Predictive HR Analytics: The Ultimate Guide for HR Leaders 2026

Businesses are increasingly turning to predictive HR analytics to make smarter, data-backed workforce decisions. Yet many still struggle to use their HR data effectively to anticipate turnover, skill gaps, and engagement issues. This MOR Software’s guide will show how predictive analytics transforms HR operations, helping leaders strengthen culture, boost retention, and plan for long-term success.
What Is Predictive HR Analytics?
Predictive HR analytics is a digital solution that helps HR teams use historical and current data to anticipate future workforce trends.
In practice, HR predictive analytics collects and examines large sets of employee information to uncover key patterns, outliers, and relationships. It applies statistical modeling and data science to help HR departments make more confident and data-backed decisions in areas like recruitment, retention, and performance.
Think of it as a system that turns unused or fragmented HR data into meaningful insights. Just as a refinery transforms raw material into something valuable, this technology converts complex workforce information into practical knowledge that supports better planning and smarter business actions.
The Logic Behind Predictive HR Analytics
Predictive HR analytics is designed to forecast workforce behavior by identifying what is likely to happen based on historical data. Imagine using it to estimate whether an employee might leave within the next year. The model studies previous resignation trends and related factors to generate accurate predictions about future turnover.
To apply predictive analytics in HR effectively, you need to combine both descriptive and predictive approaches. The process begins with collecting HR data from multiple internal systems, such as attendance records, performance reviews, and engagement surveys, and preparing it for analysis. Once the data is cleaned and structured, analysts apply descriptive statistics to understand what has already happened, followed by predictive modeling to forecast what could happen next.
While descriptive analytics focuses on explaining past events, predictive techniques help HR teams act ahead of time. Both are necessary for building advanced HR analytics that supports proactive decisions. In short, descriptive tools tell you what has occurred, but predictive models show you what to prepare for.
How Can Predictive HR Analytics Improve Company Culture?
Predictive HR analytics helps companies build stronger, more connected teams by turning workforce data into actionable insight. When HR leaders use predictive analytics for HR, they can detect early signs of disengagement, forecast potential turnover, and understand what truly influences employee morale. This knowledge allows organizations to make informed choices that directly strengthen workplace culture.
For example, analytics can reveal patterns behind why certain departments have higher satisfaction scores or why specific managers achieve better team retention. With this understanding, HR can design programs that reinforce these strengths, like mentorship, recognition systems, or leadership training, to extend positive behavior company-wide.
Beyond retention and engagement, predictive analytics supports fair and transparent practices. It uncovers hidden biases in hiring or promotion decisions, helping companies create a more inclusive environment. When used ethically, it becomes a foundation for trust, transparency, and shared accountability.
Ultimately, predictive HR analytics empowers leaders to move from reacting to culture problems to preventing them. The result is a workplace where people feel valued, motivated, and aligned with organizational goals, a culture built not by chance, but by smart, data-driven decisions.
How Does Predictive HR Analytics Help Human Resources?
Predictive HR analytics enables HR teams to foresee workforce challenges and act before they escalate. Combining advanced modeling with real-time data, predictive analytics HR helps organizations minimize risks, improve efficiency, and make more consistent, evidence-based decisions across the employee journey.

- Reduce Workforce Risks: Predictive models analyze trends in turnover, absenteeism, and declining performance, allowing HR leaders to take preventive action.
- Lower Human Error: Automation within analytics HR eliminates guesswork, reduces bias, and ensures fair assessments during hiring, evaluation, and promotion.
- Spot Top Performers: Insights reveal which skill sets and behaviors correlate with long-term success, guiding data-backed recruitment and talent development.
- Improve Hiring Quality: Predictive modeling forecasts candidate suitability and retention likelihood, helping recruiters focus on individuals who align best with company goals.
- Enhance Employee Productivity: The system uncovers engagement drivers and performance barriers, supporting initiatives that strengthen motivation and overall output.
With these capabilities, predictive HR analytics turns traditional HR into a strategic function that operates proactively. It empowers leaders to base every workforce decision on facts, not assumptions, creating a workplace that’s productive, fair, and built for long-term growth.
Practical Use Cases Of Predictive HR Analytics
The true value of predictive HR analytics lies in how it’s applied to real business challenges. We highlight some practical use cases that show how data-driven prediction helps companies strengthen leadership pipelines, hire smarter, and retain valuable talent.

Succession Planning
Using predictive HR analytics, companies can evaluate employee data to understand current skill levels, work history, and potential career growth. This insight allows HR teams to identify who is ready, or can be developed, to move into leadership roles. With this foresight, organizations strengthen their succession plans, minimize disruptions from sudden departures, and maintain a steady leadership pipeline that supports long-term stability.
Strategic Recruitment
When applied to hiring, examples of predictive analytics in HR show how data modeling shifts recruitment from a reactive to a strategic process. By studying hiring trends, performance results, and turnover patterns, HR teams can anticipate future staffing needs more accurately. This proactive approach ensures that businesses attract and retain qualified talent ahead of demand, keeping teams aligned with evolving business goals.
Retention Optimization
With predictive HR analytics, HR teams can analyze patterns behind employee turnover, engagement, and satisfaction to refine their retention plans. Using accurate data, they can identify which factors most influence departures and focus on strategies that genuinely improve morale. Instead of broad, generic programs, this approach supports tailored initiatives that meet individual needs, helping the organization retain valuable talent and maintain a committed, motivated workforce.
What Is The Difference Between Predictive And Descriptive HR Analytics?
In human resources, analytics guide smarter decisions by revealing both past patterns and future possibilities. Two core approaches, descriptive HR analytics and predictive HR analytics, work hand in hand to help organizations understand workforce behavior, improve talent management, and strengthen business planning.
Aspect | Descriptive HR Analytics | Predictive HR Analytics |
| Purpose | Reviews historical data to explain what has already occurred. | Uses existing and past data to forecast likely workforce outcomes. |
| Focus | Looks at past performance, employee trends, and operational results. | Anticipates future issues such as turnover risk or talent gaps. |
| Key Question | “What happened?” and “Why did it happen?” | “What might happen next?” and “How can we prepare for it?” |
| Techniques Used | Reporting, dashboards, and trend evaluation. | Statistical modeling, forecasting, and AI-driven prediction. |
| Business Value | Provides understanding of patterns to support decision-making. | Promotes proactive planning through actionable insights. |
| Example Use Case | Examining reasons behind last year’s attrition rate. | Forecasting who might leave next year to guide retention actions. |
Some companies also use prescriptive HR analytics, which builds on predictive models to recommend the best response to projected outcomes. When used together, these three layers of HR analytics data give leaders a complete picture, explaining the past, predicting the future, and suggesting what to do next.
Applying Predictive HR Analytics In Real HR Operations
So how does predictive HR analytics actually work inside organizations? HR departments manage massive volumes of workforce information stored in platforms like a Human Resources Information System (HRIS).
When this data is analyzed through predictive models, HR transforms from an administrative function into a strategic partner that bases decisions on measurable evidence rather than intuition. With HR predictive analytics case studies, we see how companies forecast the impact of HR policies on engagement, well-being, and overall business performance, especially when predicting and preventing costly employee turnover.
Yet, adoption remains limited. According to Deloitte’s People Analytics Maturity Model, only 17% of organizations globally had usable and integrated HR analytics data in 2018. That number, while an improvement from 8% in 2015 and 4% in 2014, shows that most companies still rely on basic reporting. Among those with access, just 2% achieved full integration with real-time and AI-enhanced systems, while the remaining 15% conducted predictive work only on an ad-hoc basis.
The gap highlights how critical it is for businesses to invest in structured data ecosystems and analytical capabilities. When done right, predictive analytics becomes a competitive advantage that allows HR teams to act with precision and shape a future-ready workforce.
Real-World Examples Of Predictive HR Analytics
The impact of predictive HR analytics becomes clear when looking at how leading organizations use it to solve real workforce problems. These real-world examples highlight how data-driven prediction improves hiring, retention, engagement, and overall business performance.
1. Predicting and Preventing Turnover at HP
Hewlett-Packard (HP), a global enterprise with over 300,000 employees, has long been recognized as a pioneer in HR predictive analytics. Despite its strong reputation, HP struggled with high turnover, especially within its sales divisions, where rates often reached 20%. On average, employees stayed only four to five years before leaving.
Such frequent turnover came with steep consequences, rising recruitment costs, productivity loss, and knowledge drain. Departing staff often took client relationships and institutional expertise with them. Research shows that replacing a mid-level employee can cost more than 150% of their annual salary, which meant millions in potential losses for HP.
To tackle this challenge, two HP data scientists combined two years of workforce data to forecast which employees were most likely to leave. Using predictive modeling, they developed a “Flight Risk” score that measured each worker’s likelihood of departure.
The insights from this predictive analytics HR project were striking. Higher pay, promotions, and strong performance ratings often correlated with lower flight risk, but the relationships weren’t always straightforward. For instance, employees who earned promotions without receiving meaningful raises were still more likely to resign.
Naturally, privacy concerns accompanied such detailed analysis. Access to the Flight Risk data was restricted to selected senior managers, who received specialized training on interpreting the scores responsibly and maintaining confidentiality.
These managers used the tool to understand key attrition drivers and design retention strategies. The system encouraged accountability by identifying risk areas that required proactive leadership action.
To simplify complex data interpretation, HP also developed an internal dashboard summarizing critical HR reporting and analytics metrics. This made it easier to monitor high-risk areas and prioritize interventions.
Ultimately, the Flight Risk system acted as an early warning mechanism. Managers could intervene before valuable employees left or plan smooth transitions when departures were inevitable. According to research cited by Siegel (2013), HP saved an estimated $300 million through this HR predictive analytics example, proving the measurable value of data-driven retention planning.
2. Predicting Hire Success at Google
In his book Work Rules!, Laszlo Bock, former Senior Vice President of People Operations at Google, explains how the company uses data and analytics as the foundation of its HR strategy. Every stage of the hiring process is guided by statistical modeling, from the questions asked in interviews to the algorithms that help predict candidate performance. These systems continuously refine themselves to identify the best possible talent.
Beyond hiring accuracy, Google also applies HR predictive analytics to forecast employee retention. For instance, analysis revealed that sales employees who fail to receive a promotion within four years are significantly more likely to leave the organization. This insight allows HR leaders to take preemptive steps, such as offering growth opportunities or additional support, to improve retention among top performers.
Google’s approach shows how predictive analytics for HR extends beyond recruitment to track post-hire success. The company monitors advanced indicators like time-to-productivity, ramp-up speed, and cost to reach peak performance. These metrics help refine future hiring decisions and ensure that every new recruit contributes effectively to long-term business outcomes.
3. Predicting Revenue Using Engagement Data
Employee engagement is often regarded as one of the strongest predictors of business performance. Engaged employees tend to be more productive, deliver higher-quality work, take fewer absences, and are less likely to leave the company.
Best Buy, the global electronics retailer, wanted to quantify this relationship and understand how engagement influenced its store revenue. By applying HR predictive analytics, the company discovered a direct financial connection: every 0.1% increase in employee engagement correlated with an additional $100,000 in revenue per store.
Recognizing the value of this insight, Best Buy began measuring engagement several times throughout the year. Frequent analysis allowed them to identify the key factors driving motivation and morale. With this data-driven approach, HR teams could design focused initiatives to improve engagement, which in turn boosted both employee satisfaction and business profitability.
4. Wikipedia Contributor Retention
Wikipedia depends on thousands of volunteer editors, known as Wikipedians, who write, review, and update content daily. The scale is massive, over 800 new pages and 3,000 edits are made every day on the English version alone, averaging more than three edits per second across the globe.
Using predictive HR analytics, Wikipedia can identify which of its 750,000 active contributors are most likely to stop participating. Tracking editing frequency, engagement history, and collaboration patterns, the platform forecasts potential drop-offs before they happen.
While the exact interventions may vary, even a simple acknowledgment, like a personalized thank-you message, can help retain contributors. Recognizing volunteer effort and re-engaging at-risk editors demonstrates how predictive analytics can be applied not only to corporate HR but also to large, community-driven environments.
5. Using Facebook Data to Improve Hiring Decisions
Recruiters often explore applicants’ social media profiles, and research suggests this may have measurable value. A study by Kluemper, Rosen, and Mossholder (2012) found that information from a candidate’s Facebook profile can help predict personality traits and even future job performance. Participants who reviewed profiles assigned “hirability” scores that explained about 8% of manager-rated performance outcomes.
While 8% may seem modest, this finding still supports the potential of HR predictive analytics in assessing soft attributes that traditional methods might overlook. Standardized personality tests remain more reliable, but when combined with other predictors, such as IQ assessments, structured interviews, and behavioral evaluations, social media insights can enhance overall accuracy.
Used responsibly, social platforms like Facebook can serve as a complementary screening tool within predictive analytics HR strategies, helping recruiters form a more holistic understanding of candidates while maintaining ethical standards and privacy safeguards.
6. Nielsen’s Predictive Retention Strategy
Nielsen, a global data and measurement company, faced retention challenges similar to those experienced by HP. After discussions with a business unit president, the Senior Vice President of People Analytics identified employee attrition as a critical issue affecting organizational stability and cost efficiency.
The analytics team conducted a detailed financial impact study and found that reducing attrition by just one percentage point could save the company approximately $5 million in business expenses. This insight highlighted how predictive HR analytics could directly influence financial outcomes through smarter workforce planning.
Applying predictive models, the team pinpointed 120 high-risk employees across key functions. For 40% of these individuals, lateral job moves were introduced to re-engage them and create new career growth opportunities. As a result, attrition among this group dropped to zero during the first six months following implementation.
Encouraged by these results, Nielsen expanded its retention initiatives globally. The overall attrition rate across the enterprise decreased by two percentage points, leading to an estimated $10 million in cost savings. The success of this HR predictive analytics example prompted the company to scale the program to seven additional countries, further strengthening workforce stability and long-term talent retention.
7. Cornerstone’s Study on Toxic Employees
Cornerstone conducted an extensive case study examining the effect of toxic employees on workplace culture and performance. In this HR predictive analytics example, the company analyzed patterns of misconduct and identified traits linked to problematic behavior. Toxic employees were defined as those most likely to engage in activities such as fraud, substance abuse, or harassment, behaviors that not only harm the organization but also poison the work environment.
Research has shown that a single toxic employee can lower a team’s productivity by 30–40%. Their presence often drives high-performing colleagues to leave, compounding the financial and cultural damage. To investigate this further, Cornerstone analyzed data from 63,000 employees, flagging cases of involuntary termination for reasons including workplace violence, falsification, or policy violations. Roughly 4% of the workforce fit the toxic profile.
Through statistical modeling, the company identified several key predictors of toxic behavior. These individuals often labeled themselves as strict rule-followers, scored poorly in attendance and dependability, and demonstrated low service orientation. Interestingly, the study found that while productivity didn’t immediately decline, toxic behavior spread quickly across teams, increasing stress and resignation rates among peers.
Financially, the impact was significant. Hiring one toxic employee cost companies an average of $12,800, compared to about $4,000 for a typical hire, excluding long-term productivity losses linked to burnout and disengagement. This research highlights how predictive HR analytics can help refine hiring processes, flag high-risk candidates early, and build a more positive and sustainable workplace culture.
How To Implement A Predictive HR Analytics System Successfully
Building a successful predictive HR analytics program requires planning, collaboration, and a strong focus on ethics and data accuracy. HR leaders can follow these core steps to ensure effective implementation.
- Define Clear Business Goals: The process begins with aligning analytics initiatives to company-wide objectives. HR teams should work with department heads to pinpoint long-term priorities and identify measurable metrics that directly support them. Linking analytics outcomes to business performance ensures that insights translate into real impact.
- Build Knowledge and Confidence: Since predictive HR analytics involves complex data modeling, HR professionals must first understand its foundations. Providing ongoing learning programs and data literacy workshops helps reduce uncertainty and improves team confidence. Partnering with data scientists or hiring HR data analysts ensures that predictive models are developed, validated, and interpreted correctly.
- Prioritize Ethics and Transparency: Every analytics HR system must safeguard fairness and prevent bias. Predictive algorithms can unintentionally favor or disadvantage specific employee groups if not carefully designed. To avoid this, companies should adhere to ethical guidelines, maintain transparency about how data is used, and uphold both corporate and HR codes of conduct. Fair treatment fosters trust, which is essential for engagement and participation.
- Apply Analytics With Purpose: Once the foundation is set, HR teams can use analytics strategically to address high-value goals. For example, predictive HR analytics can support career pathing, identify skill gaps, and guide competency-based training programs that prepare employees for future roles. By focusing on targeted business outcomes, predictive analytics becomes more than a tool, it becomes a driver of organizational growth and employee development.
Common Pitfalls And Ethical Issues In Predictive HR Analytics
While predictive HR analytics brings enormous value to workforce planning, it also introduces ethical and operational challenges that must be carefully managed. Addressing these early helps protect both employees and organizational integrity.
- Bias Prevention: Predictive models can unintentionally reinforce existing biases in recruitment, promotion, or retention if the underlying data reflects past inequities. Regular auditing, balanced datasets, and diverse data science teams are essential for minimizing bias. By monitoring algorithmic fairness, HR ensures that analytics supports equality rather than undermining it.
- Privacy and Transparency: Employees have the right to know how their personal data is collected, stored, and applied in analytical models. Being transparent about data practices builds trust and ensures compliance with privacy laws such as GDPR. Clear communication also reassures employees that HR predictive analytics is used responsibly to improve, not monitor, their experience.
- Balancing Analytics With Human Judgment: Predictive insights should guide, not replace, human decision-making. Analytics offers probability and direction, but HR leaders must interpret those results in the right context. Combining data-driven insights with empathy, experience, and professional judgment leads to better, more ethical workforce decisions.
- Accuracy and Validation: Predictive models require ongoing testing to stay reliable. Tools like validation metrics measure how closely real outcomes, such as exits, promotions, or internal moves, match predictions. Continuous validation ensures that predictive analytics HR remains accurate as workforce dynamics change, maintaining both confidence and credibility in its results.
Choosing The Right Predictive HR Analytics Tool For Your Business
Selecting the right platform for predictive HR analytics is one of the most important decisions an HR team can make. The right system allows organizations to fully harness the power of data while ensuring ease of use, security, and measurable results. The goal is to find a solution that aligns with business objectives and integrates smoothly into existing HR infrastructure.
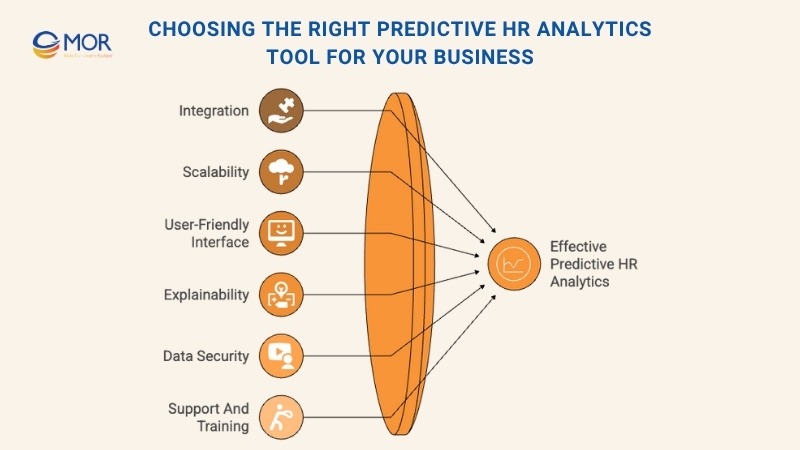
- Integration: A reliable analytics tool should work seamlessly with your current HR systems. Smooth data transfer and compatibility are essential for accurate modeling and efficient workflows. Proper integration ensures your HR reporting and analytics processes remain consistent across departments.
- Scalability: As your organization grows, your analytical capabilities should grow with it. Choose a tool that scales easily, allowing your team to expand its predictive HR analytics functions without major disruptions or costly overhauls.
- User-Friendly Interface: The best tools provide intuitive dashboards and easy-to-navigate reports. A simple, visual interface helps HR professionals interpret insights quickly and make informed decisions without relying heavily on data specialists.
- Explainability: Transparency in prediction logic is critical. Opt for a solution that explains how each prediction is generated so HR leaders can understand and trust the reasoning behind data-driven outcomes.
- Data Security and Compliance: Since HR departments handle sensitive employee information, security must be a top priority. The chosen platform should comply with privacy regulations such as GDPR and include robust safeguards to protect personal data.
- Support and Training: Even the best technology needs proper onboarding. Select vendors that provide comprehensive training and ongoing support, ensuring HR teams use the system effectively and confidently.
- Cost and ROI: Evaluate all expenses, from setup and licensing to long-term maintenance. Then, measure expected ROI by considering how predictive insights could improve retention, hiring quality, or workforce productivity.
- User Feedback and Reviews: Learning from others’ experiences is invaluable. Read reviews and connect with HR professionals who use the same tools to understand real-world performance, limitations, and best practices.
When these factors are carefully assessed, HR teams can select a predictive workforce analytics platform that enhances decision-making, strengthens people strategy, and contributes directly to business success.
The Future Of Predictive HR Analytics
As we move toward 2026, artificial intelligence continues to reshape how companies manage people and performance. The rise of automation and machine learning means HR leaders must adapt quickly to a future where data-driven workforce planning is not just a competitive edge but a requirement for sustainable growth. Organizations that understand this transformation early will be best positioned to lead.
Investing in predictive HR analytics now prepares businesses to compete effectively in a tight talent market. The blend of AI intelligence and human judgment enables smarter decisions about hiring, development, and retention. This balance between technology and empathy represents the future of HR analytics, a future where organizations use data not just to measure success, but to create more engaging, equitable, and future-ready workplaces.
Build A Custom Predictive HR Analytics Solution With MOR Software
At MOR Software, we help businesses turn workforce data into meaningful decisions through advanced predictive HR analytics solutions. With over 850 successful projects across 10+ countries, our team combines AI, data engineering, and HR technology expertise to design scalable, secure, and insightful systems tailored to each organization’s needs.
Our specialists deliver end-to-end support, from strategic consulting to full system deployment:
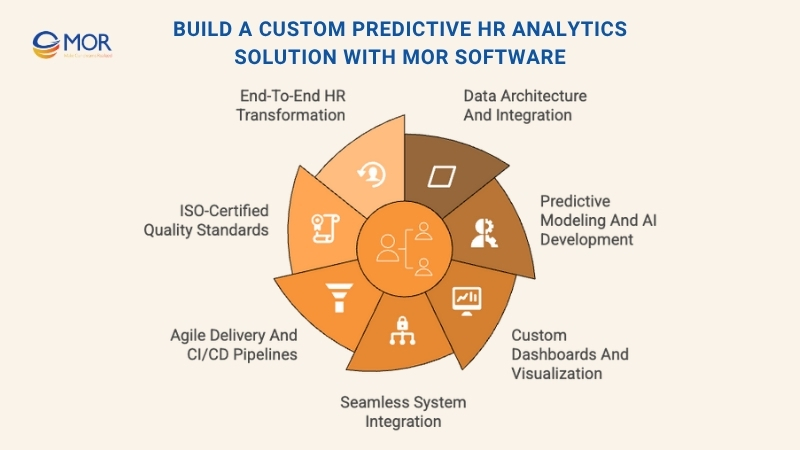
- Data architecture and integration: We design structured pipelines that connect HR data from multiple sources, HRIS, CRM, and performance systems, into one unified platform.
- Predictive modeling and AI development: Our data scientists build custom algorithms to forecast attrition risks, hiring needs, and performance trends.
- Custom dashboards and analytics visualization: We create user-friendly dashboards that make complex data easy to interpret, helping HR leaders make confident, evidence-based decisions.
- Seamless system integration: MOR Software ensures smooth connectivity with existing tools such as Salesforce, Workday, or ERP systems.
- Agile delivery and CI/CD pipelines: Our teams apply Agile methodology and version-controlled deployment to accelerate delivery while maintaining data accuracy and compliance.
MOR Software operates under ISO 27001 and ISO 9001 standards, guaranteeing data security, process transparency, and consistent quality across all projects.
With our technical depth and experience in AI-driven HR transformation, MOR Software is the trusted partner for organizations ready to move beyond traditional HR analytics. We help you predict, plan, and perform with clarity, so your people strategy aligns perfectly with your business goals.
Contact us to explore how we can build your next predictive HR analytics solution.
Conclusion
Predictive HR analytics is no longer optional. It’s a necessity for organizations that want to stay competitive, retain top talent, and make data-driven workforce decisions. By combining human expertise with advanced analytics, companies can anticipate challenges before they arise and build stronger, more agile teams. MOR Software helps businesses unlock this potential with customized, secure, and scalable solutions. Contact us today to discover how predictive analytics can transform your HR strategy and performance.
Rate this article
0
over 5.0 based on 0 reviews
Your rating on this news:
Name
*Email
*Write your comment
*Send your comment
1