Top 10 AI Tools in Healthcare Every Doctor Should Know in 2026

The demand for smarter healthcare solutions is rising, and AI tools in healthcare are proving to be the answer. From early diagnosis to personalized care, these innovations are reshaping how doctors and patients interact. This MOR Software’s guide will walk you through the top AI applications every medical professional should know in 2026.
Statistics On AI Tools In Healthcare Investment In 2025
Around 4.5 billion people still lack access to basic healthcare services, and the World Health Organization projects a shortage of 11 million health workers by 2030. AI tools in healthcare are seen as one way to close that gap and push the industry closer to universal health coverage, one of the United Nations’ major global health goals for 2030.
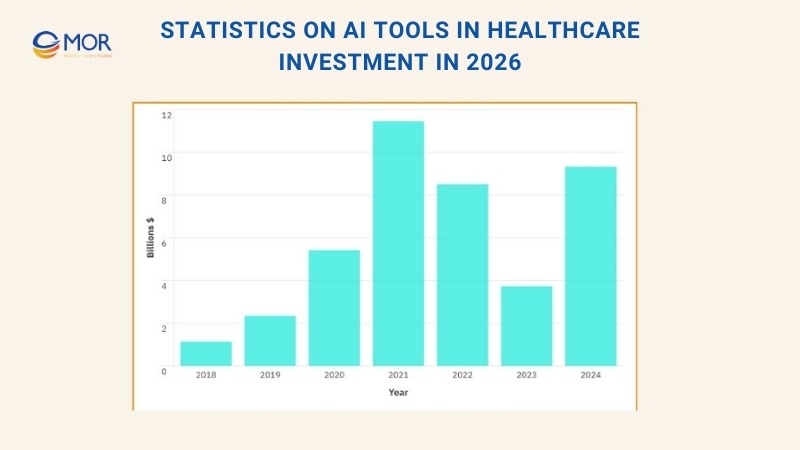
These technologies are already showing progress. Doctors are using them to detect fractures, assess patients faster in emergency departments, and flag early signs of chronic diseases. Yet adoption remains uneven. The World Economic Forum describes healthcare as “below average” compared with other industries in its uptake of AI, despite strong evidence that these solutions can change outcomes.
Investment trends highlight the challenge. Annual private spending on AI in the medical sector has grown, but the levels vary across regions and specialties. The World Economic Forum notes that digital health applications could increase efficiency, lower costs, and improve patient outcomes worldwide.
In practice, this means AI tools in healthcare industry are moving from concept to real-world use, shaping how medicine is delivered today.
As shown in the chart below, private investment in healthcare AI differs widely depending on specialty and region.
Key Benefits Of Using AI Tools In Healthcare
Unlocking the full value of AI tools in healthcare means looking beyond innovation and focusing on real outcomes. These benefits are already reshaping how providers deliver care every day.
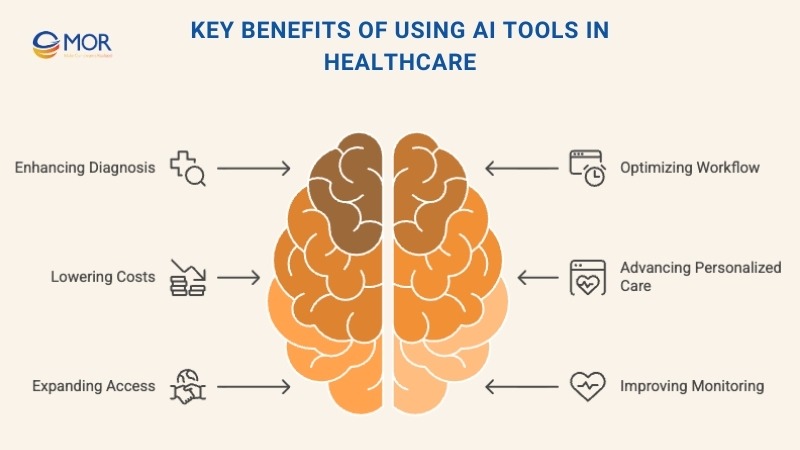
Enhancing Diagnosis And Clinical Decisions
AI tools in healthcare are reshaping diagnostics by delivering more precise results. Algorithms trained on thousands of images can identify tumors, fractures, and irregularities that even experienced eyes may overlook. These systems support treatment planning by highlighting the best options and reducing the risk of mistakes.
In a nationwide real-world study from Germany’s screening program, AI-supported double reading increased breast cancer detection by 17.6% while keeping recall rates noninferior. This shows measurable diagnostic gains at scale.
With reliable recommendations at hand, clinicians can make decisions backed by evidence and improve patient outcomes. Hospitals using AI diagnostic tools in healthcare report faster turnaround times and higher confidence in critical cases.
Optimizing Workflow And Reducing Burnout
Long hours spent filling out records or updating charts have been a persistent source of stress for many clinicians. Intelligent assistants, such as automated scribes and speech-recognition software, now take over repetitive administrative tasks.
At University of Iowa Health Care, systemwide ambient AI documentation was associated with a 30% reduction in burnout and an average 2.6 hours per week saved on after-hours documentation.
This technology lets healthcare teams redirect energy to patient care instead of paperwork. The adoption of AI services in healthcare has been linked to shorter waiting times and better patient experiences while lowering the risk of burnout for staff.
Lowering Costs And Increasing Efficiency
Healthcare systems often struggle with rising expenses. AI powered diagnostic tools in healthcare make early detection possible, catching conditions before they require costly interventions. Predictive analytics help hospitals allocate resources wisely, while machine learning accelerates drug discovery and testing.
Independent analysis estimates that applying AI and related technologies could deliver net savings of 5 to 10% across total healthcare spending when implemented at scale.
Through bringing precision and speed into routine processes, AI reduces waste and shortens development cycles. For providers, this translates into more sustainable operations without compromising quality of care.
Advancing Personalized And Preventive Care
One of the strongest advantages of modern medical AI tools is their ability to process diverse data sets, from genetic sequences to lifestyle information. By analyzing this information, systems can suggest treatments tailored to the individual rather than a general population group.
Patients benefit from personalized therapies and preventive measures that consider unique risks. This approach also improves long-term health by encouraging timely interventions and reducing the likelihood of severe disease progression.
Expanding Access And Patient Engagement
Many communities remain underserved, yet AI tools used in healthcare are starting to close the gap. Chatbots and digital assistants provide around-the-clock support in multiple languages, answer routine questions, and remind patients about follow-up care.
Virtual tools can even extend mental health support to areas without local specialists. Engaging patients more actively in their own care, these platforms strengthen trust and help reduce disparities in service delivery.
Improving Monitoring And Early Intervention
Remote monitoring has gained momentum as wearable devices and connected sensors spread. These tools track vital signs continuously and alert providers when early signs of trouble appear. AI models interpret streams of real-time data to identify risks, from irregular heart rhythms to glucose fluctuations.
A 2024 systematic review of alert-based remote monitoring reported a mean 9.6% reduction in hospitalizations and a 3% reduction in all-cause mortality. This highlights the value of early intervention.
This allows healthcare teams to act quickly and personalize interventions before complications occur. With every improvement, an AI tool in healthcare adds another layer of safety and prevention that benefits both patients and practitioners.
Top 10 Best AI Tools In Healthcare To Watch In 2026
AI in medicine is no longer futuristic. AI tools in healthcare are already driving real improvements in patient care and operations. This section highlights ten of the most valuable solutions to watch in 2026.
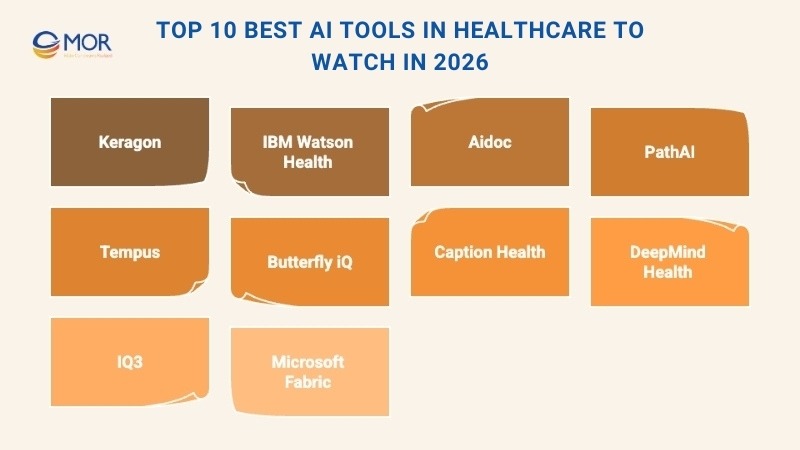
1. Keragon
Keragon is a HIPAA-compliant automation platform built for healthcare organizations that want to integrate artificial intelligence without risking data security or patient privacy.
Acting as a central hub, it connects electronic health records, scheduling systems, lab platforms, and communication tools through secure, no-code workflows. Streamlining repetitive processes and reducing manual workload, it enables teams to operate with greater efficiency while keeping sensitive information protected.
The platform helps providers automate patient intake, follow-up reminders, lab result updates, and insurance eligibility checks, giving clinicians more time for direct patient care. It also integrates AI analytics into daily operations, delivering real-time insights that support better decision-making at the point of care.
With its focus on reducing burnout, improving interoperability, and accelerating safe adoption, Keragon shows how AI tools in healthcare can modernize operations and improve patient engagement while maintaining full compliance.
2. IBM Watson Health
IBM Watson Health has long been recognized as a pioneer in applying artificial intelligence to clinical practice.
The platform combines natural language processing with machine learning to interpret vast amounts of unstructured medical data, from physician notes to peer-reviewed research and patient histories. For clinicians, this translates into faster and more reliable support when diagnosing and selecting treatments.
In oncology, Watson is especially valuable. It analyzes genetic information alongside current studies to recommend therapies tailored to each patient’s unique profile.
Acting as a digital assistant, it helps healthcare teams identify options that might otherwise be missed, improving confidence in complex decision-making. With its ability to process information at scale, Watson showcases how AI tools for doctors can directly improve accuracy and enhance patient care.
3. Aidoc
Aidoc is an AI-powered radiology platform designed to support doctors in detecting and prioritizing urgent medical conditions. The system continuously reviews imaging scans, including CTs, to spot signs of strokes, brain hemorrhages, and pulmonary embolisms.
Highlighting critical findings in real time, it reduces the strain on radiologists and ensures the most severe cases are addressed first. This faster workflow allows for timely intervention and better outcomes, making Aidoc one of the most impactful AI powered diagnostic tools in healthcare today.
4. PathAI
PathAI applies deep learning to pathology, offering doctors higher accuracy when analyzing slides and identifying disease. By scanning images with precision, it minimizes the risk of oversight caused by fatigue or human error.
This consistency gives clinicians dependable second opinions, especially in complex cancer cases where accuracy is vital. The technology highlights how AI diagnostic tools in healthcare can strengthen confidence in results and support faster treatment planning, particularly in oncology where early detection changes outcomes.
5. Tempus
Tempus is a precision medicine platform that integrates artificial intelligence with genomic sequencing and clinical data. It helps physicians predict how patients will respond to targeted therapies, ensuring that treatment strategies are based on individual profiles rather than generalized guidelines.
This approach is proving highly effective in oncology and rare diseases, where traditional models often fall short. By combining molecular insights with real-world patient records, Tempus illustrates the growing value of AI software for healthcare in tailoring care pathways.
6. Butterfly iQ
Butterfly iQ is a handheld ultrasound device powered by AI, designed to make imaging portable, intuitive, and widely available. The device connects directly to a smartphone and guides users in capturing and interpreting scans, lowering the barrier to access.
This innovation is particularly impactful in underserved regions where radiology expertise is limited. Through enabling bedside diagnostics, Butterfly iQ accelerates decisions and improves care delivery, showing how AI driven healthcare tools can extend high-quality services beyond traditional hospital walls.
7. Caption Health
Caption Health is dedicated to making ultrasound more accessible by guiding clinicians who may not have advanced imaging expertise. Through real-time AI feedback, the system shows users how to position and adjust the probe while performing a scan.
This step-by-step support allows doctors and nurses to capture accurate cardiac ultrasound images with minimal training.
Caption Health expands access to cardiac care in emergency departments and primary care clinics by lowering the barrier to performing echocardiograms. This shows the practical role of AI tools in healthcare industry.
8. DeepMind Health (by Google)
DeepMind Health, part of Google, is known for developing advanced artificial intelligence models that assist with early disease detection. Its work includes tools for identifying diabetic retinopathy and age-related macular degeneration at a stage when treatment is most effective.
In collaboration with Moorfields Eye Hospital, DeepMind created an AI system that interprets eye scans with accuracy on par with leading specialists.
This capability supports ophthalmologists in prioritizing high-risk patients and improving long-term vision outcomes. It is one of the strongest examples of AI tools in healthcare being applied to preventive care.
9. IQ3
The IQ3 probe from Butterfly Networks combines a handheld device, a smartphone, and AI software to create a portable ultrasound tool that can be used by clinicians with limited imaging experience. Built on semiconductor-based ultrasound-on-a-chip technology, it delivers high-resolution images directly to a mobile screen.
Cloud-based algorithms hosted on AWS then analyze the scans, flagging potential areas of concern. One algorithm, trained on thousands of lung ultrasound clips, can automatically count B-lines, artifacts that signal possible breathing issues, in just a few seconds.
This saves time and demonstrates the value of AI tool in healthcare settings where quick, accurate analysis is critical.
10. Microsoft Fabric
Microsoft Fabric is an analytics platform that brings together multiple healthcare data sources, electronic health records, lab systems, imaging archives, claims databases, and connected devices, into one environment. Within Microsoft Cloud for Healthcare, it supports specialized AI workloads that improve decision-making and efficiency.
Organizations can use its text analytics service to extract insights from unstructured patient information in several languages. In addition, Azure’s AI Health Bot enables the creation of virtual assistants for clinical or administrative use, while AI Health Insights supports doctors with tailored recommendations.
With these capabilities, Microsoft Fabric shows how generative AI tools with built-in compliance features for healthcare enterprises can deliver scalable, secure, and practical solutions for modern care.
Main Uses Of AI Tools In Healthcare (2026)
Artificial intelligence is shaping healthcare delivery in 2026 through five primary applications that improve accuracy, efficiency, and patient outcomes.
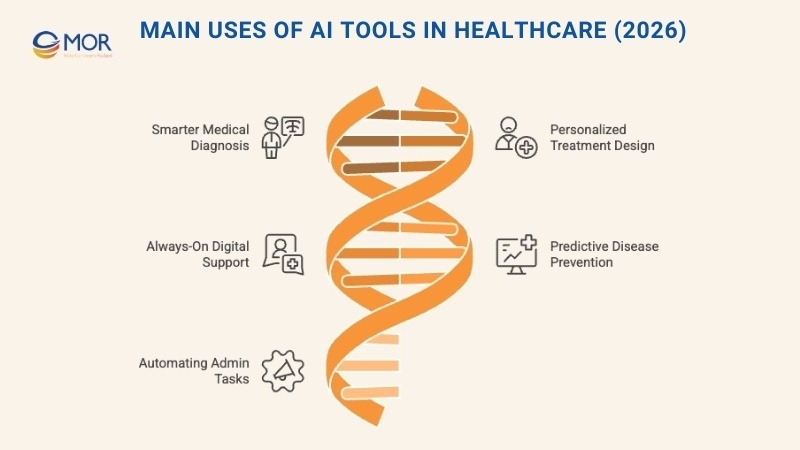
Smarter Medical Diagnosis
Hospitals and research centers are increasingly adopting AI tools in healthcare to strengthen diagnostic accuracy. At Massachusetts General Hospital and MIT, algorithms have been able to detect lung nodules with 94% accuracy compared to 65% for radiologists.
Similar results were seen in breast cancer screening, where AI reached 90% sensitivity against 78% from human experts. These findings highlight the growing role of AI diagnostic tools in healthcare for supporting physicians in detecting disease earlier and more reliably.
Personalized Treatment Design
Treatment planning is also evolving as algorithms analyze patient data across genetic, clinical, and lifestyle factors. A notable case in Japan involved IBM Watson identifying a rare leukemia subtype using genetic sequencing, with its recommendations aligning with expert conclusions 99% of the time.
Working with genetic information, past treatment history, and current health indicators, AI services in healthcare now enable physicians to craft therapies that are safer, more precise, and more adaptive to individual needs.
Data Type | Purpose | Impact |
| Genetic Data | Identify inherited risks | Improves precision therapies |
| Past Treatments | Assess prior responses | Reduces harmful reactions |
| Real-Time Health | Track ongoing conditions | Enables adaptive care plans |
Always-On Digital Health Support
Round-the-clock digital support is becoming standard as AI-powered assistants step in to provide immediate guidance.
In Mumbai, a hospital integrated its system with more than 200 lab instruments, cutting workflow errors by 40% while giving patients instant access to test reports. This shows how AI tools for doctors and patients alike can reduce delays, improve engagement, and maintain a higher level of continuous care.
Predictive Disease Prevention
Predictive analytics is giving healthcare providers the ability to detect risks earlier and intervene before symptoms appear. Siemens Healthineers, for example, introduced the Atellica® COVID-19 Severity Algorithm, which drew on data from more than 14,500 patients to forecast disease progression and complications.
As researcher Slavé Petrovski explained, many illnesses are already well advanced by the time they show visible signs.
With AI, it is possible to identify early biological signatures that point to conditions such as Alzheimer’s, COPD, or kidney disease long before they become critical. This demonstrates the growing value of medical AI tools in preventive care and long-term health management.
Automating Office And Admin Tasks
Routine administrative work is also being transformed by artificial intelligence. At Johns Hopkins Hospital, collaboration with Microsoft Azure AI has automated documentation, lab operations, and workflow processes.
These changes not only improve daily efficiency but have also contributed to savings estimated between $200 and $360 billion across the healthcare sector. A recent survey further showed that 89% of lab professionals see automation as vital to handling increased demand during staffing shortages.
These cases highlight how AI tools in healthcare are modernizing both clinical and operational tasks, paving the way for faster, safer, and more effective care delivery.
Results Of AI Tools In Healthcare So Far
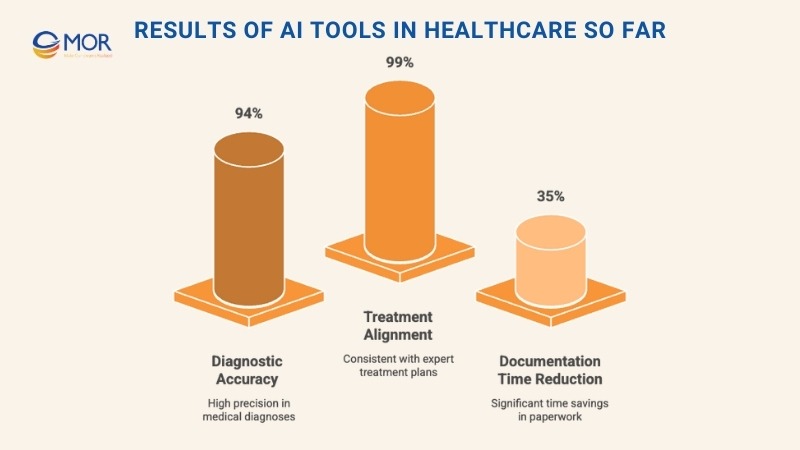
Evaluating the performance of AI tools in healthcare reveals both strong achievements and areas that still need improvement across different use cases:
Use Case | Success Metrics | Key Limitations | ROI Impact |
Medical Diagnosis | 94% accuracy in lung nodule detection, 90% sensitivity in breast cancer screening | Requires physician oversight for complex cases | Cuts diagnostic errors from a 5% baseline |
Personalized Treatment | Matches expert recommendations in 99% of scenarios | Faces integration and data security hurdles | Reduces operational costs by up to 30% |
Digital Health Support | Delivers real-time, 24/7 patient assistance | Limited ability to address nuanced clinical issues | Expands continuous access to care |
Preventive Analytics | Predicts risks across multiple chronic conditions | Dependent on data quality and availability | Lowers expenses with earlier interventions |
Administrative Automation | Cuts documentation time by 35% | Requires significant staff adaptation | Saves 66 minutes daily per provider; $200–360B potential savings |
These findings show why AI tools used in healthcare continue to gain ground. Institutions like Massachusetts General Hospital and diagnostic centers in Mumbai report shorter workflows and better outcomes. In one case, documentation time dropped by 41% through automation, while ambient voice capture cut record-keeping from two hours to just 15 minutes.
“Integration of AI into health care holds great promise as a tool to help medical professionals diagnose patients faster, allowing them to start treatment sooner. However, AI is not advanced enough yet to replace human experience, which is crucial for accurate diagnosis.”
– Stephen Sherry, Ph.D., NLM Acting Director
“Orchestration is the invisible conductor of healthcare AI, harmonizing complex workflows, integrating disparate systems and ensuring that generative AI technologies work in concert to deliver seamless, intelligent patient care.”
– Mike Thorpe, Senior Solutions Consultant, SS&C Blue Prism
The lesson is clear: AI delivers the most value when paired with human expertise. Algorithms may outperform physicians in closed-book diagnostic tests, yet clinicians excel when dealing with nuanced or complex cases. Success depends on reliable data and smooth system integration.
A strong example is the Mumbai diagnostic chain that adopted Scispot to enhance workflow efficiency and boost patient satisfaction. This blend of automation and human oversight defines how AI driven healthcare continues to evolve in 2026.
Next Steps For AI In Healthcare
The future of AI tools in healthcare depends on how well providers build on today’s progress. The next steps focus on patient care, workforce skills, and new innovations.
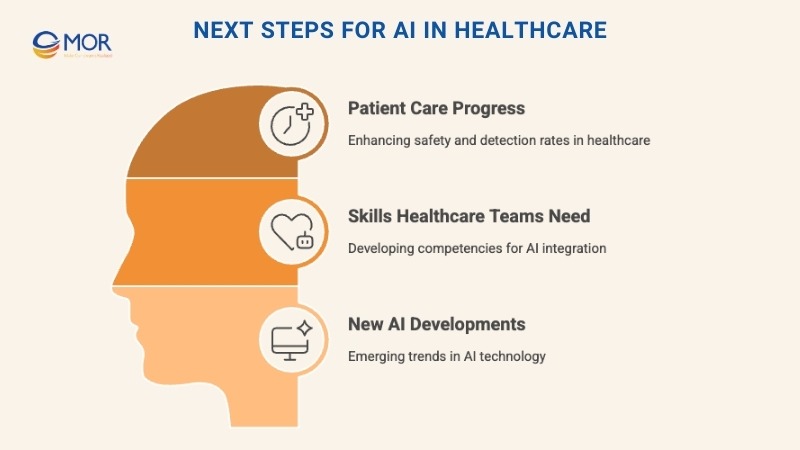
Patient Care Progress
At Mount Sinai, the deployment of an AI-powered ICU system has already shown measurable improvements in patient safety. Nurses now receive timely alerts about risks such as malnutrition, sudden deterioration, and falls, while the number of false alarms has decreased.
A 2023 study in European Radiology found that similar systems in Norway detected 93% of screen-identified cancers and 40% of interval cancers. These results prove how AI tools in healthcare can enhance outcomes, though tracking quality metrics is still resource-intensive.
In one case, monitoring required more than 108,000 person-hours and nearly $5.6 million in combined staffing and vendor costs, highlighting the need for sustainable models moving forward.
Skills Healthcare Teams Need For AI
As adoption grows, medical professionals must adapt by gaining skills that align with AI services in healthcare. Research points to several priority areas:
Competency Area | Importance | Key Focus Points |
AI Fundamentals | 86% of studies | Core concepts and clinical applications |
Ethics and Legal | 71% of studies | Responsible use and regulatory compliance |
Data Management | 43% of studies | Proper analysis and interpretation |
Communication | 43% of studies | Patient engagement and cross-team collaboration |
AI Tool Evaluation | 43% of studies | Assessing system accuracy and reliability |
“Future-proofing your career means embracing the transformative power of AI… You can remain at the forefront of this exciting field by continuously learning, practicing, and strategically integrating AI into your professional life.”
– Mobeen Lalani, Senior Analyst, Technology and Venture Development, Toronto Innovation Acceleration Partners
Ways to strengthen these skills include obtaining certifications such as CPHIMS®, joining programs dedicated to healthcare AI, participating in hackathons or pilot projects, keeping up with resources like Health IT Analytics, and attending large-scale events such as the HIMSS Global Health Conference.
With AI software for healthcare becoming a standard across hospitals and clinics, building these competencies is essential for professionals who want to thrive as the field advances.
New AI Developments On The Horizon
Emerging innovations show how AI tools in healthcare will continue to redefine patient care in the coming years. Dennis Chornenky, Chief AI Adviser at UC Davis Health, pointed to the next wave of progress:
“I’m focused on three key trends. First, the advent of autonomous AI, particularly AI agents. These are more advanced than generative AI, leveraging large language models to integrate multimodal data inputs, images, sound, labs, and generate outputs like patient histories, summaries, projections, or even presentations sent to specialists.”
Dr. Danielle Walsh of the University of Kentucky College of Medicine also emphasized the shift in physician responsibilities:
“By allowing AI to take over many of the repetitive and rote administrative tasks that burden physicians, the physician can perform more cognitive decision-making and focus more on human connections and time spent with patients.”
Some of the newest directions in AI tools used in healthcare include:
- Autonomous AI agents that support comprehensive patient care
- Systems integrating multimodal inputs, from imaging and lab results to audio records
- Improved platforms for continuous monitoring and patient communication
- Automation that reduces administrative load on clinical teams
- Smarter decision-support applications to assist with complex cases
These advancements highlight how AI driven healthcare solutions will expand physicians’ capabilities while reducing strain. As Dr. Thomas Fuchs of Mount Sinai’s Icahn School of Medicine explains:
“AI should help physicians to be faster and more effective, do new things they currently cannot do and reduce burnout.”
Which AI Tools In Healthcare Will Enterprises Adopt In 2026?
Healthcare leaders are prioritizing AI tools in healthcare that deliver measurable results, whether by improving clinician satisfaction, cutting costs, streamlining operations, or raising the standard of patient care. Several solutions are already showing strong adoption.
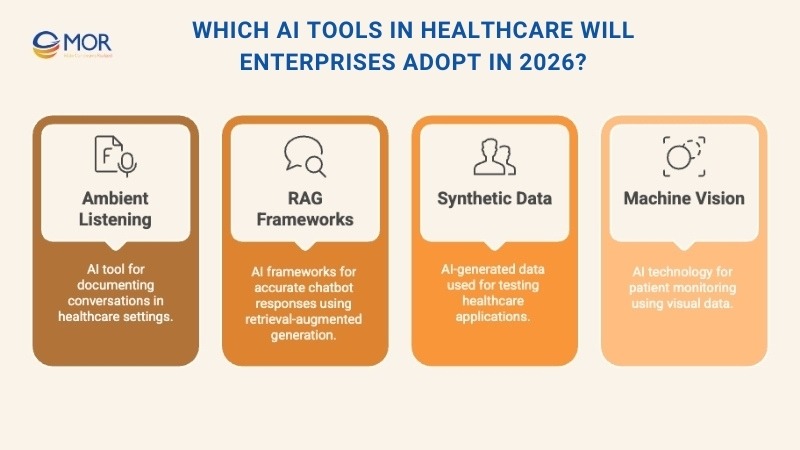
Ambient Listening For Documentation
One area gaining momentum is ambient listening, an audio-based technology powered by machine learning. Initially used by physicians and now expanding to nurses, these systems analyze patient-provider conversations in real time.
They automatically extract relevant details for clinical notes, billing, and coding, allowing staff to focus on direct interaction rather than juggling documentation tasks.
Many organizations view this technology as a natural entry point into AI because it demonstrates clear ROI. Hospitals adopting ambient listening report better clinical efficiency and lower burnout rates.
At the same time, the perceived risk has declined compared to earlier years. Today, it is often grouped with other low-barrier applications like chart summarization, making it a practical choice for enterprises beginning their AI tools in healthcare industry journey.
Ensuring Accuracy And Transparency In Generative AI
Healthcare organizations are beginning to test retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), a framework that combines vector databases with large language models. The approach allows chatbots to provide answers that are not only conversational but also grounded in up-to-date internal data.
For staff, this means more reliable responses in Q&A applications and fewer errors that can come from relying on general generative systems.
Another trend is the use of synthetic data for AI testing and validation. Because gathering quality datasets is often a challenge, synthetic data provides a safer way to refine models before they are deployed in clinical environments. At the same time, scrutiny around performance claims is growing.
Healthcare leaders want clear proof that systems deliver what they promise, and groups like the Coalition for Health AI are creating standards to guide evaluation. These steps reflect a stronger push toward building generative AI tools with built-in compliance features for healthcare enterprises, ensuring models meet both accuracy and transparency requirements.
Machine Vision Enhancing Patient Care
Adding cameras, sensors, and microphones in patient rooms is giving providers new ways to collect actionable information.
For instance, systems can detect when a patient changes position in bed and alert staff that manual intervention isn’t needed. Other sensors can flag when a patient tries to stand up, giving caregivers the chance to prevent a fall. These tools reduce risks while freeing staff to focus on more complex care needs.
As more Internet of Medical Things devices are deployed, machine vision is being combined with ambient listening to create smarter solutions. Together, these technologies allow hospitals to proactively manage patient safety and optimize workflows. With advances in AI tools in healthcare, clinical teams gain more visibility into real-time conditions, leading to better outcomes and more efficient care delivery.
Discover The Potential Of AI Tools In Healthcare With MOR Software
AI tools in healthcare are no longer just pilot experiments. Hospitals, clinics, and research centers are already using them for diagnosis support, predictive analytics, and patient management. The results are clear: better outcomes, greater efficiency, and lower costs. The real challenge for many organizations is figuring out how to safely integrate these tools into existing systems without disrupting daily operations.
MOR Software, with offices in Vietnam, Japan, Korea, and Singapore, has earned recognition through Sao Khue Awards and ISO 27001/9001 certifications. We design custom healthcare platforms powered by artificial intelligence, combining technical expertise with compliance-focused processes that meet global standards like HIPAA and GDPR.
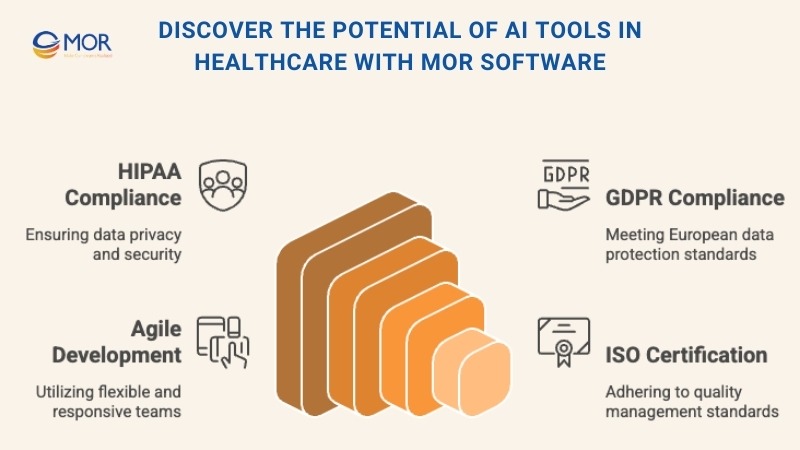
Our teams have helped providers modernize care through:
- Patient management systems that automate intake, scheduling, and follow-up.
- Imaging tools built on machine learning and computer vision to support diagnostics.
- Predictive analytics platforms that flag disease risks early and assist in treatment planning.
- Integration services that connect AI modules with EHRs, lab systems, and hospital management software.
With dedicated development teams working in agile sprints, we provide full transparency and deliver scalable AI solutions tailored to clinical needs.
AI adoption in healthcare is set to accelerate. Now is the time for providers to move from pilot projects to enterprise-grade deployments. With proven experience in software outsourcing and domain expertise, MOR Software helps turn potential into secure, production-ready applications.
Ready to explore how AI tools in healthcare can improve your operations? Contact MOR Software today to discuss your project.
Conclusion
AI tools in healthcare are proving their worth in diagnosis, treatment planning, monitoring, and administration. They bring faster decisions, safer outcomes, and reduced costs. For providers, the focus now is on scaling these tools responsibly and ensuring compliance with strict regulations. MOR Software, backed by ISO certifications and global expertise, delivers secure and tailored AI healthcare solutions. Contact MOR Software today to see how we can help you move from pilot projects to fully deployed, production-ready applications.
MOR SOFTWARE
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the best AI tool for healthcare?
Keragon is widely regarded as a top option. It is a HIPAA-compliant AI automation platform tailored for healthcare, helping organizations embed AI into both clinical and operational workflows while maintaining patient privacy and data security.
What is AI used for in the health care industry?
AI in healthcare is commonly applied to analyze patient data and medical records to identify health patterns and predict risks. This allows providers to deliver preventive care, improve treatment outcomes, and lower overall costs.
Is there a medical AI like ChatGPT?
Yes. Microsoft Azure Health Bot is one example. It serves as a healthcare-focused virtual assistant, capable of answering patient questions, performing symptom checks, and guiding users through health-related concerns.
Is there a medical GPT?
MedicalGPT is now used in telemedicine settings to provide quick, reliable medical advice. It helps reduce consultation time, supports patient education, and improves overall satisfaction with healthcare services.
How to incorporate AI in healthcare?
To safely integrate AI in healthcare, organizations need to start by mapping out their entire system. Understanding the data landscape and ethical considerations helps identify the right models, data sources, and processes for adoption.
When was AI first used in healthcare?
AI began appearing in healthcare during the 1970s. Early efforts focused on digitizing patient records and exploring ways to integrate computerized intelligence into medical decision-making.
Can AI fully replace doctors?
AI cannot replace doctors. It plays a supportive role in tasks like diagnosis, workflow automation, and treatment recommendations, but it lacks the empathy and nuanced judgment that physicians provide.
Is there a free AI tool for medical diagnosis?
Some basic AI-powered health check tools are available for free. However, most advanced AI diagnostic platforms require subscriptions or integration into healthcare systems.
Is AI more accurate than doctors?
AI has shown higher accuracy in some narrow diagnostic tasks, particularly in imaging. Still, it complements rather than replaces human expertise, as doctors bring broader medical judgment and context.
What is the future of AI in healthcare?
AI will expand its role in patient care, hospital operations, and research. Generative AI and automation are expected to improve efficiency, address labor shortages, and create scalable healthcare solutions in the years ahead.
Which is the first hospital to use AI?
Agent Hospital, developed at Tsinghua University in 2024, became the world’s first AI-powered hospital. It combines virtual AI agents with real-world clinical care and pilot testing.
Can AI do surgery?
AI-assisted robots are progressing toward autonomous surgical tasks. Recently, a robot successfully performed part of a gallbladder surgery without direct human control, responding to instructions like a trainee surgeon.
Did Bill Gates say AI will replace doctors?
Yes. Bill Gates stated that AI will significantly reduce the need for human roles in sectors like medicine and education within the next decade, predicting a shift in how these fields operate.
Rate this article
0
over 5.0 based on 0 reviews
Your rating on this news:
Name
*Email
*Write your comment
*Send your comment
1