IoT Development Services: Powering Intelligent Connected Solution

IoT development services are no longer optional when systems need to scale, connect, and deliver real-time insight. Many teams struggle with fragmented devices, slow data flow, and solutions that never quite fit. This MOR Software’s guide breaks down how these services turn connected ideas into reliable, business-ready systems.
What Are IoT Development Services?
IoT development services describe specialized professional support for creating Internet of Things ecosystems. These systems consist of intelligent, connected device networks that gather data, share information, and trigger actions automatically.
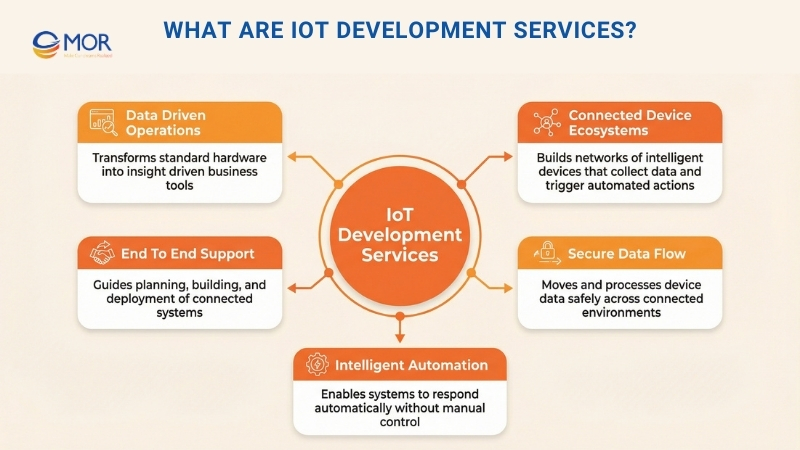
This type of custom IoT development services supports organizations as they plan, build, and deploy connected environments that link physical devices, move data securely, process insights, and support automation and remote control, allowing standard hardware to operate as intelligent, data-driven systems that strengthen daily operations and business decision making.
>>> The rise of connected devices pushes more businesses to look for IoT app development services that can solve real problems and support long term growth. Let's explore the top providers and find a partner that fits your goals.
Core Services Offered By IoT Development Services
At the foundation of IoT solution delivery is the combination of hardware components such as sensors and devices, software layers including applications and dashboards, and connectivity options like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, 5G, or LPWAN to support real-time interaction between systems and users.
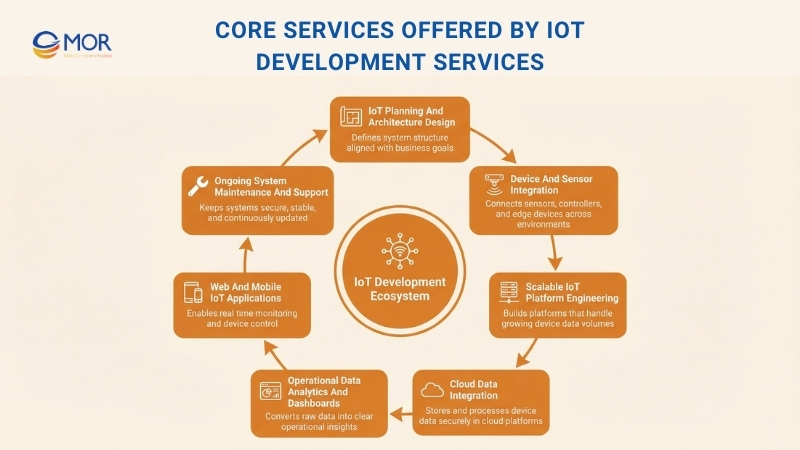
These services usually cover:
- IoT Planning and Architecture Design: Identifying business requirements and defining an appropriate IoT architecture that supports long-term goals.
- Device and Sensor Integration: Linking sensors, edge devices, and controllers that collect data and send it across connected environments.
- Scalable IoT Platform Engineering: Creating scalable platforms capable of processing large volumes of data generated by connected devices as part of broader IoT firmware development services.
- Cloud Data Integration: Managing secure storage and processing of device data through cloud platforms such as AWS IoT, Azure IoT Hub, or Google Cloud IoT.
- Operational Data Analytics and Dashboards: Converting raw device data into clear insights through dashboards, reports, and monitoring views.
- Web and Mobile IoT Applications: Delivering mobile and web applications that let users monitor, control, and review device activity in real time.
- Ongoing System Maintenance and Support: Keeping systems connected, secure, and updated through ongoing monitoring and technical support.
In short, these solutions help organizations bridge physical operations with digital systems. A manufacturer, for instance, can link factory equipment to an analytics platform that identifies early signs of failure, which helps lower downtime and control operational costs.
Key Benefits Of IoT Development Services For Businesses
The use of connected technology is no longer optional. It has become a strategic advantage that allows organizations to automate workflows, control spending, and deliver more intelligent customer interactions. Below are the main business benefits delivered through modern IoT development services, designed to support growth across industries.
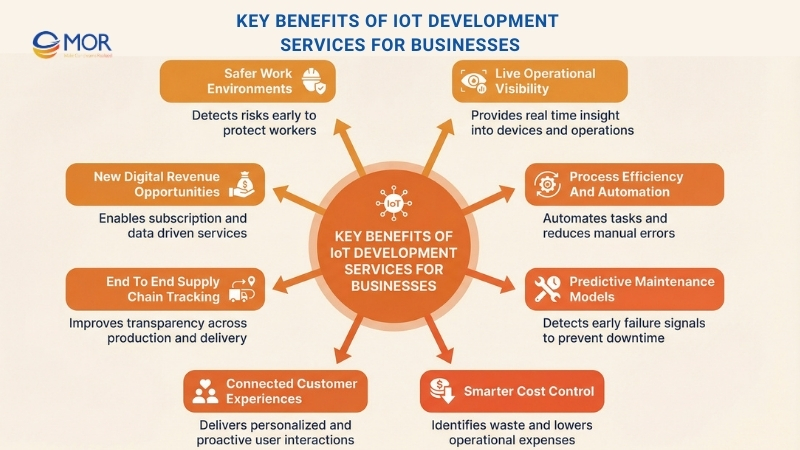
Live Operational Visibility
Connected systems continuously gather and share data from devices, sensors, and equipment, giving teams real-time visibility into daily operations. This level of awareness supports faster decisions, early issue detection, and quick responses when something goes wrong. These outcomes are often achieved through well-structured IoT development solutions that align data flow with operational needs.
Example: A logistics company can identify a vehicle failure instantly and redirect shipments without manual coordination.
Process Efficiency And Automation
Connected platforms automate routine tasks, lower the risk of manual mistakes, and improve how resources are used. In manufacturing environments, teams can automate inspections, track machine performance, and adjust production flows to raise output levels while reducing downtime.
Predictive Maintenance Models
Rather than reacting after a breakdown occurs, sensors monitor early warning signals and support predictive maintenance strategies. This approach helps limit unexpected failures, extend equipment lifespan, and reduce repair expenses.
Example: A power facility using connected monitoring can track turbine vibration and heat levels to identify faults before a shutdown happens.
Smarter Cost Control
Analytics from connected systems help uncover waste in energy use, staffing levels, and material consumption. When teams track performance in real time, they can cut unnecessary expenses and support long-term stability.
Example: Smart factories that rely on energy monitoring through connected platforms often lower electricity usage by 20 to 30 percent.
Connected Customer Experiences
Connected technology enables personalized, connected, and proactive services across customer touchpoints. Wearable fitness devices, for instance, send user data to mobile applications that suggest tailored workout routines or nutrition plans, often delivered through IoT mobile app development services. This ongoing interaction improves satisfaction and builds stronger loyalty over time.
End-To-End Supply Chain Tracking
Tracking tools powered by connected devices make every stage of production and delivery visible in real time. This level of insight helps reduce delays, limit losses, and strengthen responsibility across supply chain operations.
New Digital Revenue Opportunities
Connected systems support data-driven business models, including subscription monitoring services and digitally enabled products that extend value beyond the initial sale.
Example: Automotive brands now provide connected vehicle services that generate recurring income in addition to traditional car sales.
Safer Work Environments
Connected devices monitor surroundings, identify risks, and send alerts to teams immediately. In factories, smart helmets or environmental sensors can detect gas leaks or extreme temperatures, which helps protect workers and reduce safety incidents.
Step-By-Step IoT Development Services Process
Creating a connected system follows a structured path that combines planning, execution, and ongoing refinement. The outline below shows how professional IoT development services guide an idea from early concept to a fully connected and intelligent solution.
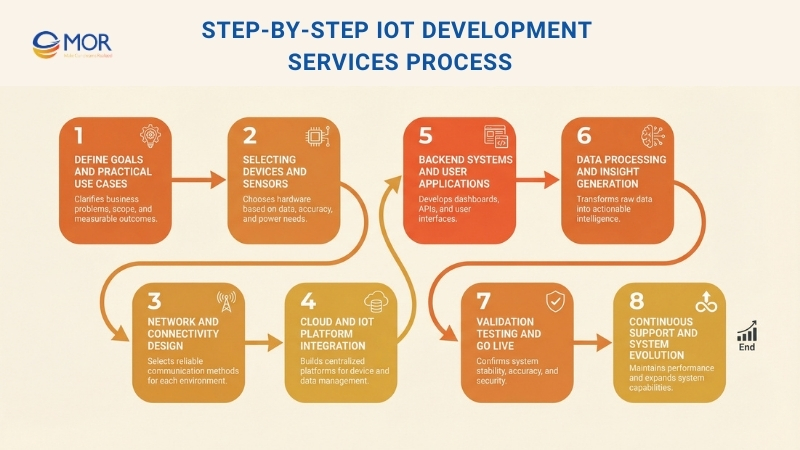
Step 1: Define Goals And Practical Use Cases
The process begins with identifying the problems to address and the results the business expects.
Example use cases:
- Smart cities improving traffic coordination
- Manufacturing teams reducing equipment downtime
- Healthcare organizations tracking patient health remotely
Clear definition of scope, objectives, and measurable KPIs shapes system architecture decisions and supports tailored planning often associated with custom IoT software development services.
Step 2: Selecting Devices And Sensors
The next phase focuses on choosing suitable devices, sensors, and microcontrollers based on:
- The type of data required, including temperature, motion, or pressure
- Accuracy needs and response time expectations
- Power usage and communication range
Example: A logistics provider may rely on GPS trackers and RFID sensors to support real-time asset visibility across transport routes.
Step 3: Network And Connectivity Design
Stable connectivity supports uninterrupted communication between devices and cloud systems. Based on the operating environment and specific use case, teams select options such as Wi-Fi, 4G or 5G, LoRa, or Bluetooth. In agricultural scenarios, connected platforms often rely on LoRaWAN to achieve long-range coverage across rural locations.
Step 4: Cloud And IoT Platform Integration
Information gathered from connected devices is stored and processed through platforms like AWS IoT Core, Azure IoT Hub, or Google Cloud IoT, supported by reliable IoT development software.
This phase includes:
- Configuring tools for device management
- Establishing communication protocols including MQTT, CoAP, and HTTP
- Applying encryption methods and security controls
The objective is to build a centralized and scalable environment that supports real-time system performance.
Step 5: Backend Systems And User Applications
Engineering teams develop backend services to manage data pipelines and APIs, followed by web and mobile interfaces used for monitoring and control. This layer is commonly delivered through IoT application development services that connect users directly to live device data.
Example:
- A dashboard that displays machine uptime and system status
- A mobile app that sends alerts when air quality levels change
Commonly used technologies include Node.js, React.js, Angular, Python, and TypeScript.
Step 6: Data Processing And Insight Generation
This phase centers on transforming raw device data into practical insights through analytics, AI automation, or machine learning models that support informed decisions.
Examples:
- Anticipating equipment failures
- Detecting energy waste patterns
- Estimating future product demand
Visualization platforms such as Power BI, Grafana, or Looker Studio present this information in clear and actionable formats.
Step 7: Validation, Testing, And Go-Live
Thorough testing confirms system stability, performance, and security before release.
This step covers:
- Verifying device interoperability
- Running connectivity stress assessments
- Checking data accuracy
- Conducting security penetration reviews
After validation, the solution moves into live production environments.
Step 8: Continuous Support And System Evolution
Connected systems need ongoing oversight to maintain availability, security, and performance levels.
Regular support activities include:
- Updating firmware and software components
- Tracking connectivity health and data movement
- Expanding the system with new features or devices
A mature approach to IoT development services continues well beyond launch. It adapts over time using operational data, user input, and emerging technology to keep systems improving and responsive.
Real-World Applications Powered By IoT Development Services
Connected technologies have changed how many industries operate, shifting legacy setups into intelligent and connected networks. Below are some of the most influential use cases of IoT development services across major sectors, supported by modern internet of things software solutions.
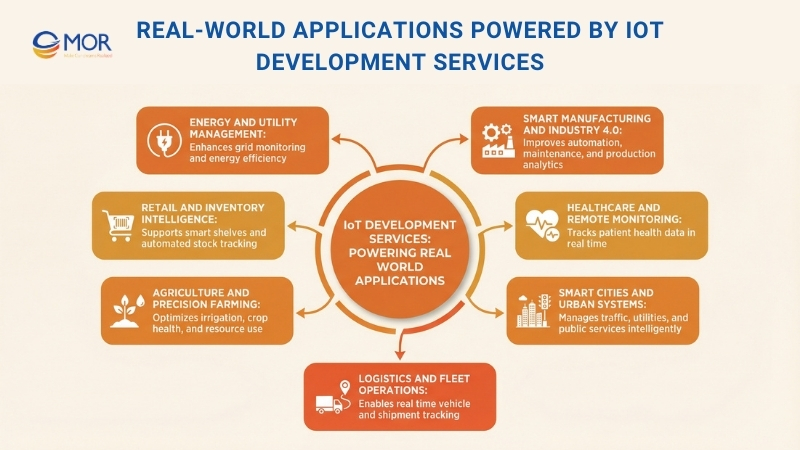
Smart Manufacturing And Industry 4.0
Connected systems support predictive maintenance, machine automation, and production analytics within manufacturing environments. Sensors installed on equipment capture performance data in real time, allowing engineering teams to identify potential failures before disruptions occur. These initiatives are often delivered through IoT product development services that combine hardware, software, and connectivity into a single production-ready solution.
Example: BMW uses connected sensors to monitor assembly lines, helping reduce operational downtime by more than 30 percent.
Healthcare And Remote Monitoring
Connected medical devices such as smartwatches and remote monitoring kits track vital indicators including heart rate, oxygen saturation, and blood pressure. This information flows directly to healthcare professionals, enabling real-time evaluation and timely intervention.
Example: Philips HealthSuite allows hospitals to monitor patients remotely, which helps lower readmission rates and improve ongoing care.
Smart Cities And Urban Systems
Connected technology supports the development of smarter and more sustainable cities. Common applications include traffic coordination, waste handling, automated street lighting, and public safety monitoring, all managed through centralized control systems.
Example: In Barcelona, connected waste bins alert city teams when they need servicing, which helps cut operational costs by around 30 percent.
Logistics And Fleet Operations
Within logistics, connected platforms support real-time tracking of vehicles, cargo, and deliveries. This visibility improves route planning, lowers fuel usage, and helps meet tighter delivery schedules, often supported through a dedicated IoT app development service for drivers and operations teams.
Example: DHL relies on connected sensors to monitor shipments worldwide, which improves transparency and operational efficiency.
Agriculture And Precision Farming
Connected sensors track soil moisture, weather patterns, and crop health, allowing farmers to manage irrigation and growing conditions more accurately. These systems help raise yields while limiting water and resource waste.
Example: John Deere uses connected tractors and equipment to support precision farming practices that increase productivity and reduce unnecessary resource use.
Retail And Inventory Intelligence
Retail teams rely on connected systems to support smart shelves, automated inventory tracking, and more personalized customer experiences across physical locations. These setups often depend on IoT app development services that connect in-store sensors with real-time dashboards and alerts.
Example: Amazon Go locations use connected cameras and sensors to enable cashier-less shopping experiences.
Energy And Utility Management
In the energy sector, connected platforms improve efficiency through smart meters, grid monitoring, and predictive maintenance practices. Utilities gain better control over consumption patterns and system stability across large networks.
Example: Tesla Powerwall combines connected monitoring with energy storage systems to support remote management and usage tracking.
Connected technology applies across industries rather than a single use case. It acts as the foundation of digital transformation, linking devices, data, and operational decisions in one continuous flow. Organizations that adopt IoT development services today position themselves for long-term innovation, operational efficiency, and sustained competitive advantage.
IoT Development Challenges And Ways To Overcome Them
Although connected technology creates strong opportunities, building and running a smart ecosystem comes with real challenges. Organizations must manage technical, operational, and strategic issues to achieve successful adoption of IoT development services. The sections below outline common obstacles and practical ways to address them.
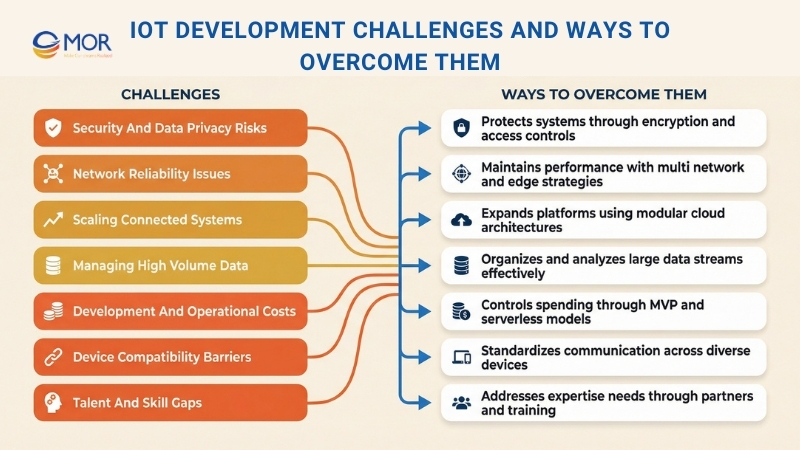
Security And Data Privacy Risks
Challenge: With billions of connected devices in use, IoT environments attract cyber threats. Data leaks, unauthorized access, and weak endpoints can affect both sensitive information and overall system reliability.
Solution:
- Apply end-to-end encryption using TLS or SSL standards.
- Enforce secure device authentication along with role-based access control (RBAC).
- Update firmware regularly to close known security gaps.
- Use cloud security tools such as AWS IoT Defender or Azure Security Center.
Example: Healthcare platforms built on connected systems rely on encrypted data transmission to meet HIPAA requirements and safeguard patient records.
Network Reliability Issues
Challenge: Connected systems rely on stable communication across devices and locations. Weak coverage or unstable networks can cause data interruptions and inconsistent performance.
Solution:
- Adopt multi-network connectivity options including 4G, 5G, LoRa, and Wi-Fi.
- Use edge computing to handle data locally during connection outages.
- Design fallback processes that keep operations running during disruptions.
Example: Agricultural monitoring systems often use LoRaWAN to maintain reliable communication even in remote rural areas.
Scaling Connected Systems
Challenge: As device numbers increase, platforms must process larger data volumes while maintaining stable performance. Many connected environments struggle to grow efficiently, especially in custom IoT projects with complex requirements.
Solution:
- Rely on cloud-based infrastructure such as AWS IoT Core or Google Cloud IoT.
- Design a modular architecture that supports horizontal expansion.
- Tune databases like DynamoDB or InfluxDB to handle high data throughput.
Example: Smart city platforms use scalable cloud architectures to operate millions of connected sensors at the same time.
Managing High-Volume Data
Challenge: Connected environments generate large amounts of structured and unstructured information. Without proper handling, valuable insights can be overlooked or lost.
Solution:
- Set up data lakes and processing pipelines to organize incoming information.
- Apply real-time analytics tools such as Apache Kafka or Power BI.
- Use AI and machine learning models to derive actionable insights from raw data streams.
Development And Operational Costs
Challenge: Connected initiatives often require investment in hardware, cloud services, software creation, and long-term support, which can increase overall costs.
Solution:
- Begin with a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) to confirm feasibility.
- Adopt serverless architectures like AWS Lambda or Azure Functions to limit infrastructure spending.
- Select open-source IoT frameworks during early development phases.
Example: Many startups launch IoT MVPs first to test assumptions before moving into full-scale deployment.
Device Compatibility Barriers
Challenge: Connected environments often include devices that rely on different protocols and data formats, which creates integration difficulties across systems.
Solution:
- Standardize communication through protocols such as MQTT, CoAP, or OPC-UA.
- Build an API-first architecture to support smooth system integration.
- Apply middleware layers for device coordination and data normalization.
Talent And Skill Gaps
Challenge: Connected initiatives demand knowledge across hardware engineering, cloud platforms, networking, and AI. This combination of skills is difficult to find in a single team of IoT developers.
Solution:
- Work with experienced IoT development companies that bring cross-domain expertise.
- Invest in structured training programs for internal technical teams.
- Use IoT platform-as-a-service (PaaS) offerings to lower technical complexity and reduce reliance on specialized resources.
How To Select The Right Partner For IoT Development Services?
Selecting the right IoT application development services company plays a major role in turning a connected idea into a stable and scalable product. A strong partner combines technical expertise with industry knowledge to support design, development, and deployment of connected systems. Below is a practical guide to evaluating a suitable partner for IoT development services.
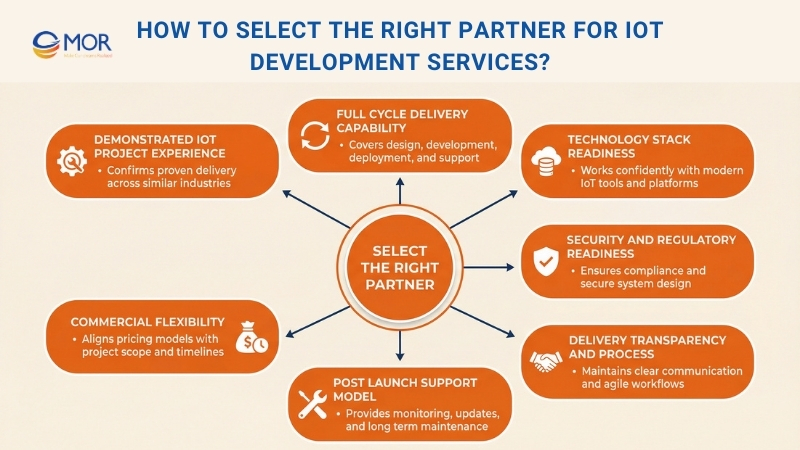
Demonstrated IoT Project Experience
Prioritize teams with hands-on experience across a wide range of connected initiatives, from smart home environments to industrial systems. Review their portfolio, client feedback, and case studies to confirm they have delivered similar solutions within your sector.
Tip: A partner with direct experience in industries like healthcare, logistics, or manufacturing can help lower delivery risks and shorten time to market.
Full-Cycle Delivery Capability
Your qualified partner should manage the entire project lifecycle, covering early consulting and prototyping through development, testing, deployment, and long-term support.
End-to-end coverage supports smoother collaboration and consistent technical standards throughout delivery.
Key capabilities to evaluate include:
- Hardware and firmware integration
- Cloud and backend system development
- IoT platform customization
- Mobile and web application delivery
- Ongoing monitoring and support services
Technology Stack Readiness
Confirm that your provider works confidently with modern IoT tools, frameworks, and platforms, including:
- Cloud: AWS IoT, Azure IoT Hub, Google Cloud IoT
- Connectivity: MQTT, CoAP, BLE, Zigbee, LoRaWAN
- Hardware: Raspberry Pi, Arduino, ESP32
- Programming: Node.js, Python, Java, C++
- Databases: DynamoDB, PostgreSQL, MongoDB
A capable team can choose a technology stack that supports performance needs, future growth, and cost control across connected systems.
Security And Regulatory Readiness
Connected platforms often process sensitive and operational data, which makes a security-first approach essential from day one.
When reviewing potential partners, ask about:
- Data encryption methods
- Secure API design
- Compliance with standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, or ISO
- Identity and access management practices
Delivery Transparency And Process
A reliable partner maintains clear communication and applies an Agile or DevOps-driven process to support regular updates and timely delivery. Frequent demos and structured feedback cycles help keep expectations aligned throughout the project lifecycle.
Post-Launch Support Model
Connected platforms need ongoing improvement, firmware updates, and performance adjustments after release. A dependable partner provides 24/7 support, real-time system monitoring, and predictive maintenance services to keep operations running without disruption.
Commercial Flexibility
Strong providers balance delivery quality with reasonable cost structures. It is important to review engagement options such as fixed-cost, time and material, or dedicated team models so pricing aligns with project scope, complexity, and delivery timelines.
IoT Development Services Costs And Timelines (2026 Estimates)
Planning a connected initiative requires early clarity around budget and delivery timelines. Costs for IoT development services vary based on solution scope, device volume, data processing needs, security requirements, and integration depth. The table below outlines typical cost ranges and timelines businesses can expect in 2026, based on current market benchmarks and project complexity.
Project Type | Typical Cost (USD) | Estimated Timeline | Key Inclusions (Examples) |
Simple IoT App / Consumer IoT | $20,000 – $50,000 | 2 to 4 months | Basic monitoring, single device support, simple cloud dashboard |
Mid-Level IoT Solution | $50,000 – $100,000 | 4 to 8 months | Multi-device support, cloud integration, analytics dashboards |
Advanced Enterprise IoT System | $100,000 – $500,000+ | 6 to 12+ months | Predictive analytics, AI and ML integration, ERP and system integration |
Industrial / Custom Hardware IoT Deployment | $100,000+ (Hardware and Software) | 6 to 18+ months | Custom sensors, gateways, ruggedized hardware |
Full IoT Ecosystem (Smart City / Large Deployment) | $500,000+ | 12 to 24+ months | Edge computing, real-time analytics, large-scale device fleet |
MOR Software: Your Trusted Partner For IoT Development Services
We help businesses turn connected ideas into systems that work in the real world. Our team builds IoT development services that connect devices, data, and operations without adding friction.
We start with the business goal, not the tech stack. That keeps IoT projects focused on outcomes like uptime, cost control, and faster decisions.
We handle the full delivery scope. From device and sensor integration to cloud platforms, dashboards, and user apps, everything moves as one system. No handoffs. No blind spots.
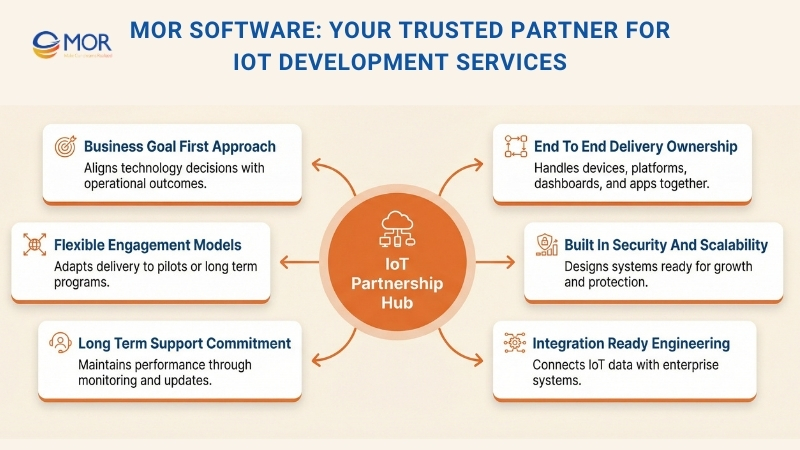
Security and scale are built in from day one. We design for encrypted data flows, clear access control, and growth across devices, users, and locations. Systems stay stable as usage increases.
Our engineers work comfortably across cloud-native environments, real-time data pipelines, and integration-heavy architectures. That matters when IoT data needs to sync with ERP, analytics, or internal platforms.
Support does not stop at launch. We stay involved with monitoring, updates, and system tuning so IoT platforms keep pace with changing needs.
Engagement stays flexible. We adapt delivery models to fit pilots, phased rollouts, or long-term programs, based on timeline and budget, not rigid contracts.
This is how we approach IoT projects that move from concept to daily operations without losing momentum.
The Future Direction Of IoT Development Services Beyond 2026
Connected technology has moved far beyond a short-term trend. It now forms the foundation of the digital economy. By 2026, more than 30 billion devices are expected to be connected worldwide, changing how industries operate, how cities function, and how people interact with technology each day. Organizations that invest in IoT development services today are preparing for long-term gains in innovation, efficiency, and customer experience.
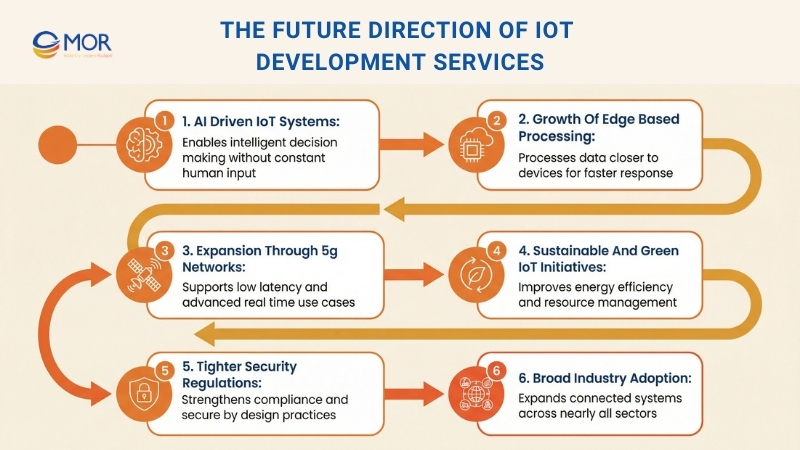
Below is an overview of how this space continues to evolve and what lies ahead.
AI-Driven IoT Systems
The integration of artificial intelligence with connected platforms, often called AIoT, is reshaping how decisions are made. This approach turns connected devices into intelligent systems that respond to data without constant human input.
AI-enabled connected platforms can:
- Detect equipment issues automatically
- Improve logistics planning in real time
- Adapt user experiences based on behavior patterns
Example: Manufacturing facilities that apply AIoT can identify production irregularities early, which helps cut downtime by up to 40 percent.
Growth Of Edge-Based Processing
As connected environments generate larger data volumes, edge-based processing continues to gain momentum. Instead of sending all information to centralized cloud platforms, data is handled closer to the device source.
This shift supports:
- Faster system responses
- Reduced network bandwidth usage
- Stronger data privacy controls
Example: Autonomous vehicles depend on edge-based processing to make immediate navigation decisions without relying entirely on cloud connections.
Expansion Through 5g Networks
The global rollout of 5G networks is accelerating the growth of connected systems. With very low latency and faster data transfer, 5G supports advanced use cases that were not practical before.
These include:
- Smart cities supported by connected infrastructure
- Real-time automation in industrial environments
- Immersive AR and VR experiences linked to connected devices
Example: Smart hospitals apply 5G-enabled connected devices to support remote robotic procedures with minimal delay.
Sustainable And Green IoT Initiatives
As sustainability becomes a priority, Green IoT plays a growing role in lowering environmental impact across industries.
Connected platforms help improve:
- Energy consumption control
- Water usage efficiency
- Waste management processes
- Distribution of renewable energy
Example: Smart grid systems rely on connected sensors to balance electricity demand and reduce energy waste, supporting more sustainable power networks.
Tighter Security Regulations
As connected ecosystems expand, cybersecurity regulations continue to strengthen worldwide. Both public and private organizations are placing greater emphasis on:
- Data protection measures
- IoT identity and access management
- End-to-end encryption and compliance standards
Example: The EU Cyber Resilience Act requires connected systems to follow secure-by-design principles to protect user information.
Broad Industry Adoption
Connected systems continue to expand across nearly every sector, from agriculture to aerospace. In the coming years, connected ecosystems will become standard in many fields, supported by scalable IoT development services that adapt to different operational needs.
Key areas of adoption include:
- Healthcare: Smart wearables and remote patient monitoring platforms
- Retail: Automated checkout systems and real-time inventory updates
- Construction: Equipment tracking and predictive maintenance solutions
- Education: Smart classrooms supported by connected devices
Conclusion
IoT development services play a central role in how businesses connect devices, manage data, and make faster decisions at scale. The right approach turns complexity into systems that stay reliable, secure, and ready to grow. With a clear process and the right partner, connected platforms become practical tools, not ongoing problems. If you’re planning your next IoT initiative, contact MOR Software to discuss how we can design and deliver a solution that fits your real operational needs.
MOR SOFTWARE
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are IoT development services?
IoT development services focus on building systems that connect physical devices to software platforms. These systems collect data, transmit it through networks, process it, and present results through dashboards or applications.
Which industries commonly use IoT development services?
Manufacturing, logistics, healthcare, retail, agriculture, energy, and smart city projects frequently rely on IoT solutions. Any operation that depends on real-time data from physical assets can apply IoT.
What components make up a typical IoT solution?
A standard IoT system includes devices or sensors, network connectivity, a backend platform, data processing logic, and user-facing applications. Security and device management are also core parts.
How long does it take to build an IoT system?
Project timelines depend on scope and complexity. A small proof of concept may take weeks, while production systems with integrations and analytics usually take several months.
How is security handled in IoT development?
Security is addressed through encrypted data transmission, secure device authentication, access control, and regular software updates. Monitoring tools are often used to detect risks early.
What connectivity options are available for IoT projects?
IoT systems may use Wi-Fi, cellular networks like 4G or 5G, Bluetooth, or LPWAN technologies such as LoRaWAN. The choice depends on range, power usage, and data needs.
Can IoT systems scale as more devices are added?
Yes, scalable IoT systems are designed with cloud-based infrastructure and modular architecture. This allows them to handle growth in devices, users, and data volume.
How is IoT data used after collection?
Collected data is analyzed to monitor operations, detect issues, predict failures, or support decision making. Results are often shown through dashboards, alerts, or system integrations.
What is edge computing in IoT?
Edge computing processes data close to the device instead of sending everything to the cloud. This reduces latency, lowers bandwidth use, and supports faster responses.
What should businesses prepare before starting an IoT project?
Businesses should define clear goals, practical use cases, and operational requirements. Planning for security, system integration, and long-term maintenance is also important early on.
Rate this article
0
over 5.0 based on 0 reviews
Your rating on this news:
Name
*Email
*Write your comment
*Send your comment
1