AI in Manufacturing: Top 15 Real Use Cases Driving Innovation

Rising costs and unpredictable demand are pressing challenges for factories today. AI in manufacturing offers practical answers, from predictive maintenance to AI use cases in manufacturing that improve quality and efficiency. This MOR Software’s guide explores how global manufacturers are applying AI to modernize operations and gain a competitive edge.
What Is AI In Manufacturing?
AI in manufacturing is transforming how factories operate by handling tasks that range from early product design to final quality checks. It automates repetitive processes, supports workers on assembly lines, and improves accuracy across every production stage.
Through processing massive datasets, it spots patterns and forecasts outcomes faster than traditional methods, cutting down workflow overlap and giving managers better visibility into operations. It also tracks raw material use, helping businesses strengthen supply chains and prevent costly shortages.
The role of AI goes further than data analytics. On the factory floor, AI-powered robots work independently or side by side with employees to detect issues as they happen. These systems can report faults instantly, reducing downtime and waste.
As algorithms grow more advanced, AI in manufacturing industry operations will continue to see higher productivity and lower costs, proving how central the technology has become to modern production.
How Does AI In Manufacturing Work?
AI in manufacturing is widely applied to collect and analyze live production data, giving managers a clearer and more connected picture of factory operations. This visibility helps track critical performance benchmarks such as machine uptime, production volume, and equipment effectiveness. By integrating with Internet of Things (IoT) sensors, augmented reality tools, and ERP platforms, AI creates a steady stream of information that leaders can use to refine each stage of the production cycle.
With this broader data ecosystem, companies can improve planning, avoid bottlenecks, and maintain stronger operational control.
Beyond analytics, AI-powered systems bring unmatched precision to specific tasks. Paired with digital design software and 3D modeling, AI shortens the time required for prototyping while limiting material waste. During active production, these tools keep a constant watch on machinery, signaling when parts need attention before breakdowns occur.
This predictive approach lowers the chances of sudden downtime and keeps output running smoothly. By combining accuracy with foresight, AI applications in manufacturing deliver measurable gains across both design and production.
Why AI In Manufacturing Is Important?
AI is now influencing nearly every sector, and production is no exception. Reports from Markets and Markets predict the global AI in manufacturing market will reach about $20.8 billion by 2028, up sharply from $3.2 billion in 2023, representing a compound annual growth rate of 45.6%.
Grand View Research echoes this trend, noting rising demand for managing massive datasets and the growing reliance on ML models, IoT devices, and industrial robots across factories worldwide.
Understanding both the potential and the limits of these technologies, manufacturers can craft implementation strategies that target their exact requirements. This level of planning clarifies how, where, and when to adopt AI for maximum effect. Such strategies are not only practical but also deliver strong financial outcomes.
An IBM global study found that top-performing organizations deploying production AI achieved an ROI of 13%, more than twice the overall average of 5.9%.
Key Benefits Of Using AI In Manufacturing
Expectations around AI in manufacturing continue to rise. A survey from the Manufacturing Leadership Council found that 70% of companies believe AI could bring major or moderate advantages across 31 areas of performance, production, and supply chain management. Yet only 22% currently track AI with defined metrics. Understanding the real value of these eight benefits of AI in manufacturing helps leaders measure outcomes more effectively.
- Smarter maintenance and operations: AI and ML analyze machine performance data to plan service before breakdowns occur. This predictive style cuts downtime, lowers expenses, and extends asset life.
- Higher quality and accuracy: AI-based quality checks compare goods against strict benchmarks to flag defects early. Adjustments can also be made quickly when designs change or orders require customization.
- Better production workflows: With automation, AI highlights inefficiencies and streamlines processes. Employees gain time to focus on complex issues and strategy.
- Supply chain and inventory control: AI delivers live updates on inventory status and supply flow. Combined with demand forecasting, this keeps stock levels balanced, avoiding losses tied to shortages or overstocking.
- Faster product design and development: Designers can build digital twins with AI and AR to test ideas virtually. These models help refine products, troubleshoot remotely, and improve long-term performance.
- Lower costs and stronger value: AI-powered analytics give clear visibility into what works and what doesn’t. The result is cost savings, faster turnaround, and greater competitiveness in the market.
- Improved safety and compliance: Cobots and smart monitoring systems take over dangerous or repetitive work. AI can also track workplace conditions to reduce risks and maintain regulatory standards.
- Room for innovation: As businesses grow, AI scales with them. By connecting with IoT devices and smart sensors, AI in factory automation continues to generate insights that support adaptation and long-term advantage.
Top 15 Proven Use Cases For AI In Manufacturing
Modern companies are adopting AI, ML, and automation to strengthen existing workflows and design new ways of working that raise both efficiency and profit margins. From predictive equipment care and training programs to market forecasting and process control, AI in manufacturing is proving valuable across multiple fronts. Below is the first of 15 major use cases where the technology is reshaping production.
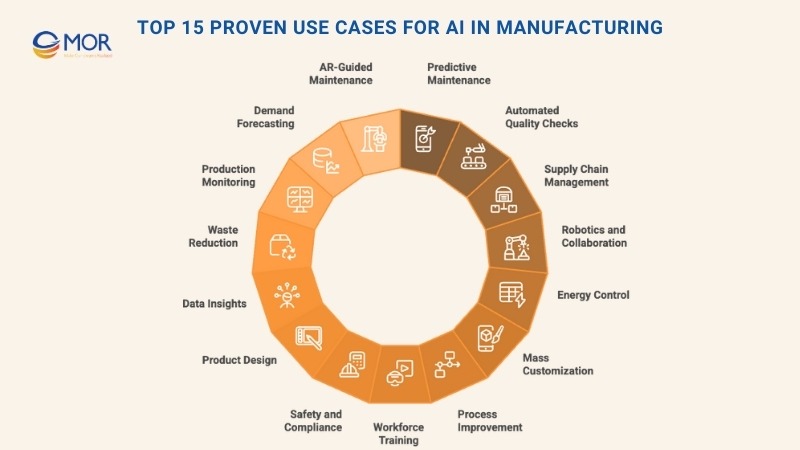
1. Predictive Equipment Care
Manufacturers invest anywhere from thousands to billions in machinery, making asset protection a top concern. Through continuous monitoring and learning from operational data, AI can predict when service is needed. This reduces the risk of sudden breakdowns and costly downtime, while letting managers schedule maintenance during the least disruptive times.
Taking a proactive stance ensures equipment runs at maximum efficiency, lengthens its working life, and supports smarter planning for upgrades or replacements in the future.
2. Automated Quality Checks
With AI in manufacturing, ML-driven systems can evaluate products against strict quality standards in real time across different stages of production. Take automotive plants as an example, where AI tools scan each surface of a vehicle to detect even the smallest flaws that humans might miss.
This meticulous checking process allows manufacturers to uphold high standards, reduce material waste, and keep customer satisfaction strong, even when handling complex or customized orders.
3. Smarter Supply Chain Management
Today’s supply chains are complex and prone to disruption, but AI in manufacturing provides tools to keep them efficient and resilient. By analyzing procurement data, predicting demand, and managing inventory in real time, AI creates more accurate planning cycles.
Advanced analytics can uncover hidden trends or weak spots, such as vendors falling short on performance. Once these issues are visible, companies can strengthen operations by fine-tuning material levels or diversifying their supplier base, keeping production steady and costs under control.
4. Robotics And Collaborative Machines
In modern plants, robotics and cobots are central to improving productivity and workplace safety. These AI-driven machines handle repetitive, detail-heavy jobs like assembly with speed and precision. Equipped with advanced sensors, they can track progress and work safely alongside people on the shop floor.
Taking on hazardous or physically demanding tasks, cobots reduce risks for employees and allow them to focus on solving problems and driving innovation. In automotive facilities, for instance, cobots are often used to manage the delicate installation of dashboards, ensuring every unit meets strict safety and quality standards.
5. Intelligent Energy Control
Energy use is a growing concern, and AI in manufacturing is helping businesses gain tighter control. By examining data on equipment operation and production schedules, AI identifies inefficiencies and suggests optimized run times that cut waste.
In practice, these systems can regulate HVAC units based on real-time occupancy or machine activity, keeping factories at stable temperatures without overspending on utilities. Linked with IoT devices, AI solutions continuously track consumption, spot unusual spikes, and recommend immediate adjustments to keep energy costs in check.
6. Mass Customization With AI
One of the standout strengths of AI in manufacturing is its capacity to reconfigure equipment automatically, removing the need for manual adjustments. This makes it far easier to deliver customized products without driving up costs or slowing production.
Beyond assembly, AI can also support logistics by guiding packaging teams to choose the right materials for each order, reducing handling time and lowering the chance of damage in transit. At the same time, smarter planning helps avoid overproduction and builds stronger customer loyalty through tailored experiences.
7. AI-Driven Process Improvement
AI gives manufacturers sharper visibility across production by spotting inefficiencies and suggesting better ways of working. Depending on their needs, leaders can act on these insights directly or allow AI to carry out changes automatically.
In many cases, this is how AI in factories refines the movement paths of robotic arms to reduce unnecessary actions, accelerating assembly lines while maintaining quality and safety. This precision in fine-tuning operations not only increases throughput but also makes factories more profitable in the long run.
8. AI-Powered Workforce Training
The role of AI in manufacturing is not limited to machines and processes, it also supports the workforce itself. AI helps shorten the learning curve for new hires and assists experienced staff in adapting to updated procedures.
Through simulations and immersive training with augmented or virtual reality, employees can practice handling complex equipment at their own pace in a safe setting.
On top of that, AI tools provide real-time guidance on the job, from quick feedback and machine status updates to instant troubleshooting support. This leads to stronger performance, higher confidence, and improved worker satisfaction.
9. AI For Safety And Compliance
Beyond robotics, AI has become a crucial ally in maintaining workplace safety. By continuously scanning factory environments, it detects risks early and ensures workers are following safety requirements.
For instance, AI can monitor whether protective gear is worn correctly and notify supervisors immediately if rules are broken. It can also track new regulatory updates and adjust compliance protocols automatically. This proactive system, reinforced by human oversight, lowers accident rates and prevents costly penalties or production interruptions.
10. AI-Enhanced Product Design
AI in manufacturing accelerates the way products are designed and built while keeping precision and consistency intact. With the support of ML and advanced analytics, design teams gain a wide set of options for creating new products that match market demands.
Digital simulations powered by AI can also run stress tests on prototypes before any physical version is made. This approach is especially valuable when developing complex or costly goods, as it shortens design cycles, reduces material waste, and helps companies deliver products faster while meeting shifting customer expectations.
11. Advanced Data Insights
AI excels at processing massive volumes of information in a fraction of the time it would take human analysts. By uncovering hidden patterns in real time, these tools guide smarter decisions around production, inventory levels, and process improvements.
For example, AI can spot small equipment irregularities and recommend timely repairs before output is affected. This level of analysis not only supports smoother day-to-day operations but also builds a more agile environment where manufacturers can respond quickly to market or production changes.
12. Cutting Down Material Waste
Sustainability and efficiency are now core goals, and AI in manufacturing helps companies achieve both by lowering material waste without sacrificing product standards. Through analyzing production data, AI uncovers usage patterns and suggests smarter ways to manage resources.
In textiles, for example, AI-powered cutting systems can adjust layouts to make the most of every piece of fabric. Even small gains in material efficiency translate into significant cost savings over time, particularly in industries that rely on mass production.
13. Live Production Monitoring
When AI systems are embedded throughout production lines, manufacturers gain real-time insight into every phase, from early assembly to final delivery. This visibility allows teams to correct issues immediately, ensuring problems don’t cascade into larger setbacks.
For instance, AI can monitor throughput on an assembly line and alert managers if output slows or defects increase. With this level of oversight, companies can keep quality consistent and maintain steady customer satisfaction.
14. AI Forecasting For Market Demand
Forecasting powered by AI in manufacturing helps companies sync production with actual demand by examining past sales, market shifts, and customer buying patterns. This reduces the risks of overstocking or empty shelves.
Manufacturers can also rely on AI to decide how products should be distributed across different outlets, ensuring every store maintains the right balance. Doing so, they avoid excess storage, cut carrying costs, and keep inventory flowing in line with real demand.
15. AR-Guided Maintenance And Training
Augmented reality brings digital instructions directly into the physical workspace, giving technicians real-time access to diagrams, updates, and repair guides without taking their hands off the equipment. This speeds up maintenance, minimizes downtime, and boosts accuracy.
In training environments, AR recreates real-world tasks so employees can practice safely before working on actual machines. For example, trainees can follow guided steps through a detailed assembly process, gaining confidence and precision before they move onto live production floors.
Key Challenges Of AI In Manufacturing
No technology is flawless. When integrating AI in manufacturing, companies must weigh several hurdles that can influence the success or failure of deployment. Below are six of the most common challenges manufacturers encounter.
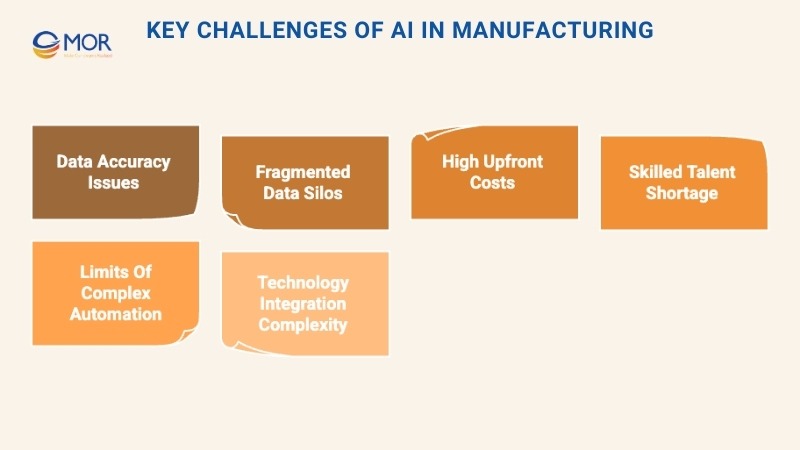
- Data accuracy: AI systems are only as effective as the data provided. Before rollout, businesses need to review their datasets for reliability and ensure measuring tools, like scales used for raw materials, are properly calibrated. This gives AI a strong foundation to work from and supports ongoing analysis. Still, human oversight remains essential to validate results.
- Data fragmentation: Access to diverse, unified datasets is critical. Many manufacturers face siloed information that can distort predictions or leave blind spots. Breaking down these barriers, often with ERP platforms capable of handling large-scale integration, is a necessary step before full adoption.
- High investment requirements: From infrastructure upgrades to employee training, costs can climb quickly. To manage budgets, some firms turn to AI cloud for manufacturing, shifting expenses to third-party providers who handle the upkeep. This reduces capital outlays and simplifies ongoing maintenance.
- Shortage of skilled talent: Finding and keeping people with the right expertise is another barrier. Nearly half of leaders in Fictiv’s 2023 State of Manufacturing Report admitted difficulty in recruiting and retaining qualified staff, particularly engineers. Partnering with specialists helps companies design practical strategies and verify long-term improvements.
- Limits of complex automation: Although AI has advanced rapidly, it struggles with intricate processes that rely on subjective or broad decision-making. Organizations with highly complex workflows may need to temper expectations and consult experts to pinpoint where AI adds the most value.
- Technology complexity: AI itself can be challenging to understand and often operates alongside other advanced tools like IoT networks, connected devices, or even blockchain systems. To maximize value, companies may need outside advisors for planning, implementation, and continuous training to keep pace with new developments.
Real-World Examples Of AI In Manufacturing
The adoption of AI in manufacturing has moved beyond theory into daily reality, as seen in leading companies worldwide. These AI in manufacturing examples include Ford deploying cobots on assembly lines and BMW enhancing quality control with custom AI platforms. Each case shows how the technology is reshaping production processes and proving its value on the factory floor.
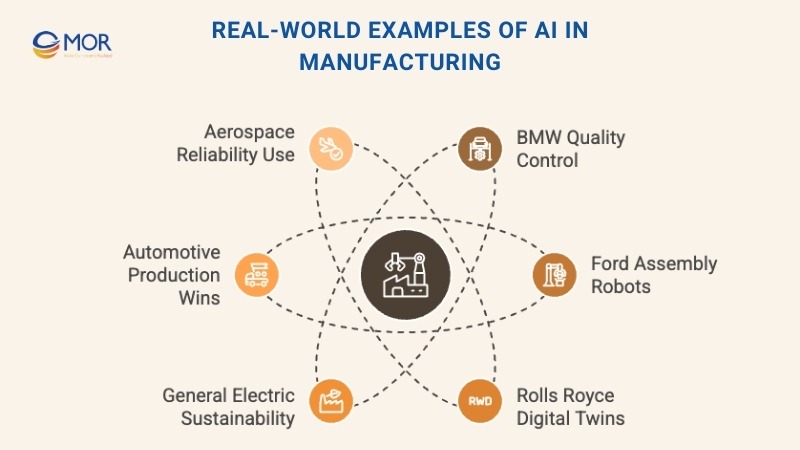
BMW Group – AI-Driven Quality Control
BMW demonstrates how central AI has become to modern automotive plants. The company created its own platform, AIQX (Artificial Intelligence Quality Next), to automate inspection processes.
Using advanced cameras and sensors, the system evaluates vehicles in real time as they move along the conveyor belt. Algorithms analyze this data instantly and deliver direct feedback to workers through smart devices, ensuring flaws are caught quickly and production standards remain consistently high.
Ford – AI Robots In Assembly
More than a hundred years after Henry Ford transformed car production with the moving assembly line, the company continues to drive innovation. Today, AI in manufacturing is part of Ford’s assembly operations, where robotic arms powered by AI install metal converters into place.
While carrying out this repetitive task, the system learns continuously, refining the most efficient way to assemble each part and improving speed and accuracy on the line.
Rolls Royce – Digital Twins For Engines
To improve reliability in aviation, Rolls Royce built a digital twin platform that combines data from its entire fleet of engines. AI can monitor engine health, anticipate problems, and recommend maintenance before failures occur by analyzing both historical and real-time inputs.
This predictive approach not only keeps engines running smoothly but also enhances safety and overall performance in the aerospace sector.
General Electric – Sustainability Through AI
In 2024, General Electric introduced Proficy for Sustainability Insights, an AI-based platform designed to help manufacturers balance productivity with environmental responsibility. Merging operational data with sustainability metrics, the system allows plants to manage energy and resources more effectively.
At the same time, it tracks climate-related requirements for compliance, giving manufacturers both profitability and accountability in one integrated solution.
The Future Of AI In Manufacturing
In only a few years, AI in manufacturing has advanced at remarkable speed, and the pace shows no signs of slowing. Smarter systems will require less human input, machines will communicate more seamlessly, and AI will handle increasingly complex tasks within production environments. As this shift continues, the technology will shape not just operations but the entire way factories function.
These changes bring both challenges and opportunities. Companies that delay adoption risk falling behind competitors who embrace more adaptive production systems and workforce augmentation. The outcome will be faster, smarter factories capable of delivering higher value. Over time, as AI becomes a standard tool, the frenzy of innovation will give way to more strategic uses. Leaders will focus less on short-term wins and more on aligning AI’s output with business goals, cementing its role as a core element of the manufacturing software stack.
Introduce AI Into Your Manufacturing With MOR Software
MOR Software empowers manufacturers to adopt AI with confidence. Our teams combine expertise in IoT, automation, and cloud platforms to deliver solutions that cut downtime, improve quality, and strengthen supply chains.
With ISO-certified processes and Agile delivery, we create secure, scalable systems tailored to your goals. From predictive maintenance to AI-powered digital twins, we’ve helped global enterprises modernize operations and stay competitive. Partner with MOR Software to bring smart manufacturing to life.
Conclusion
AI in manufacturing is no longer experimental, it’s a proven driver of efficiency, quality, and growth. From predictive maintenance to smarter supply chains, its use cases are reshaping how factories operate and compete. The companies that act now will secure lasting advantages, while late adopters risk falling behind. With MOR Software as your partner, you can confidently harness AI to modernize operations and prepare your business for the future of smart manufacturing. Contact us today to get started.
Rate this article
0
over 5.0 based on 0 reviews
Your rating on this news:
Name
*Email
*Write your comment
*Send your comment
1