What Is Blockchain Software Development? Guide, Tools, Best Tips

Blockchain software development has shifted from a niche interest to a must-know topic for tech leaders and digital innovators. The demand is growing fast, but building blockchain applications isn’t the same as building traditional software. It brings new rules, risks, and rewards. This MOR Software’s guide will walk you through everything you need to know from how it works to the tools that make it possible.
What is Blockchain Software Development?
Blockchain software development is the process of designing, building, and managing decentralized applications that rely on blockchain networks to store and verify data.
These systems offer a high level of transparency and integrity by recording information in blocks that are cryptographically secured and linked across a peer-to-peer network.
Industry analysts expect global spending on blockchain solutions to hit about $19 billion in 2024, up from $6.6 billion just three years earlier, showing how fast teams are moving from pilots to production.
In practice, many organizations partner with a blockchain software development company to navigate compliance and architecture decisions.
The field covers a wide range of use cases. Teams use it to create smart contracts that automatically enforce rules. Others build dApps that give users control over their data and transactions. Many projects also include token ecosystems, which are used for payments, access, or governance.
Nearly nine in ten enterprises surveyed say they already deploy blockchain in some fashion or plan to invest within the next twelve months, a trend echoed across executive and institutional circles
Unlike traditional software that stores data on a centralized server, blockchain applications rely on distributed ledgers. Each participant in the network holds a synchronized copy of the ledger. This setup eliminates single points of failure and makes tampering nearly impossible.
To work effectively, blockchain software combines knowledge from several disciplines:
- Cryptography to secure information and protect identities
- Computer science to structure code, networks, and architecture
- Economics and game theory to design fair and sustainable systems
Some of the most widely used platforms in blockchain development include:
- Ethereum: Supports smart contracts and dApps, ideal for DeFi and NFT projects
- Hyperledger Fabric: Built for enterprise applications with permissioned access and privacy features
- Solana: Known for speed and scalability, suited for high-volume use cases like games or finance
As of mid-2025, DeFi protocols on these and other networks secure more than $129 billion in total value locked, underlining the scale already reached by on-chain finance
Whether you're exploring DeFi, supply chains, or digital identity tools, blockchain software development gives you a foundation that’s built for trust and resilience.
What is Blockchain Software Development?
Key Features of Blockchain Software Development
Blockchain software is built differently from conventional systems. Its strength comes from several core features that make it secure, transparent, and resistant to failure. Each feature adds a layer of trust and functionality that traditional software can’t offer.
Decentralization
Instead of relying on a central server, blockchain distributes control across a network of nodes. Each node has a copy of the full ledger and participates in validating transactions. This design limits the influence of any single party and ensures the system continues operating even if some nodes fail.
As a result, decentralization boosts transparency and encourages users to trust the system without relying on a central authority.
Immutability
Data recorded on the blockchain is permanent. Once a block is added, it’s mathematically sealed and linked to previous blocks using cryptographic hashes.
This means records can’t be deleted or changed without alerting the entire network. Whether you're tracking asset transfers or verifying contract terms, immutability ensures a clear and auditable trail.
Consensus Mechanisms
To prevent fraud and confirm accuracy, blockchain networks use consensus algorithms. These include:
- Proof of Work (PoW): Requires nodes to solve cryptographic puzzles before adding a block
- Proof of Stake (PoS): Allows validators to confirm transactions based on the amount of cryptocurrency they hold and are willing to “stake”
Consensus ensures that only valid transactions are added to the chain. It’s how decentralized systems reach agreement without a central referee.
Enhanced Security
Security is built into the system at every level. Blockchain uses strong cryptographic techniques, including public and private key encryption, to protect data and identities.
Public keys allow users to receive information, while private keys authorize actions. Together, they secure everything from token transfers to smart contract execution.
Networks also use multi-factor authentication, hashing algorithms, and access controls to keep data safe and intact. The need for these layered defenses is clear, since hackers still stole about $2.2 billion from crypto platforms in 2024.
Smart Contracts
These are pieces of self-executing code stored directly on the blockchain. When predefined conditions are met, the contract runs automatically.
Smart contracts replace intermediaries by enforcing rules without human input. They’re commonly used for tasks like processing payments, managing supply chain triggers, or issuing tokens.
Since the code can’t be altered after deployment, it’s essential to test thoroughly before launch.
Distributed Ledger
Every node in the blockchain holds a synchronized version of the ledger. When a new block is confirmed, all nodes update their records to match.
This system ensures transparency, since no transaction can happen without being recorded across the network.
Whether users are participating in public or private blockchains, they can verify data independently at any time.
Key Features of Blockchain Software Development
Main Types of Blockchain Software Development
Blockchain development isn't one-size-fits-all. It spans from foundational protocol work to user-facing apps. Each type requires different skills, tools, and responsibilities. Knowing the difference helps teams staff their projects correctly and choose the right development path.
Core Blockchain Development
Core development focuses on building and maintaining the actual blockchain protocol. This includes designing the consensus mechanism, node communication, block validation rules, and the underlying architecture that makes the network run.
Core developers often:
- Create new blockchain platforms or customize existing ones
- Optimize performance and scalability of the network
- Manage protocol updates, forks, and security patches
- Set up the infrastructure for smart contracts and apps to run on
Their job is to make sure the network is reliable, secure, and performs well under real-world conditions. Without this layer, applications built on top can’t function properly.
Blockchain Software/Application Development
This type of development involves building applications that run on top of blockchain platforms. It’s where most visible blockchain innovation happens, think wallets, NFT marketplaces, DeFi apps, and DAO tools.
App developers typically:
- Write and test smart contracts using languages like Solidity or Rust
- Build front-end interfaces using frameworks like React.js or Vue.js
- Connect the front end to the blockchain using Web3.js or Ethers.js
- Handle API integrations with wallets, payment services, oracles, and off-chain systems
This layer is user-facing. It translates blockchain functionality into tools and services that people and businesses can actually use. While core devs build the roads, app developers build the vehicles.
Main Types of Blockchain Software Development
Essential Skills for Blockchain Software Development
Blockchain software development blends several technical domains. Developers need to understand distributed systems, smart contracts, and frontend-backend integration. Below are the core skills every blockchain developer should master to build production-ready apps and systems.
- Smart contract development: Writing smart contracts is central to most blockchain projects. Developers should be proficient in Solidity (for Ethereum) or Rust (for platforms like Solana and NEAR). Understanding gas limits, reentrancy issues, and upgrade patterns is also key for secure contract logic.
- Backend programming experience: Blockchain apps still require traditional server-side skills. Languages like Node.js, Python, and Java are often used to build APIs, business logic, and database integration for hybrid systems that interact with off-chain services.
- Frontend framework knowledge: Most dApps are accessed via a web interface. Developers should be comfortable using React.js, Vue.js, or Next.js to create clean, responsive, and intuitive UIs. Experience with mobile development (e.g., React Native or Flutter) is also a plus for wallet apps and tools.
- Blockchain fundamentals: A strong grasp of how distributed ledgers work is non-negotiable. This includes knowledge of hashing algorithms, public-private key encryption, peer-to-peer networks, consensus models, and the structure of transactions and blocks.
- Library integration (Web3.js, Ethers.js): Connecting apps to blockchain networks relies on tools like Web3.js and Ethers.js. These libraries allow frontend and backend applications to read data from the chain, send transactions, and interact with deployed smart contracts.
- Security awareness: Blockchain projects often deal with assets or sensitive data. Developers must understand common vulnerabilities such as overflow bugs, logic flaws in contracts, phishing vectors, and how to write testable, auditable code.
- Analytical and debugging skills: Bugs in smart contracts can be costly and irreversible. Developers need to think critically, trace issues through async systems, and use testing frameworks to simulate different transaction states before launch.
- Teamwork and collaboration: Successful blockchain projects often involve multidisciplinary teams: developers, auditors, product managers, and legal advisors. Strong communication and the ability to document and explain code clearly make a big difference.
Essential Skills for Blockchain Software Development
Key Steps in Blockchain Software Development
Building blockchain software requires more than just coding smart contracts. From strategy to post-launch support, each stage of development must be handled with precision. Here's how to build a blockchain solution the right way.
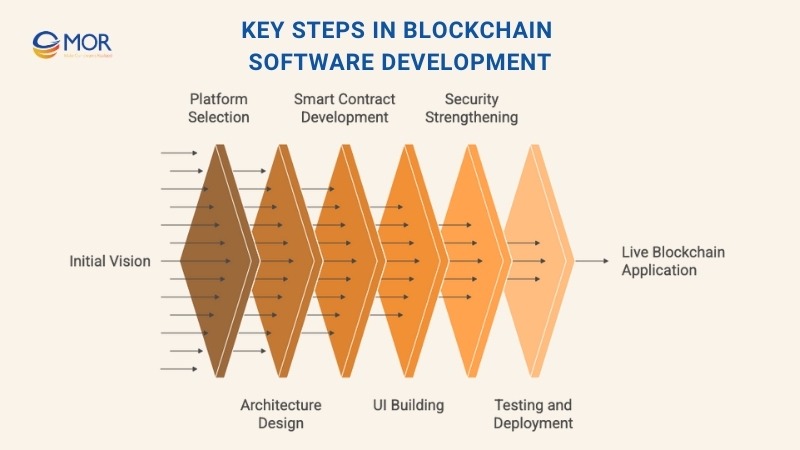
1. Clarify Your Vision
Start by defining what the software should achieve. Are you building a payment platform, supply chain system, or identity solution? Clear goals shape the architecture, tools, and team you'll need.
Be specific about desired outcomes: increased transparency, faster transactions, automated workflows, or compliance tracking. Without this step, it's easy to burn time on features that don’t serve the core mission.
2. Choose the Right Platform
Not all blockchains are created equal. Choose a platform based on your use case, scalability needs, and required functionality.
Examples:
- Ethereum: Great for dApps and DeFi, with a large ecosystem and mature tooling
- Hyperledger Fabric: Ideal for enterprise systems that require permissioned access
- Solana: High-speed, low-fee platform suited for gaming and real-time transactions
Look at performance benchmarks, community support, and how the platform handles updates. Real-world case studies can help gauge how each one holds up under pressure.
3. Design the Architecture
This step lays out the blueprint: who can access what, how the data flows, and which consensus model to use.
Plan for scalability and resilience. Decide if your network will be public or private, how nodes will interact, and how governance will work.
Make decisions about:
- Node roles
- Permissions and identity management
- Failover strategies
- Governance rules
Your architecture will shape how your system evolves over time, so get it right early.
4. Write and Test Smart Contracts
Smart contracts run your app logic. Write them in a secure, modular way using best practices from audited templates.
Test everything using tools like Truffle, Hardhat, or Foundry. Focus on edge cases, input validation, and logic consistency.
Every function should be stress-tested on a testnet. Any missed bug can result in financial loss or irreversible failure post-launch.
5. Build the User Interface
Design an interface that hides the blockchain’s complexity but still provides clarity and trust.
Use modern frameworks like React.js or Next.js to build responsive apps.
Make sure your wallet integrations (e.g., MetaMask, WalletConnect) are smooth, secure, and consistent.
The goal is simple: let users complete tasks without confusion or technical friction.
6. Strengthen Security
Security isn’t a final step. It’s ongoing. Start with:
- Role-based access control
- End-to-end encryption
- Input sanitization
- Secure storage of private keys and sensitive data
Use tools like MythX, Slither, or manual audits to spot vulnerabilities in smart contracts. Regular penetration testing should be part of your development schedule.
7. Test, Deploy, and Refine
Before going live, simulate usage across multiple layers:
- Unit testing for individual functions
- Integration testing for how modules interact
- Load testing for performance under stress
Deploy to a testnet and gather feedback. Once stable, launch on mainnet.
After launch, monitor logs, fix bugs quickly, and iterate on features based on real-world use. When you are developing on the blockchain, thorough unit tests and audits become non-negotiable.
Key Steps in Blockchain Software Development
Must-Have Tools for Blockchain Software Development
Every blockchain developer relies on a core set of tools to write, test, deploy, and monitor their code. These tools speed up workflows, reduce bugs, and simplify the process of building dApps and smart contracts. Teams rely on mature blockchain development software such as:
1. Solidity
Solidity is the go-to language for writing smart contracts on the Ethereum blockchain. Designed with developers in mind, it blends familiar syntax from JavaScript, C++, and Python, making it easier to pick up for those coming from web or backend development backgrounds.
Key features include:
- Support for inheritance and reusable libraries
- Strong typing and user-defined complex types
- Compatibility with DeFi, DAO, and NFT ecosystems
- Active community and frequent updates from the Ethereum Foundation
It’s perfect for building secure, scalable decentralized applications that run on Ethereum or EVM-compatible networks. Smart contract engineers use crypto programming languages like Solidity to build reliable on-chain logic.
2. Solc
Solc is the Solidity compiler that transforms your smart contract code into low-level bytecode, ready for execution on the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). It plays a crucial role in every stage of development, from testing to production deployment.
There are two main versions:
- Native Solc written in C++ for performance and accuracy
- Solc-js, the JavaScript version for browser-based or lightweight environments
- Both support contract optimization and ABI generation
- Widely integrated into frameworks like Truffle and Remix for seamless workflows
Solc is ideal for developers who need fast, accurate contract compilation and deep integration with the Ethereum development stack.
3. Truffle
Truffle is a full development framework for Ethereum. It includes built-in support for compiling, linking, deploying, and testing smart contracts.
Features include:
- Scriptable migrations
- Contract abstraction
- Integration with Mocha for automated testing
- Network management and build pipelines
It’s one of the oldest and most trusted tools in the Ethereum ecosystem.
4. Remix IDE
Remix is a web-based IDE used to write, test, and debug Solidity smart contracts.
It’s great for beginners and pros alike, with features such as:
- Real-time compiler feedback
- Gas estimation
- Static analysis tools
- Built-in JavaScript VM for testing
Remix is often the first stop when prototyping new smart contract logic.
5. Ganache
Ganache is a personal blockchain used for Ethereum development. It allows developers to deploy contracts, run tests, and inspect states without needing to connect to an actual testnet.
With a local blockchain instance, you can:
- Track gas usage
- Manipulate block time
- Simulate real-world conditions
It’s perfect for rapid testing and experimentation before moving to public testnets.
6. Chainlink
Chainlink is a decentralized oracle network that connects smart contracts to off-chain data sources like APIs, webhooks, and real-world events.
With Chainlink, smart contracts can access:
- Price feeds for DeFi apps
- Weather or sports data
- IoT device readings
It’s critical for any blockchain app that needs trusted external data.
7. MetaMask
MetaMask is a browser extension and mobile app that acts as a wallet and gateway to blockchain networks.
Users can:
- Store and manage their private keys
- Sign transactions securely
- Connect to dApps and approve interactions
MetaMask is essential for dApp usability and smart contract testing in real user conditions.
8. Alchemy Supernode & Alchemy NFT API
Alchemy provides powerful infrastructure APIs that help developers access blockchain data without running their own nodes.
Key features include:
- Supernode: Reliable connection to Ethereum and other chains
- NFT API: Tools to mint, track, and display NFTs without complex backend logic
Alchemy helps teams scale quickly and handle production-grade workloads.

Must-Have Tools for Blockchain Software Development
Real-World Use Cases for Blockchain Software Development
Blockchain software development is not just for crypto startups. It's solving real problems across industries by making transactions more transparent, secure, and verifiable. These examples show how decentralized solutions are being put to work.
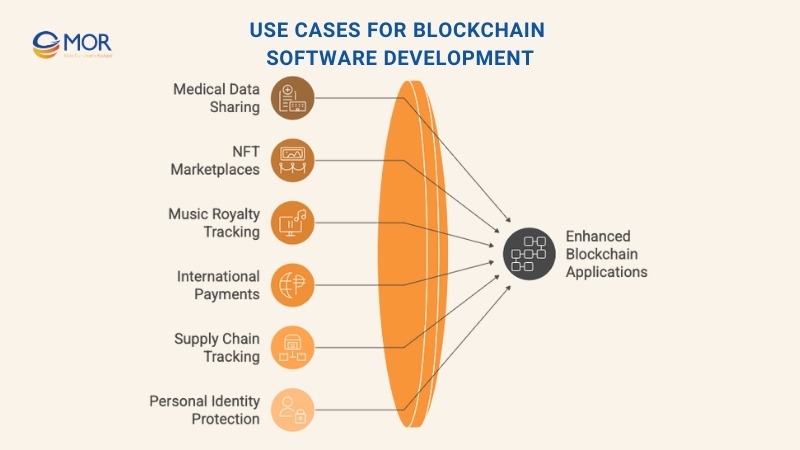
- Secure sharing of medical data in healthcare: Secure sharing of medical data in healthcare: Hospitals use blockchain to share patient records safely. Smart contracts manage access, reduce errors, and improve care coordination..
- NFT marketplaces for creators and collectors: Digital artists and content creators use blockchain to mint and sell NFTs. Marketplaces built on Ethereum or Flow allow users to verify ownership, transfer assets, and earn royalties automatically. Everything is recorded on-chain, preventing counterfeits and proving scarcity.
- Music royalty tracking for transparency in payments: Smart contracts automate royalty distribution in the music industry. When a song is streamed or downloaded, the blockchain records it instantly and pays out to rights holders based on predefined splits. Artists see faster, more accurate compensation without intermediaries.
- International payments with fast settlements: Blockchain reduces cross-border payment delays. Platforms like Ripple or Stellar settle transactions in seconds, not days. Businesses avoid high fees and currency conversion costs while gaining real-time tracking and auditability.
- Streamlined supply chain and logistics tracking: IBM and Maersk use blockchain to trace goods from origin to delivery, logging each step immutably. This cuts fraud, reduces paperwork, and proves authenticity. IBM estimates full digitization could save carriers $38 billion a year.
- Personal identity protection: Blockchain can store verifiable credentials, like digital IDs or academic certificates. Users control their identity and only share necessary data. Governments and universities are experimenting with blockchain passports, licenses, and diplomas.
- Real estate transactions and property management: Blockchain enables faster closings, transparent title records, and smart contracts for rental agreements. Tokenized property ownership is also becoming more common, letting people invest in fractional real estate via dApps.
- IoT device management: With thousands of devices transmitting data daily, blockchain helps secure and verify actions. Decentralized ledgers record commands and responses between machines, preventing tampering and improving accountability in smart cities and factories.
- In-game purchases and digital assets in gaming: Blockchain lets players own in-game assets like weapons, land, or skins. These items can be traded or sold across platforms, creating a true digital economy. Projects like Axie Infinity and Decentraland are leading examples.
For projects that need specialized features such as zero-knowledge proofs or unique tokenomics, custom blockchain software development can deliver a tailored architecture.
Real-World Use Cases for Blockchain Software Development
Best Practices for Blockchain Software Development
Researchers project the overall blockchain technology market will reach roughly $1.43 trillion by 2030, growing at more than 90% annually. underscoring the importance of following solid engineering and security practices as the ecosystem scales.
Whether you’re building your first dApp or scaling an enterprise-grade platform, following proven practices helps reduce risk and deliver lasting value. These tips come from real-world experience across industries and projects.
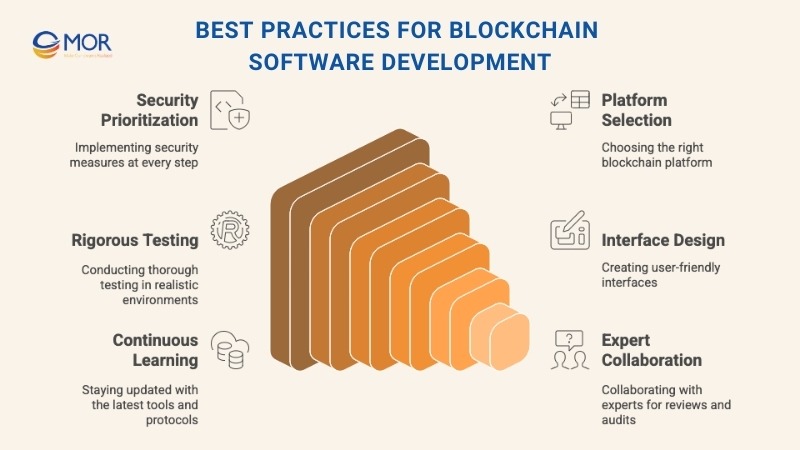
- Always define clear, measurable goals and requirements before starting: Without clear direction, development drifts. Set functional goals (e.g., token issuance, transaction tracking) and technical goals (e.g., throughput, latency). Know what success looks like early.
- Prioritize security at every stage, especially in smart contract development and key management: Bugs in deployed smart contracts are expensive and public. Follow secure coding standards. Use static analyzers and formal verification tools. Never store private keys in code. Always use hardware wallets or secure key vaults in production.
- Choose the blockchain platform that best fits your project’s unique needs: Ethereum might work for NFTs, but Hyperledger could be better for supply chains. Match features with your requirements: performance, governance, cost, ecosystem. Don’t pick the most popular platform by default.
- Rigorously test your code using real-world scenarios and testnets: Write tests that reflect how users will actually interact with the system. Use Ganache, Hardhat, or Truffle to run simulations. Deploy to public testnets like Goerli or Mumbai before going live.
- Keep user experience in mind, design clean, simple interfaces for complex systems: Don’t let blockchain complexity spill into the UI. Hide hash strings, show clear status messages, and make wallet connections easy. Users shouldn’t need to be blockchain experts.
- Stay updated with emerging tools and protocols for continuous improvement: The ecosystem changes fast. Subscribe to dev blogs, follow GitHub activity, and explore new SDKs, frameworks, and standards. Staying current can help you catch new vulnerabilities or efficiency gains early.
- Collaborate with experienced developers and auditors for peer reviews and audits: Blockchain development isn’t a solo sport. Bring in trusted peers to review your architecture and code. For production smart contracts, get formal audits from reputable firms.
Best Practices for Blockchain Software Development
Conclusion
Blockchain software development is reshaping how we build and secure digital systems. From finance to healthcare, gaming, and supply chain, its use cases keep growing, and so does the demand for skilled teams and reliable tools. Full-stack blockchain software development services now cover discovery workshops, audits, and 24-7 node maintenance, giving innovators a clear path from concept to scale.
Adopting blockchain in software development often starts with a small proof of concept, then grows quickly when results prove solid. A trusted blockchain development company publishes public audits, maintains transparent roadmaps, and guides you through every phase. If your organization is ready to explore or expand its blockchain ambitions, MOR Software is here to help. Contact us today and discover how our crypto development expertise can turn your vision into reality.
Rate this article
0
over 5.0 based on 0 reviews
Your rating on this news:
Name
*Email
*Write your comment
*Send your comment
1