Cloud Computing in Healthcare: Benefits, Risks & Uses in 2025

Managing data, improving care, and staying compliant. It’s a lot to juggle. That’s why more providers are turning to cloud computing in healthcare to simplify operations and scale smarter. From system integration to AI-powered diagnostics, this technology is reshaping how care gets delivered. In this guide, MOR Software will break down the benefits, risks, and real-world uses of cloud computing in healthcare industry, and show how your team can make the shift with confidence.
What is Cloud Computing in Healthcare?
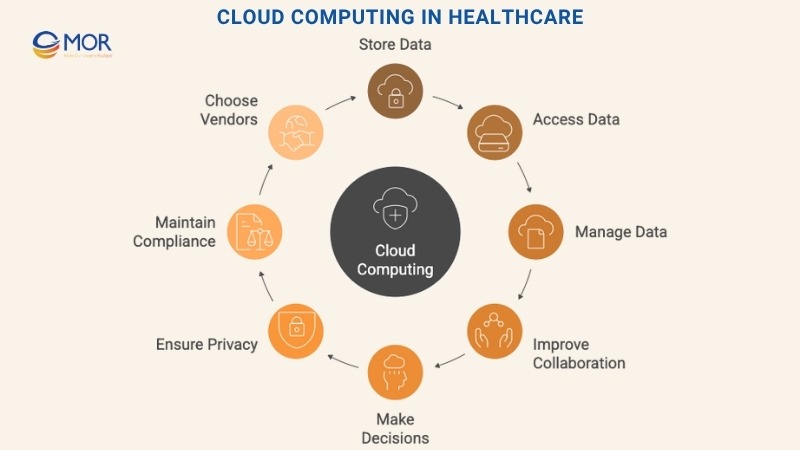
Cloud computing in healthcare means using internet-based platforms to store, access, and manage patient information instead of relying on local servers. This includes everything from electronic medical records (EMRs) to high-resolution medical images.
With this model, doctors, nurses, and administrators can reach critical data from any connected device, whether they’re in the hospital or off-site. It enables smoother collaboration across teams and faster decision-making during patient care.
By adopting cloud technology in healthcare, organizations gain scalable infrastructure that adjusts to growing data needs. It also opens the door for integrated systems, real-time analytics, and remote care tools.
Still, while the benefits of cloud computing in healthcare are compelling, lower hardware costs, improved access, and smarter workflows, It’s not without challenges. Providers need to address data privacy, compliance risks, and vendor reliability to make it work effectively.
What is Cloud Computing in Healthcare?
Cloud Computing in Healthcare Market Insights for 2025
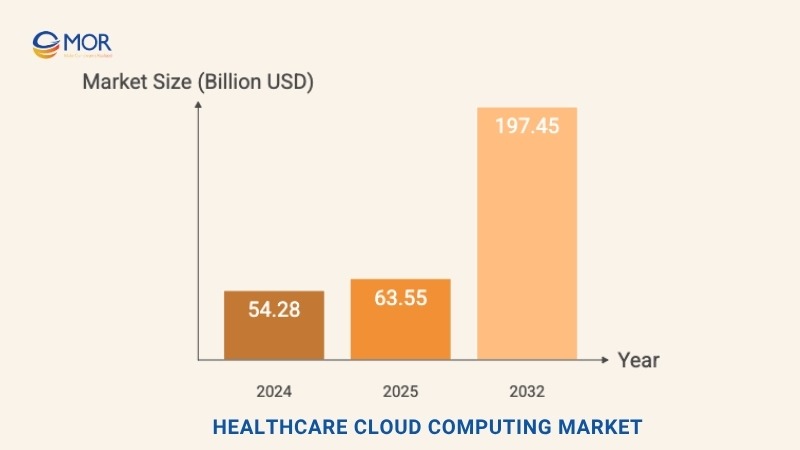
The demand for cloud computing in healthcare continues to grow fast in 2025, with the global market reaching $63.55 billion. Forecasts suggest this figure could climb to $197.45 billion by 2032, rising at a CAGR of 17.6%.
A recent HIMSS survey reports that more than 82% of healthcare providers have already moved operations to the cloud. The surge is driven not just by storage needs but by the rise of SaaS platforms, which power everything from scheduling systems to cloud-based healthcare apps with real-time analytics and chatbot integration.
These cloud-based solutions are also fueling innovation in remote patient monitoring, Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) devices, and mobile-first care delivery. A study shows that using cloud services led to a 43% drop in reported security incidents.
Beyond that, healthcare providers are doubling down on emerging tech like AI, machine learning, blockchain, and IoT. Hospitals and clinics are rolling out robotic process automation and encrypted data sharing powered by cloud tools.
The cloud computing in healthcare industry is also closely tied to blockchain growth, with projections showing the market jumping from $831.54 million in 2024 to nearly $179 billion by 2034, led by U.S. adoption.
Differences Between Cloud Computing in Healthcare and Traditional On-premise Systems
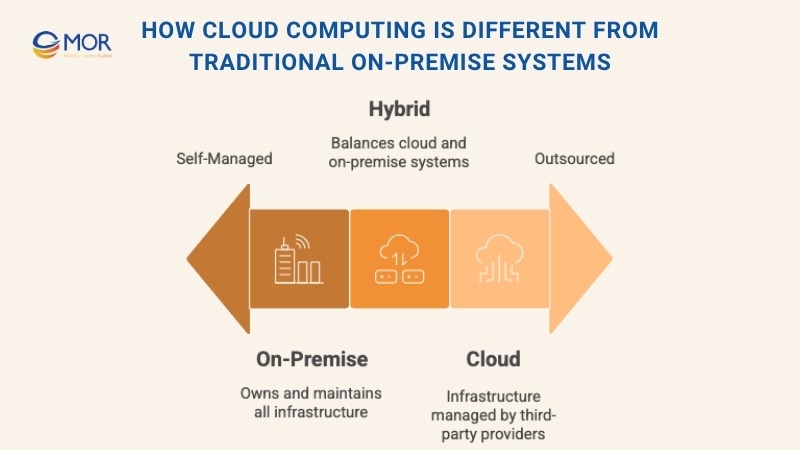
When comparing cloud computing in healthcare to traditional on-site IT setups, the biggest differences lie in how resources are managed and paid for. With legacy systems, healthcare facilities must invest heavily in their own servers, software, and IT staff to keep everything running on-site.
In contrast, cloud and healthcare models shift the infrastructure burden to external providers. These platforms are accessed through online subscriptions or usage-based pricing, removing the need for hospitals to own and maintain physical hardware.
The benefits go beyond cost savings. Cloud-based systems offer better reliability, faster recovery in case of failure, and easy access to patient data from anywhere with an internet connection. IT teams can shift their focus from maintenance to strategic improvements.
That said, most providers today don’t rely entirely on one system. A hybrid model, mixing cloud services with existing on-premise infrastructure, is often used to meet varying performance, storage, and compliance requirements.
Choosing the right setup depends on factors like data privacy, workload type, and how fast the organization needs to scale.
Differences Between Cloud Computing in Healthcare and Traditional On-premise Systems
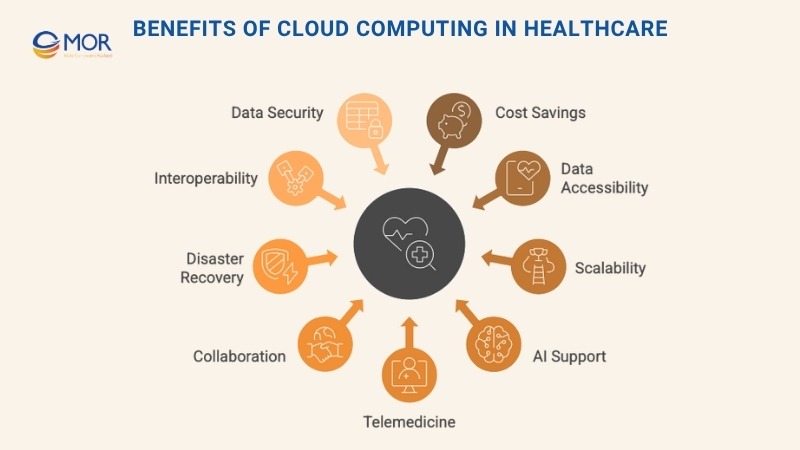
Key Benefits of Cloud Computing in Healthcare
Adopting cloud computing in healthcare offers more than just a shift in infrastructure. It opens the door to better care delivery, faster data access, and smarter use of resources. Below are some of the most impactful benefits healthcare organizations experience when moving to the cloud.
Key Benefits of Cloud Computing in Healthcare
Cost Savings Through Pay-as-you-Go Models
One of the biggest advantages of cloud computing in healthcare is its ability to lower costs. Rather than spending heavily upfront on hardware and maintenance, providers pay only for the resources they use.
Studies suggest that cloud technology in healthcare can reduce IT-related expenses by up to 30% compared to traditional systems. This shift eliminates capital spending on servers, frees up physical space previously used for equipment, and cuts down on in-house IT labor.
With this model:
- There’s no need to maintain bulky infrastructure
- Costs scale based on usage
- Fewer full-time IT specialists are required
- More facility space can be dedicated to patient care
Improved Data Accessibility
Cloud-based healthcare platforms make it easier for both medical professionals and patients to access essential information.
Providers can instantly retrieve electronic medical records (EMRs), imaging files, and lab results from any secure device. That means fewer delays, quicker diagnoses, and better-informed decisions.
Patients also benefit by viewing their own test results and doctor notes through online portals, giving them more control over their health journey.
Scalability for Growing Needs
Healthcare systems often experience unpredictable spikes in demand. With cloud infrastructure, services can expand or contract as needed without delays or costly overhauls.
This flexibility proved essential during the COVID-19 pandemic, when overwhelmed systems had to scale fast. Cloud-based setups allowed many public health departments to respond in real time and maintain uptime under pressure.
This kind of scalability makes cloud computing in healthcare especially valuable for handling growing patient databases and expanding service coverage.
Support for AI and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning thrive on large datasets, which is where cloud computing shines. With scalable power and storage, healthcare organizations can apply advanced algorithms to clinical and operational data.
Some real-world applications include:
- Early disease detection using image analysis
- Predictive models that identify patient risk
- Automated transcription and documentation using natural language processing
Companies like Philips are already using platforms like AWS to develop and launch new AI-driven tools faster, showing how cloud and healthcare work together to advance diagnostics and treatment planning.
Enhanced Telemedicine and Remote Care Delivery
Cloud computing in healthcare has made remote care more scalable, stable, and responsive. Virtual visits, remote diagnostics, and chronic condition monitoring are all supported through cloud-based telehealth platforms. These systems became essential during the COVID-19 pandemic and they’ve stayed that way since.
Today, many platforms connect directly with wearable devices like smartwatches and glucose sensors. This lets healthcare teams view real-time health data, track symptoms, and act faster when patients need help.
Cloud-integrated AI chatbots take it even further. They deliver health tips, behavior reminders, and sleep insights automatically, offering helpful guidance without increasing staff workload.
Modern telehealth platforms now commonly include:
- Live video consultations
- Remote patient monitoring dashboards
- Integration with wearables and mobile apps
- Secure, HIPAA-compliant communication and data exchange
Together, these tools support personalized care, stronger engagement, and better outcomes, without needing a clinic visit.
Better Collaboration Across Healthcare Teams
Cloud computing in healthcare makes it easier for providers to work together, no matter where they’re located. Doctors, nurses, and specialists can access and update patient records in real time, cutting delays and reducing errors.
Instead of juggling paper charts or siloed systems, care teams collaborate through shared dashboards, secure chat, and built-in video tools. This speeds up treatment planning and improves consistency in patient care.
The American Medical Association reports that 85% of physicians believe secure cloud messaging improves how they exchange clinical information. It’s not just faster. It’s safer and more coordinated.
Cloud-based EHR platforms now let providers:
- Track patient recovery across visits
- Manage medications and appointment schedules
- Communicate securely within and between care teams
- Support both in-clinic and mobile health workers
With the right infrastructure, collaboration becomes smoother and more secure.
Improved Disaster Recovery and Data Backup
One of the standout benefits of cloud computing in healthcare is its ability to keep services running even during unexpected failures. When disaster strikes, whether it’s a power outage, cyberattack, or natural event, cloud-based backups keep critical data protected and accessible.
Unlike traditional systems that depend on manual recovery, modern cloud platforms use automated processes and redundant data centers located in different regions. If one site fails, another takes over with minimal disruption.
For example, Southeast Iowa Regional Medical Center cut its recovery time by 67% after migrating its EHR system to AWS. That kind of result shows how cloud-based healthcare systems support faster, more reliable recovery, without the downtime.
Enhanced Interoperability Between Systems
A persistent issue in healthcare is disconnected data. Different departments, clinics, and systems often can’t share records smoothly. That’s where cloud technology in healthcare stands out.
By using centralized, cloud-based platforms, healthcare providers can unify data across various systems, making it easier to coordinate care. The result? Smoother workflows, fewer repeated tests, and a better overall patient experience.
Cloud interoperability tools also support API integration, enabling seamless data exchange between old systems and new apps, no more siloed platforms slowing things down.
Strengthened Data Security
Keeping patient data safe is non-negotiable. Cloud computing in healthcare now comes with security built into every layer, data encryption, strict access controls, user authentication, and continuous system monitoring.
Leading cloud platforms are designed to meet HIPAA and GDPR requirements, helping healthcare organizations store and manage Protected Health Information (PHI) securely. Centralized dashboards and real-time alerts give IT teams the visibility to detect and address threats before they become incidents.
Whether it’s a hospital system or a digital health app, cloud-based systems make it possible to safeguard sensitive records while still enabling remote access and rapid collaboration. With the right architecture in place, security and cloud scalability go hand in hand.
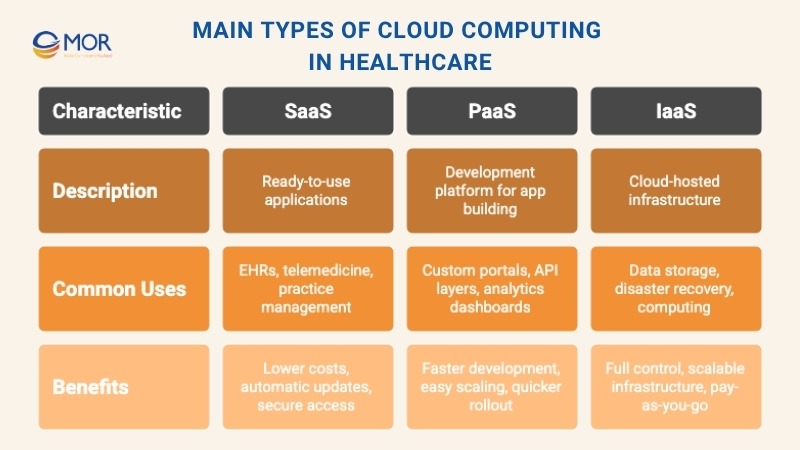
Main Types of Cloud Computing in Healthcare
There are three main models of cloud computing in healthcare, each designed to serve different needs within medical environments: SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS. These service layers help healthcare providers handle everything from patient care tools to backend systems more efficiently.
Main Types of Cloud Computing in Healthcare
SaaS (Software as a Service)
SaaS delivers fully developed applications over the internet, which are hosted and updated by external vendors. Providers simply log in to use the software, no installations or server maintenance needed.
Use cases in healthcare cloud computing companies include:
- Electronic Health Records (EHRs): Clinicians can securely access and update patient files from anywhere.
- Telemedicine platforms: Enable virtual consultations and remote monitoring, reducing physical appointments.
- Practice management tools: Simplify billing, scheduling, and admin workflows.
Benefits:
- Lower upfront investment, since no on-site hardware is required
- Automatic updates with no disruption to care
- Secure access across different devices and locations
PaaS (Platform as a Service)
PaaS gives developers a ready-to-use cloud environment to create and launch custom apps without worrying about servers or networking. This is useful for hospitals building specialized tools or connecting existing systems.
Healthcare applications include:
- Custom patient portals and appointment tools
- Interoperability layers using APIs to connect different systems
- Analytics dashboards powered by patient data
Benefits:
- Speeds up development and testing cycles
- Grows with usage demands without infrastructure upgrades
- Supports quicker launches of digital health tools
IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)
IaaS offers on-demand computing infrastructure, virtual machines, storage, and networks, managed through the cloud. Hospitals can install their own software while outsourcing the hardware layer.
Examples in the cloud computing in healthcare industry:
- Storing and backing up large datasets like imaging files or research data
- Disaster recovery systems that kick in during hardware failure
- High-performance computing (HPC) for areas like genomics or AI-powered diagnostics
Benefits:
- Greater control over software and security settings
- Scalability without expensive server purchases
- Reduced capital expenses with pay-as-you-use billing
Each of these types of cloud computing in healthcare plays a vital role in helping providers modernize their operations, scale services quickly, and deliver care more efficiently.
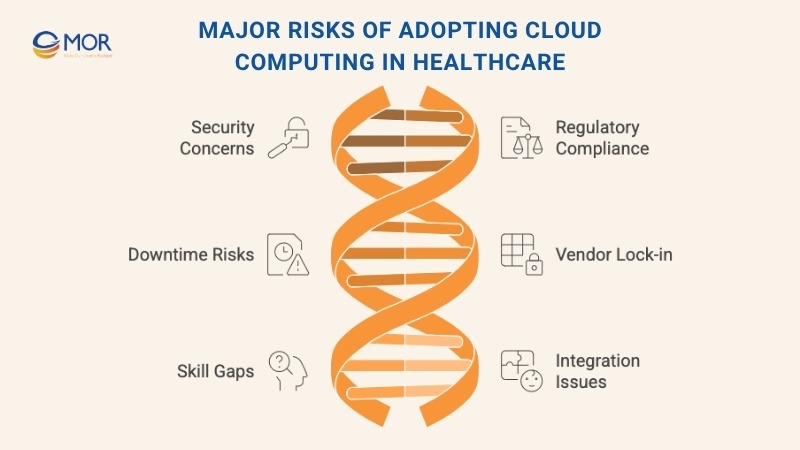
Major Risks of Adopting Cloud Computing in Healthcare
While cloud computing in healthcare continues to unlock huge potential, it doesn’t come without complications. As more providers shift to the cloud, concerns around security, compliance, and technical complexity have become more urgent. Let’s break down some of the most pressing risks.
Major Risks of Adopting Cloud Computing in Healthcare
Data Breaches and Unauthorized Access
Security remains the top reason healthcare leaders hesitate to fully embrace public cloud services. A recent study found that 71% of organizations had to revert some cloud-based applications to on-premise environments due to cybersecurity concerns.
And the stakes are high. On average, each breach in the cloud computing in healthcare industry costs roughly $6.45 million, far more than in most other sectors.
Compliance with HIPAA and GDPR
Regulatory compliance is another minefield. Both HIPAA and GDPR impose strict requirements, but they don’t always align.
HIPAA gives 60 days for breach notification, while GDPR requires it within 72 hours. GDPR allows patients to request full data erasure, whereas HIPAA mandates long-term record retention. This legal friction creates serious challenges for organizations that operate across regions or serve international patients.
To stay compliant, healthcare providers must conduct full-scale risk assessments and put strong safeguards in place, even though no cloud vendor can be officially HIPAA-certified.
Downtime and Connectivity Disruptions
Unlike on-premise setups, cloud based healthcare systems depend on consistent internet access. A network outage, even for a few minutes, can jeopardize patient safety, especially during surgery or ICU monitoring.
For context, every minute of downtime costs providers around $7,900.
In one notable case, Oracle Health experienced a five-day outage due to a maintenance error, disrupting care across several hospitals. Remote areas with low bandwidth may also struggle to run cloud-hosted systems efficiently.
While edge computing can help, hybrid models introduce new layers of technical complexity.
Vendor Lock-in and Migration Barriers
Choosing a single cloud vendor might simplify things at first, but it can backfire later. Proprietary systems, unique APIs, and incompatible infrastructures make switching providers difficult and expensive.
That’s why many organizations turn to multi-cloud strategies. But juggling multiple platforms requires deep in-house expertise, especially in environments where security and uptime are non-negotiable.
Gaps in Internal Cloud Knowledge
Most hospitals rely on third-party vendors for digital tools rather than building their own. This often leaves teams without the in-house skills to manage, secure, or optimize their cloud environments.
Legacy systems may still run outdated software, posing further risks. To fully adopt cloud solutions, healthcare teams need to upskill in areas like DevOps, data privacy, and platform-specific configurations.
Challenges with System Integration
Bringing older on-premise systems into the cloud and healthcare ecosystem isn’t always seamless. Healthcare data lives in a range of formats, HL7, DICOM, FHIR, and legacy vendors don’t always play nicely with modern platforms.
Moving years of clinical records into a cloud data lake demands time-intensive ETL (extract, transform, load) processes. Without standardized practices, integrating these systems can become a costly, technical headache.
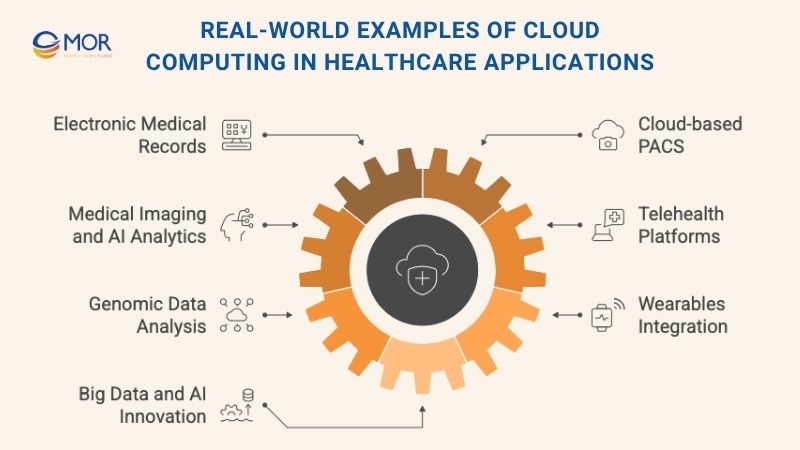
Real-world Examples of Cloud Computing in Healthcare Applications
Healthcare providers across the globe are adopting cloud computing in healthcare to transform operations, improve patient outcomes, and reduce infrastructure strain. By using cloud platforms to host records, run diagnostics, and manage workflows, organizations gain flexibility, speed, and better cost control.
This shift enables remote access to medical data, drives real-time collaboration across teams, and supports advancements in AI, automation, and big data analytics.
Real-world Examples of Cloud Computing in Healthcare Applications
Electronic Medical Records (EMRs) on Cloud Platforms
Cloud-hosted electronic health record systems give healthcare teams instant access to patient data from any location, while minimizing physical infrastructure needs.
These platforms replace high upfront costs with subscription-based models and reduce IT complexity significantly. A few success stories include:
- Mount Sinai moved its Epic EHR to Microsoft Azure’s high-capacity instances, supporting up to 50 million database actions.
- Tufts Medicine migrated its EHR to AWS, cutting legacy maintenance and improving security.
- Southeast Iowa Regional Medical Center configured AWS as a secondary site for its MEDITECH EHR, reducing recovery time by 67%.
Centralizing EMRs in the cloud also improves interoperability across systems, making care coordination faster and more efficient.
Cloud-based PACS for Medical Imaging
Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS) have moved beyond local storage to the cloud, where they’re more accessible and easier to manage.
Benefits include:
- Secure, remote access to imaging files
- Elimination of manual backups and transfers
- Reduced hardware requirements
- Faster access and improved reliability
Philips HealthSuite Imaging, for instance, leverages AWS to boost availability and streamline radiology workflows.
Medical Imaging and Analytics
MRI, CT, and X-ray files are massive and require serious computing power. Cloud platforms meet these demands while unlocking AI-driven image analysis.
At Rush University, cloud-based AI tools analyze radiology scans and doctor notes to extract hidden insights. These solutions help automate triage, flag critical findings, and allow radiologists to review images from any secure location.
Telehealth Platforms Using Cloud Infrastructure
The combination of telemedicine and cloud computing in healthcare has redefined how care is delivered.
Doctors use cloud-hosted platforms for secure video visits, encrypted messaging, and remote monitoring, all while staying HIPAA-compliant.
Teladoc Health uses a cloud infrastructure to support real-time virtual care. Patient portals that show lab results, messages, or prescriptions are also typically cloud-based for uptime and scalability.
Genomic Data Analysis Powered by the Cloud
Genomic research involves huge data volumes that traditional systems can’t handle efficiently. The cloud makes this work faster and more affordable.
For example, AWS HealthOmics supports organizations like AstraZeneca, whose platform can process 51 billion genomic tests per day.
With cloud systems, researchers around the world can access unified, secure datasets without moving files physically. One project processed 12,000+ RNA samples for under $0.10 each, proving the scalability and cost-effectiveness of cloud models.
Wearables Integrated with Cloud Platforms
Wearable devices play a growing role in preventive and chronic care. When connected to cloud infrastructure, they provide continuous data for real-time analysis.
A cardiovascular wearable designed for postpartum monitoring, for instance, transmits waveform data to the cloud for instant evaluation of vitals like heart rate and blood oxygen.
Cloud integrations like these power predictive health insights, improve early intervention, and give providers and users access to real-time metrics.
Big Data and AI for Healthcare Innovation
The cloud enables the kind of heavy lifting needed for advanced analytics and AI applications. Hospitals now build cloud-based data lakes that combine EHRs, imaging, genomics, and public health data.
Tools like IBM Watson Health use cloud-powered AI to analyze medical images and detect early signs of disease. At Rush University, a health equity analytics platform on AWS is helping close life expectancy gaps by linking social and medical data.
By bringing large, diverse datasets into one secure environment, cloud computing in healthcare supports predictive care, research innovation, and smarter health interventions.
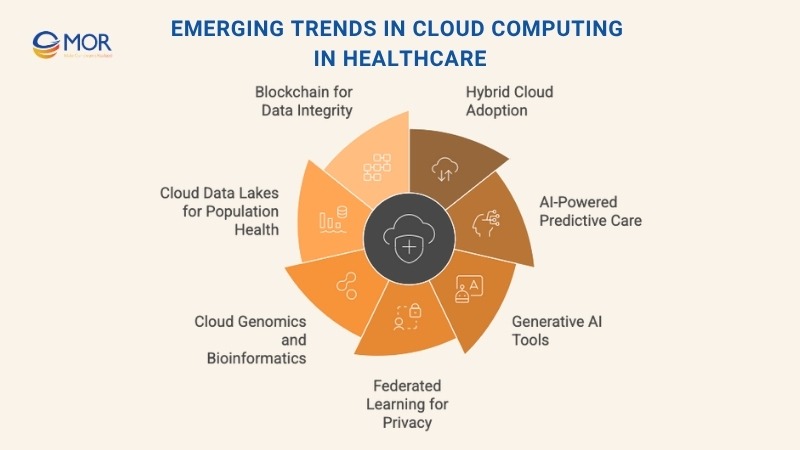
Emerging Trends in Cloud Computing in Healthcare
The role of cloud computing in healthcare is quickly expanding beyond storage and infrastructure. New trends show how this technology is shaping smarter, faster, and more secure healthcare models, from predictive analytics to AI-enhanced decision-making.
Emerging Trends in Cloud Computing in Healthcare
Growth of Hybrid Cloud Models in Healthcare
Many hospitals are shifting toward hybrid cloud setups that combine the security of private infrastructure with the flexibility of public cloud platforms.
This model allows healthcare IT teams to manage sensitive data on-premise while taking advantage of scalable cloud services for less critical workloads. As needs change, workloads can shift seamlessly across environments.
Healthcare administrators favor this setup for its ability to reduce capital expenditure, support disaster recovery, and maintain compliance with data regulations.
Cloud Integration with AI for Predictive Care
Cloud technology in healthcare is now a backbone for artificial intelligence systems that support personalized care.
By bringing together genomic, clinical, social, and financial data, providers can uncover patterns that improve disease prediction and treatment planning. Research shows that 75% of healthcare firms plan to invest in AI within the next year.
Cloud platforms provide the speed, storage, and compute power needed to analyze this data on a massive scale, enabling earlier interventions and more targeted therapies.
Rise of Gen AI Tools in Medical Software
Cloud computing in healthcare is accelerating the adoption of generative AI tools that support doctors with faster, smarter decision-making.
For instance, Google Cloud’s Gen App Builder enables clinicians to query patient data using natural language, simplifying how they generate summaries, review histories, or produce radiology notes.
These generative AI tools, now integrated directly into cloud platforms, are being used to:
- Draft clinical documentation automatically
- Provide real-time symptom triage and treatment suggestions
- Reduce administrative burden and response times
With these capabilities embedded in cloud-native systems, providers can scale smarter care without overloading their teams.
Federated Learning for Privacy-Safe AI
Protecting patient privacy is non-negotiable. That’s why cloud and healthcare projects are now exploring federated learning, which allows AI models to be trained across multiple facilities without moving patient data.
The Mayo Clinic Platform, for example, hosts data securely on its own cloud while allowing external algorithms to operate in a controlled environment. This enables multi-hospital research collaboration without breaching HIPAA rules.
Cloud vendors are building privacy-focused enclaves and tools to support these distributed AI systems at scale.
Genomics and Bioinformatics in the Cloud
Next-gen sequencing and personalized medicine produce enormous datasets, far beyond the limits of local servers.
That’s where healthcare cloud computing companies step in. Providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud now offer specialized platforms for bioinformatics teams to store, query, and analyze genomic data with precision and speed.
Tools like NoSQL databases and scalable storage engines help researchers crunch billions of records daily, accelerating insights and lowering operational overhead.
Cloud-based Data Lakes and Population Health Insights
Many healthcare systems are creating centralized cloud repositories that merge clinical, genomic, and socio-economic data. These data lakes allow researchers to study entire populations and apply precision medicine at scale.
Gilead and Moderna use cloud data architectures to fast-track drug development and model disease trends. Services like AWS HealthLake and Azure Health Data Services support large-scale epidemiology, health equity studies, and predictive public health tools.
Blockchain to Strengthen Data Trust
Some early adopters are testing blockchain technologies hosted on the cloud to secure patient data and transactions.
Blockchain ledgers can record every access point, consent change, or prescription delivery in an immutable format, helping verify data integrity and build patient trust.
While still in trial stages, these cloud based healthcare solutions could offer tamper-proof logs that satisfy both compliance needs and long-term transparency goals.
How MOR Software Can Help You Adopt Cloud Computing Technology
Adopting cloud computing in healthcare takes more than switching servers, it demands healthcare-savvy engineers, airtight compliance, and software built to scale. MOR Software brings all of that together in one team.
We support healthcare providers at every step, from planning to deployment:
- Deep experience building HIPAA-compliant cloud apps, portals, and platforms
- 1,200+ engineers and AI/ML specialists across Vietnam, Japan, and Korea
- Custom development for EHRs, telehealth, AI diagnostics, and mobile apps
- Agile delivery with CMMI Level 3-certified processes
- Support for SaaS, IaaS, and hybrid cloud infrastructures
- Clear focus on performance, data security, and long-term maintainability
- Trusted by global enterprises, health startups, and digital product teams
Whether you're migrating from legacy systems or building something new, MOR Software helps your team move fast without breaking standards.
Conclusion
Cloud computing in healthcare isn’t just a tech upgrade, it’s a strategic move that helps providers deliver faster, smarter, and more connected care. From lowering costs and improving accessibility to enabling AI-driven insights and remote monitoring, the benefits are clear. But the risks are real too. Data security, compliance, and technical complexity require careful planning and the right partners.
That’s where MOR Software comes in. We bring real healthcare experience and cloud know-how to build secure, scalable systems that deliver results. Whether you're upgrading infrastructure or launching a new health-tech solution, we make cloud adoption simple, compliant, and future-ready. Contact MOR Software today to get started.
Rate this article
0
over 5.0 based on 0 reviews
Your rating on this news:
Name
*Email
*Write your comment
*Send your comment
1