Hybrid Cloud Strategy: Complete Guide To Benefits And Deployment
Is your business looking for a more flexible and cost‑efficient approach to IT infrastructure? A well‑designed hybrid cloud strategy can be the key to balancing performance, scalability, and security. In this guide, MOR Software explores the benefits, challenges, and best practices for implementing this combined strategy effectively, helping enterprises maximize the value of their technology infrastructure.
What Is A Hybrid Cloud Strategy?
A hybrid cloud strategy is a comprehensive plan to deploy and manage a hybrid cloud environment. It combines private cloud and public cloud resources to leverage the advantages of both. Private cloud is used for sensitive data and mission‑critical workloads, while public cloud handles scalable operations, helping organizations optimize costs, improve flexibility, and maintain strong security.
Example: An e‑commerce platform stores customer information in a private cloud for security, while using public cloud resources during seasonal sales to manage high traffic and ensure smooth performance.

What Is A Hybrid Cloud Strategy?
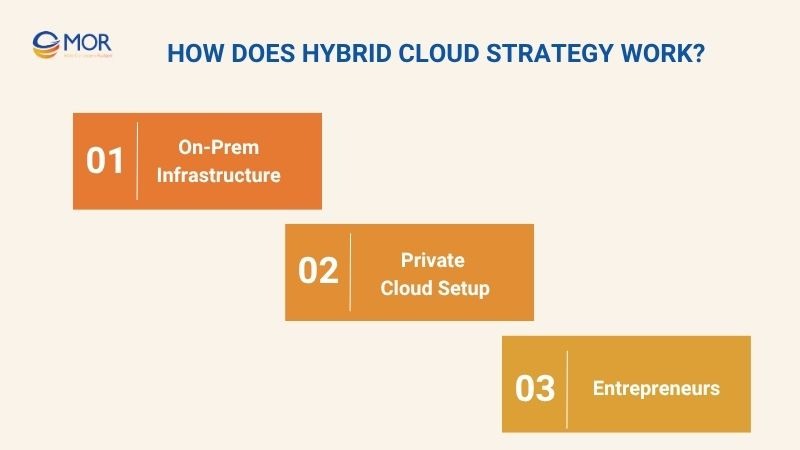
How Does Hybrid Cloud Strategy Work?
To ensure a hybrid cloud strategy operates effectively, organizations must coordinate several key components seamlessly. Below are the essential factors for this strategy to maximize performance and meet critical security requirements.
On‑Prem Infrastructure
In a hybrid cloud strategy, on‑prem infrastructure refers to the IT systems located within an organization’s internal data center. This model allows businesses to store and process sensitive data on‑site, ensuring security, direct control, and compliance requirements.
When combined with private cloud and public cloud, on‑prem infrastructure helps create a flexible environment: critical workloads are processed on‑site, while tasks requiring rapid scaling or cost optimization can be moved to the cloud.
This is a key factor that enables a hybrid cloud strategy to both optimize performance and maintain data security.
Private Cloud Setup
In a hybrid cloud strategy, the private cloud is a cloud environment deployed exclusively for a single organization. The private cloud offers full control and high security, making it especially suitable for:
- Workloads containing sensitive data: Finance, healthcare, and personal information.
- Applications requiring strict compliance: according to standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, or ISO.
- Systems that demand stable performance and low latency.
A private cloud can be deployed on existing on‑prem infrastructure or at the data centers of hybrid cloud providers, depending on security needs, budget, and expansion strategy. Combining the private cloud with the public cloud creates a balance between flexibility and security within the overall strategy.
Public Cloud Services
The public cloud is a crucial component in a hybrid cloud strategy thanks to its ability to provide flexible resources, rapid scalability, and cost efficiency. Businesses can leverage the public cloud to:
- Deploy workloads with seasonal spikes or sudden expansion needs.
- Test and develop new services without large investments in on‑prem infrastructure.
- Optimize operating costs through a pay‑as‑you‑go model.
The public cloud is offered by hybrid cloud providers and links to private cloud and on‑prem infrastructure via connectivity and policy‑based management. This integration helps businesses maximize overall performance while maintaining security and compliance.
How Does Hybrid Cloud Strategy Work?
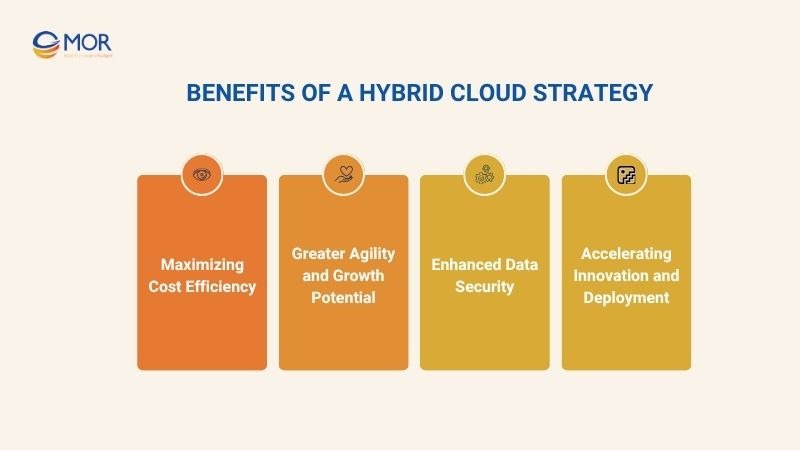
Benefits Of A Hybrid Cloud Strategy
A hybrid cloud strategy offers businesses a range of practical benefits. This section will explore the key advantages that this strategy brings to business operations and growth.
Maximizing Cost Efficiency
One of the biggest advantages of a hybrid cloud strategy is its ability to optimize operational costs. Stable workloads with high security requirements run in a private environment.
Tasks that require rapid scaling or are highly variable are moved to the public cloud. This allocation helps reduce initial capital investment. At the same time, businesses can maintain reasonable operating costs and minimize wasted resources.
Greater Agility and Growth Potential
A hybrid cloud strategy gives businesses the flexibility to respond to market changes. Combining private infrastructure with public cloud services allows resources to scale up or down quickly as needed.
This adaptability enables businesses to expand operations, explore new markets, and drive sustainable growth. In addition, 67% of companies using hybrid cloud report higher innovation levels and faster product deployment compared to traditional approaches.
Enhanced Data Security
Data security is always a top priority in any technology environment. According to surveys, 78% of IT professionals believe that hybrid cloud provides better security than public cloud alone.
A hybrid cloud strategy helps businesses strengthen data protection. Sensitive data can be stored and processed in a private cloud or on‑prem infrastructure, where strict controls and security policies are applied.
Accelerating Innovation and Deployment
A hybrid cloud strategy enables businesses to test, develop, and deploy new solutions more quickly.
Once finalized, applications can be officially deployed on the private cloud or across multiple environments to optimize performance. This flexibility shortens time‑to‑market and supports continuous innovation to maintain a competitive edge.
Benefits Of A Hybrid Cloud Strategy
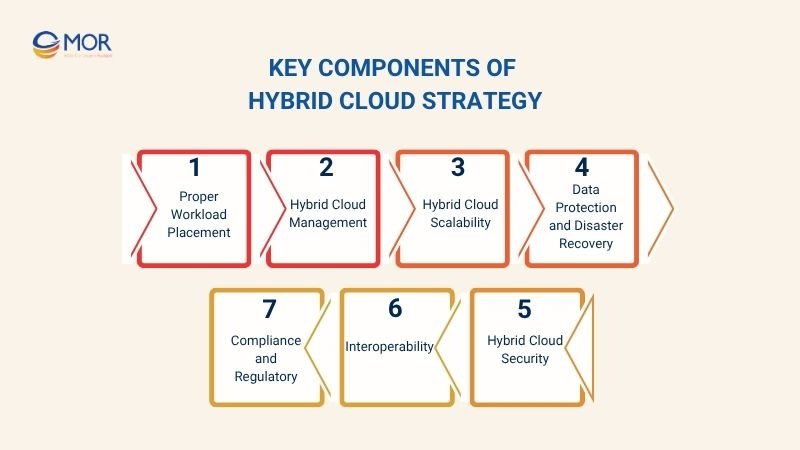
Key Components Of Hybrid Cloud Strategy
To maximize the effectiveness of a hybrid cloud strategy, businesses must focus on the core components during the design and operation process. Below are the key factors that determine the success of this strategy.
Proper Workload Placement
In a hybrid cloud strategy, proper workload placement directly impacts performance, cost efficiency, and security. Each type of workload has its requirements in terms of resources, data sensitivity, and compliance standards.
For example, an e‑commerce business may host its payment systems and customer data on a private cloud to ensure compliance with PCI DSS. Meanwhile, its marketing website and seasonal promotion campaigns can run on a public cloud to take advantage of flexible scalability and reduce pressure on internal infrastructure.
Hybrid Cloud Management
In a hybrid cloud strategy, management plays a central role in ensuring the entire architecture operates efficiently and consistently. Management goes beyond basic resource tracking. It also includes workload orchestration, cost control, and keeping different deployment environments synchronized.
Weak management can lead to inefficient resource usage, unexpected cost spikes, and degraded service performance. To address this, enterprises should adopt integrated management platforms for centralized monitoring.
Hybrid Cloud Scalability
Scalability ensures that resources can be quickly scaled up to handle peak traffic. It can also be scaled down during low‑demand periods to avoid resource waste and maintain high performance.
The ability to dynamically scale workloads between environments is one of the key advantages of a hybrid cloud. This capability helps businesses balance cost efficiency with operational agility.
Data Protection and Disaster Recovery
In a hybrid cloud strategy, data protection and disaster recovery are critical for ensuring uninterrupted business operations. Data protection safeguards sensitive information from system failures or cyberattacks, while disaster recovery restores systems quickly after major incidents.
According to industry reports, nearly 80% of businesses using cloud‑based disaster recovery solutions report significantly reduced downtime. Without a clear strategy, organizations risk losing critical data and suffering severe financial and reputational damage.
Hybrid Cloud Security
Security is a foundational element of any hybrid cloud strategy. Without robust security layers, a hybrid environment can be vulnerable to attacks, data breaches, and loss of customer trust.
To maintain strong protection, enterprises should implement strict access control, real‑time monitoring, and adopt the latest security standards. Effective security measures not only minimize risks but also strengthen trust in the overall hybrid cloud infrastructure.
Interoperability
Poor compatibility can lead to system conflicts, management difficulties, and disrupted data flows. To mitigate these risks, enterprises should prioritize solutions that support open standards and strong API integrations. Regular testing is also essential to ensure seamless operation across all hybrid environments.
Compliance and Regulatory
Compliance is essential in any enterprise hybrid cloud strategy, especially for organizations in multiple jurisdictions or regulated industries.
For example, a multinational bank must comply with regulations such as GDPR, CCPA, and PCI DSS. Its hybrid setup stores EU customer data in GDPR‑compliant centers, while payment data runs in PCI DSS‑compliant environments.
Key Components Of Hybrid Cloud Strategy
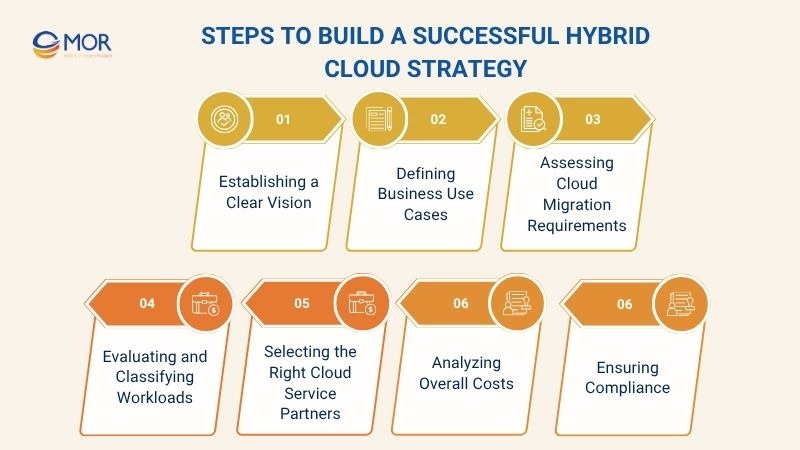
Steps To Build A Successful Hybrid Cloud Strategy
To implement a hybrid cloud strategy successfully, enterprises must follow a well‑defined process. Below are the key steps that ensure the strategy is effective and delivers measurable value to the business.
Establishing a Clear Vision
A clear vision helps enterprises set long‑term objectives and balance performance, cost, and security in their hybrid cloud strategy. This vision should answer key questions:
- What does the business want to achieve with hybrid cloud?
- Is the primary goal cost optimization, scalability, or regulatory compliance?
Identifying these priorities eliminates unsuitable deployment directions and focuses resources on areas that deliver the greatest impact.
Defining Business Use Cases
For a hybrid cloud strategy to deliver real value, enterprises must define each business use case clearly instead of setting vague objectives.
For example: A financial organization may use hybrid cloud to process real‑time transactions. Leveraging the scalability of public cloud during peak demand while storing customer data in an encrypted, compliance‑ready private environment.
Each use case should outline performance requirements, latency thresholds, and security needs to design the right architecture.
Assessing Cloud Migration Requirements
Assessing migration requirements goes beyond creating an application and data inventory. It also involves analyzing interdependencies between systems.
For example, if an e‑commerce website is connected to an on‑premises inventory system, migrating it to the cloud requires a plan to keep data exchange smooth. Businesses should also choose the right migration method - “lift‑and‑shift” for minimal changes, or “refactor” for better cloud performance.
Evaluating and Classifying Workloads
Classifying workloads in a hybrid cloud strategy requires a clear evaluation matrix. Each workload should be assessed based on resource consumption (CPU, RAM, IOPS), security requirements (encryption, access control), data sensitivity, and traffic variability.
The classification results identify which workloads are best suited for public, private, or multi‑cloud deployments. This ensures both optimal performance and long‑term cost efficiency.
Selecting the Right Cloud Service Partners
Selecting cloud partners is not just about choosing well‑known vendors. Enterprises should review the provider’s Service Level Agreement (SLA) and API integration support.
Analyzing Overall Costs
Analyzing hybrid cloud costs should follow the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) approach, which includes both direct costs (infrastructure services, storage, bandwidth) and indirect costs (management, security, staff training).
Businesses must also account for potential expenses such as data egress charges and integration of multi‑environment management tools. The financial plan should include a 3–5 year cost optimization scenario, not just the initial deployment phase.
Ensuring Compliance
Ensuring compliance in a hybrid cloud strategy requires integrating regulatory standards into the architecture from the design stage. Enterprises should map data according to jurisdiction, implement encryption that meets required standards (AES‑256, TLS 1.3), and automate compliance reporting.
Steps To Build A Successful Hybrid Cloud Strategy
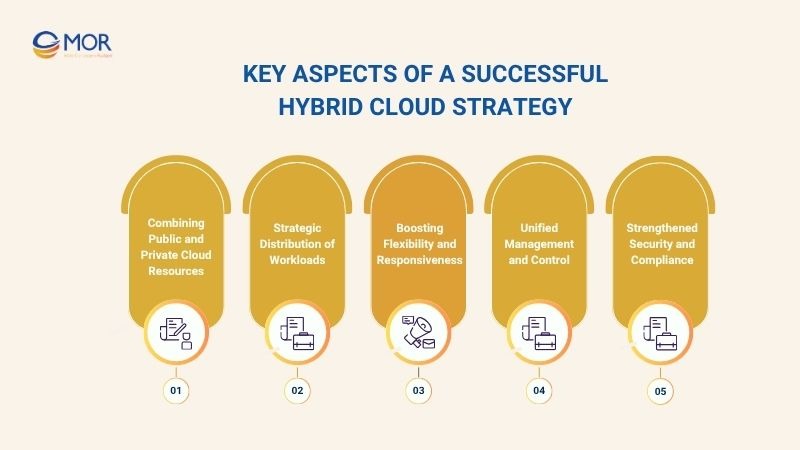
Key Aspects Of A Successful Hybrid Cloud Strategy
For a hybrid cloud strategy to succeed, enterprises must focus on key factors that optimize performance and sustain competitive advantage. Below are the critical aspects that ensure the system operates with flexibility and long‑term efficiency.
Combining Public and Private Cloud Resources
In an effective hybrid cloud strategy, combining public cloud and private cloud goes beyond simply assigning workloads based on security levels. The focus lies in designing an integrated architecture that allows both environments to operate as a unified system.
- Development and testing can run on the public cloud to leverage rapid scalability.
- Production workloads are hosted on the private cloud to maintain security and stability.
- Connectivity is established through an API gateway or VPN, ensuring smooth and continuous data flow.
- Access is synchronized with SSO and MFA to enhance protection.
This approach allows both environments to complement each other instead of functioning in isolation.
Strategic Distribution of Workloads
In a hybrid cloud strategy, strategic workload distribution plays a critical role in ensuring performance and optimizing costs. Instead of assigning workloads solely based on data sensitivity, allocation should consider the processing characteristics of each system.
For example: During a new product launch, marketing workloads and AI customer feedback analysis can run on the public cloud for rapid scaling.
Once operations stabilize, workloads can be shifted back to the private cloud for long‑term cost optimization.
Boosting Flexibility and Responsiveness
In a hybrid cloud strategy, flexibility means the system can quickly adapt to business needs, while responsiveness refers to the ability to react promptly to new situations.
By combining public and private cloud resources, enterprises can scale resources up or down rapidly and deploy new applications without interrupting operations. This ensures service continuity while enabling the business to respond to market changes immediately.
Unified Management and Control
In a hybrid cloud strategy, unified management allows enterprises to control all environments from a single platform rather than handling each one separately.
A centralized management solution provides complete visibility over performance, costs, and security across both public and private cloud environments. This integrated control simplifies operations, reduces risks, and improves overall efficiency.
Strengthened Security and Compliance
In a hybrid cloud strategy, security is not just about adding firewalls or encrypting data. It requires a proactive approach. Instead of securing each environment separately, enterprises should establish a unified security policy that applies consistently across both public and private cloud.
For compliance, instead of quarterly checks, enterprises can integrate real‑time compliance scanning tools. This allows immediate alerts if, for example, European customer data is accidentally stored on servers outside the EU, enabling corrective action before GDPR violations occur.
Key Aspects Of A Successful Hybrid Cloud Strategy
Challenges To Overcome With A Hybrid Cloud Strategy
During the implementation of a hybrid cloud strategy, enterprises often face a range of challenges. Below are the most common obstacles an enterprise hybrid cloud strategy must address to ensure optimal performance.
Managing Diverse Cloud Infrastructure
Each environment often comes with its own technologies, management tools, and interfaces, which can lead to infrastructure fragmentation.
To address this, organizations should adopt a unified management platform that provides centralized monitoring of performance, security, and costs across all environments. Standardizing deployment processes and leveraging API integration can help align infrastructure and ensure a seamless hybrid multi cloud strategy.
Addressing Legacy System Dependencies
In an enterprise hybrid cloud strategy, legacy systems often become roadblocks because they are not fully compatible with modern cloud platforms. This can create challenges in integration, maintenance, and performance optimization.
To overcome this, enterprises can use containerization or API wrapping to bridge legacy systems with modern cloud platforms. These methods enable older systems to operate within a hybrid multi cloud strategy without major disruptions or costly full migrations.
Handling Rapid Data Growth
A hybrid cloud strategy enables enterprises to scale storage flexibly. However, the rapid growth of data remains a significant challenge. Distributing storage across multiple cloud environments and on‑premises infrastructure can complicate management, security, and cost optimization.
An effective approach is data tiering: frequently accessed data is stored on high‑performance environments such as public cloud, while infrequently accessed data is moved to lower‑cost options such as private cloud or cold storage.
Coping with Hardware Shortages
A hybrid multi cloud strategy reduces dependency on a single physical environment. However, when on‑premises resources such as servers or storage face hardware shortages, operations can still be disrupted.
Enterprises can leverage cloud bursting to handle spikes in demand. Standardizing infrastructure configurations and automating deployment processes further reduces the pressure on in‑house hardware upgrades and ensures consistent availability.
Mitigating Cybersecurity Risks
In a hybrid cloud strategy, data and applications are distributed across multiple environments, expanding the attack surface. While 78% of organizations believe hybrid cloud provides better security compared to public cloud alone, the distributed nature of systems introduces additional complexity.
To mitigate risks, enterprises should implement a unified security framework that includes end‑to‑end encryption (e.g., AES‑256, TLS 1.3), multi‑factor authentication (MFA), continuous monitoring, and automated threat detection.
Integrating compliance automation tools helps ensure adherence to standards such as GDPR and PCI DSS, reducing both security and legal risks in an enterprise hybrid cloud strategy.

Challenges To Overcome With A Hybrid Cloud Strategy
Set Up A Hybrid Cloud Strategy With MOR Software
At MOR Software, we develop a hybrid cloud strategy tailored to each enterprise, ensuring flexibility, security, and performance that align with specific business needs. Rather than applying a one‑size‑fits‑all model, we optimize infrastructure and application distribution to meet both current demands and future growth.
Key advantages of implementing a hybrid cloud strategy with MOR Software:
- Architecture design based on real business needs: Customized for each industry and growth objective.
- Smart resource allocation: Assigning the right environment for each workload to maximize performance and cost efficiency.
- Seamless legacy system integration: Using containerization, API gateways, and middleware to connect existing systems with modern platforms.
- Centralized management: Monitoring performance, costs, and security for the entire infrastructure from a single control panel.
- Enhanced security and compliance: Implementing full data encryption, multi‑layer authentication, and adherence to ISO 27001, GDPR, PCI DSS.
- Rapid scalability: Automatically adjusting resources up or down to maintain service stability as demand changes.
In Conclusion
A well‑planned hybrid cloud strategy is essential for businesses seeking to maintain a competitive edge. MOR Software partners with enterprises to design, deploy, and manage hybrid cloud infrastructures that ensure performance, security, and compliance at scale. Contact MOR Software today to start building a strategy that drives your business forward!
Rate this article
0
over 5.0 based on 0 reviews
Your rating on this news:
Name
*Email
*Write your comment
*Send your comment
1