What is Salesforce Integration API? A Complete Beginner's Guide

Is your business managing too many disconnected tools and messy, manual data workflows? Are you considering integrating these tools with Salesforce to streamline operations? The Salesforce Integration API is the key to seamless, secure, and efficient connectivity, transforming Salesforce into your unified business hub.
What is Salesforce Integration API?
In the era of digital transformation, businesses increasingly demand seamless connectivity between CRM systems and other platforms to optimize operational efficiency. This is where the Salesforce API Integration plays a crucial role. Before diving deeper into the Salesforce Integration API, let’s first clarify what Salesforce CRM is.
Definition of Salesforce CRM
Salesforce CRM is the world’s leading customer relationship management platform, enabling businesses to build, maintain, and grow strong relationships with customers. According to a report by IDC, Salesforce has maintained the #1 position in the global CRM market for 12 consecutive years, holding a market share of 20.7%.
More than just a customer data storage system, Salesforce CRM empowers organizations to optimize the entire customer journey. Thanks to its high customizability, Salesforce CRM has become the central hub for business operations for hundreds of thousands of companies worldwide.
What is an API (Application Programming Interface)?
An API (Application Programming Interface) is a set of rules and protocols that allow different software systems or applications to communicate and exchange data with each other. It acts as a bridge or intermediary, enabling independent applications to integrate, access, or share functionalities without needing to understand the internal workings of the other system.
Definition of Salesforce Integration API and Its Role
The Salesforce Integration API is a set of application programming interfaces that allows external systems to connect directly and exchange data with Salesforce. It is a foundational tool that makes API integration in Salesforce seamless, fast, and secure.
The main role of the Salesforce API Integration is to act as a bridge between Salesforce and other systems within an organization. It enables businesses to:
- Automate workflows across different platforms.
- Synchronize customer data in real-time.
- Reduce manual tasks and data entry errors.

Definition of Salesforce Integration API
Key Benefits of Salesforce Integration API
API integration in Salesforce enables seamless connectivity between systems and delivers significant business value throughout operations and growth. Below are the most notable advantages companies gain when they choose to integrate with the Salesforce API.
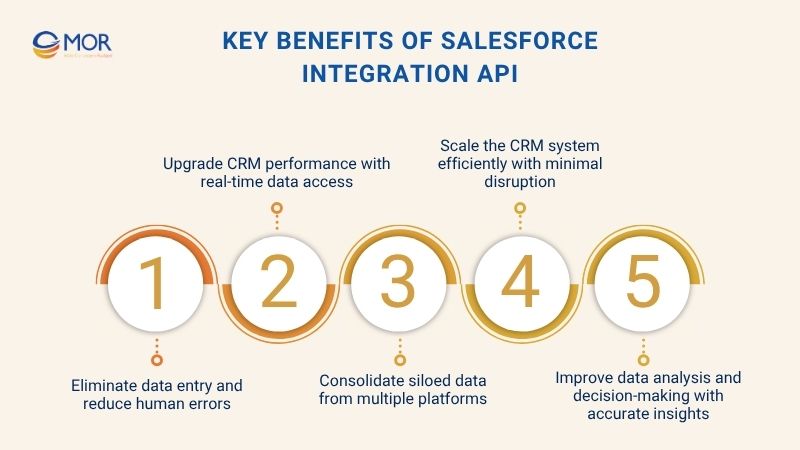
Eliminate data entry and reduce human errors
One of the most significant benefits of Salesforce API integration is its ability to automate data entry across systems. Automated CRM systems typically achieve data accuracy rates of 99% or higher, compared to manual data entry error rates of 1 - 4%.
Instead of spending valuable time manually inputting data from sales, marketing, accounting, or customer service platforms into Salesforce, the Salesforce Integration API enables automatic and seamless data synchronization.
This allows employees to focus on higher-value tasks such as sales consulting, customer care, and delivering better user experiences. As a result, they can contribute more strategically to brand growth and revenue generation.
Upgrade CRM performance with real-time data access
A powerful CRM is not just a database for storing customer information; it must also provide timely and accurate data to support fast, informed decision-making. With the Salesforce Integration API, businesses can easily connect Salesforce with external systems to enable real-time data synchronization.
Real-world example:
A delivery company uses Salesforce to manage customers and orders, while its delivery tracking system is built on a separate platform. Previously, the customer support team had to make calls or manually check the tracking system every time a customer asked, “Where is my order?”
After integrating Salesforce with the tracking system via API, support agents can now simply open the customer profile in Salesforce. It is easier to instantly view order status, delivery vehicle location, and estimated arrival time pulled in real time from the logistics system.
Consolidate siloed data from multiple platforms
In daily operations, many businesses use separate systems to manage different departments. However, when data is scattered across multiple platforms, teams struggle to gain a complete view of customer interactions and business performance. This challenge is commonly known as siloed data.
With the Salesforce Integration API, organizations can easily connect and consolidate data from multiple platforms into a single source of truth. Information from sales, marketing, customer support systems, and even third-party sources like chatbots, websites, or point-of-sale (POS) systems can be synced into Salesforce either in real time or in batch mode.
Scale the CRM system efficiently with minimal disruption
As a business grows, so do its needs for managing more data, users, and integration processes. However, if the Salesforce CRM API lacks flexibility, scaling operations can lead to high costs, downtime, and technical risks.
Real-world example:
A tech startup initially used Salesforce solely for customer relationship management. As it expanded into international markets, the company needed to integrate global payment systems, warehouse management software, and BI tools for better analytics. Instead of replacing the entire CRM, the company leveraged Salesforce APIs to seamlessly connect these new systems.
Improve data analysis and decision-making with accurate insights
In the data-driven era, the ability to make fast yet accurate decisions is critical for businesses. When data is integrated into a centralized platform, Salesforce CRM, organizations gain a 360-degree view of their operations.
This allows leaders and analysts to build reports, dashboards, and forecasting models with greater accuracy. Studies show that organizations that effectively integrate data can increase their decision-making speed by up to 30%, thanks to reduced time spent searching for and processing information from multiple sources.
Key Benefits of Salesforce Integration API
Common Salesforce Integration API Types Explained
Salesforce offers a variety of APIs to meet the diverse integration needs of businesses. Understanding the most common Salesforce API types enables organizations to choose the most effective integration solutions, optimizing system performance and ensuring robust security.
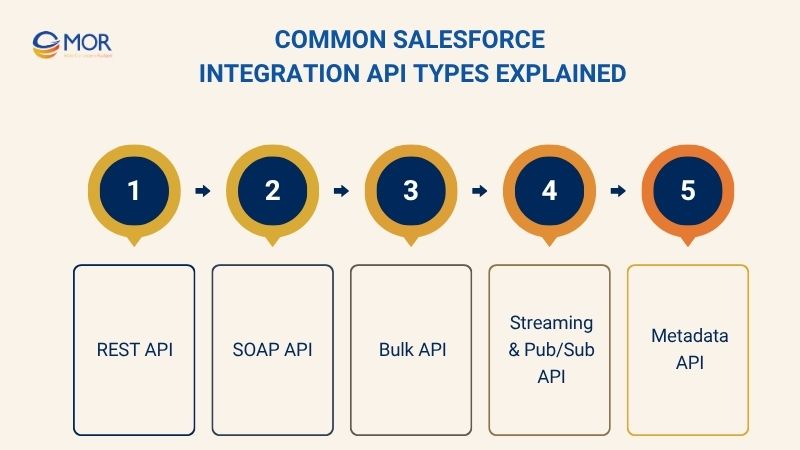
REST API
REST API is the most commonly used API in Salesforce, known for its simplicity and flexibility. It is built on the RESTful architecture, utilizing the HTTP protocol to transmit data and JSON format for requests and responses.
Key characteristics:
- Easy integration with modern systems such as web applications, mobile apps, and chatbots.
- Lightweight communication makes it easy to test and debug.
- Supports single record operations as well as small batch data processing.
When to use:
- Connecting frontend applications like websites or mobile apps to Salesforce.
- Systems requiring fast, lightweight communication without the complexity of SOAP.
- Scenarios that need frequent data updates, high interactivity, and quick responses.
SOAP API
SOAP API is a protocol-based API that uses the Simple Object Access Protocol to enable structured, secure, and reliable communication between Salesforce and external systems. It is widely used in enterprise environments that require strict security measures, transactional integrity, and well-defined data structures.
Key Characteristics:
- Utilizes XML format for clearly structured and validated data exchange.
- Supports advanced security standards like WS-Security, making it ideal for finance, banking, and government applications.
- Suitable for complex transactions and operations that demand data integrity and reliability.
When to use:
- For secure integration with large enterprise systems.
- When strict compliance and data integrity are required.
- For complex transactions and bulk data processing.
Bulk API
Bulk API is designed to handle large volumes of data efficiently in Salesforce. It processes thousands to millions of records asynchronously in batches. This makes it ideal for data migration, mass updates, and large-scale integrations that require high performance and scalability.
Key Characteristics:
- Processes data in batches asynchronously to optimize performance and reduce API call limits.
- Supports large data volumes, from thousands to millions of records in a single operation.
- Ideal for importing, updating, or deleting large datasets without impacting system performance.
When to Use:
- Large data migrations or imports
- Bulk updates or deletes
- High-volume data processing
Streaming & Pub/Sub API
Streaming & Pub/Sub API enables real-time event-driven integration between Salesforce and external systems. Instead of constant polling, applications subscribe to events and receive instant notifications, reducing system load and improving responsiveness.
Key Characteristics:
- Supports real-time data and event processing.
- Minimizes latency in information exchange.
- Ideal for applications requiring immediate updates, such as alerts, order status changes, and customer notifications.
When to use:
- Real-time event processing needs.
- Instant data synchronization.
- Automation and notification systems.
Metadata API
Metadata API allows developers and administrators to manage Salesforce metadata, including custom objects, fields, workflows, and page layouts, through programmatic access. It is essential for automating deployment, migrating configurations between environments, and maintaining a consistent setup across Salesforce orgs.
Key Characteristics:
- Enables automated deployment and retrieval of metadata components.
- Supports version control and continuous integration processes.
- Helps maintain consistency across multiple Salesforce environments.
When to Use:
- Deploying changes between Salesforce environments.
- Automating configuration management.
- Managing metadata for large or complex Salesforce orgs.
Criteria | REST API | SOAP API | Bulk API | Streaming & Pub/Sub API | Metadata API |
Primary Use Case | Lightweight integration for web/mobile apps | Structured, secure transactions | High-volume data migration and processing | Real-time event notifications | Manage configuration and deployment metadata |
Communication Protocol | HTTP + JSON | SOAP + XML | HTTP + JSON/XML | HTTP + CometD (Bayeux protocol) | HTTP + XML |
Data Volume Handling | Single or small batch operations | Complex and structured operations | Thousands to millions of records | Event-based, not designed for bulk data | Metadata only (config/data structure) |
Real-Time Capability | Yes, suitable for fast transactions | Limited real-time capabilities | No, asynchronous processing | Yes, real-time event-driven | No |
Security & Structure | Basic security, lightweight | Advanced security (WS-Security) | OAuth-based, supports secure bulk ops | OAuth, SSL encryption | Standard OAuth and metadata control |
Ease of Implementation | Easy to implement, developer-friendly | More complex, needs detailed setup | Moderate, requires batch handling logic | Moderate to complex, needs event setup | Moderate, focused on system admins/devs |
Common Salesforce Integration API Types Explained
Popular Salesforce Integration Architectures
Choosing the right integration architecture plays a crucial role in ensuring that your Salesforce system operates reliably, remains flexible, and scales efficiently. Below are the most commonly adopted integrations with salesforce API architectures used by businesses across various industries:
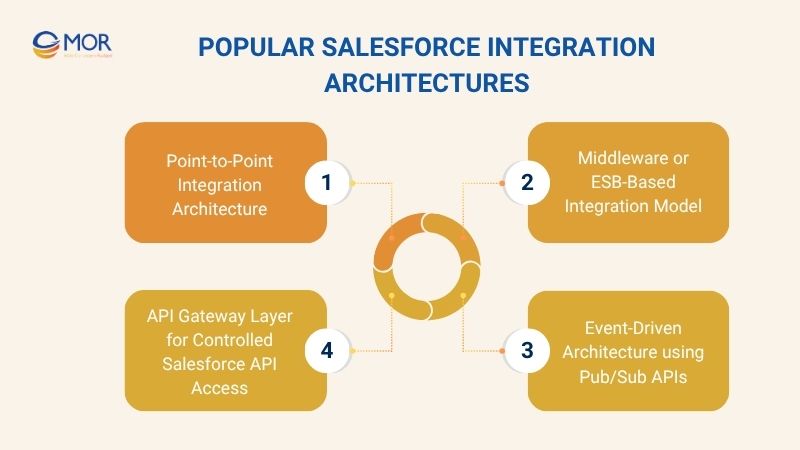
Point-to-Point Integration Architecture
The Point-to-Point integration architecture is the simplest model among Salesforce integration solutions. In this approach, systems are connected directly via APIs without using any middleware or integration layer. Each connection is individually established between Salesforce and an external system, allowing for quick implementation and low initial cost.
Advantages:
- Easy to set up, ideal for small businesses or systems with limited integration points.
- No need for middleware platforms like ESB or iPaaS.
- Optimized for simple and small-scale integration use cases.
Limitations:
- Difficult to scale as the number of systems increases (n+1 connections).
- Challenging to manage, maintain, and monitor in the long term.
- Higher risk of failure due to tight coupling between systems.
Middleware or ESB-Based Integration Model
In organizations with complex IT ecosystems, directly connecting each system to Salesforce using point-to-point integration can quickly become unmanageable. A more scalable and maintainable approach is to use a middleware or Enterprise Service Bus (ESB) architecture.
Instead of building separate connections for every system, all applications communicate through a central integration layer. Common platforms used in this model include MuleSoft (a Salesforce company), Dell Boomi, Apache Camel, Workato, and other iPaaS (Integration Platform as a Service) solutions.
Advantages:
- High scalability and reusability of integrations.
- Centralized monitoring and error handling.
- Decouples systems to reduce interdependencies.
- Supports advanced integration patterns like data transformation, orchestration, and routing.
Limitations:
- Higher initial investment and operational costs.
- Requires experienced technical staff to design and maintain.
- Can introduce latency if not optimized properly.
Event-Driven Architecture using Pub/Sub APIs
In an event-driven architecture, systems communicate by sending and receiving events instead of calling APIs or syncing data on a schedule. Salesforce supports this model through its Streaming API and Pub/Sub API, allowing external systems to subscribe to events like data changes, user actions, or business triggers and react in real time.
Advantages:
- Enables real-time data synchronization across systems.
- Eliminates the need for continuous API polling, reducing resource usage.
- Supports asynchronous and scalable system design.
- Allows for loose coupling between systems, improving maintainability.
Limitations:
- Requires more complex infrastructure and setup, such as message brokers (e.g., Kafka, Google Pub/Sub).
- Error handling and event replay logic can be challenging.
- May not be suitable for legacy systems that lack event-driven capabilities.
API Gateway Layer for Controlled Salesforce API Access
An API Gateway acts as a secure intermediary between Salesforce and external systems. Instead of allowing each application to directly access Salesforce APIs, all requests pass through the API Gateway, where they are authenticated, authorized, and routed accordingly.
This architecture enhances control over API traffic, improves security, and simplifies monitoring, logging, and rate limiting.
Advantages:
- Strengthens security by centralizing authentication and access control
- Simplifies API management with unified policies and routing
- Reduces load on Salesforce by enabling caching and request throttling
- Integrates easily with monitoring and logging tools
Limitations:
- Higher cost and complexity, especially with enterprise-grade API gateways
- May introduce slight latency due to the extra processing layer
- Requires technical expertise to configure routing rules and security policies
Criteria | Point-to-Point | Middleware / ESB | Event-Driven (Pub/Sub) | API Gateway Layer |
Implementation Complexity | Low – direct connections between systems | High – requires configuration of an intermediary platform | Medium – requires event logic and subscription setup | Medium – involves routing, policies, and authentication setup |
Scalability | Low – becomes difficult to scale with system growth | High – easy to add new systems through centralized integration | High – supports scalable and modular event-based integration | High – enables unified API access and flexible routing |
Stability & Maintainability | Low – changes in one system may affect all others | High – changes are isolated and managed via middleware | Medium – depends on event reliability and async error handling | High – centralized control, logging, and monitoring simplify maintenance |
Real-Time Responsiveness | Low – typically batch-based or scheduled sync | Medium – real-time possible but with added complexity | High – instant responses based on published events | Medium – depends on backend capabilities and API caching |
Cost of Setup & Maintenance | Low initially, but rises significantly as system complexity increases | High – requires investment in middleware tools and technical resources | Medium – some complexity in setup, but cost-effective at scale | Medium to High – depends on the API Gateway solution (open-source or commercial) |
Control & Security | Low – decentralized and hard to manage access controls | High – middleware enforces centralized data governance and security | Medium – requires well-defined event access and authentication | Very High – strong access control, throttling, authentication, and security enforcement |
Popular Salesforce Integration Architectures
How to Integrate with Salesforce API Step-by-Step
Here is a step-by-step guide to help you integrate with the Salesforce API effectively and efficiently.
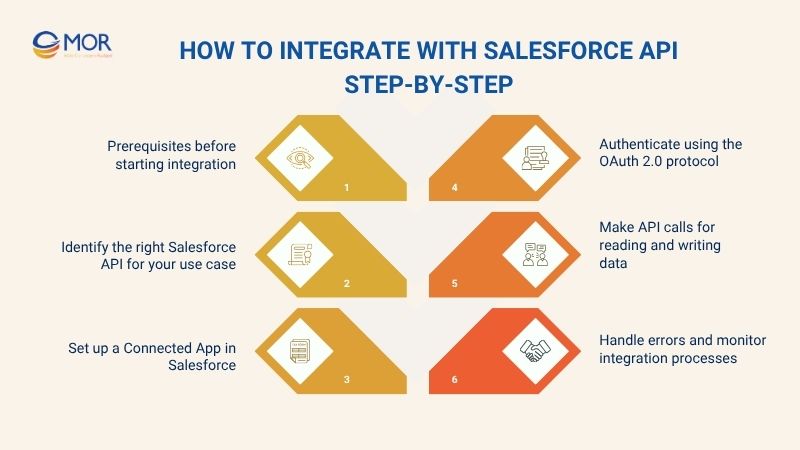
Prerequisites before starting integration
Before starting the Salesforce API integration process, businesses must ensure that all necessary prerequisites are in place. Proper preparation helps avoid unexpected errors, ensures secure data exchange, and allows the integration process to run smoothly and efficiently.
- Valid Salesforce account and edition: Not all Salesforce editions provide API access. Make sure to verify your current Salesforce edition to ensure it's eligible for integration.
- Clearly defined integration scope and goals: Determine which systems will be connected to Salesforce, what type of data will be exchanged, how frequently the data should be synced, and whether the integration requires high-performance or enhanced security.
- Basic technical knowledge: Your team should understand core API protocols such as REST and SOAP, be able to use essential HTTP methods (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE), and work with data formats like JSON and XML.
Identify the right Salesforce API for your use case
After meeting the essential prerequisites, the next step is to choose the most suitable Salesforce API based on your organization’s specific integration goals. This decision should be made by evaluating both technical and business requirements, such as:
- Does your data need to be updated in real time? If yes, prioritize Streaming API or Pub/Sub API. If not, consider using Batch or Bulk API.
- What is the volume of data transferred in each operation? For small, quick transactions, use the REST API. For large-scale data loads, go with the Bulk API.
- Is the system being integrated as a web/mobile app or an enterprise/legacy application? For web/mobile, REST API is typically the best fit. For ERP or legacy systems, a SOAP API may be required due to its structured and secure communication.
- Do you need to work with Salesforce’s metadata and configuration? Use the Metadata API to handle custom objects, layouts, and settings programmatically.
Set up a Connected App in Salesforce
To integrate any external system with Salesforce via API, you must first set up a Connected App. This app acts as a gateway that enables secure communication between Salesforce and your application.
Steps to create a Connected App:
- Log in to Salesforce, go to Setup → App Manager → click New Connected App.
- Enter basic info: App Name, API Name, and Contact Email.
- Under API (Enable OAuth Settings):
- Check Enable OAuth Settings
- Set a Callback URL (e.g., https://yourapp.com/callback)
- Add required OAuth Scopes (e.g., api, refresh_token, full)
- Click Save and wait ~10 minutes for activation.
- After creation, copy the Consumer Key and Consumer Secret for use in authentication.
Authenticate using the OAuth 2.0 protocol
Once the Connected App is set up, the next step is to authenticate with Salesforce using the OAuth 2.0 protocol. OAuth ensures secure and token-based access without needing to expose user credentials directly.
Common OAuth 2.0 flows:
- Authorization Code Flow: Recommended for web applications with user interaction.
- Client Credentials Flow: Suitable for backend integrations (e.g., server-to-server).
- Username-Password Flow: Less secure; only use in controlled internal environments.

Example for authenticating using the OAuth 2.0 protocol
Make API calls for reading and writing data
After authentication, use the access token to make secure API calls to Salesforce. The most common interface is the REST API, but others (SOAP, Bulk, etc.) can be used depending on the use case.

Alt: Example for making API calls for reading and writing data
Handle errors and monitor integration processes
To ensure a stable and secure Salesforce API integration, it's essential to implement robust error handling and real-time monitoring mechanisms throughout the Salesforce integration lifecycle.
Monitoring and debugging tips:
- Enable Debug Logs in Salesforce to trace user and system activity
- Use tools like Postman, cURL, or middleware platforms to log API requests and response payloads
- Leverage Event Monitoring, Named Credentials, and Integration Users to improve security, auditability, and observability
- Integrate with Salesforce API with third-party monitoring platforms such as New Relic, Datadog, or push logs to your internal log management system for end-to-end tracking
How to Integrate with Salesforce API Step-by-Step
Real-World Use Cases of Salesforce Integration API by System Type
Integrating Salesforce with various external systems not only enables seamless data synchronization but also helps build a connected digital ecosystem. Depending on the type of system, the Salesforce Integration API can deliver distinct business values. Below are some common real-world integration scenarios categorized by system type:
Integration with Internal Operational Systems
Salesforce Integration API enables seamless connectivity between Salesforce and critical business systems such as ERP, accounting software, and HRM platforms. Centralizing data and automating workflows helps streamline operations and eliminate manual errors.
A Gartner study found that integrating data in real time can boost operational efficiency by as much as 40% and shorten the time needed to gain actionable insights by 30%.
Real-World Use Cases:
- ERP Systems (SAP, Odoo, Oracle, Microsoft Dynamics...)
Scenario: A distribution company uses SAP to manage inventory and orders, while the sales team works within Salesforce. Every time they need to check stock availability, sales reps must manually log into SAP, causing delays and data misalignment.
Solution: Salesforce is integrated with SAP via REST API to synchronize real-time inventory levels, order statuses, and pricing. All relevant data is displayed directly inside Salesforce, eliminating the need to switch between platforms.
Results:
- 90% reduction in order processing time
- Near-zero errors in overselling out-of-stock items
- Faster, data-driven decisions from the sales team
- Accounting and Financial Software (QuickBooks, Xero, Zoho Books, etc.)
Scenario: The sales department uses Salesforce to manage leads and deals, while the accounting team uses QuickBooks for billing and payments. Payment updates were shared via emails or spreadsheets, leading to delays and miscommunication.
Solution: Salesforce is integrated with QuickBooks using REST API. Invoices and payment statuses are automatically synced back to Salesforce, giving sales reps real-time visibility into customer financials.
Results:
- 70% reduction in time spent on payment reconciliation
- Real-time access to payment status
- Faster collections and reduced revenue leakage
- HRM Systems (Workday, BambooHR, SAP SuccessFactors...)
Scenario: A B2B service company uses Salesforce for managing clients and contracts, while HR operations run on BambooHR. New hires or terminations were not reflected in Salesforce promptly, creating permission and access control risks.
Solution: Salesforce is integrated with BambooHR using Pub/Sub API. Employee lifecycle events (onboarding, offboarding, role changes) trigger automatic updates to user roles and access levels in Salesforce.
Results:
- Improved internal security through automated access control
- Reduced IT workload in user management
- Always up-to-date user data in Salesforce
Integration with Customer Support Systems
The Salesforce Integration API enables businesses to directly connect customer support platforms and ticketing systems to their Salesforce CRM. Through this integration, customer data such as interaction history, ticket status, and conversation logs is automatically updated in real time within Salesforce.
Real-World Use Cases:
- Call Center / IVR Systems
Situation: A large financial services company receives hundreds of thousands of customer calls annually. Previously, call center agents had to manually verify customer information in Salesforce, resulting in long wait times and a poor caller experience.
Solution: By integrating their IVR and CTI systems with Salesforce using the REST API and CTI Adapter, the company enabled screen pop functionality, automatically fetching and displaying customer data as soon as the call connects. The system also logs calls and creates cases automatically in Salesforce.
Results:
- Increased customer satisfaction scores by 10–25% thanks to improved caller experience
- Saved millions of dollars annually by improving agent productivity and reducing operating costs
- Chatbots (Zalo, Messenger, website, etc.)
Situation:
A Fintech startup used chatbots on Zalo and Messenger for customer support, but interactions were not recorded in Salesforce, leading to fragmented data and missed growth opportunities.
Solution: The chatbot was integrated using REST API and middleware solutions (e.g., Zapier or custom connectors) to automatically create Leads or Cases in Salesforce for each user interaction.
Results:
- Lead capture from chatbots increased by 40%, as AI-powered chatbots automated data collection and engagement
- Customer query resolution time reduced by 50%, improving immediate response and satisfaction
- With centralized data in Salesforce, the marketing team could run more targeted campaigns and workflows.
- Ticketing systems (Zendesk, Freshdesk, etc.)
Situation: A SaaS company manages customer support via Zendesk and tracks leads and opportunities in Salesforce. Without integration, support agents and sales reps lacked visibility into shared customer interactions, leading to inefficient handoffs and fragmented communication.
Solution: Integrate Zendesk with Salesforce Service Cloud using native connectors or middleware (e.g., MuleSoft). This enables bi-directional syncing of ticket data, statuses, and support history, allowing Sales and Support teams to access a unified customer profile in real time.
Results:
- Eliminated manual handoffs between Sales and Support by syncing data automatically
- Improved interdepartmental collaboration with shared customer context
- Enhanced customer experience through better First Contact Resolution (FCR) and seamless omnichannel support
Integration with Sales & Marketing Tools
Integrating Salesforce with sales and marketing platforms enables businesses to automate lead capture and personalize outreach based on real-time behavior. With Salesforce Integration API, tools like HubSpot, Shopify, or POS apps can sync seamlessly to ensure unified customer engagement across channels.
Real-World Use Cases:
- E-commerce Platforms & Lead Capture Websites
Situation:
An online retail brand operated multiple landing pages and e-commerce stores. However, customer and lead data had to be entered manually into Salesforce, causing delayed responses and missed conversion opportunities.
Solution:
The business integrated Shopify and WooCommerce with Salesforce using REST API and webhooks. Middleware platforms like Zapier or MuleSoft enabled real-time syncing of leads, transactions, and cart activity directly into Salesforce.
Results:
- Faster lead capture and follow-up workflows
- Improved customer experience through real-time data sync
- Increased conversion opportunities from abandoned cart recovery
- Marketing Automation Tools (HubSpot, Mailchimp, ActiveCampaign…)
Situation:
A B2B company used HubSpot for email marketing while managing its sales funnel in Salesforce. Disconnected systems made it hard to track campaign performance and follow up effectively on engaged prospects.
Solution:
The marketing platform was integrated with Salesforce via native connectors or REST API. Customer activities such as form fills, email opens, and link clicks were pushed automatically to Salesforce, enabling smarter lead scoring and segmentation.
Results:
- Better sales and marketing alignment
- Streamlined lead nurturing with accurate engagement data
- More efficient follow-ups and personalized outreach
- POS & Mobile Sales Applications
Situation: A retail business used mobile sales apps and in-store POS systems to process transactions, but the data was not reflected in Salesforce, leading to fragmented customer profiles and poor sales visibility.
Solution: The POS and mobile systems were connected to Salesforce using REST API integration. Sales activities were logged automatically into CRM in real time, updating customer records with recent transactions.
Results:
- Unified view of online and offline customer behavior
- More accurate reporting and inventory tracking
- Improved loyalty marketing based on complete customer history
Integration with Analytics & Reporting Tools
Integrating Salesforce with analytics platforms allows businesses to unlock deeper insights from CRM data. By syncing Salesforce with BI tools or cloud data platforms like companies can build unified dashboards, visualize performance metrics, and make informed, data-driven decisions.
Real-World Use Cases:
- BI tools (Power BI, Tableau, Looker…)
Situation: A global SaaS company wanted to combine Salesforce opportunity data with product usage metrics stored in a separate database. However, without integration, teams had to manually export and reconcile reports, slowing down strategic decisions.
Solution: Salesforce data was connected to Tableau via the Salesforce Connector and synced regularly with a centralized data warehouse. This enabled real-time dashboards combining CRM and operational metrics.
Results:
- Faster executive reporting with consolidated dashboards
- Enhanced forecasting accuracy using complete sales + usage data
- Reduced manual effort in data preparation
2. Google Data Studio and BigQuery
Situation: A digital marketing agency used Salesforce to manage clients and campaigns, but reported performance using Google Data Studio. The disconnect between systems caused delays and inconsistencies in client reporting.
Solution: Salesforce data was exported to BigQuery using scheduled ETL jobs and connected to Google Data Studio for dynamic reporting. All campaign performance and customer insights were updated automatically.
Results:
- Consistent and automated client reporting
- Real-time access to key performance indicators
- Improved decision-making through centralized analytics
Real-World Use Cases of Salesforce Integration API by System Type
Important Considerations When Using Salesforce Integration API
While the Salesforce Integration API offers powerful connectivity across systems, businesses must still pay close attention to several key factors to ensure the integration process remains efficient, stable, and compliant with security and regulatory standards.
API call limits and optimization techniques
Salesforce enforces daily API usage limits based on your edition and the number of user licenses. Exceeding these limits can lead to throttling, delayed responses, or denied requests, making it crucial to manage and optimize API calls effectively.
Key Techniques to Optimize API Usage:
- Use Bulk API for large data operations: Ideal for mass inserts, updates, or deletions to reduce the number of individual calls.
- Implement caching mechanisms: Avoid unnecessary repeated requests for static or infrequently updated data.
- Use Composite or Batch APIs: Combine multiple operations into a single API call to reduce overhead.
- Monitor API usage proactively: Use tools like the System Overview page in Salesforce Setup or call the /limits endpoint to track current consumption.
Error handling and retry strategies
During Salesforce API integration, implementing proper error handling and retry strategies is essential to ensure system stability and continuity.
Common errors when calling the Salesforce API:
- 401 Unauthorized – Token has expired
- 403 Forbidden – Insufficient access permissions
- 404 Not Found – Resource does not exist
- 429 Too Many Requests – API call limit exceeded
- 5xx Server Error – Internal server error from Salesforce
Security compliance and API access control
When integrating with the Salesforce API, data security must be a top priority, especially for organizations handling sensitive customer, financial, or healthcare data. Implementing modern authentication standards such as OAuth 2.0 is essential to enforce secure access control and role-based permissions across connected applications.
According to the IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2023, the average cost of a data breach reached $4.45 million, marking a 2.3% increase from the previous year
Important Considerations When Using Salesforce Integration API
Conclusion
As digital transformation accelerates, integrating your systems with Salesforce CRM is no longer a luxury; it's a strategic imperative. With the Salesforce Integration API, businesses gain a robust, secure, and scalable foundation for connecting Salesforce to a wide range of platforms. Ready to integrate Salesforce with your ecosystem?
MOR SOFTWARE
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is Salesforce Integration API?
It’s a set of APIs that allows external systems to connect and exchange data with Salesforce securely and efficiently.
What types of APIs are available in Salesforce?
Salesforce offers REST API, SOAP API, Bulk API, Streaming/Pub/Sub API, and Metadata API, each serving different integration needs.
Do I need a developer to integrate with the Salesforce API?
Not always. Basic tasks can use no-code tools, but complex or large-scale integrations often require developer expertise.
Can I build an app using only Salesforce APIs without using its UI?
Yes. Many apps, such as chatbots or mobile tools, operate entirely via API without needing the Salesforce interface.
Rate this article
0
over 5.0 based on 0 reviews
Your rating on this news:
Name
*Email
*Write your comment
*Send your comment
1