Black Box Testing and White Box Testing: Complete 2026 Comparison
Choosing between black box testing and white box testing can get tricky, especially when speed, coverage, and code quality are all on the line. Many teams struggle to balance user-focused testing with deep technical checks. This MOR Software’s guide will break down the key differences, best use cases, and how to combine both methods for reliable, secure, and maintainable software in 2026.
Understanding Black Box Testing
To understand how black box testing and white box testing work together, it’s helpful to look at each on its own. We’ll start with how black box testing evaluates software from the outside.
What Is Black Box Testing?
Black box testing and white box testing are two core approaches in software quality assurance, and this method focuses strictly on what the system does, not how it does it.
In black box testing, testers examine the application’s outputs in response to different inputs, without ever looking at the source code or inner workings. It’s about checking behavior, usability, and results against the specs.
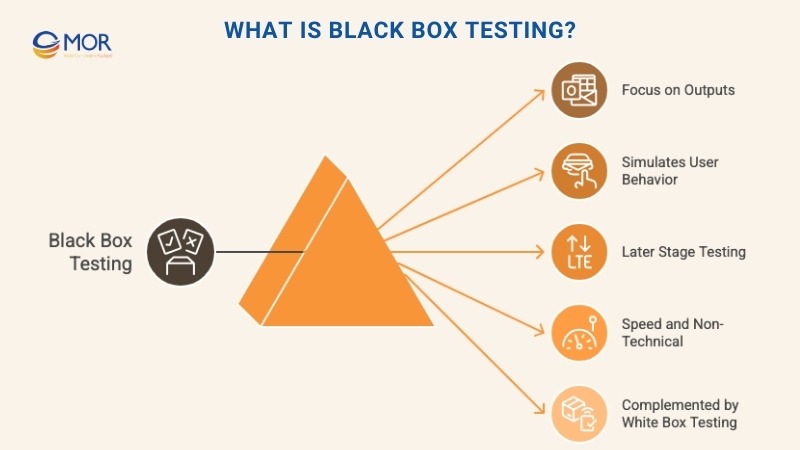
This type of testing is fast to apply, especially in later stages like user acceptance or beta phases. Since testers don’t need programming knowledge, it’s often used to simulate real-world user actions. But because it skips the internal structure, black box testing alone can miss logic flaws hidden deep in the code.
That’s why we usually pair it with white box testing to catch what one method might overlook. Together, they create a more balanced view of software performance and reliability, key if you're serious about shipping solid products.
To see where this fits, it helps to review the full software development lifecycle and how testing improves delivery at every stage.
Key Types Of Black Box Testing
Black box testing and white box testing cover different areas of software behavior, and when it comes to black box testing, there are several practical methods teams use to cover all angles:
- Functional testing: Checks the system’s response to specific inputs to confirm it works as expected. If users click a button or enter data, this test verifies that the output matches the intended behavior.
- Non-functional testing: Focuses on performance, load handling, and overall reliability under various conditions. It answers questions like: Is the app fast enough? Can it scale?
- Usability testing: Examines the interface and experience from a real user’s point of view. Testers look for easy navigation, intuitive design, and clear visual structure.
- Compatibility testing: Runs the software on different devices, browsers, operating systems, and networks to make sure it behaves consistently across environments.
- Exploratory testing: Testers try different flows and functions without following a script. This freeform method often reveals unexpected bugs.
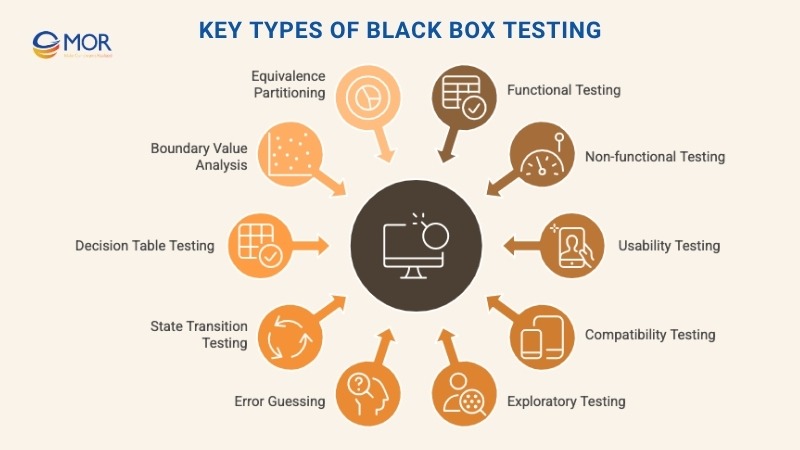
- Error guessing: Experienced testers use instinct and past knowledge to identify where things might go wrong, often catching issues early that aren’t covered by written test cases.
- State transition testing: Checks what happens when the system moves between different states, for instance, multiple failed login attempts or switching user modes.
- Decision table testing: Covers combinations of inputs and expected results. Testers map out rules and outcomes to make sure all paths behave correctly.
- Boundary value analysis (BVA): Looks at the edges, minimums, maximums, and limits. These are common places where bugs pop up.
- Equivalence partitioning: Groups similar inputs into classes. If one value works in a group, it’s assumed the others will too, which speeds up test coverage.
These types of black box and white box testing are often mixed in modern QA teams to widen coverage without duplicating effort. In real-world applications, black box test cases pass about 75% of the time, with the remaining 25% often uncovering functional or UI bugs, especially through boundary value and equivalence class testing.
Understanding White Box Testing
Now let’s shift to the other side of the equation. White box testing looks inside the code to catch what external tests might miss.
What Is White Box Testing?
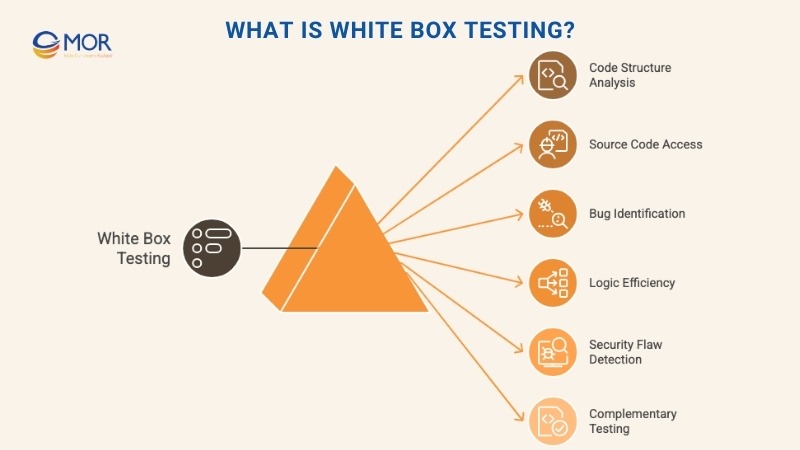
Unlike black box testing, white box testing dives straight into the code. Also known as clear or glass box testing, it focuses on how the software works internally. Testers examine logic, structure, loops, paths, and individual functions to verify whether everything runs correctly behind the scenes.
With white box testing, the goal is to track the full flow, from input to output, while checking how each line of code behaves. This helps uncover hidden bugs, logic flaws, or inefficient code that might slow performance or cause security gaps.
A comprehensive study found that combining white box techniques like unit testing and code reviews can lead to a defect detection rate of up to 90%, far surpassing black box-only approaches.
This approach takes more time and technical knowledge since testers need access to source code, design files, and architecture details. Still, the depth it provides is unmatched. You don’t just find issues, you gain a clear view of software health and can improve maintainability and security moving forward.
For that reason, pairing white box testing and black box testing often gives teams stronger confidence in overall software quality.
Key Types Of White Box Testing
To balance black box testing and white box testing, teams rely on specific techniques that look closely at code structure and logic. Here are the most common types of white box testing used in software projects:
- Loop testing: Examines each loop, whether it's a for, while, or nested loop, to make sure it starts, runs, and ends as expected under all valid and edge-case conditions.
- Mutation testing: Intentionally introduces slight changes in the code (mutations) to check if the current tests catch the errors. If they don’t, it’s a signal the test suite is missing something.
- Path testing: Covers every possible execution route in the application logic. This ensures no segment of code is skipped or left untested.
- Conditional testing: Focuses on logical if, else, and switch conditions, verifying each scenario to make sure outcomes are accurate and logical.
- Statement testing: Confirms that each individual line of code runs at least once. This type of testing helps surface unreachable or redundant code. Studies show that white box testing using statement and branch coverage can push overall code coverage above 85%, especially in CI/CD pipelines.
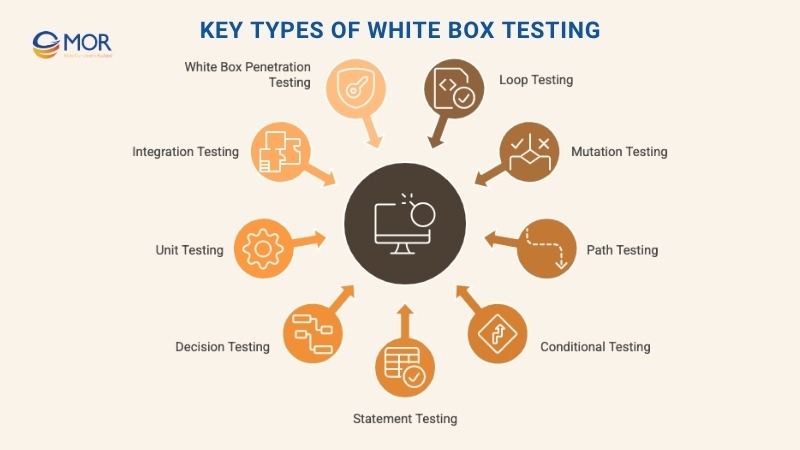
- Decision (branch) testing: Checks all possible branches in the code, whether decisions go left, right, or fail. Each outcome should behave correctly.
- Unit testing: Zeroes in on the smallest parts of the code, like functions or methods, to confirm they work properly on their own, with clear input and output.
- Integration testing: After unit testing, this step checks how different parts of the system interact. It validates that modules connect and communicate without issues.
- White box penetration testing: Simulates an internal attack using full access to the system. Testers use code, credentials, and architecture knowledge to probe for security flaws. Veracode reports that this method detects up to 80% of known vulnerabilities before deployment, making it a crucial layer in secure SDLC strategies.
These testing styles cover everything from simple statements to full system integrations. Used alongside blackbox vs whitebox strategies, they give developers the depth needed to release secure, well-performing apps.
Key Goal Differences In Black Box And White Box Testing
Understanding the goals behind each method helps clarify how they contribute to software quality. Below we’ll break down what black box testing and white box testing each aim to achieve.

Black Box Goals
The goals of black box testing revolve around how the software performs from a user’s perspective:
- Functionality: Confirm the software reacts correctly to user inputs and meets feature requirements.
- Usability: Evaluate how intuitive and user-friendly the interface is across key flows.
- Data handling: Verify that the application properly stores, processes, and retrieves data without errors or corruption.
- Performance analysis: Measure how the system holds up under load, including speed, stability, and resource usage.
- Error handling: Check the software’s ability to manage invalid inputs gracefully without breaking or freezing.
White Box Goals
Now compare that to white box testing, which has a different focus:
- Code coverage: Make sure every condition, loop, and path in the codebase gets tested at least once.
- Concurrency issues detection: Identify bugs caused by multi-threading or parallel execution, especially where data might get overwritten or delayed.
- Logic verification: Review the flow of logic inside the code to spot missteps or bad decisions that might cause failures.
- Vulnerabilities detection: Dig into the system to uncover security risks that could lead to exploits or unauthorized access.
- Integration verification: Test how different code modules connect and exchange data to confirm everything flows as designed.
- Boundary testing: Assess how code reacts near edge-case inputs, using values just below, at, or above the expected range.
This breakdown of white box testing vs blackbox testing shows how the two testing types target different risks. Using both methods together builds a safer, more resilient product.
Category | Black Box Testing | White Box Testing |
Focus | External behavior and outputs | Internal logic, structure, and code execution |
Functionality Goal | Confirm the app works as intended from a user’s point of view | Ensure each line of code behaves as expected |
User Experience | Validate UI flow, navigation, and overall usability | Not a priority; doesn't test user-facing elements |
Data Handling | Check data input/output for accuracy and reliability | Analyze how data flows through code paths |
Performance Check | Test speed, load, and stability under different conditions | Less commonly used for performance unless tied to code efficiency |
Error Detection | Spot crashes or bugs triggered by invalid inputs | Uncover logic flaws, unreachable code, and missed branches |
Security Testing | Limited visibility into security flaws | Deep scan for vulnerabilities and unsafe coding practices |
Integration Testing | Tests the app as a whole or with external systems | Validates internal module connections and API calls |
Edge Case Coverage | Often misses logic hidden deep in code | Performs boundary testing for extreme or edge input values |
Code Coverage | Unknown, since code is not reviewed | High, tests all logical paths, decisions, and conditions |
Pros And Cons Of Black Box Testing And White Box Testing
Choosing between black box testing and white box testing depends on the project’s goals, budget, and development phase. Each method brings its own set of strengths and tradeoffs that can affect speed, coverage, and accuracy.
Strengths Of Black Box Testing
Why teams often lean on black box testing:
- Works across any application: Testers don’t need to see the code. That means it works whether the app is built in Python, Java, or a mix of stacks. It’s perfect for testing systems with complicated backends or multiple services.
- Improves user experience: Since testers act like real users, this method catches bugs that break flows, confuse people, or create friction. It helps teams spot UX issues before users do.
- Less bias from developers: Because testers focus on what the software does, not how it’s written, they’re less likely to overlook errors due to assumptions about the code. It brings a fresh, outsider perspective to QA.
- Affordable and fast to run: No deep technical skills needed. Black box testing is often faster and cheaper, especially when doing acceptance or system-level tests. That’s useful for teams working under tight budgets or short deadlines.
These strengths show why white and black box testing both have a place in balanced test strategies. Up next, where black box testing can fall short.
Limitations Of Black Box Testing
While black box testing and white box testing complement each other well, black box testing has its weak spots:
- Misses parts of the code: Because testers don’t look at the source code, some logic paths or functions may never get tested. That leaves gaps where bugs can hide undetected.
- Test design can be hit or miss: Without knowing the system’s internal flow, testers often guess which inputs might cause issues. This can lead to duplicate, shallow, or incomplete test cases.
- Harder to trace bugs: When a test fails, figuring out why can be tricky without access to the code. That slows down bug fixes and might lead to miscommunication between testers and developers.
This is where black and white box testing together makes a stronger combo, black box spots surface issues, white box helps track them down.
Pros and Cons of Black Box Testing
Pros | Cons |
Works on any application without needing code access | Limited visibility into internal logic and code coverage |
Mimics real-world user behavior, improving UX testing | Test case design often relies on guesswork |
Reduces tester bias by separating development and testing | Difficult to trace the root cause of bugs without seeing the code |
Faster and more affordable, no need for technical knowledge | Some logic paths may never be tested |
Easy to scale across versions and platforms | Cannot detect internal security vulnerabilities |
Strengths Of White Box Testing
Teams turn to white box testing when they need deeper control and visibility. Its benefits often outweigh the effort, especially in projects that demand high reliability.
- Full code visibility: With access to every line, testers can create detailed tests that cover all branches, loops, and conditions. That kind of coverage means fewer bugs sneak through unnoticed.
- Finds hidden logic flaws: This method is great at catching bugs buried in complex code logic or overlooked edge cases. It also flags insecure or inefficient code that could affect performance or security.
- Supports long-term maintenance: By fixing code issues early, teams build cleaner, easier-to-manage applications. That lowers tech debt and smooths out future updates or feature changes.
- Fits well with automation: Many white box tests can be built into CI/CD pipelines. That means faster releases and fewer manual checks, especially useful in frequent-release cycles.
In short, white box and black box testing in software testing work better together, but white box shines when it comes to control, structure, and long-term code health.
Limitations Of White Box Testing
While white box testing delivers deep insights into code quality, it also comes with tradeoffs that can impact resources and release timelines:
- Needs technical experts: To do it right, testers must understand code, logic, data structures, and algorithms. That often means hiring senior-level engineers, which can push up testing costs.
- Doesn’t reflect user experience: Since this method focuses on what’s under the hood, it may miss issues in layout, navigation, or real-world use. Usability bugs can slip through unless paired with black box testing.
- Slower testing cycles: Analyzing code paths, writing detailed tests, and running them takes time, especially in complex systems. This can delay sprints or increase dev costs if not managed carefully.
This is why many QA teams blend white box and black box testing in software testing projects. Each fills the gaps the other leaves behind, giving you both code confidence and a better user experience.
Pros and Cons of White Box Testing
Pros | Cons |
Full access to code allows for thorough logic and path testing | Requires testers with strong programming and system design skills |
Finds hidden bugs, logic errors, and security flaws | Can be time-consuming, especially in large or complex systems |
Supports automation in CI/CD pipelines | May overlook usability or frontend issues |
Improves code quality and long-term maintainability | Higher cost due to the skill and time needed |
Helps ensure secure, efficient internal architecture | Less effective at simulating real-world user behavior |
Who Handles Black Box Testing And White Box Testing Tasks?
Different testing types call for different skill sets. When it comes to black box testing and white box testing, the roles vary depending on access to code and the focus of the testing.

Black Box Testers
Black box testing is usually carried out by:
- QA testers: These professionals test based on specs and user stories. They focus on functionality, usability, and how well the software meets requirements.
- Domain experts or analysts: People who understand the business logic behind the app. They validate whether the software behaves correctly in real-world use cases.
- Beta users: Real users brought in during pre-release phases. Their feedback helps catch usability issues and unexpected behavior before launch.
White Box Testers
White box testing, on the other hand, is handled by:
- Developers: Since they write the code, they’re well-equipped to test it. Developers often write unit tests and help cover core logic paths.
- Technical testers: These are QA engineers with coding skills. They know how to write test scripts, inspect logic, and evaluate internal systems.
- Security engineers: They dig deep into code to perform security audits and simulate attacks, helping teams uncover vulnerabilities before bad actors do.
When blended together, white box and black box testing in software testing provide full-spectrum coverage, technical depth from inside the code and real-world reliability from the outside.
Skill Requirements For Black Box Testing Vs White Box Testing
The expertise needed for black box testing and white box testing is quite different.
Black box testing relies more on understanding how the software should behave. Testers need to know the product’s requirements, expected outputs, and user flows, but not how the code is written. It’s ideal for those with strong analytical thinking and a user-first mindset, even if they don’t have a programming background.
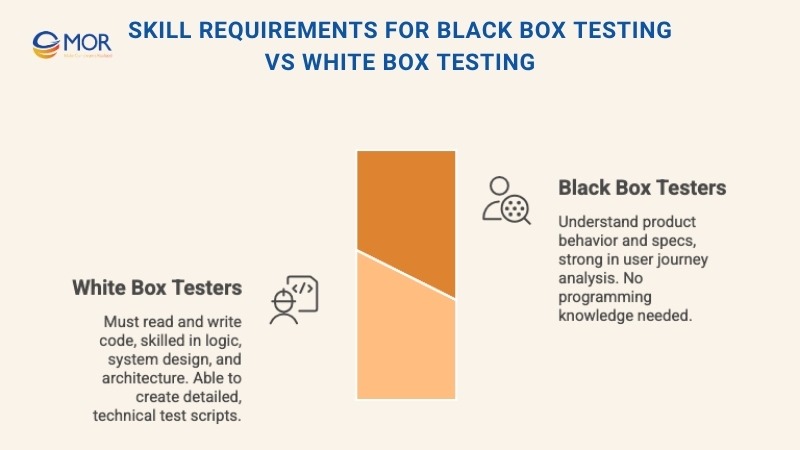
White box testing, by contrast, demands solid coding skills. Testers must be able to read and understand code, follow complex logic, and work with algorithms and system architecture. This kind of testing is better suited for engineers who can write scripts, evaluate logic paths, and dive deep into the technical details.
That contrast in skillset is what makes black vs white box testing a good pairing, one checks how things work for users, the other ensures the code behind it all holds up.
Choosing Between Black Box Testing And White Box Testing
Every project has its own goals, risks, and pace. That’s why black box testing and white box testing each fit different moments in the development cycle. Picking the right one depends on what you’re testing and when.
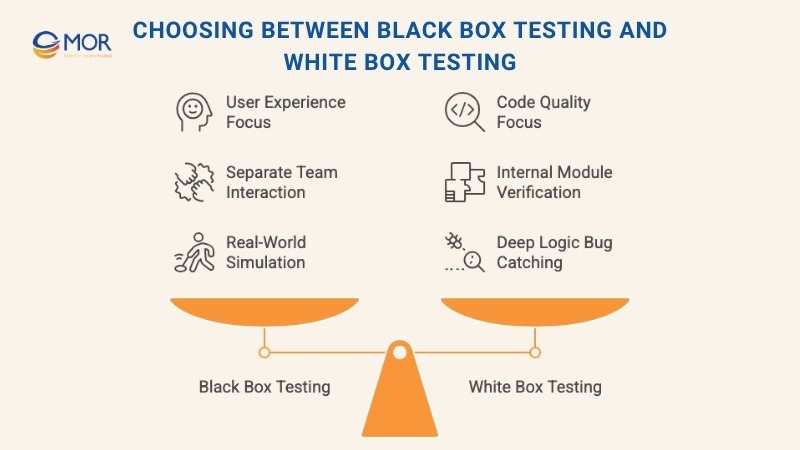
When Black Box Testing Works Best
Use black box testing in situations like these:
- When functionality and UX matter most: If your priority is how the app feels and functions for users, black box testing is the go-to. It helps spot broken flows, confusing layouts, or missing features from a user’s lens.
- When testers and developers work separately: This method keeps testing independent. QA teams don’t need to see the code, so they can test without influence or assumptions.
- When software evolves through multiple releases: Black box testing scales well. It’s easy to apply across new builds and versions to make sure each update still works as expected.
- When tests should reflect real-world behavior: This type of testing mimics how customers actually use the product. It reveals issues you’d miss by only focusing on code.
These scenarios highlight where white box testing and black box testing each shine, and why many teams choose to mix both for broader coverage.
When White Box Testing Is A Better Fit
White box testing plays a key role in high-stakes or technically complex builds. It’s the better option when:
- Code quality needs to be airtight: If long-term maintainability and clean code are top priorities, white box testing helps spot weak logic, hidden bugs, or bloated functions early.
- You’re working with heavy logic or security layers: Apps built around complex algorithms, sensitive data, or custom security protocols benefit from internal code inspection. White box tests can validate each step and catch edge-case failures.
- You need to uncover deep logic flaws or vulnerabilities: This testing method goes straight into the source. It’s ideal for finding problems that surface only through direct inspection, things black box testing might miss.
- APIs or modules must connect flawlessly: When your software integrates with other systems, internal testing ensures that data flows, authentication, and connections hold up under pressure.
For any project involving tight integrations or critical performance, mixing white box and black box testing in software testing helps cover all bases, from user flow to backend logic.
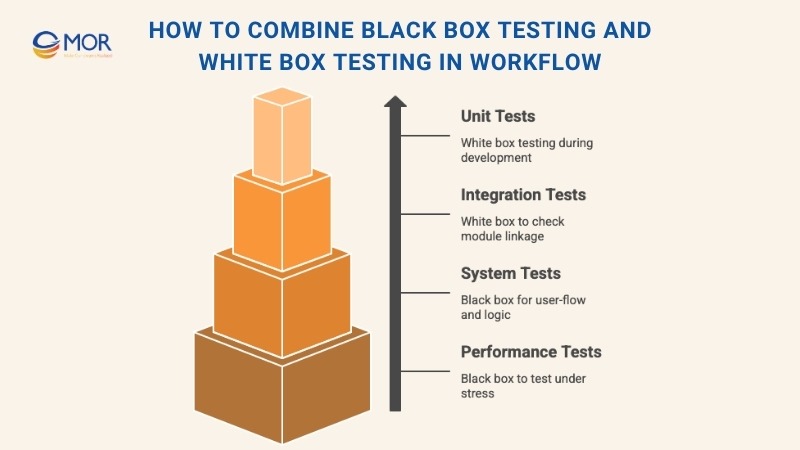
How To Combine Black Box Testing And White Box Testing In Workflow
The best QA strategies don’t choose between black box testing and white box testing, they use both. When combined, these two methods cover gaps the other might leave behind. That’s how teams ship software that’s functional, user-friendly, secure, and stable.
Start by mapping testing activities across different phases:
- Unit testing (white box): Developers run this during coding to check each function or module individually. It helps catch logic errors and bad code early.
- Integration testing (white box): Verifies that connected components work well together. It uncovers data mismatches and communication issues between modules.
- System testing (black box): Focuses on the full app from a user’s view. This is where you check end-to-end workflows, business rules, and visual interactions.
- Performance testing (often black box): Assesses speed, load handling, and reliability under different usage conditions.
A smart sequence is to apply black box testing during early functional checks, then layer in white box testing for technical deep-dives. This staggered model ensures both frontend behavior and backend logic are validated without delay.
Blending black box and white box testing in software testing creates stronger coverage and helps deliver better results, fewer bugs in production, smoother updates, and happier users.
How MOR Software Supports Secure and Reliable Testing
At MOR Software, we build QA and testing services into every stage of software development. From manual and automated test scripts to performance checks and security assessments, our solutions are tailored to your project’s scope and stack.
We apply Agile practices, offer full-cycle testing, and support both black box testing and white box testing strategies. Whether you need to validate functionality, verify internal code, or scale across platforms, we help teams catch bugs early and deploy with confidence.
We also provide ongoing support, documentation, and team training to ensure testing is consistent, effective, and easy to maintain. See our full QA & Testing capabilities.
Conclusion
Both black box testing and white box testing play a crucial role in delivering high-quality software. One focuses on user experience, the other digs into code integrity. You don’t need to choose one over the other, most successful teams combine them to cover more ground, catch more issues, and ship better products faster.
At MOR Software, we apply both methods across projects to make sure what we build works smoothly on the surface and runs cleanly under the hood. Want to strengthen your testing strategy? Contact us to get started.
MOR SOFTWARE
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What does black box testing mean in software development?
Black box testing checks how software behaves from the outside, without digging into its source code. Testers focus on what happens when specific inputs are given and whether the output matches expectations.
How is white box testing different from black box testing?
White box testing looks inside the software. Testers analyze code, logic, and internal processes to build test cases that cover all paths. This helps uncover hidden bugs and improve code structure.
When is black box testing most useful?
Use black box testing when you care most about how the app functions for users. It’s especially helpful for complex apps or when different teams handle development and testing. It also supports quick checks between releases.
Why combine black box and white box testing?
Blending both black box vs white box testing gives you full coverage. Black box testing catches user-facing issues, while white box testing finds code-level problems. Together, they build a better, more reliable product.
How can an AI-driven platform like Harness support testing?
Harness speeds up testing by using AI to manage service levels, automate security checks, and sync workflows. It helps teams test smarter, fix issues faster, and ship with confidence.
What makes white box testing valuable for code quality?
White box testing helps spot logic flaws, security gaps, and unused code early on. It keeps your code clean, reduces bugs, and supports long-term stability.
Rate this article
0
over 5.0 based on 0 reviews
Your rating on this news:
Name
*Email
*Write your comment
*Send your comment
1