Difference Between Machine Learning and AI: The 2025 Guide

Curious about the difference between machine learning and AI? You’re not alone. The tech world throws these terms around, and it’s easy to get caught in the buzz. If you’ve ever wondered what is the difference between machine learning and AI, or you’re just tired of seeing vendors treat them like twins, this MOR Software’s guide cuts through the noise.
Quick Answer – What’s the Real Difference?
Let’s not waste time. The difference between machine learning and AI comes down to scope. Artificial intelligence is the grand vision. Machines acting with ‘intelligence’ in a way that mimics humans. Machine learning is one technique that gets us there, built around finding patterns in data and learning from them.
Put simply: all machine learning is AI, but not all AI is machine learning. Think of AI as the whole toolbox, and machine learning as one tool inside. You’ll hear people use both terms for everything from spam filters to self-driving cars.
But if you want to explain the difference between machine learning and AI in one sentence: AI is the ambition; machine learning is the method.
What Is Artificial Intelligence?
Basic Definition and Origins
Artificial intelligence, or AI, is the idea that a machine can ‘think’ and solve problems in ways we usually associate with humans. The roots of AI stretch back to the 1950s, when computer scientists first dreamed of machines that could play chess, translate languages, or ‘understand’ speech.
Today, AI means much more than just playing games. At its core, AI covers any technology designed to mimic human reasoning, learning, or perception. That includes old-school rules-based systems, expert advisors, and even the friendly bot answering your questions on a retail website.

Key Capabilities of AI
What sets AI apart? It’s not just about ‘smart’ software. True AI aims for things like:
- Reasoning: Making choices, not just following scripts.
- Learning: Getting better with experience or feedback.
- Self-correction: Adjusting actions or suggestions when new info comes in.
You’ll find AI at work in robotics (think assembly lines or delivery drones), voice assistants like Alexa, and expert systems that crunch data for doctors or lawyers. Natural language processing (NLP) lets machines ‘understand’ text or speech, while computer vision helps them recognize faces or objects.
McKinsey’s latest survey shows 78% of companies already use AI in at least one business function, up from 72% just months earlier. This shows how fast these capabilities are spreading.
What Is Machine Learning?
Core Concept of Machine Learning
So, where does machine learning fit? It’s a subfield of AI, focused on one thing: helping computers ‘learn’ from data, so they can spot patterns or make predictions without being told exactly what to do every time.
Instead of relying on step-by-step instructions, basic machine learning uses algorithms to process piles of information. These algorithms get ‘trained’ on historical data. Over time, they spot trends and get smarter at making guesses or decisions.
If someone asks, is there a difference between machine learning and AI, just point to this: machine learning isn’t about imitating the full range of human intelligence. It’s about letting computers learn from examples, and then using what they’ve learned to solve specific problems.
That demand is real: according to Statista, the global machine-learning market is on track to reach $105.45 billion by 2025, more than double its size just a few years ago.
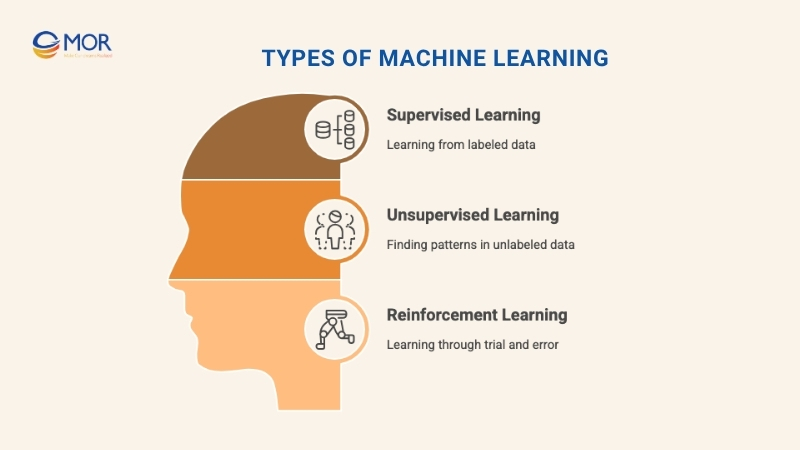
Types of Machine Learning
Machine learning comes in three main flavors:
- Supervised learning: The machine learning algorithms learns from labeled data (think: photos tagged as ‘cat’ or ‘dog’).
- Unsupervised learning: The system finds patterns in unlabeled data, such as grouping customers by shopping habits.
- Reinforcement learning: The machine learns through trial and error, improving with each attempt like teaching a robot to walk or a program to master chess.
Each type has its place, from recognizing spam emails to managing inventory or recommending movies.
Common ML Applications
You’ve probably seen machine learning in action, even if you didn’t realize it. Some everyday use cases include:
- Spam filters: Sorting your inbox, learning what to keep and what to junk.
- Recommendation engines: Suggesting what song to play next, or which product you might buy.
- Fraud detection: Flagging suspicious transactions at banks.
These aren’t just fancy tricks. Companies depend on machine learning to personalize your experience and protect your data. Often behind the scenes, with no fanfare.
This matters because, as Nielsen points out, 88% of people still trust recommendations from people they know. That’s exactly what good algorithms try to mimic.
Difference Between Machine Learning and AI: Key Comparisons
Let’s get to the nuts and bolts. We’ve broken down how the difference between machine learning vs AI plays out in real business and technology settings.
Goals and Capabilities
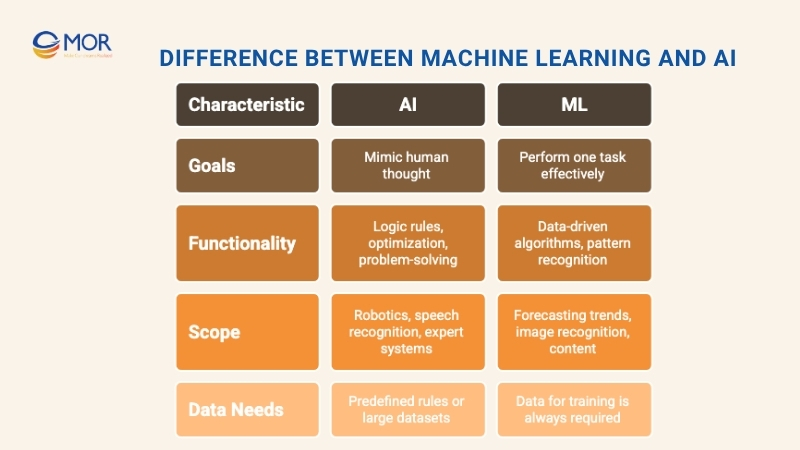
- AI aims to create machines that can reason, plan, or ‘think’ for themselves. The goal is to solve a broad range of problems, sometimes even outside the data the system was trained on.
- Machine learning is more focused: it wants to recognize patterns and make predictions, usually for a specific task. It’s less about ‘general’ intelligence, and more about doing one job very well.
How They Work
- AI can use a mix of rules, logic trees, optimization routines, and even creativity to reach its goals. Classic AI might follow a series of IF-THEN statements or complex decision maps.
- Machine learning relies on algorithms and statistical models that ‘learn’ from data. Feed it enough examples, and it starts to recognize patterns and adapt its answers.
Scope and Applications
- AI covers a wide area: robotics, speech recognition, expert systems, chatbots, and beyond.
- Machine learning is more specialized, powering predictive analytics, image classification, or personalized marketing.
Data Needs and Training
- AI systems might work from a set of rules (less data needed), or they might require big training datasets if they use learning-based techniques.
- ML always depends on data to train machine learning model. The more data you provide, the better it gets.
How AI and Machine Learning Compare in Real-World Use
Artificial Intelligence (AI) | Machine Learning (ML) | |
Scope | Broad, covers all ‘smart’ tech | Subset of AI, data-driven |
Objective | Mimic human intelligence | Learn from data to predict |
Data Needs | Can be rule-based or data-driven | Always needs lots of data |
Output | Reasoning, planning, perception | Predictions, classifications |
Common Tools | Logic, rules, NLP, robotics | Algorithms, neural nets, stats |
Use Cases | Chatbots, robots, voice assistants | Spam filters, recommendations |
Talent Needed | Broad AI, cognitive science, etc. | Data science, statistics |
How AI and Machine Learning Are Connected?
The relationship between AI and machine learning trips up a lot of people. The easiest way to remember? Machine learning and AI aren’t rivals. Instead, machine learning is just one approach for achieving AI.
Think of AI as the destination. There are many roads: machine learning, expert systems, rules-based logic, and more. Right now, machine learning is the busiest road because it delivers results.

Yet, you’ll find AI projects that don’t use machine learning at all (think classic chess programs), just as you’ll find machine learning used for tasks that don’t look much like ‘AI’ in the traditional sense.
Deep Learning and Neural Networks: A Step Further
Where Deep Learning Fits In
Let’s zoom in. Deep learning is a branch of machine learning that uses artificial neural networks with many layers (‘deep’ networks). These networks are inspired by how the human brain processes information, though nobody claims they work exactly the same way.
Deep learning has powered huge leaps in accuracy for image recognition, speech translation, and language understanding. It works best when you have massive amounts of data and strong computing power.
And this isn’t just hype. Bloomberg Intelligence expects generative AI to bring in $1.3 trillion annually by 2032, reflecting how valuable deep learning has become.

So, if you’re comparing the difference between machine learning and AI and deep learning, the answer is layered: deep learning is part of machine learning, which is part of AI.
Real-World Examples
- Image recognition: Your phone’s photo app groups pictures by faces using deep learning.
- Voice assistants: Siri and Alexa ‘understand’ your speech, thanks to deep neural networks.
- Autonomous vehicles: Self-driving cars use deep learning to spot signs, lanes, and hazards in real time.
Real-World Applications: AI and Machine Learning at Work
AI and machine learning aren’t just tech buzzwords. They drive real business value when used right.
- Banking: Banks use machine learning for fraud detection, scanning millions of transactions to flag anything suspicious. AI-Driven Banking chatbots handle customer queries 24/7.
- Healthcare: Machine learning helps doctors read medical scans, predict disease risk, and suggest treatments. AI systems streamline hospital operations or monitor patients remotely.
- eCommerce: Ever get a product suggestion that’s almost scary-accurate? That’s machine learning analyzing your browsing and purchase history. AI personalizes your shopping, speeds up support, and even runs warehouse robots.
- Manufacturing: AI-powered robots assemble products, inspect quality, and keep lines moving. Predictive maintenance powered by machine learning keeps machines from breaking down.

Not only that, ‘behind-the-scenes’ algorithms work hand-in-hand with customer-facing AI. Think of Spotify’s recommendations: when you listen to a song, machine learning suggests your next favorite, while AI powers the virtual assistant that helps you search.
Or take fraud prevention in banks. Machine learning flags unusual activity. AI systems can step in to interact with customers, resolve issues, or escalate to a human if needed.
Why Understanding the Difference Matters for Your Business?
Knowing the difference between machine learning and AI isn’t just academic. It saves money, guides hiring, and helps you pick the right partners.
- Vendors may label everything as ‘AI’ when it’s just basic machine learning
- Choosing the right solution depends on your goal: ML fits personalization, forecasting, and automation, while AI handles reasoning, decision-making, and human-like interaction
- Hiring gets clearer: ML projects need data scientists, while AI may call for experts in robotics, linguistics, or cognitive science
- The real win comes from matching the right tool to the right problem. Get it wrong, and you risk wasting time, talent, and budget
TechCrunch reports that venture capitalists funneled nearly 70 billion USD into North American AI and ML startups during the first four months of 2025, a signal that savvy investors draw the same distinction you do.
Conclusion
The difference between machine learning and AI keeps coming up for a reason. If you want smarter tech for your business, you need to know what you’re getting and what you actually need. Machine learning brings the data muscle, helping systems adapt and predict. AI is the bigger goal, bringing intelligence and automation into real-world workflows.
Ready to make smarter choices? Contact MOR Software’s experts and start turning buzzwords into business wins. Looking for more? Check out the MOR homepage or dive into our AI & ML app solutions. The future belongs to teams who know the difference, and know how to use it.
MOR SOFTWARE
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Are all AI models based on deep learning?
Not at all. Deep learning is one approach, popular for complex data like images or speech, but many AI systems don’t use neural networks at all.
Is machine learning the same as AI?
No. All machine learning is AI, but not all AI is machine learning. AI is the broader field; machine learning is a specialized branch.
Can you have AI without machine learning?
Yes. Classic AI systems (like chess programs or expert systems) use rules and logic without any learning from data.
So what’s the main difference for decision-makers?
The difference between machine learning and AI comes down to breadth and technique. AI is the umbrella. Machine learning is one tool underneath. Make sure your vendors and your team know which you’re talking about.
Rate this article
0
over 5.0 based on 0 reviews
Your rating on this news:
Name
*Email
*Write your comment
*Send your comment
1