What is a Framework in Software? Definition & Examples
Understanding what is a framework in software can significantly enhance your development capabilities, allowing you to leverage existing solutions for common problems. This MOR Software's article delves into the definition, benefits, and examples of frameworks to give you a comprehensive understanding of their role in software development.
What Is A Programming Framework?
A programming framework is a set of pre-written code that provides a structured foundation for developing software applications.
It includes libraries, tools, and best practices that streamline the development process by offering reusable components.

Frameworks are designed to support the development of specific types of applications, such as web, mobile, or desktop apps, ensuring consistency and reducing redundancy in coding.
Some popular programming frameworks are Ruby on Rails, Angular, Laravel or Django.
>>> Let's take a look on topic on MOR Blog!
What Is Framework In Software?
A framework in software is an abstraction that provides a reusable structure for building applications. It acts as a template that includes predefined classes, methods, and tools to facilitate development.

Understanding what a framework in software is can significantly improve productivity, as it allows developers to focus on the unique aspects of their project while leveraging the generic functionality provided by the framework. This leads to more efficient, maintainable, and scalable software solutions.
>>> Will AI replace software developers or simply reshape how they work? If your team wants to build smart, future-ready products, contact MOR Software. We are ready to support your next project with the right expertise.
Why Should We Use Frameworks In Software Development?
Understanding what a framework in software is and how it benefits development projects is essential for modern software engineering. Here are top reasons why frameworks should be used in software development in every ICT companies:
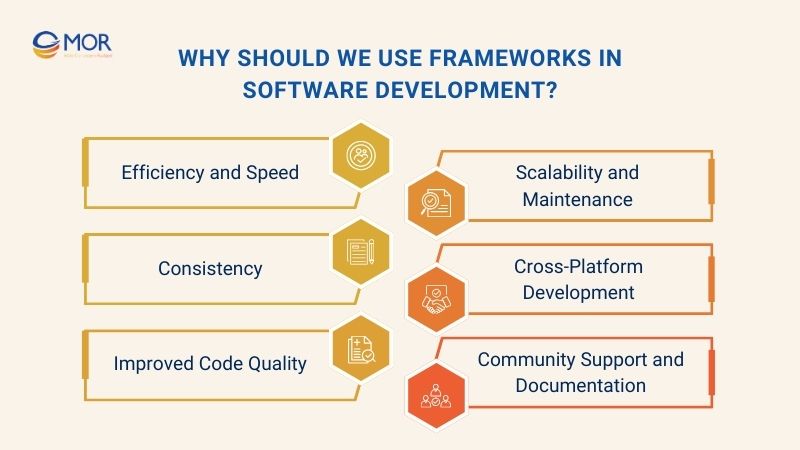
Efficiency and Speed
Frameworks significantly enhance efficiency and speed in software development by providing pre-built components and tools, allowing developers to focus on specific functionalities rather than reinventing the wheel.
For example, using frameworks like Django for Python or Laravel for PHP, developers can rapidly set up and deploy web applications, leveraging built-in features like authentication and database management to save considerable development time.
Consistency
Frameworks promote consistency across development projects by enforcing a standardized structure and coding conventions. This ensures that all team members adhere to the same guidelines, making the codebase uniform and easier to understand. For instance, frameworks like Angular and React enforce a component-based architecture, facilitating consistent and maintainable code throughout the project
Improved Code Quality
Frameworks contribute to improved code quality by providing best practices and design patterns that developers can follow. These frameworks include built-in functionalities for debugging and testing, which help in identifying and rectifying errors early in the development process.
For example, Spring Framework for Java includes comprehensive software testing tools that enhance the reliability and robustness of the final product.
Scalability and Maintenance
Frameworks support scalability and ease of maintenance by providing a modular architecture, which allows developers to add or modify features without disrupting the existing system. This is crucial for growing applications that require regular updates and enhancements.
Frameworks like Express for Node.js enable developers to create scalable server-side applications with minimal effort.
Cross-Platform Development
Frameworks facilitate cross-platform development, enabling developers to create applications that run seamlessly on various operating systems and devices.
For instance, React Native allows developers to build mobile applications for both iOS and Android using a single codebase, significantly reducing development time and resources.
Community Support and Documentation
Frameworks come with extensive community support and documentation, providing developers with valuable resources and guidance. This helps in resolving issues quickly and staying updated with the latest best practices.
Popular frameworks like Django, Laravel, and Angular have vibrant communities and comprehensive documentation, making it easier for developers to find solutions and improve their skills.
Types of Software Frameworks
Different types of software frameworks cater to various aspects of development, including front-end, back-end, and mobile frameworks. Below, we explore these categories and their examples in detail.
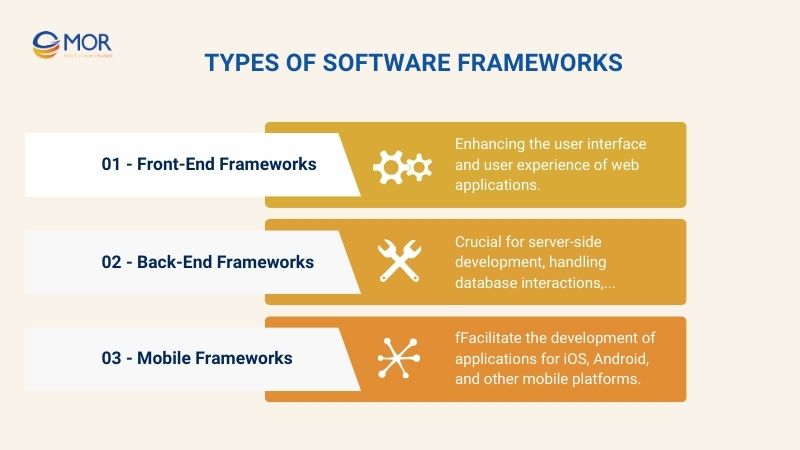
Front-End Frameworks
Front-end frameworks focus on enhancing the user interface and user experience of web applications. These frameworks provide pre-written code, tools, and libraries to simplify the development process.
Notable examples include React, Angular, and Vue.js. React, developed by Facebook, allows developers to build interactive UIs efficiently.
These front-end frameworks help developers create responsive, high-performing web applications by providing reusable components and robust tools.
Back-End Frameworks
Back-end frameworks are crucial for server-side development, handling database interactions, user authentication, and business logic.
Popular back-end frameworks include Django, Ruby on Rails, and Express.js. Django, a high-level python framework for web development, is renowned for its "batteries-included" approach, providing numerous built-in features.
These back-end frameworks streamline server-side development, ensuring efficient and scalable applications.
Mobile Frameworks
Mobile frameworks facilitate the development of applications for iOS, Android, and other mobile platforms.
Examples of popular mobile frameworks include React Native, Flutter, and Xamarin. React Native, developed by Facebook, allows developers to build cross-platform mobile apps using JavaScript.
These mobile frameworks help developers achieve high performance and native-like experiences while reducing development time and effort.
>>> Vietnam software outsourcing companies attract steady attention from teams that want strong delivery without extra layers of cost or confusion. Let's pick top IT outsourcing companies in Vietnam that match your goals and avoid slow, risky choices.
Popular Software Frameworks in 2026
In 2026, several frameworks have gained prominence due to their robust features and efficiency. Below are some of the most popular software frameworks used today.
React

React, developed by Facebook, remains one of the leading front-end frameworks. Known for its efficiency in building interactive user interfaces, React allows developers to create reusable UI components.
It is widely used for agile web development, particularly in creating single-page applications (SPAs).
Angular

Angular, maintained by Google, is a comprehensive front-end framework that provides a complete solution for building large-scale applications. Its two-way data binding and dependency injection features make it a powerful tool for developing dynamic web applications.
Angular is popular for enterprise-level projects due to its robust performance.
Django

Django is a high-level Python framework that promotes rapid development and clean, pragmatic design. It is renowned for its security features and scalability, making it ideal for back-end web development.
Django's "batteries-included" approach means it comes with a wide array of built-in functionalities.
Spring Boot

Spring Boot, part of the larger Spring framework, simplifies the development of production-ready applications in Java. It is known for its ability to create stand-alone, production-grade Spring-based applications with minimal configuration.
Spring Boot is particularly favored for building microservices.
Flutter

Flutter, developed by Google, is a UI toolkit for building natively compiled applications for mobile, web, and desktop from a single codebase.
Using the Dart programming language, Flutter offers a fast development process and expressive UI components, making it a popular choice for cross-platform mobile development.
Node.js

Node.js is a runtime environment that allows developers to execute JavaScript on the server side. Its non-blocking, event-driven architecture makes it suitable for developing scalable network applications.
Node.js is widely used for building fast and efficient back-end services, such as APIs for web and mobile applications.
How To Choose The Right Framework For Your Project?
Here are key steps to help you choose the best framework for your project.

Assessing Project Requirements
The first step in choosing a framework is to thoroughly assess your project requirements.
Identify the scope, goals, and specific needs of your project. Consider factors such as the type of application (web, mobile, or desktop), the expected load and performance requirements, and any specific functionalities you need.
For instance, if you're developing a high-performance web application, frameworks like React or Angular might be suitable due to their robust capabilities in handling complex user interfaces and real-time data updates.
On the other hand, for a mobile app, frameworks like Flutter or React Native offer cross-platform capabilities, reducing development time and costs.
Comparing Framework Features
Once you have a clear understanding of your project requirements, the next step is to compare the features of different frameworks.
Evaluate each framework based on its performance, scalability, ease of use, and community support.
For example, Django is known for its security features and scalability, making it ideal for large-scale web applications. Spring Boot simplifies the development of Java applications and is favored for creating microservices.
Additionally, consider the availability of documentation and community support. Frameworks with a strong community, like Node.js and Angular, provide extensive resources, tutorials, and plugins, which can significantly speed up development and problem-solving.
Key Differences Between Libraries and Frameworks
Libraries are collections of pre-written code that developers can call upon to perform specific tasks. They provide a set of functions or methods that can be used as needed, allowing for flexibility and ease of use.
Frameworks, on the other hand, offer a structured foundation for building applications. They provide a skeleton where the application defines the specifics, allowing developers to focus on the unique aspects of their project.
Here's a short comparison between libraries and frameworks:
Feature | Library | Framework |
Definition | Collection of pre-written code for specific tasks | Structured foundation for building applications |
Control | Developer calls the library | Framework calls the developer's code |
Flexibility | High flexibility and freedom | Enforces a specific structure |
Examples | jQuery, Math library | Angular, Django |
Usage | Used to perform specific functions | Provides the overall architecture |
Learning Curve | Generally easier to learn | Can be more complex to master |
Case Studies: Successful Projects Using Various Software Frameworks
PEOPLE - Human Resources Management Platform
About the project
PEOPLE is an intricate enterprise social network service tailored for internal business use, extensively trusted by numerous Japanese banks and corporations. It boasts over 30 modules, including employee management, internal communication networks, specific role assignments, and management by objectives.

How the Software Frameworks are used in this project
MOR Software leveraged several key software frameworks to ensure the PEOPLE platform met all performance and usability criteria as follow:
- CakePHP: This powerful PHP framework was utilized to manage the backend operations of the PEOPLE system. CakePHP facilitated rapid development and ensured that the system remained modular, scalable, and maintainable.
Its built-in features, such as ORM and scaffolding, enabled MOR Software to handle complex data interactions efficiently, essential for the extensive employee management modules required by CYDAS.
- VueJS: On the frontend, VueJS was employed to create a dynamic and responsive user interface. This progressive JavaScript framework allowed MOR Software to develop a seamless user experience, which is crucial for the internal communication and task management modules.
VueJS's reactivity system provided real-time updates and a highly interactive interface, enhancing user engagement and productivity.
Conclusion
Understanding what is a framework in software can greatly enhance your development process by providing a structured foundation and pre-built components. By leveraging frameworks, developers can focus on creating high-quality applications more efficiently. Choosing the right framework for your project is crucial for achieving optimal performance and scalability.
MOR SOFTWARE
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What does a framework mean in software development?
In software development, a framework is a structured set of tools and reusable components that helps developers build applications more efficiently. It provides ready-made resources such as APIs, libraries, debuggers, and compilers designed for a specific programming language, enabling faster development and smoother deployment.
What is a framework, and what are some examples?
A framework is a reusable software foundation—similar to a blueprint—that handles common development tasks so developers can focus on building unique features. Popular examples include Django (Python), Ruby on Rails (Ruby), Angular and React (JavaScript), Spring (Java), .NET (C#), and mobile frameworks like Flutter and React Native.
What is a simple framework?
A simple framework is a lightweight development tool designed to help build applications quickly without the complexity of large, enterprise-level systems. These frameworks focus on essential features, making them ideal for small projects or rapid prototyping.
What are some examples of software frameworks?
Well-known software frameworks include Laravel for PHP development, Oracle Application Development Framework, Cactus Framework for high-performance scientific computing, Pipedream for workflow automation, Php4Delphi, and OpenSilver for modernizing legacy Microsoft applications using WebAssembly.
Is Python a programming language or a framework?
Python is a high-level, general-purpose programming language. It is widely known for its readable syntax and versatility. Frameworks such as Django and Flask are built on top of Python but are not part of the language itself.
What are the main components of a framework?
A framework typically includes a core system that defines structure and rules, implementation layers that handle specific functionalities, and a profile or configuration layer that customizes behavior for different use cases.
What is the most widely used framework today?
As of recent global developer surveys, Node.js remains one of the most widely used frameworks, followed closely by React.js. Their popularity is driven by performance, scalability, and strong community support.
How can a framework be explained simply?
A framework can be explained as an organized system that defines how software components work together. It standardizes development practices by providing tools for coding, testing, and debugging, helping developers build reliable applications faster and more consistently.
Rate this article
0
over 5.0 based on 0 reviews
Your rating on this news:
Name
*Email
*Write your comment
*Send your comment
1