Top 8 Major Consensus Mechanisms in Blockchain [2026 Comparison]

Consensus mechanisms are the foundation of blockchain security and trust. Yet with options like PoW, PoS, and newer models, choosing the right consensus mechanism in blockchain is not easy. This guide from MOR Software breaks down the top 8 types, compares their strengths, and shows which models fit today’s blockchain needs.
What Are Consensus Mechanisms?
A consensus mechanism is the process and code that allows a blockchain network to agree on the current state of its data. Instead of relying on manual checks or centralized authorities, blockchain platforms use these mechanisms to confirm transactions and maintain trust.
This approach removes the need for slow, error-prone human validation and ensures that cryptocurrencies and distributed ledgers operate smoothly and securely.
McKinsey estimates that tokenized financial assets could reach about 2 trillion dollars by 2030, which shows why strong consensus design matters.
How Do Consensus Mechanisms Work?
At their core, consensus mechanisms are protocols that let decentralized networks agree on a single version of the truth. Since blockchain has no central authority, nodes rely on mathematical rules and communication processes to validate transactions and add new blocks.
Each consensus algorithm follows a unique approach. In Proof of Work, miners solve complex puzzles to secure the chain, while in Proof of Stake, validators lock tokens as collateral to confirm transactions. Other models, like DPoS or pBFT, use voting systems or committee structures to reach agreement faster.
What all of these methods share is the ability to prevent fraud, double spending, or manipulation. By requiring economic resources, identity checks, or community participation, they make attacks expensive or impractical, keeping the enterprise blockchain secure and trustworthy.
Key Benefits Of Consensus Mechanisms
The strength of any blockchain lies in its consensus mechanism. Beyond validating transactions, these systems bring clear advantages that improve trust, security, and performance across decentralized networks.
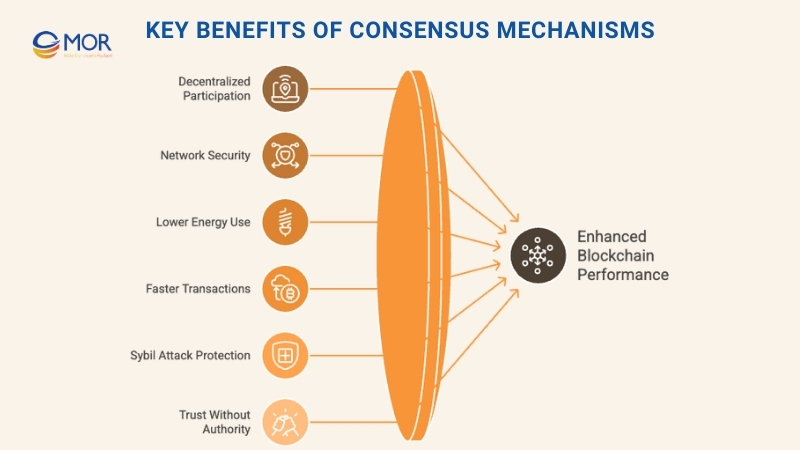
Decentralized Participation
A consensus mechanism allows wide participation in validating transactions, ensuring that no single party controls the network. This decentralized model strengthens trust and reduces risks of concentrated power.
On Ethereum, the Beacon Chain coordinates around one million validators, each posting 32 ETH, which shows how broad participation can be at scale.
Network Security
Some blockchain consensus mechanisms are highly secure because they demand either vast computing power or strict validator agreement. These safeguards make it difficult for attackers to manipulate transactions.
Bitcoin’s hashrate averaged about 910 exahashes per second in mid April 2025, up roughly 44% year over year. This raises the economic cost to attack the network.
Lower Energy Use
The U.S. Energy Information Administration reports Cambridge’s 2023 point estimate for Bitcoin electricity use at about 120 terawatt hours, with a range from 67 to 240 TWh.
Modern approaches like Proof of Stake cut back on energy demands. This energy-conscious design makes validation more sustainable compared to older systems.
Faster Transactions
Blockchain platforms like Delegated Proof of Stake deliver quicker confirmations. By limiting the number of validators, the process runs smoother and supports greater scalability.
Visa’s analysis notes that Solana typically averages around 400 transactions per second and can surge beyond 2,000 TPS during peak demand, with block times of roughly 400 milliseconds. This is how high throughput PoS networks can support fast confirmations.
Protection Against Sybil Attacks
By requiring resources such as computing power or staked coins, a consensus system discourages fake nodes and minimizes the risk of network flooding by malicious actors.
Trust Without Central Authority
Consensus enables trustless cooperation. Participants can exchange value and data with confidence, knowing decisions come from distributed agreement, not a central party.
Defense Against Data Alteration
A consensus algorithm protects records from tampering. Once information is validated, it becomes nearly impossible to alter without detection, preserving ledger integrity.
Top 8 Major Types Of Consensus Mechanisms
Over the years, blockchain has introduced a variety of consensus mechanisms to balance speed, security, and fairness. We’ll look at the top 8 major models shaping networks today.
Proof Of Work (PoW)
Proof of Work is one of the earliest and most widely used consensus mechanisms in blockchain. It relies on economic incentives and game theory, and has powered well-known blockchains like Bitcoin, Litecoin, and Dogecoin. In PoW, miners perform complex calculations to validate new blocks, a process known as mining.
A simple analogy explains the idea. Imagine a puzzle contest where the first person to solve the puzzle wins. At first, the puzzle grid is small, but as more players join, organizers make the grid larger, making it harder. Some participants even build special machines to solve puzzles faster, giving them a better chance of winning.
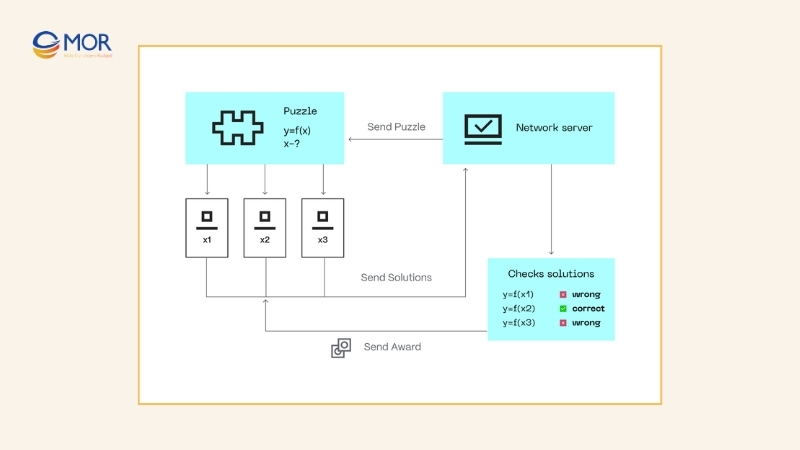
That mirrors
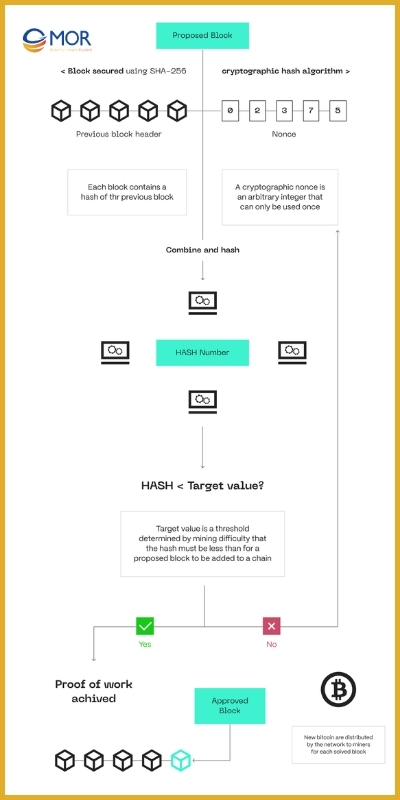
Any miner who solves the cryptographic challenge first announces it to the network. Other nodes then verify the solution. Once validated, the block is added to the chain. Different blockchains use distinct hash functions, with Bitcoin adopting SHA-256. Besides keeping the consensus algorithm running, this process strengthens security, since carrying out an attack would require enormous and costly computing power.
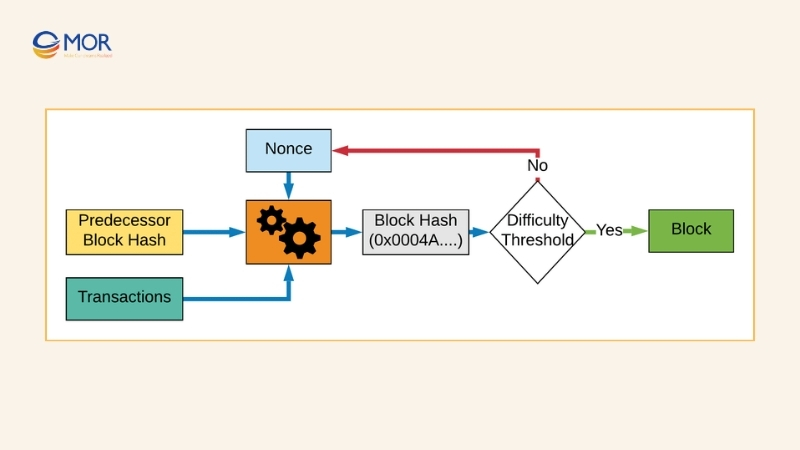
Mining difficulty adjusts as more computational resources enter the system, keeping the process balanced. Miners compete to discover a valid nonce, and those who succeed earn block rewards. While finding the correct solution demands significant effort, confirming a mined block is relatively straightforward, which helps maintain trust and transparency.
Strengths
Decentralized Structure. Proof of Work strengthens smart contract blockchain networks by allowing anyone with time and resources to mine. The validation power is spread widely, preventing a small group from gaining dominance. With no central control, a PoW blockchain operates as a true consensus mechanism in blockchain.
High Security Levels. PoW systems are extremely hard to attack. Gaining majority control would require impossible levels of computing power, making threats like a 51% takeover unlikely. Bitcoin’s history with PoW shows the resilience of this security model.
Reasonable Scalability. Scalability is necessary for growth, and while PoW networks are not the fastest, scaling improvements have made them more practical. These upgrades help networks handle millions of users with better cost efficiency.
Weaknesses
Slow Block Creation. Because mining difficulty rises as more participants join, transactions take longer. This leads to slower confirmations and can reduce overall usability.
Heavy Energy Use. Running PoW requires specialized hardware that consumes massive amounts of power. Studies reveal Bitcoin’s annual energy usage exceeds that of entire countries, which is a major reason some projects moved to Proof of Stake.
Hardware Limitations. Unlike many other blockchain consensus mechanisms, PoW depends on mining machines such as ASICs. This makes it harder for casual users to participate compared to systems that only need standard computers.
High Computational Expense. Both the setup and operation of PoW mining are costly. A single mining unit can cost thousands of dollars, and the ongoing power requirements add significant expenses.
Bandwidth Demands. Running a PoW node also needs strong internet connections. For instance, miners may need at least 50 Kbps speed, around 20 GB in monthly downloads, and nearly 200 GB in uploads. These demands can exclude participants in regions with weaker infrastructure.
Proof Of Stake (PoS)
Proof of Stake is a widely adopted consensus mechanism that relies on validators staking their native tokens to secure the network. Instead of solving heavy computations like in PoW, validators commit a portion of their assets, giving them the right to propose and validate blocks. This approach reduces costs, increases efficiency, and makes networks more accessible.
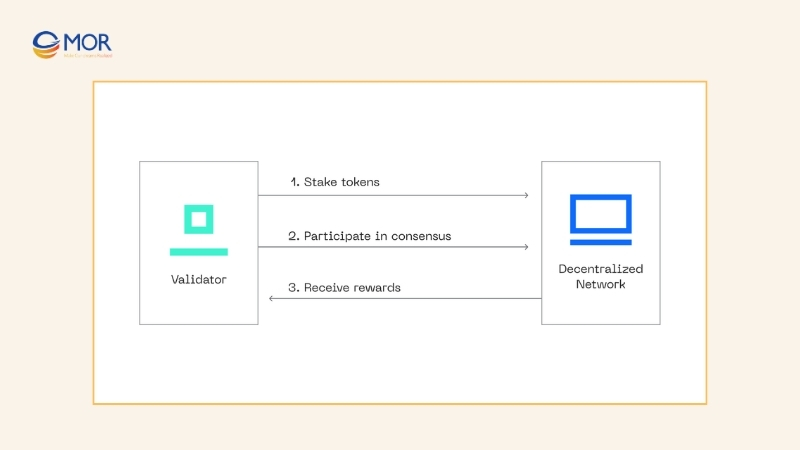
Ethereum officially transitioned from PoW to PoS in 2022 to address energy consumption and scalability challenges. Other popular projects such as Cardano and Tezos have also integrated PoS into their designs, showing its appeal as a practical alternative.
In decentralized finance, staking means locking tokens in a contract to earn rewards. The consensus mechanism blockchain version of staking has added weight, validators must maintain honest behavior. If they attempt to cheat, they risk losing their locked assets through penalties.
Each validator is responsible for both creating blocks and validating blocks proposed by others. Dishonesty results in direct financial loss, similar to how miners in PoW lose their investment in hardware and electricity.
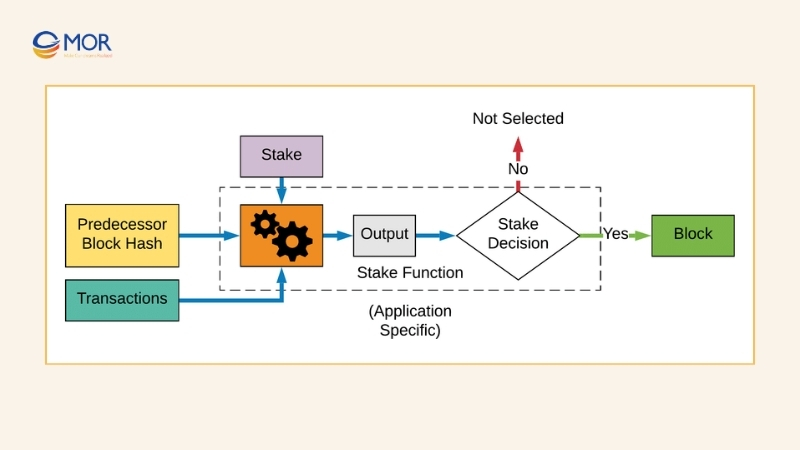
In PoS, though, the cost is tied to assets at stake rather than physical equipment, making the algorithm blockchain approach more sustainable and adaptive.
Strengths
Fast Block Creation. Unlike Proof of Work where adding a block can take minutes, PoS creates blocks in seconds. This makes transaction confirmation much faster.
High Transaction Throughput. With quick block generation, networks using PoS can handle a larger volume of activity without delays.
Energy Conscious Design. Proof of Stake is far less energy-intensive compared to mining-based models. Research shows PoS consumes about 99% less energy than PoW, since validators are chosen by stake instead of solving puzzles.
Scalable Network Growth. PoS can expand to support more users and transactions without losing speed. While scalability is strong, it is still somewhat behind what certain PoW models can achieve.
No Specialized Hardware Needed. Validators only need basic devices like CPUs and storage drives. This lower entry point encourages wider participation in the consensus mechanism blockchain process.
Weaknesses
Risk Of Centralization. In PoS, those with larger amounts of tokens to stake can gain more influence. This could lead to a small group dominating decisions within the network.
Lower Penalties For Misconduct. Some PoS networks set relatively low barriers to entry. That means validators might not lose much if they are penalized for dishonest activity. For example, on Cardano the minimum requirement is 25,000 ADA, worth only about $9,600. This limited financial risk reduces the deterrence against bad behavior compared to more resource-intensive consensus mechanisms.
Delegated Proof Of Stake (DPoS)
Delegated Proof of Stake was introduced in 2014 by Daniel Larimer as an evolution of Proof of Stake. It is now applied by popular blockchains like Tron and Cosmos. Unlike regular PoS where anyone who locks tokens may become a validator, DPoS limits that role to a smaller group of chosen representatives called “witnesses.”
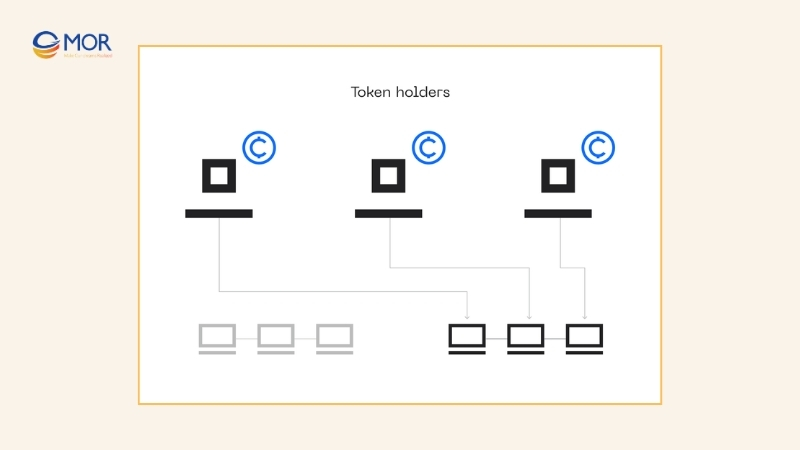
In this system, token holders stake their assets to elect witnesses who validate blocks and secure the chain on their behalf. If a witness misbehaves, the community can vote to remove them, making the process more democratic. This voting mechanism ensures that participants still influence decision-making even if they are not directly validating blocks.
Strengths
Improved Scalability. Because only a limited number of witnesses make decisions, DPoS reaches consensus faster. This allows the consensus mechanism to process a much higher volume of transactions.
Energy Friendly Design. As a variation of Proof of Stake, DPoS does not depend on heavy computing power. Witnesses are chosen based on staked wealth, making the system more energy-conscious.
Low Transaction Costs. Since blocks are produced quickly and congestion is minimal, transaction fees stay low compared to slower consensus mechanism blockchain models like PoW.
Weaknesses
Semi-Centralized Control. Critics argue that relying on a small group of witnesses introduces an element of centralization. This structure can resemble a council of decision-makers rather than a fully distributed network.
Risk of 51% Attacks. Because only a few witnesses manage block production, collusion between them is possible. If enough witnesses cooperate, they could make malicious changes or even halt the chain.
Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (pBFT)
The Byzantine Generals Problem highlights how difficult it is to reach agreement when some participants act dishonestly. The pBFT consensus mechanism was designed to address this issue by allowing the network to achieve agreement as long as two-thirds of the nodes remain honest. Platforms such as Hyperledger and Fabric rely on this method to maintain secure operations.
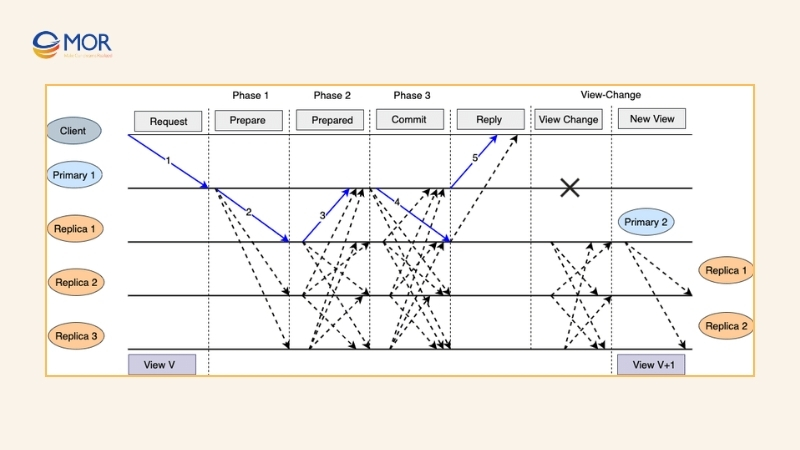
In a pBFT system, nodes are divided into two groups: primary nodes, which act as leaders, and secondary nodes, which serve as backups. At the end of each consensus round, the primary node rotates, preventing any single participant from holding authority for too long. Still, if more than one-third of the nodes are dishonest, the system’s security may be compromised.
Strengths
Energy-Efficient Model. Unlike Proof of Work, pBFT does not depend on high computational effort. This makes it easier and more practical for businesses to operate nodes without heavy costs.
High Transaction Throughput. Because nodes quickly communicate and validate transactions, pBFT achieves fast performance. Once a decision is made, it is final, removing the need for additional block confirmations and reducing delays.
Weaknesses
Limited Scalability. pBFT works well in smaller environments but struggles to scale to very large networks. As the number of transactions grows, the extensive communication required between nodes slows the process.
Vulnerability To Sybil Attacks. If an attacker controls enough dishonest nodes, they could disrupt operations. In this consensus mechanism blockchain model, once dishonest nodes exceed one-third of the total, they can manipulate or block transaction approvals.
Proof Of Weight (PoWeight)
A team of six MIT researchers led by Yossi Gilad introduced the Proof of Weight consensus mechanism for Algorand. Their goal was to design a solution to the Byzantine Generals’ Problem by using weight-based selection. This consensus crypto model assigns each participant a weight proportional to the tokens in their account.
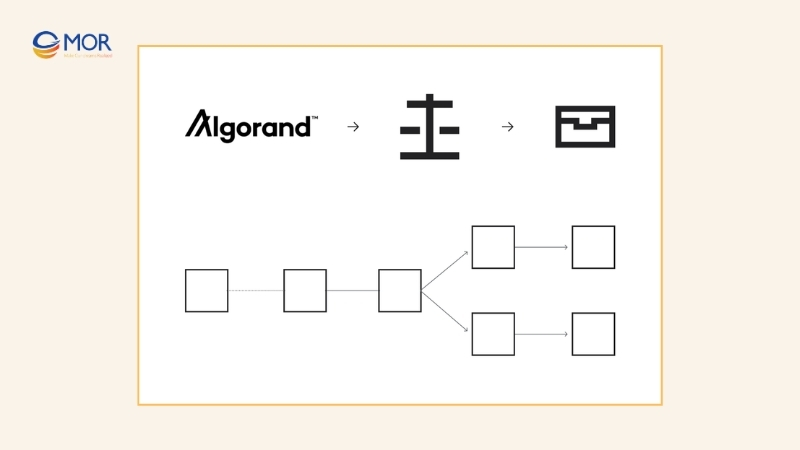
In PoWeight, a committee of validators is chosen at random, but the chances of selection depend on user weight. This randomness ensures that dishonest actors cannot easily take control. For the system to stay secure, honest participants must collectively hold at least two-thirds of the total value in the network.
Although it may resemble Proof of Stake, PoWeight differs in one important way: users do not need to lock or stake their tokens. Simply holding assets in a wallet is enough to be considered in the committee selection process.
Strengths
Flexible And Scalable. PoWeight serves as a template that protocols can customize to fit their needs. For example, Filecoin applies a version called Proof of Spacetime, where weight is based on the amount of data stored rather than tokens. This adaptability highlights how creative projects can use this consensus mechanism.
Fast Transaction Confirmation. Since only selected committee members validate transactions, blocks are confirmed more quickly than in systems where all users must participate.
Energy Conscious Operation. Unlike computation-heavy models, PoWeight does not consume significant power. Users simply need to hold assets, making it a more sustainable approach.
Weaknesses
Lack Of Incentives. Unlike PoW or PoS, this model does not offer validators direct rewards for participating. Without financial motivation, some users may be less committed to keeping the network secure.
Risk Of Semi-Centralization. Because validation rests with a small committee, the system can drift toward centralization. If these members act dishonestly, they could collude and undermine trust.
Proof Of Capacity (PoC)
Proof of Capacity, also known as Proof of Space, was formally introduced in 2015 by Stefan Dziembowski and Sebastian Faust. Burstcoin became the first project to apply this consensus mechanism. Instead of relying on computing power, miners demonstrate their eligibility by showing available storage space.
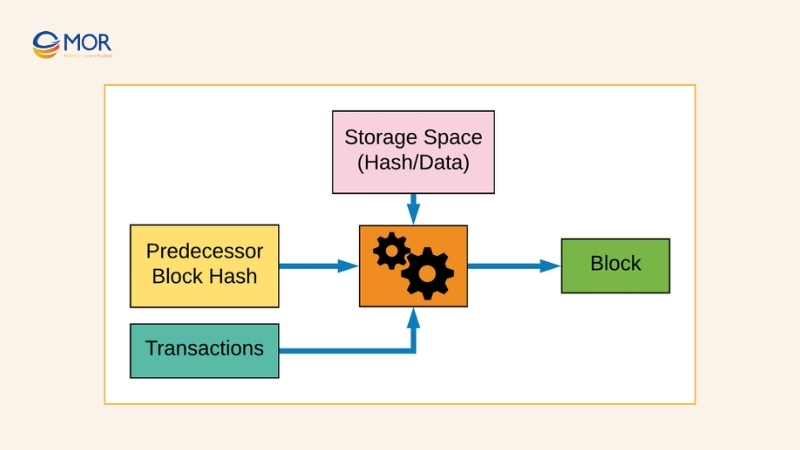
Before mining begins, participants prepare their drives by plotting nonces. The number of nonces depends on the amount of storage they can allocate. When the network issues a puzzle, the miner with the nonce closest to the correct hash wins. In this way, the more disk space a miner has, the higher their probability of success.
Strengths
No Expensive Hardware Needed. PoC is easy to set up. Miners simply use regular hard drives to plot nonces, which can even outperform costly ASICs for this process.
Encourages Decentralization. Since hard drives are affordable and widely available, more users can take part in validation. This broad participation strengthens the consensus mechanism in blockchain by avoiding dependence on a small group of elite miners.
Weaknesses
Vulnerability To Grinding Attacks. PoC networks face the risk of miners manipulating puzzles to favor their stored nonces. This allows them to mine blocks more often than others and gain disproportionate rewards.
Storage-Based Advantage. Miners with large-capacity drives hold an edge over others. More storage means more nonces, giving them an unfair advantage compared to those with smaller setups.
Proof Of Authority (PoA)
Some blockchains risk being compromised when they allow validators without proper checks. To address this, the Proof of Authority consensus mechanism requires validators to prove both their identity and commitment before joining the network.
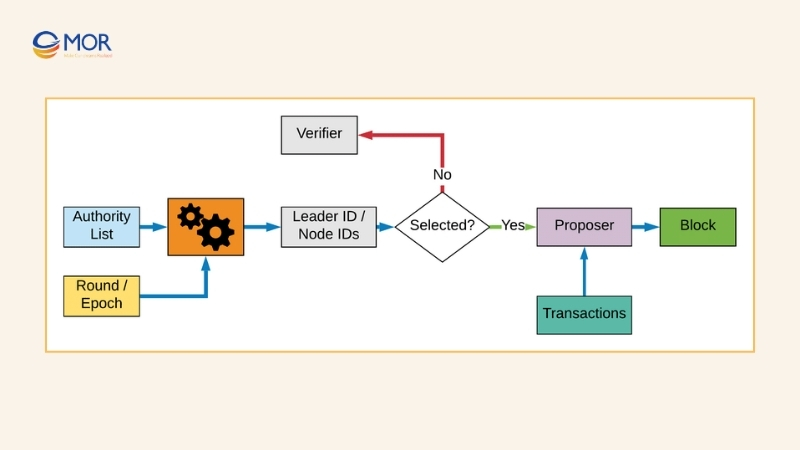
In PoA, validators undergo a vetting process where their real-world identity is verified. This makes it easier to hold them accountable if they attempt dishonest actions. Alongside identity, validators must also stake assets, combining reputation with financial commitment. In practice, they pledge both their coins and their credibility to secure the chain.
Strengths
Fast Transaction Validation. With only a small group of approved validators, PoA finalizes transactions quickly, improving efficiency.
Strong Security Measures. Because validators are pre-approved and identifiable, malicious behavior can be punished. Legal and financial accountability adds another layer of protection to this consensus algorithm.
Lower Energy Demand. While some resources are still required, PoA consumes far less energy than Proof of Work, making it more practical for frequent transactions.
Weaknesses
Limited Decentralization. Since only a handful of validators are approved, decision-making power is concentrated. This reduces the open and distributed nature of the system.
Loss of Anonymity. Unlike many blockchain consensus mechanisms that protect validator privacy, PoA requires identities to be public, sacrificing anonymity for accountability.
Proof Of Importance (PoI)
The NEM blockchain introduced the Proof of Importance consensus mechanism as an upgrade to Proof of Stake. While PoS evaluates validators mainly by how many tokens they lock away, PoI looks at a broader range of factors to encourage real network activity.
This model assigns a score to each participant based on three variables:
- The balance of tokens in their account.
- How frequently they transact with others on the network.
- The overall volume of those transactions.
By considering both token ownership and transaction behavior, PoI promotes active participation instead of passive holding. In effect, it motivates users to spend, trade, and interact while still securing the chain.
Strengths
Built-In Sybil Resistance. Because importance is tied to transaction history and token balance, it becomes very costly to create fake accounts or nodes. This strengthens the consensus mechanism blockchain against Sybil attacks.
Discourages Hoarding. Unlike PoS where assets remain locked, PoI keeps tokens in circulation, supporting healthier economic activity across the network.
Encourages Broader Participation. Rewards are not only about staking size. Active engagement in transactions also increases validator importance, giving more users a chance to contribute meaningfully.
Weaknesses
Bias Toward Wealthier Users. Accounts transacting in higher volumes gain higher importance scores, giving wealthier participants a natural edge in validation.
Lower Incentives For Validators. Because PoI focuses on importance rather than raw block production, node operators may earn fewer rewards compared to those in traditional staking-based consensus mechanisms. This makes it less attractive as a business model.
Consensus Mechanisms Summary Table
To make the comparison clearer, we’ve gathered the main consensus mechanisms into a single table. It highlights their advantages, drawbacks, and real-world use cases.
Consensus Mechanism | Advantages | Disadvantages | Protocols Using It |
| Proof of Work (PoW) | Decentralized structure, strong security, reasonable scalability | Slow block creation, high energy use, hardware reliance | Bitcoin, Dogecoin, Litecoin |
Proof of Stake (PoS) | Fast block times, high throughput, energy efficient, scalable, no special hardware needed | Risk of centralization, weaker penalties for misconduct | Ethereum, Cardano, Tezos |
Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) | Scalable design, low-cost transactions, energy efficient | Semi-centralized, vulnerable to 51% attacks | Tron, EOS, Ark |
Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (pBFT) | Energy efficient, high throughput, quick finality | Limited scalability, exposed to Sybil attacks | Hyperledger Fabric, Zilliqa |
Proof of Weight (PoWeight) | Customizable, scalable, fast confirmations, low energy demand | No validator incentives, risk of semi-centralization | Algorand, Filecoin, Chia |
Proof of Capacity (PoC) | Easy setup, no special hardware, promotes decentralization | Grinding attack risk, large storage advantage | Burstcoin, Permacoin |
Proof of Authority (PoA) | Fast validation, strong accountability, lower energy cost | Limited decentralization, loss of anonymity | VeChain, Palm Network, Xodex |
Proof of Importance (PoI) | Resistant to Sybil attacks, prevents hoarding, rewards participation | Favors wealthy users, fewer incentives for validators | NEM |
>>> Read more on MOR Blog about blockchain now!
Which Consensus Model Works Best?
There is no single winner when it comes to the “best” consensus mechanism. Among all options, Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS) remain the most widely adopted in blockchain networks.
PoW provides unmatched resilience against majority, or 51%, attacks. Its reliance on computational power makes manipulation extremely costly. Yet, this strength comes with a drawback, massive energy consumption. Mining consumes vast amounts of electricity, which has drawn criticism from regulators, businesses, and environmental groups worldwide.
PoS takes a different path. It is far more energy efficient since validators are chosen based on staked assets rather than raw processing power. Technologies like sharding also make it easier to validate multiple blocks simultaneously, giving PoS better scalability than PoW in certain conditions.
Still, both approaches struggle with centralization. In PoW, large mining operations dominate and leave little room for smaller miners. In PoS, participants with large stakes are far more likely to be selected to validate blocks and earn rewards, giving wealthier players a clear advantage.
This concentration of influence is not unique to these models. It is, to some degree, an inherent trait of most consensus algorithms. The trade-off between security, fairness, and energy efficiency remains central to the ongoing debate about which model serves blockchain as a service best.
Need Guidance? MOR Software Can Help
Comparing multiple blockchain consensus mechanisms can feel overwhelming. Each model comes with its own strengths and weaknesses, from the security of Proof of Work to the energy efficiency of Proof of Stake. Choosing the wrong one may lead to high costs, centralization risks, or limited scalability.
That’s where MOR Software comes in:
- Expert Consultation: We assess your business goals, scale, and technical needs to recommend the most suitable consensus model.
- Custom Development & Deployment: Our blockchain developers build blockchain systems using PoW, PoS, DPoS, pBFT, and the latest mechanisms.
- Security and Efficiency First: We help balance strong protection, cost optimization, and transaction performance.
- Long-Term Partnership: From testing to scaling, we provide ongoing support and upgrades for your blockchain solutions.
With proven experience in blockchain and distributed systems, MOR Software delivers solutions that are secure, efficient, and ready to grow with your business.
Contact us today to explore how we can support your blockchain journey.
Conclusion
The world of consensus mechanisms is diverse, from the security of Proof of Work to the efficiency of Proof of Stake and the adaptability of models like DPoS, PoWeight, or PoI. Each design serves a purpose, but no single approach solves every challenge. That’s why businesses must carefully evaluate scalability, energy usage, security, and fairness before deciding which path to follow.
If you’re exploring blockchain for your business, contact us to see how we can turn the right consensus model into a real competitive advantage.
MOR SOFTWARE
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the types of consensus mechanisms?
There are several well-known consensus mechanisms including Proof of Work (PoW), Proof of Stake (PoS), Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), Proof of History (PoH), Proof of Authority (PoA), Proof of Elapsed Time (PoET), and Proof of Burn (PoB). Each follows a unique method for validating transactions and securing the blockchain.
What do you mean by consensus mechanism?
A consensus mechanism is the set of rules and protocols in a blockchain that allow participants to agree on the state of the ledger. It ensures that all nodes synchronize their data and validate transactions consistently.
What is the consensus mechanism in CFA?
In the CFA context, a consensus mechanism is the process through which nodes on a distributed ledger agree on the shared record. This typically requires validating transactions first, then confirming agreement among participants before updating the ledger.
What is the Kafka consensus mechanism?
Kafka’s approach is often referred to as a voting-based consensus model. In Hyperledger Fabric, it provides trust by ensuring that participating nodes coordinate and agree on transaction order and validation.
What are the 4 levels of consensus?
The four levels of consensus include: full agreement and support, agreement with some reservations, disagreement but allowing the decision to move forward, and complete opposition that blocks the decision.
How many consensus mechanisms exist currently?
Currently, blockchain systems rely on about eight main consensus mechanisms, including Proof of Work, Proof of Stake, Delegated Proof of Stake, Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance, and others.
What are the main objectives of a consensus mechanism?
The main goals are to secure the blockchain, prevent fraudulent transactions, and keep the ledger accurate. By achieving agreement among participants, it ensures fair and transparent digital exchanges.
Is consciousness a consensus mechanism?
Some thinkers describe consciousness metaphorically as a consensus mechanism. It integrates past experiences and present perceptions to form decisions that shape future actions.
Which consensus mechanism is used by Bitcoin?
Bitcoin operates on the Proof of Work (PoW) system. It requires miners to solve mathematical puzzles to validate blocks, a process that was adapted by Satoshi Nakamoto for decentralized currency.
What type of consensus mechanism does Ethereum use?
Ethereum uses a Proof of Stake (PoS) system. Unlike Bitcoin’s Proof of Work, PoS relies on validators who stake their tokens to confirm transactions in an energy-efficient way.
What is the difference between PoW and PoS?
PoW depends on miners solving cryptographic problems, which requires significant computing power. PoS, on the other hand, selects validators based on how many tokens they hold and are willing to stake.
How does PoS select validators?
Validators in PoS are chosen according to the size and duration of their staked tokens. This design maintains security and minimizes energy consumption.
What are the different types of consensus mechanisms?
The main categories include Proof of Work (PoW), Proof of Stake (PoS), Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT), Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT), and Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAG).
What is an example of a consensus model?
One example is reintegrative shaming theory, where individuals are held accountable for wrongdoing without attaching stigma, promoting agreement on acceptable behavior.
What are the common consensus algorithms?
Proof of Work (PoW) remains the most widely used, supporting over 75 percent of cryptocurrency market capitalization. It involves solving cryptographic puzzles by adjusting a nonce.
What is a consensus method?
A consensus method is a decision-making approach where all participants contribute to reaching a shared solution. The outcome is considered a win-win since everyone accepts the final choice.
What is the new consensus mechanism?
Consensus mechanisms are evolving, but Proof of Work and Proof of Stake remain the dominant models for blockchains. They provide trust, security, and agreement across decentralized networks.
Where is Consensus 2026?
The 2026 Consensus event will be held in Toronto, notable as the birthplace of the world’s first Bitcoin and Ethereum exchange-traded funds.
Rate this article
0
over 5.0 based on 0 reviews
Your rating on this news:
Name
*Email
*Write your comment
*Send your comment
1