Conversational AI In Healthcare: Transforming The Future Of Care
In recent years, an increasing number of healthcare facilities have adopted automated systems to support consultations, send appointment reminders, and deliver test results. These are not just simple chatbots. They are part of a broader transformation driven by conversational AI in healthcare. This article explores its capabilities, challenges, and potential impact in depth.
What Is Conversational AI In Healthcare?
Conversational AI in healthcare refers to artificial intelligence systems specifically designed for the medical field, enabling natural interactions between humans and machines through spoken or written language. This technology includes chatbots, virtual assistants, automated response systems, etc.
In today’s healthcare environment, healthcare conversational AI plays a crucial role in enhancing communication between patients and healthcare providers. By offering instant responses, accurate information, and personalized guidance, conversational AI reduces the workload for medical staff while improving the patient experience.
Additionally, conversational AI integrates seamlessly with telehealth platforms and patient portals. This helps create a connected digital healthcare ecosystem that is more intelligent, accessible, and efficient than ever before.

What Is Conversational AI In Healthcare?
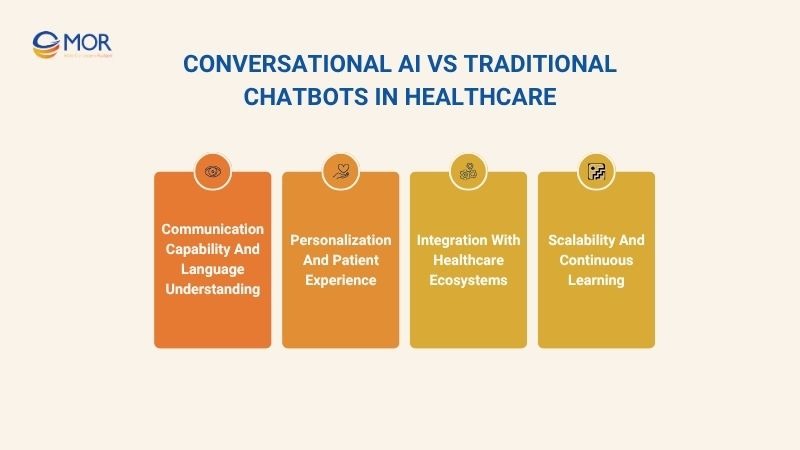
Conversational AI Vs Traditional Chatbots In Healthcare
Although traditional chatbots have played an important role in healthcare, the emergence of conversational AI in healthcare has marked a significant leap forward in patient experiences. So, what are the key differences between conventional chatbots and modern conversational AI?
Communication Capability And Language Understanding
Traditional chatbots rely on pre-programmed scripts and keyword matching. They are effective only when users follow a predefined set of commands. For example, if a patient types "Book appointment," the chatbot responds correctly. However, if the same intent is phrased differently, like "I’d like to see a doctor today," a traditional chatbot may fail to respond appropriately.
In contrast, conversational AI in healthcare leverages natural language processing (NLP) to understand user intent regardless of how the question is phrased. It can interpret incomplete, non-standard, or ambiguous input and respond contextually. For instance, if a patient says, “I’ve been coughing all day, should I see someone?”, a conversational AI system can identify the intent to seek care and recommend available specialists or next steps.
Personalization And Patient Experience
One of the limitations of traditional chatbots is their one-size-fits-all responses. These systems rely on fixed scripts and deliver the same information to every user, regardless of their unique health background.
But healthcare conversational AI can access patient health records and even data from wearable health devices to provide tailored responses.
Integration With Healthcare Ecosystems
Traditional chatbots often operate in silos and are limited to basic functions. They rarely integrate with electronic health records (EHRs), billing systems, or telehealth platforms, resulting in fragmented patient journeys.
In contrast, conversational AI technology in healthcare is built to integrate seamlessly with the broader digital ecosystem. It can sync with EHRs, retrieve lab results, process insurance details, and even support virtual care workflows.
Scalability And Continuous Learning
Traditional chatbots are difficult to scale. Expanding their functionality requires manual reprogramming, and performance often declines when handling high volumes of queries or new use cases.
Meanwhile, the conversational AI in the healthcare market is rapidly evolving, with platforms that support large-scale deployments and continuous learning from real-world interactions. These systems can identify emerging patterns in patient queries and improve accuracy over time without constant human intervention.
For example, when thousands of patients begin asking about a new flu outbreak, conversational AI for healthcare can quickly recognize the trend, update responses, and even alert healthcare providers to anticipate a surge in demand.
Conversational AI Vs Traditional Chatbots In Healthcare
Criteria | Traditional Chatbot | Conversational AI in Healthcare |
Data Security & Compliance | Basic security often lacks full HIPAA or GDPR compliance | Built-in encryption, compliant with HIPAA, GDPR, and industry standards |
Language Support | Limited to major languages, lacks nuance | Supports multiple languages with advanced natural language understanding |
Ease of Maintenance | Manual updates required, not scalable | Learns and improves continuously, easy to maintain and scale |
Deployment Time | Faster to deploy due to simplicity | Requires more time for integration with healthcare systems |
Cost of Implementation | Lower upfront cost, limited long-term ROI | Higher initial investment, better long-term efficiency, and ROI |
Response Style | Scripted, rigid, lacks contextual understanding | Dynamic, context-aware, tailored to individual patient data |
User Engagement | Low, users often drop off | High engagement, personalized interaction improve retention |
Overview Of The Conversational AI In Healthcare Market
The conversational AI in healthcare market is experiencing rapid growth. Currently valued at USD 13.53 billion in 2024, and projected to reach USD 48.87 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 23.84% from 2025 to 2030. This surge reflects rising global demand for AI-powered patient engagement and personalized digital healthcare experiences.
North America leads the adoption of healthcare conversational AI, driven by robust digital health infrastructure and favorable regulatory environments. However, Asia-Pacific (APAC) is emerging as the fastest-growing region, fueled by high population density. Meanwhile, Europe continues to expand AI implementation across national health systems, especially in countries like the UK, Germany, and France.
Key players shaping the space include Microsoft (Nuance), IBM Watson Health, and Google Health. Besides, it has fast-growing startups like Babylon Health, Ada Health, Infermedica, K Health, and Hyro.
For example, Microsoft’s acquisition of Nuance has enabled AI-based clinical documentation solutions now used in over 77% of U.S. hospitals

Overview Of The Conversational AI In Healthcare Market
Key Benefits Of Conversational AI In Healthcare
With the rapid rise of the AI era, more healthcare organizations are embracing this technology to improve care quality and streamline operations. Conversational AI enhances the patient experience and delivers significant benefits for healthcare providers. Below are the key advantages for both sides.
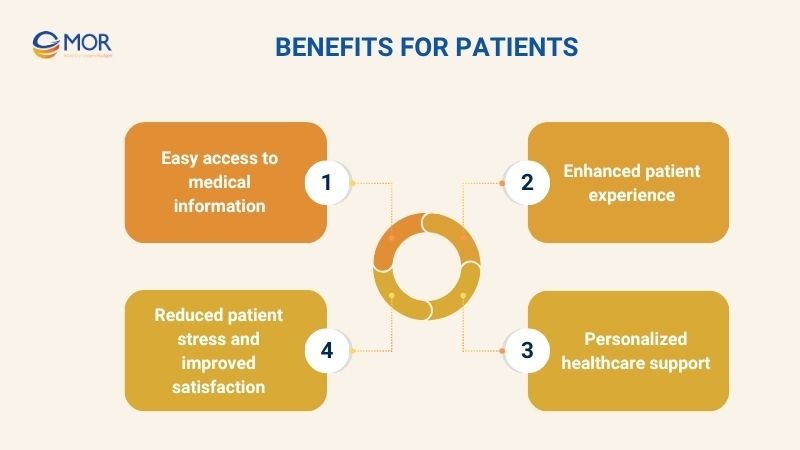
Benefits For Patients
For patients, conversational AI for healthcare is more than just a communication tool. It's a trusted companion throughout their healthcare journey. The following benefits highlight how this technology is improving access, personalization, and overall satisfaction.
Easy access to medical information
Accessing medical information is no longer limited to tech-savvy individuals or those living near healthcare facilities. Conversational AI empowers everyone, including elderly patients and people in remote areas easily retrieve accurate medical information through text or voice.
According to a report by Accenture, 40% of working hours in healthcare can be supported by conversational AI. These systems operate 24/7, instantly answering common queries about symptoms, prescriptions, vaccination schedules, and more.
Enhanced patient experience
When applying healthcare conversational AI, the patient journey becomes more streamlined and easier to follow. From the initial step of accessing information to scheduling appointments, completing medical forms, and navigating within healthcare facilities, everything is supported quickly and accurately by AI systems.
Previously, calling a call center often meant long wait times, busy lines, or being redirected to the wrong department. Now, conversational AI in healthcare provides near-instant responses at any time, without limitations on volume or hours. Patients receive consistent and complete guidance, reducing confusion and anxiety during their care process.
Personalized healthcare support
Healthcare conversational AI can access individual medical records and treatment history to provide highly personalized recommendations. Traditional chatbots often deliver generic responses without considering personal factors.
Example: When a patient asks, “What should I eat after surgery?”
- Traditional chatbot: “You should eat light, easy-to-digest food and drink plenty of water.”
- Healthcare conversational AI: “Based on your medical record, I see you have a history of diabetes. You should limit carbs and avoid high-glycemic foods. Let me suggest a diet plan tailored to your condition.”
Reduced patient stress and improved satisfaction
Beyond functional support, conversational AI in healthcare offers significant emotional value. In many cases, patients feel anxious due to complex procedures or long waiting times and because they feel unheard and neglected. A study involving 901 patients in Poland revealed that unfriendly attitudes from medical staff were the most influential factors contributing to patient dissatisfaction.
Healthcare conversational AI helps change that. These systems are always available, respond with patience, and put the patient at the center of the interaction. The feeling of having a constant “companion” gives patients a sense of support, control, and peace of mind throughout their care journey.
Benefits For Patients
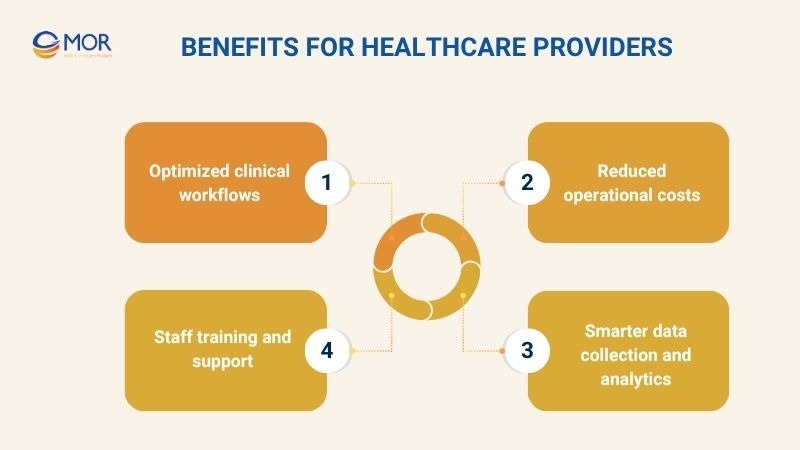
Benefits For Healthcare Providers
For medical centers, conversational AI in healthcare also acts as a powerful tool to improve operational efficiency and internal workflows. Here’s how it supports healthcare providers at scale.
Optimized clinical workflows
One of the most significant benefits of healthcare conversational AI is its ability to automate repetitive tasks in clinical workflows. Routine operations such as symptom collection, patient triage, and appointment reminders can be efficiently handled by AI workflow assistant healthcare tools.
For example, Omega Healthcare Management Services, a healthcare revenue cycle firm, leveraged AI tools to automate 60–70% of administrative tasks, including data collection, medical coding, and billing processes.
The results were substantial:
- Saved over 15,000 human work hours per month through automation
- Reduced document processing time by 40%
- Cut response time by 50%
Reduced operational costs
Conversational AI in healthcare reduces staffing costs and cuts expenses caused by human errors and delays. Instead of relying on a large number of call center agents or front-desk staff, AI systems can simultaneously handle hundreds of conversations with high accuracy.
Furthermore, a report by McKinsey and Harvard indicates that AI could help the U.S. healthcare system save 5 - 10% of total healthcare spending, equivalent to $200–360 billion annually.
Smarter data collection and analytics
Unlike traditional data collection methods, healthcare conversational AI captures patient interaction data in real time. The data gathered is comprehensive and standardized. It is making it easier to integrate into centralized healthcare management systems.
Staff training and support
Beyond serving patients, conversational AI in healthcare can also function as an internal learning platform. Instead of relying on costly, scheduled training sessions, medical staff can directly ask the AI system about clinical protocols, new regulations, or how to handle specific medical scenarios.
The AI can store a hospital’s internal knowledge base, regularly updated with guidelines from the Ministry of Health or international organizations.
Benefits For Healthcare Providers
Top 10 Use Cases Of Conversational AI In Healthcare
As digital transformation in healthcare accelerates, conversational AI in healthcare has moved beyond the pilot phase. Below are 10 standout use cases that demonstrate its growing impact across the healthcare ecosystem.
Automated appointment booking
Instead of waiting on hold with call centers, patients can now schedule medical appointments through conversational AI systems. This is one of the most widely adopted use cases of healthcare conversational AI, seen in both international and Vietnamese medical facilities.
These AI systems automatically handle rescheduling, cancellations, and real-time synchronization with doctors' calendars. As a result, administrative workload is reduced, human errors are minimized, and patients receive timely service from the right healthcare provider.
AI-powered symptom triage
When patients describe their symptoms, conversational AI systems use NLP to analyze input, assess severity, and recommend the appropriate next step. Unlike manual triage processes, AI ensures a standardized and consistent approach to initial symptom evaluation. This helps reduce unnecessary hospital visits and allows healthcare facilities to focus on truly urgent cases.
Example: If a patient says, “I feel tired and slightly short of breath after getting vaccinated.”
The AI will follow up with clarifying questions and cross-reference with clinical guidelines.
- If symptoms are within the expected post-vaccination range, the patient will be advised to rest at home.
- If red flags are detected, the system will suggest visiting a nearby clinic or hospital.
Medication and follow-up reminders
One of the leading causes of treatment failure is that patients forget to take their medication or miss follow-up appointments. Conversational AI in healthcare can proactively send reminders at the right time via text messages, apps, or voice calls.
For chronic patients such as those with diabetes or hypertension, the system can also monitor daily health indicators and issue alerts. A study by Labovitz on stroke patients using an AI-powered app showed that medication adherence increased by 67% in the group taking DOACs, confirmed through blood level testing.
Post-operative patient monitoring
After discharge, patients still require continuous monitoring to ensure proper recovery. Conversational AI in healthcare acts as a virtual nursing assistant, checking in with patients daily to track their condition and detect potential warning signs such as prolonged pain, swelling, or adverse drug reactions.
When abnormalities are identified, the system can trigger alerts to the assigned physician or automatically schedule an earlier follow-up appointment. This proactive monitoring reduces the risk of complications, a critical factor in controlling healthcare costs and improving care quality.
Nutrition and lifestyle consultation
Unlike printed materials or one-time advice, conversational AI in healthcare can deliver personalized lifestyle and nutrition guidance based on real-time data. These insights are gathered from electronic health records, wearable devices, and daily patient feedback.
For example, after colorectal surgery, the AI system can automatically adjust dietary recommendations if signs of constipation or dehydration are detected. If the patient is not physically active, the AI may suggest light exercises tailored to their current condition and recovery phase.
Patient feedback collection and data visualization
At every touchpoint in the healthcare journey, conversational AI systems can automatically prompt patients to provide feedback. These surveys are personalized based on the specific service received.
The data is then visualized on an analytics dashboard, segmented by:
- Department or unit
- Service type
- Satisfaction score
Example: If, over three days, 18 out of 100 patients report “long wait before seeing the doctor” in the Endocrinology Department, the AI system will automatically flag the issue, notify the head nurse, and suggest potential solutions.
Health insurance inquiry resolution
Instead of sifting through dense insurance documents or waiting in line at the insurance desk, patients can now simply ask an AI assistant: “Is my herniated disc surgery covered by health insurance?”
The AI system accesses the patient’s administrative data, then cross-references it with the procedure list reimbursed under the Circular or the applicable policy database.
It delivers a customized response based on individual conditions, such as:
- 80% of inpatient fees are covered at a provincial hospital
- High-end medical supplies like titanium implants are not included
- Referral documents required for full reimbursement
In addition to coverage details, the healthcare insurance chatbot can walk the patient through the payment and claim process, including:
- Required documentation
- Estimated approval timelines for co-existing commercial insurance
- Out-of-pocket costs
Inpatient coordination for complex hospitalized cases
For patients with multiple comorbidities requiring care from several departments (e.g., stroke combined with diabetes and kidney complications), conversational AI can act as the central coordinator:
- Aggregate treatment plans from Neurology, Endocrinology, and Nephrology departments
- Update medication schedules, nursing tasks, and special care routines
- Send alerts if there are overlapping injection times or missed lab tests
Workflow:
- The lead physician enters medical orders into the HIS system.
- AI reads and categorizes the treatment roadmap by department → flags conflicts or scheduling delays.
- Each day, the chatbot sends the treatment schedule to the patient or caregiver (e.g., 8:00 AM abdominal ultrasound, 10:00 AM blood draw, 3:00 PM nutrition consultation).
- If the patient shows abnormal signs (e.g., SpO₂ < 90%), AI will automatically suggest ICU transfer and send alerts to the on-duty physician.
Fast and secure lab result notifications
Traditionally, patients have to wait hours at the hospital for test results, wasting valuable time. Now, they can return home while the system continues to process their labs. Once diagnostic results are validated in the LIS system, conversational AI will:
- Send secure notifications to the patient via digital portals, using proper identity encryption
- Summarize results in plain language (e.g., “Your blood sugar level is higher than normal. This may be related to diabetes.”)
- Recommend next steps: for example, book an appointment with an endocrinologist
Mental health and wellness chatbots
People experiencing mental health issues often hesitate to open up to other humans due to stigma, fear of judgment. However, AI-assisted mental healthcare models trained under Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) frameworks can engage with patients daily to:
- Ask about their emotional state each day
- Guide breathing exercises, mindfulness practices, or positive thinking techniques
- Detect recurring behavioral patterns (e.g., social withdrawal, self-criticism...)
If the chatbot detects high-risk signals, such as keywords like “hopeless” or “don’t want to go on,” the system will automatically flag the case as urgent and ensure human intervention within 1–2 hours.
Top 10 Use Cases Of Conversational AI In Healthcare
Key Considerations Before Implementing Conversational AI In Healthcare
Before implementing conversational AI in healthcare, medical organizations must carefully evaluate several critical factors. Below are four key areas every hospital or clinic should assess before integrating conversational AI into their healthcare delivery.
Data privacy and compliance
In the healthcare sector, patient data is classified as highly sensitive (PHI). When conversational AI is integrated into tasks like virtual consultations, appointment scheduling, or medication reminders, the system inherently gains access to a patient’s medical records.
This elevated access makes data privacy and compliance a critical concern. In 2023, the largest ransomware attack on Change Healthcare exposed the personal data of approximately 190 million individuals, costing over $1.6 billion in recovery efforts.
To mitigate such threats, healthcare organizations must ensure their AI systems are fully compliant with regional health data protection frameworks such as HIPAA (USA), GDPR (EU), or Vietnam’s Decree 13/2023. This includes implementing end-to-end data encryption, maintaining controlled data storage, and guaranteeing patients the right to access, modify, or delete their data.
Ensuring accuracy and reliability
Unlike chatbots used in e-commerce or customer support, conversational AI in healthcare cannot operate in a fully autonomous way. Healthcare is a high-stakes domain where every decision can directly impact a patient’s life or safety.
Therefore, it’s essential to implement a “human-in-the-loop” model. AI supports early-stage interactions, but critical medical decisions are always reviewed and approved by qualified clinicians.
Case Example:
A patient interacts with an AI chatbot and describes: "I'm experiencing chest pain on the left side, shortness of breath, and fatigue. I also had a mild fever yesterday."
If the AI makes the decision independently, the system might interpret these symptoms as signs of a mild respiratory infection or flu, and recommend home monitoring or scheduling a routine check-up in the coming days.
If a human reviews the case, upon receiving the AI alert, a nurse or physician re-evaluates the symptoms. With clinical experience, they may recognize potential red flags for acute conditions such as a heart attack or pulmonary embolism, and immediately advise the patient to go to the emergency department for urgent care.
Language and contextual limitations
Real-world deployment in healthcare still faces significant challenges related to language and contextual understanding. One major issue is that patients rarely use precise medical terminology.
Instead, they often describe symptoms using everyday language, sometimes mixed with slang, regional dialects, or even misspellings. Without proper NLP training tailored to these nuances, AI systems can easily misinterpret or miss critical information.
Additionally, elderly patients or those with lower education levels may communicate in a roundabout way, lack clarity, or struggle to describe symptoms systematically.
For instance, in the Mekong Delta region of Vietnam, a patient might say:
“I’ve been feeling sore all over, kinda restless, and like I can’t catch my breath... maybe it’s just the weather acting up or I caught a draft or something.”
While an experienced physician may identify a serious issue, such as early signs of hypertension, respiratory distress, or even a post-vaccine reaction. A poorly trained AI healthcare chatbot could easily misclassify or overlook the symptoms entirely.
Upfront investment and training needs
Conversational AI in healthcare is not a plug-and-play solution. Successful implementation requires significant upfront investment. A fully functional system must be connected to the hospital's HIS (Hospital Information System) and synchronized with data from outpatient clinics, diagnostic departments, nursing records, and more.
The costs go beyond the AI software license. Organizations must also account for server infrastructure, data security, ongoing maintenance, and comprehensive training programs for staff. Ensuring proper adoption across administrative, clinical, and IT teams is critical to long-term success.
Key Considerations Before Implementing Conversational AI In Healthcare
In Conclusion
Conversational AI in healthcare enhances operational efficiency and contributes to more humane and inclusive healthcare services. When patients can access accurate information at the right time, care becomes more equitable. Considering implementing a healthcare chatbot or conversational AI system for your facility? Now is the time to take action. Don’t miss the opportunity to lead in the future of healthcare innovation!
Rate this article
0
over 5.0 based on 0 reviews
Your rating on this news:
Name
*Email
*Write your comment
*Send your comment
1