS) provides a cloud-based way to connect different systems, making it easier to link applications with an HRIS. These platforms help automate workflows and keep employee data synchronized across tools.
Because they are typically low-code, iPaaS solutions work well for organizations with smaller technical teams or limited engineering resources.
Point-To-Point Integrations
Point-to-point HRIS integrations are often the most affordable but also the least efficient option. This method connects an employer’s HRIS directly with other operational tools without the use of APIs or third-party platforms.
While simple in concept, it quickly becomes difficult to manage and nearly impossible to scale. Any change in one system usually requires updates across several other connections.
Still, if integration needs are minimal and personalization is a top priority, point-to-point HRIS integration can work as a short-term solution.
Each integration method comes with its own strengths and limitations. The table below compares the most common approaches, helping you evaluate which option best fits your technical capacity and long-term goals.
Type of Integration | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Custom API Integrations | - High flexibility - Fully customizable user experience | - Heavy development effort - Hard to scale - Ongoing maintenance is complex |
| Unified APIs | - Easy to scale HRIS integrations - Standardized data - Low development effort - Simple to maintain | - Limited customization - Dependent on stability of the unified API |
| Native Integrations | - Bundled with the HRIS - Direct control over data | - Limited connections - May incur extra costs - Support may be inconsistent - Scaling is resource-heavy |
| iPaaS Solutions | - Low-code setup - Suitable for companies with smaller tech teams | - Poor scalability - Often tailored to narrow use cases |
| Point-To-Point Integrations | - Cost-effective at the start - Highly personalized - Works for minimal integration needs | - Resource-intensive - Complex to maintain - Not scalable |
Challenges In HRIS Integration Projects
Even the most carefully planned HRIS integration projects come with obstacles. From data consistency to vendor restrictions, these challenges can slow progress and increase costs if not addressed early.
Maintaining Data Quality And Consistency
One of the biggest challenges in HRIS integration is ensuring accuracy, completeness, timeliness, and uniformity across multiple systems. Without strong data governance, businesses risk compliance issues, security gaps, and inaccurate reporting. Establishing clear standards makes it possible to align data coming from different sources.
Tip: When connecting with multiple HR analytics tools, consider using a tool that normalizes data into a common format. This step can save engineering resources and prevent errors from mismatched fields.
Limited API Access And Complex Vendor Partnerships
A common barrier in HRIS integrations is that many HR systems do not provide public APIs. Access often requires a formal partnership, including security audits, legal agreements, and added fees. Some vendors even require a minimum customer threshold before allowing integration. For startups with limited resources, this makes it difficult to build essential connections quickly.
Ongoing Upkeep And Monitoring
Regular upkeep is essential to keep data accurate and reliable after an HRIS integration goes live, especially when the integration supports customer-facing functions. Common maintenance tasks include:
- API version control: Custom integrations must adapt to version changes in HRIS APIs to maintain compatibility when updates are released.
- Updated documentation: Some HR system providers may not refresh developer documentation often, or they may not provide it in the required language. This increases the workload for technical teams.
- Monitoring and logging: To maintain a smooth experience, it is important to track the performance and stability of each integration. Engineering teams also need to review logs regularly and respond quickly to errors.
High Costs Of One-To-One Integrations
Building and maintaining direct one-to-one HRIS integrations requires significant time, money, and developer effort. From HR strategic plan and coding to testing and ongoing updates, each connection can consume hundreds of engineering hours every year.
The cost often reaches tens of thousands or even hundreds of thousands of dollars annually for a single integration.
This method is also inefficient, as the resources spent on maintaining one connection could instead be used to improve product features or expand functionality. For many companies, relying solely on this approach makes scaling unsustainable.
Scaling Across Multiple Systems
Scalability is one of the toughest challenges in HRIS integration projects. Each new connection requires developers to study provider documentation, interpret unique data models, write custom code, run extensive testing, and provide ongoing support. Once the number of HRIS integrations grows beyond three or four, the workload can quickly become overwhelming.
To address this, organizations often turn to integration platforms or API aggregators. These solutions simplify the scaling process and free up technical resources, allowing teams to focus on building innovative features rather than being weighed down by endless integration maintenance.
Simplify HRIS Integrations With MOR Software
Connecting payroll service in Vietnam, benefits, recruiting, and workforce tools into one unified system is never simple. Many HR leaders face constant challenges with fragmented platforms, manual data entry, and compliance risks. That’s where MOR Software comes in.
We design and build custom enterprise applications that integrate HRIS with payroll, ERP, accounting, and collaboration systems. Our dedicated teams focus on creating scalable solutions that fit both current operations and long-term strategies.
With MOR Software JSC, businesses can:
- Automate payroll and benefits processes by connecting HRIS with finance systems.
- Integrate applicant tracking and onboarding workflows directly into HRMS platform.
- Sync employee data across tools like Slack, Microsoft Teams, or ERP systems to cut down on manual updates.
- Build custom APIs or deploy iPaaS solutions tailored to your specific integration needs.
Our experience spans industries from finance to healthcare, where accuracy, compliance, and scalability are non-negotiable. By combining technical expertise with a deep understanding of HR processes, we simplify complex HRIS integrations and help organizations reduce costs, minimize errors, and improve employee experience.
If you’re planning your next HRIS integration project, MOR Software can help you do it faster, smarter, and with long-term stability. Contact us to discuss your needs.
Conclusion
A thoughtful HRIS integration empowers HR teams to eliminate data silos, cut repetitive tasks, and deliver a better employee experience. By connecting payroll, benefits, recruiting, training, and collaboration systems, businesses gain accurate, real-time information that supports smarter decision-making. The right HRIS integration platform ensures scalability, compliance, and long-term efficiency, giving HR leaders the tools they need to focus on strategy instead of administration.
At MOR Software, we bring deep technical expertise and proven industry knowledge to simplify even the most complex integration projects. Ready to unlock the full potential of your HRIS? Contact us today.
MOR SOFTWARE
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is an HRIS integration?
An HRIS integration connects your Human Resources Information System (HRIS) with other applications and platforms, allowing information to move automatically between them. This reduces manual data entry, improves accuracy, and creates a smoother workflow across your HR and business processes.
What does HRIS stand for?
HRIS stands for Human Resources Information System. It is a software solution that organizations use to manage and automate essential HR tasks such as payroll, attendance, scheduling, and employee benefits administration.
What are examples of HRIS systems?
Some widely used HRIS platforms include BambooHR, Workday HCM, Oracle Fusion Cloud HCM, SAP SuccessFactors, Paycor, Namely, Rippling, and Gusto. These systems provide businesses with tools to handle different aspects of workforce management.
What are the four types of HRIS?
HRIS platforms can be grouped into several categories. Operational HRIS manages employee records and performance data. Tactical HRIS supports decision-making in areas like recruitment and training. Strategic HRIS helps align workforce planning with long-term business goals. Comprehensive or limited-function HRIS combines features depending on organizational needs.
Is HRIS an ERP system?
No, an HRIS is not the same as an ERP. ERP systems cover multiple business areas such as finance, supply chain, and operations in addition to HR. An HRIS focuses only on people management processes like payroll, compliance, and onboarding. If your main priority is HR automation, an HRIS is usually more suitable.
What are the three top HRIS systems?
Leading HRIS platforms often highlighted for 2025 include Rippling for quick setup and scalability, Gusto for small to mid-sized companies, and BambooHR for its user-friendly design. Other popular options include SAP SuccessFactors, Workday, and UKG Pro.
Is SAP an HRIS system?
Yes, SAP offers an HRIS solution called SAP SuccessFactors Employee Central. It is a cloud-based platform that helps companies standardize HR operations globally and provides insights for better workforce decision-making.
What is CRM and HRIS?
A CRM is a Customer Relationship Management system, which manages customer interactions and sales processes. An HRIS is a Human Resources Information System, focused on employee management. Businesses often use both alongside other tools like Project Management Systems and Performance Management Systems to streamline operations across departments.
Is Excel an HRIS system?
Excel itself is not an HRIS system. While it can be used to store and manage HR-related data in spreadsheets, it lacks automation, security, and integration features found in dedicated HRIS platforms.
What are the five functions of HRIS?
An HRIS typically supports several core functions. These include maintaining employee records, collecting time and attendance data, managing benefits enrollment, processing payroll, and supporting recruitment and onboarding. Many systems also offer performance reviews, compliance tracking, and training modules.
What are the four major components of HRIS?
The main components of an HRIS generally include a central database for employee information, tools for time and labor management, payroll functions, and benefits administration. Many systems also provide recruitment modules, employee self-service portals, and retention tools.
Rate this article
0
over 5.0 based on 0 reviews
Your rating on this news:
Name
*Email
*Write your comment
*Send your comment
1