Explore 20 dApp Examples Transforming Industries in 2026

Blockchain isn’t just about cryptocurrency anymore. Today, dApp examples are redefining how people trade, play, and connect online, without relying on centralized control. This MOR Software’s guide will explore the top dApps examples shaping 2026, showing how real-world industries are transforming through decentralization and innovation.
What Are Decentralized Apps (dApps)?
Decentralized applications (dApps) are open-source software programs that run on blockchain-based peer-to-peer networks rather than a central server. To give a sense of scale, the dApp ecosystem averaged 24 million daily unique active wallets in Q1 2025, showing usage that’s far beyond a niche.
Unlike traditional apps owned and managed by a single company, dApps give users full control of their data and activity.
Think of it this way: when you post on a social platform like Twitter, the company can remove your content or suspend your account at any time. But in a blockchain-based version built as a dApp, no central authority can do that. Once your content is published, it’s stored across a distributed network that nobody owns or can alter. The base network regularly records roughly 645,000 active Ethereum addresses in a day. This is a sign of wide participation.
This design reflects the core dApp meaning, software driven by community consensus instead of corporate control. Each action is verified by multiple participants across the network, keeping the process transparent and tamper-proof. In fact, the developer community behind this technology continues to expand, with over 39,000 new crypto developers joining in 2024 and seasoned contributors reaching record activity levels. Their collective effort strengthens verification across networks and reinforces the transparency that defines decentralized systems.
Many examples of dApps on Ethereum already show how this model transforms ownership, governance, and trust in the digital world.
Core Requirements Of dApps
Anyone can create or use content on decentralized applications (dApps) without interference from a single authority. For these systems to function fairly and securely, they must follow a few key principles.
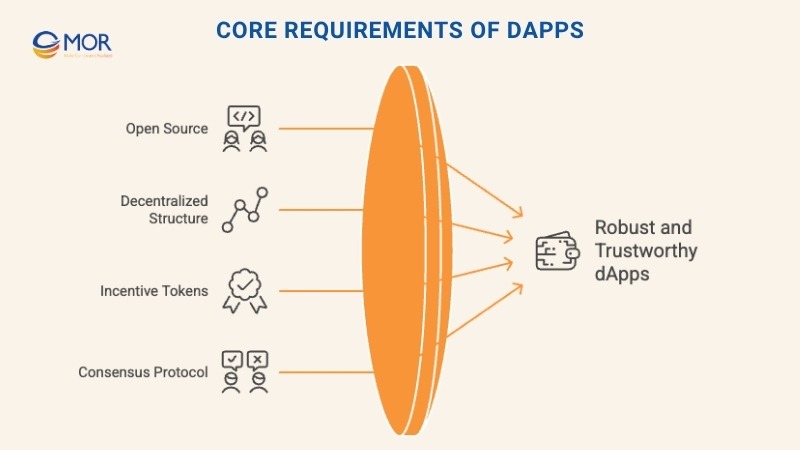
- Open Source: A dApp must have publicly available code that anyone can review or contribute to. Updates or changes should only occur when the majority of the community agrees, keeping governance transparent and democratic.
- Decentralized: All data and activities in a dApp should be stored across a public blockchain instead of a central server. This setup ensures transparency, security, and resilience against manipulation or data loss.
- Incentive: Users who contribute to a dApp network are rewarded through cryptographic tokens. These digital assets create motivation for users to validate transactions, secure the network, and sustain long-term participation.
- Protocol: Every dApp follows a clear set of rules known as a consensus protocol. This protocol defines how participants verify actions and maintain proof of value across the system.
These core elements shape how dApps development operates today. Whether built on Ethereum or other blockchains, they guarantee fairness, openness, and self-sustainability within the decentralized ecosystem.
How Do dApps Work?
A dApp runs its backend code on a decentralized peer-to-peer network rather than a single centralized server. Its frontend and user interface can still be built using standard web technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. What makes it unique is that the front end can be stored on decentralized hosting services such as IPFS, keeping both the app logic and interface distributed.
Although they look and feel like traditional apps, dApp examples operate differently under the hood. Instead of relying on a central authority, they use blockchain networks to handle logic, transactions, and data validation through smart contracts.
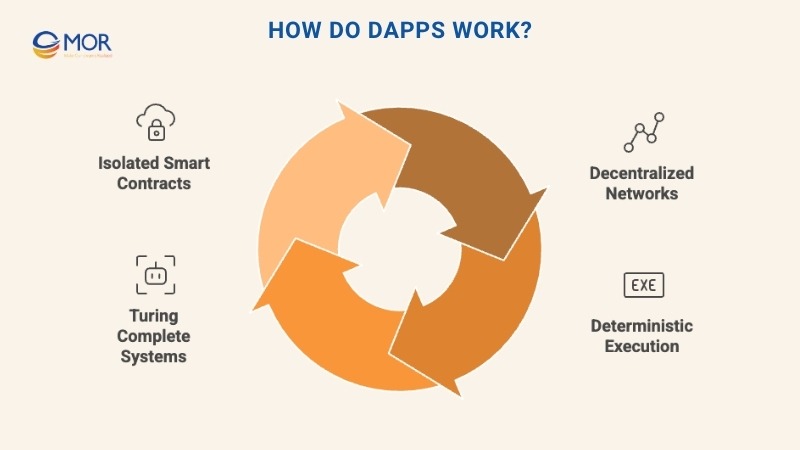
Here’s how their core mechanisms work:
- Decentralized: Most Ethereum dApps run on public blockchain networks that are transparent and community-managed.
- Deterministic: Each dApp executes the same function consistently, regardless of where or how it’s run.
- Turing Complete: These apps can process any computation when supplied with sufficient resources.
- Isolated: Smart contracts inside a dApp execute within an Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), which protects the blockchain from potential bugs or errors.
Combining these traits, developers can build a dApp that’s reliable, tamper-resistant, and independent from centralized control, redefining how digital services are created and maintained.
Top dApp Examples and Projects to Watch in 2026
The decentralized ecosystem continues to grow rapidly, with groundbreaking projects driving innovation across finance, gaming, and social platforms. Below are the top dApp examples to keep an eye on in 2026 as they redefine how blockchain is used in the real world.
1. Lido
Lido is one of the best dApps leading the decentralized finance space. It’s a liquid staking platform where users can stake Ethereum and other proof-of-stake assets such as Solana, Polygon, Polkadot, and Kusama. Unlike traditional staking, Lido enables users to keep their funds liquid. When someone stakes ETH on Lido, they receive a tokenized version called stETH, which can be used across other DeFi platforms for lending, yield farming, or collateralized loans.
The protocol is governed by Lido DAO, a decentralized organization that uses its native token, LDO, for voting and decision-making. Each token represents one vote, giving users a say in how the platform evolves. By 2023, Lido’s market cap exceeded $1 billion, making it one of the best dApp examples shaping decentralized finance.
Lido plays a vital role in the Ethereum dApps ecosystem because it lowers the barrier to staking ETH. Without services like Lido, individuals would need at least 32 ETH to run a validator node, something that’s often unaffordable for average users. With Lido, there’s no minimum staking requirement, allowing anyone to participate in securing the network.
Still, like most DeFi protocols, Lido isn’t risk-free. Smart contract vulnerabilities or governance challenges within the DAO can affect users. Even so, it remains one of the most impactful dApps projects, showing how decentralization can make staking more accessible and inclusive.
2. Uniswap
Uniswap is one of the most popular dApps examples in the decentralized finance ecosystem and the world’s largest decentralized exchange (DEX). Launched in 2018, it enables users to trade cryptocurrencies directly from their wallets without intermediaries. Instead of using centralized order books, Uniswap relies on automated liquidity pools. Users known as liquidity providers (LPs) deposit funds into these pools and earn a portion of trading fees in return. Each contributor receives a token that represents their share of the pool and can redeem it anytime to claim their earnings. The platform charges a small 0.3% fee on trades, automatically distributed among LPs.
Unlike traditional exchanges that match buyers and sellers, Uniswap uses an automated market maker (AMM) model. Prices are determined by an algorithm that adjusts according to supply and demand within the pool. Arbitrage traders also play a role by keeping prices close to the overall market value, creating a self-balancing system that supports consistent liquidity.
As one of the best dApps built on Ethereum dApps infrastructure, Uniswap never takes custody of user funds. All trades happen through smart contracts, giving users full control over their assets. This non-custodial design makes Uniswap more secure for those who manage their dApp wallet responsibly.
Governed by the UNI token, Uniswap operates as a decentralized autonomous organization (DAO). UNI holders can vote on future upgrades and protocol changes. By mid-2023, UNI had become one of the top 20 cryptocurrencies globally, cementing Uniswap’s reputation as the top dApp for decentralized trading in 2026.
3. Aave
Aave stands among the most innovative dApp examples in decentralized finance, serving as a leading platform for crypto lending and borrowing. Built entirely on smart contracts, Aave connects lenders and borrowers directly in a peer-to-peer ecosystem. Borrowers can access overcollateralized loans by depositing cryptocurrencies as collateral, ensuring security for both parties. If the collateral value drops below the required loan-to-value ratio, the protocol automatically liquidates part of it to maintain stability. Typically, users can borrow up to around 80% of their deposited assets.
Lenders, in turn, contribute funds to Aave’s liquidity pools and earn interest generated by borrowers. These returns vary depending on demand, with annual percentage yields (APYs) typically ranging between 2% and 30%. Supported assets include ETH, DAI, USDC, USDT, and Aave’s native governance token, AAVE.
One of Aave’s most distinctive features is the flash loan mechanism. These loans allow users to borrow and repay funds within a single transaction, enabling arbitrage and short-term trading strategies without upfront capital. This concept has made Aave a standout in dApps development, showing how blockchain automation can expand financial opportunities.
Governed by AAVE token holders, the platform operates as a decentralized autonomous organization. Users can stake AAVE to earn extra yield and participate in governance decisions. As one of the best dApps in the DeFi space, Aave continues to redefine lending by merging transparency, automation, and flexibility across the dApps list shaping Web3 finance in 2026.
4. Curve
Curve is one of the standout dApp examples in decentralized finance, operating as a decentralized exchange (DEX) built on an automated market maker (AMM) model. While platforms like Uniswap focus on supporting a wide range of crypto assets, Curve specializes in stablecoins and wrapped tokens. Its liquidity pools often include assets with similar values, such as DAI, USDC, or wrapped Bitcoin (wBTC), which helps maintain price stability and minimize volatility.
This design allows Curve to keep trading fees and slippage low while reducing the risk of impermanent loss for liquidity providers. By focusing on stability rather than speculation, the platform attracts investors and traders who value predictable returns and efficient swaps. For instance, if a pool contains both DAI and USDC, and too much USDC enters the pool, the algorithm slightly lowers its price. Traders buy the discounted asset, and through arbitrage, the pool automatically rebalances itself, no human intervention required.
Even in pools that include assets like wBTC, which can fluctuate in value, the protocol maintains balance by ensuring relative stability among tokens within the same pool.
Curve’s precise AMM model and community-driven governance make it a key player in dApps development and one of the best dApps for low-risk DeFi strategies. As part of the Ethereum dApps ecosystem, it continues to set the standard for efficiency, stability, and trust in decentralized trading.
5. Axie Infinity
Axie Infinity remains one of the most recognized dApp examples in the blockchain gaming world. Developed by Sky Mavis, it introduced millions to the concept of play-to-earn gaming. The game lets players buy, breed, and battle digital creatures called Axies, each represented as a unique NFT. Players earn Smooth Love Potion (SLP) tokens by winning battles, which can be traded or used to enhance gameplay.
At its peak, Axie Infinity became a source of income for many in countries like the Philippines, where thousands left traditional jobs to play full-time. During the height of its popularity, the rewards players earned often surpassed local wages. But when SLP’s value dropped, the model became unsustainable, causing a sharp decline in daily active users.
Critics have also pointed out that the gameplay itself lacks excitement and depth, with many players admitting they participated mainly for financial gain. This shift from entertainment to profit undermined the game’s long-term appeal.
Still, Axie Infinity remains a landmark in dApps development, showing how blockchain can merge finance, gaming, and digital ownership. With its governance token AXS and community-driven updates, it continues to influence the dApps list of Web3 gaming innovations. If Sky Mavis revitalizes the experience, Axie could again become one of the best dApps bridging entertainment and decentralized economies.
6. MakerDAO
MakerDAO is one of the most influential dApp examples in decentralized finance, designed to function as a decentralized reserve bank on the Ethereum dApps network. It powers the DAI stablecoin, which maintains its value through over-collateralization rather than relying on a central authority.
To generate DAI, users lock assets such as ETH or other approved tokens into MakerDAO’s smart contracts, creating a collateralized debt position (CDP). For example, minting $1,000 worth of DAI requires roughly $1,500 in ETH as collateral, maintaining a 150% collateralization ratio. Safer assets like USDC require less collateral, around 125%, due to their lower volatility. This mechanism ensures the DAI token stays stable even in fluctuating market conditions.
Users can also deposit their DAI back into the system to earn interest through the DAI Savings Rate (DSR), allowing them to grow their holdings while contributing to overall network liquidity.
Governance lies at the heart of MakerDAO’s model. Holders of the platform’s native MKR token vote on important decisions, including which assets qualify as collateral, how interest rates are set, and the system’s total debt limits.
MakerDAO has expanded beyond DeFi into real-world finance, even facilitating loans like a $7.8 million credit for a Tesla repair center in California. This milestone demonstrates how the development can merge decentralized systems with tangible financial use cases, positioning MakerDAO among the best dApps shaping the future of banking.
7. Synthetix
Synthetix is one of the most innovative dApp examples in decentralized finance, enabling users to trade synthetic assets that mirror the prices of both cryptocurrencies and real-world commodities. These assets, known as “synths,” track everything from major fiat currencies like USD and EUR to indexes, precious metals like gold and silver, and even inverse crypto tokens that rise when the underlying asset falls. This system allows investors to gain exposure to a wide range of markets without directly holding the underlying assets.
While Synthetix provides the underlying infrastructure, actual trading takes place on Kwenta, its decentralized exchange (DEX). Unlike traditional order books or automated market maker models, Kwenta uses a peer-to-peer mechanism powered by decentralized oracles to determine asset prices. The platform’s native SNX token serves both as collateral for synths and as a governance asset that gives holders influence over system decisions.
Users who stake their SNX tokens earn a share of trading fees, typically between 0.3% and 1%, collected from transactions on Kwenta. They can also deposit synths into liquidity pools on Curve or Uniswap, earning extra yield and contributing to the wider DeFi ecosystem.
Governance in Synthetix is handled through three distinct DAOs: protocolDAO, which manages smart contract upgrades; grantsDAO, which funds developer initiatives; and synthetixDAO, which allocates resources to major ecosystem projects. This layered governance model makes Synthetix one of the top dApps for decentralized trading innovation.
8. PancakeSwap
PancakeSwap is one of the most active dApp examples in the decentralized exchange market, ranking just behind Uniswap in trading volume. Built on the BNB Smart Chain (formerly Binance Smart Chain), PancakeSwap uses an automated market maker (AMM) model where users trade directly through liquidity pools rather than relying on intermediaries. Participants who provide liquidity earn a portion of trading fees, while the platform’s native token, CAKE, can be staked in dedicated SYRUP pools to earn additional rewards. The exchange charges a modest 0.2% fee per transaction, reinforcing its low-cost appeal for DeFi users.
What truly differentiates PancakeSwap is its playful, gamified design. Users can win unique NFTs, which can then be staked for bonus rewards, adding an element of fun and engagement to traditional trading. The platform also hosts daily lotteries, where participants can earn NFTs or CAKE tokens, creating a steady cycle of community participation.
Beyond trading, PancakeSwap operates an Initial Farm Offering (IFO) platform, its version of token launches. Here, users can invest in new tokens while yield farming simultaneously, earning passive income as part of their participation.
9. Splinterlands
Splinterlands is one of the leading dApp examples in blockchain gaming, blending collectible NFTs with competitive strategy gameplay. Built on the Hive blockchain, it’s a digital trading card game where players collect, trade, and battle with more than 280 unique NFT cards. Each card has distinct abilities and attributes, like speed, armor, and different attack types (melee, ranged, or magic), that influence battle outcomes. Players can join ranked matches, tournaments, and daily quests to earn in-game rewards and enhance their decks.
Unlike many blockchain games limited to a single ecosystem, Splinterlands supports cross-chain interoperability. Players can connect with multiple blockchains, including Ethereum, Wax, and Tron, making it easier to trade and move digital assets between platforms. This flexibility adds long-term value and accessibility for its player base.
Because the game runs on Hive, transactions are fast and inexpensive, allowing developers to push updates regularly without disrupting gameplay. This structure makes Splinterlands one of the dApps in the gaming sector, scalable, engaging, and community-driven.
10. Steemit
Steemit stands as one of the most successful dApp examples in the social media space, operating as a fully decentralized content-sharing platform built on its own Steemit blockchain. It hosts a thriving ecosystem of more than 300 connected dApps, including projects like Utopian, which funds open-source blockchain initiatives, and DTube, a decentralized video platform comparable to YouTube or Vimeo.
What makes Steemit unique is its reward-driven model. Instead of relying on ads or centralized monetization, it pays users for creating and curating quality content. The system distributes rewards in the form of STEEM tokens, the platform’s native cryptocurrency. Posts that receive more upvotes and engagement earn higher rewards. This process is powered by Steemit’s Proof-of-Brain algorithm, which calculates payouts based on community-driven reputation and engagement metrics.
Beyond content creation, users can also launch their own Smart Media Tokens (SMTs) on the network, each built on the same Proof-of-Brain principle. This flexibility allows creators and communities to design their own reward systems and token economies.
Merging blockchain with social engagement, Steemit reshapes online publishing into a user-powered economy.
11. DeFi Kingdoms
DeFi Kingdoms is one of the standout dApp examples blending decentralized finance with gaming. Built on the Harmony One blockchain, it merges classic role-playing game (RPG) mechanics with play-to-earn functionality, allowing users to explore a medieval-inspired virtual world filled with NFT-based assets and decentralized finance tools. The game integrates a built-in decentralized exchange (DEX) modeled after Uniswap V2, enabling players to trade or swap NFTs and tokens seamlessly within the same ecosystem.
Players can roam through towns, visit the Tavern to rent or sell heroes, deposit tokens in the Bank for staking, and cultivate digital assets in the Gardens. Each hero is represented as an NFT with unique stats such as stamina, wisdom, mana, and agility, which improve as they complete battles and earn rewards. This combination of exploration, strategy, and financial participation gives DeFi Kingdoms a rich, immersive appeal reminiscent of early RPGs like Runescape.
The ecosystem is powered by the JEWEL token, which serves as both a governance asset and an in-game currency for purchasing items or participating in liquidity pools.
12. Alien Worlds
Alien Worlds is a leading dApp example in the blockchain gaming space, designed as a cross-chain metaverse that spans Ethereum, BNB Smart Chain, and WAX. Players, known as “Explorers,” can earn rewards by purchasing or renting NFT-based land and tools, mining digital resources, and participating in the game’s decentralized governance structure. Each activity contributes to the in-game economy, powered by the Trillium (TLM) token.
The TLM token serves multiple purposes within Alien Worlds. Players can stake their holdings to influence decisions in one of several Planet DAOs, each with its own rules and economy. This governance model allows users to shape how rewards are distributed and how the metaverse evolves, giving players true ownership and control over their digital environment.
What makes Alien Worlds especially unique among Ethereum dApps is its integration with external platforms like Minecraft, where players can also earn TLM tokens. This bridge between gaming ecosystems helps expand the reach of the metaverse and strengthens community engagement.
13. Compound
Compound is one of the most established dApp examples in decentralized finance, operating as a lending and borrowing protocol built on Ethereum. It enables users to supply assets such as ETH, WBTC, USDC, USDT, DAI, ZRX, REP, SAI, and BAT into smart contracts to earn interest or use them as collateral for crypto loans.
When users deposit their assets, the protocol locks them into liquidity pools and automatically pays interest in the same cryptocurrency they supplied. Borrowers can then take out loans against their deposits, with borrowing limits determined by each asset’s risk profile. Stablecoins like USDC typically allow higher loan-to-value (LTV) ratios, while more volatile tokens like BAT have stricter limits to maintain system stability.
Governance is handled through the platform’s COMP token. Holders of COMP can vote on changes to the protocol, including updates to interest models, reserve factors, and treasury operations. Additionally, Compound distributes small amounts of COMP to both borrowers and lenders every day, rewarding participation and encouraging decentralization.
As one of the earliest Ethereum dApps to popularize algorithmic lending, Compound helped define the foundation for today’s DeFi ecosystem.
14. Decentraland
Decentraland is one of the most recognizable dApp examples in the metaverse space, combining virtual reality, NFTs, and blockchain into a fully decentralized digital world. Built on the Ethereum blockchain, it allows users to explore, build, and monetize virtual environments while maintaining complete ownership of their assets.
At its core, Decentraland operates as both a VR platform and an open-world metaverse governed by the Decentraland DAO. Control of the platform lies with holders of the LAND token, each representing a unique parcel of virtual real estate. Players can purchase, develop, or trade these NFT-based plots, with some pieces of land selling for $3.5 million during the market peak.
Beyond real estate, users can buy and sell digital wearables for their avatars, attend virtual concerts, host events, and participate in mini-games. Every interaction and transaction within Decentraland happens through smart contracts, ensuring transparency and verifiable ownership.
15. X2Y2
X2Y2 is one of the fastest-growing dApp examples in the NFT marketplace sector, offering creators and collectors a decentralized platform packed with advanced trading and analytics tools. Built on the Ethereum network, it supports popular features like profit sharing, rarity tracking, real-time notifications, and bulk listing, all designed to make NFT trading more efficient and rewarding.
A key feature of X2Y2 is its profit-sharing model. Users who stake the platform’s native X2Y2 token receive a share of all trading fees generated across the marketplace, creating a steady incentive for community participation. Its bulk listing and bulk purchasing tools also save users considerable gas fees, allowing multiple NFTs to be listed or bought in a single transaction instead of paying for each one separately.
The platform’s real-time alert system automatically notifies users via email when bids or purchases occur, helping active traders stay informed. Meanwhile, the integrated rarity tracker delivers precise analytics and pricing history for every NFT listed, supporting smarter investment decisions.
16. Sudoswap
Sudoswap is one of the most distinctive dApp examples in the decentralized exchange ecosystem, designed specifically for NFT trading rather than fungible tokens. Built on the Ethereum blockchain, it uses an automated market maker (AMM) model similar to Uniswap but tailored for NFTs. This approach eliminates the need for traditional order books, allowing users to buy and sell NFTs instantly through liquidity pools.
What sets Sudoswap apart is its ability to reduce NFT price volatility and promote open, censorship-resistant trading. Unlike centralized marketplaces such as OpenSea or Rarible, users on Sudoswap can trade any NFT without restrictions or approval from intermediaries. This freedom makes it a preferred choice for those seeking full control over their digital assets.
However, the platform intentionally removes royalty mechanisms, meaning creators do not receive automatic payments when their NFTs are resold. This decision has sparked debate within the community but aligns with Sudoswap’s goal of enabling pure peer-to-peer transactions without additional fees.
Governance is handled through the platform’s native SUDO token, giving holders the ability to vote on updates and liquidity rules.
17. Frax Finance
Frax Finance is one of the most innovative dApp examples in the stablecoin ecosystem, designed to create a balance between algorithmic and collateralized stability. Built on the Ethereum blockchain, Frax introduced FRAX, the world’s first partially-collateralized, algorithmic stablecoin. This hybrid model combines crypto-backed reserves with algorithmic adjustments to maintain a stable value close to one U.S. dollar.
The system operates through two tokens: FRAX, the stablecoin, and FXS, its governance and utility token. Users can exchange FRAX and FXS within the protocol, and arbitrage traders help stabilize FRAX’s price whenever it diverges from its peg. This mechanism allows Frax to maintain balance without being fully reliant on collateral reserves.
Unlike MakerDAO’s DAI, which is overcollateralized, FRAX requires only partial collateral. This approach increases scalability, allowing the ecosystem to expand faster but also introducing higher risk compared to fully backed stablecoins like DAI or USDC.
18. MetaWin
MetaWin has become one of the most engaging dApp examples in blockchain-based gaming and entertainment, redefining how players experience online casinos. Operating as a decentralized crypto gaming platform, MetaWin combines lottery-style contests, slot games, and live dealer experiences within a transparent, blockchain-driven environment. Every transaction and outcome is verifiable, ensuring fairness without reliance on centralized operators.
What makes MetaWin stand out among best dApps in its category is its rewards system. Players can earn not only crypto and cash prizes but also blue-chip NFTs and the platform’s exclusive MetaWinner NFTs. These NFTs act as access passes to premium games, bonus rounds, and special events, introducing a layer of ownership and utility rarely seen in traditional gaming.
19. 1inch
1inch is one of the smartest dApp examples in decentralized trading, designed to solve the liquidity and pricing gaps that often occur across decentralized exchanges. As a DEX aggregator, it scans and compares rates from multiple exchanges in real time, ensuring users get the best possible prices for their trades. Instead of relying on a single platform like Uniswap or Balancer, 1inch automatically splits and routes transactions through the most efficient paths across more than 75 liquidity sources.
Operating on Ethereum, BNB Smart Chain, and Polygon, 1inch connects with major protocols including Uniswap, Balancer, Curve, and the 0x ecosystem. This aggregation process reduces slippage, lowers transaction costs, and optimizes execution speed, all without requiring users to give up control of their assets.
The platform is governed by the 1INCH token, introduced in late 2020. Token holders can participate in decision-making about protocol updates, fee structures, and new integrations.
19. 1inch
1inch is one of the smartest dApp examples in decentralized trading, designed to solve the liquidity and pricing gaps that often occur across decentralized exchanges. As a DEX aggregator, it scans and compares rates from multiple exchanges in real time, ensuring users get the best possible prices for their trades. Instead of relying on a single platform like Uniswap or Balancer, 1inch automatically splits and routes transactions through the most efficient paths across more than 75 liquidity sources.
Operating on Ethereum, BNB Smart Chain, and Polygon, 1inch connects with major protocols including Uniswap, Balancer, Curve, and the 0x ecosystem. This aggregation process reduces slippage, lowers transaction costs, and optimizes execution speed, all without requiring users to give up control of their assets.
The platform is governed by the 1INCH token, introduced in late 2020. Token holders can participate in decision-making about protocol updates, fee structures, and new integrations.
20. Lens Protocol
Lens Protocol is one of the most forward-thinking dApp examples reshaping the future of social networking through decentralization. Built on the Polygon blockchain, it functions as a social graph framework that gives creators full ownership of their content, communities, and data. Unlike traditional social media platforms, where user information is controlled by corporations, Lens empowers users to move freely between platforms while keeping their profiles, followers, and posts intact.
When a user creates a profile, the system automatically generates a dynamic NFT that contains all their social interactions, posts, comments, likes, and shares. This means the user’s activity and identity exist permanently on-chain, fully owned by them. Followers also receive “follow NFTs,” which act as proof of connection and can even enable unique benefits or access to exclusive content.
Through Lens’ follow module, creators can monetize their communities directly by setting up either one-time or subscription-based fees for followers. This opens new possibilities for gated content, premium experiences, and creator-driven social economies.
With its open-source design, Lens Protocol enables developers to build new decentralized platforms and applications using its infrastructure.
Why Are Decentralized Applications Important?
Decentralized applications (dApps) are transforming how people exchange information, assets, and value. Their open, peer-to-peer nature removes traditional barriers in finance, communication, and digital ownership, reshaping how users interact online.
Cost and Efficiency
Since dApp examples operate on decentralized networks, they remove the need for intermediaries like banks or centralized platforms. This structure cuts operational costs, increases transaction speed, and improves scalability across industries. With smart contracts handling agreements automatically, users can manage their finances, assets, or data directly, no middleman required. This shift is already influencing how companies approach dApps development for real-world efficiency gains.
Security
Built on blockchain, dApps rely on cryptographic verification and distributed consensus to secure data. Once recorded, information can’t be altered without network-wide agreement, making it virtually tamper-proof. This immutable structure enhances trust and protects sensitive records across finance, healthcare, and government systems.
Accessibility
Because they exist on public blockchains, dApps are available to anyone with an internet connection. They don’t depend on geographic boundaries, bank accounts, or third-party approval. This global reach gives individuals access to digital assets, services, and financial tools once limited to major institutions, expanding inclusion and opportunity worldwide.
Transparency
Every transaction within a dApp is visible on a shared ledger. Users can track activity, confirm authenticity, and hold participants accountable without relying on a central authority. This transparency builds confidence, especially across decentralized ecosystems where users expect fairness and proof of integrity.
Together, these features show why dApps goal examples extend far beyond finance, they represent a shift toward a transparent, secure, and user-owned digital future.
Real-World Applications Of Dapp Examples Across Industries
Decentralized applications (dApps) eliminate intermediaries by allowing users to interact directly through blockchain-based systems. They’re already redefining industries by powering everything from smart contracts and gaming to decentralized finance and social networks.
Many dApp examples automate trust-based interactions that once required third parties. Some power self-executing financial contracts, decentralized exchanges, or community-driven social platforms. Others support secure voting, identity management, and transparent governance. Even web browsers are integrating dApps as plugins that handle crypto payments, advertising, and donations.
Below are some of the most common real-world applications of dApps development:
- Financial Services: Powering peer-to-peer exchanges, lending, and asset transfers without banks or brokers.
- Supply Chain Management: Using blockchain to track goods from origin to delivery, ensuring authenticity and accountability.
- Identity Verification: Storing and validating personal or institutional data securely for passports, voting, or digital access systems.
- Real Estate: Enabling direct property sales between buyers and sellers while keeping ownership records and deeds immutable on-chain.
- Healthcare: Maintaining patient records, prescriptions, and clinical data on decentralized ledgers to prevent data breaches.
- Education: Hosting decentralized learning ecosystems where students and teachers connect without institutional restrictions.
- Social Media: Supporting censorship-free platforms where creators own their content and communities.
- Predictive Markets: Powering decentralized forecasting systems where users can stake and trade on event outcomes.
These dApps goals examples show how decentralization is expanding from finance into everyday life, creating systems that are transparent, secure, and owned by their users.
Risks And Scams Associated With Dapps
While dApp examples have opened new opportunities in digital finance and ownership, they’ve also created room for scams and exploitation. Because these platforms are decentralized and often anonymous, tracing or punishing fraud can be challenging.
One of the most common threats comes from Ponzi schemes, where returns to earlier investors are paid with funds from new ones rather than real profits. Such schemes can appear legitimate on blockchain platforms until they collapse, leaving participants with major losses.
Fake initial coin offerings (ICOs) are another serious risk. Scammers may promote new tokens or dApps development projects, promising innovation or high returns but disappearing after raising money. Without proper oversight, investors have little protection once funds are transferred.
Phishing attacks are also frequent in the crypto space. Hackers create fake wallet sites, dApp interfaces, or emails that mimic legitimate projects to steal private keys or login details. Meanwhile, some malicious dApps contain hidden code that installs malware, exposing user wallets or devices to theft.
Because transactions on the blockchain are irreversible, users must research before connecting their dApp wallet to any platform. Verifying project legitimacy, checking smart contract audits, and relying on trusted sources are essential precautions in this rapidly expanding ecosystem.
Pros And Cons Of Using dApps
Like any emerging technology, dApp comes with both opportunities and limitations. Understanding their strengths and weaknesses helps businesses decide how to adopt and scale decentralized solutions effectively.
Main Advantages
The biggest strength of dApp examples lies in privacy and control. Transactions on these platforms are executed through smart contracts, allowing two parties to exchange value or information without revealing personal identities or relying on intermediaries. This peer-to-peer model ensures greater autonomy and data protection for every user.
Supporters of free expression also view dApps as a path toward censorship-resistant communication. Because no single authority controls a blockchain, decentralized social platforms can operate without fear of content removal or political interference. Messages and posts, once published, remain accessible across the network.
In addition, Ethereum dApps provide developers with a flexible framework for experimentation. Builders can design innovative blockchain-powered solutions for industries such as banking, gaming, healthcare, retail, and social media. The modular design of dApps development allows for fast deployment and continuous innovation across sectors.
Fast Fact: The concept of a smart contract dates back to 1996, introduced by American cryptographer Nick Szabo while studying at the University of Washington. His idea of programmable agreements laid the foundation for today’s decentralized applications and blockchain automation.
Key Disadvantages
While dApp examples show enormous promise, they’re still in an experimental phase. Scalability remains one of the biggest challenges. As more applications compete for blockchain resources, networks can experience congestion, slower transactions, and higher gas fees, issues that limit mass adoption.
Another hurdle is usability. Most traditional apps are intuitive and polished, while many dApps still lack smooth interfaces or clear navigation. To attract mainstream users, developers must focus on creating a seamless end-user experience that matches or surpasses centralized platforms. Without that, adoption may stay limited to tech-savvy audiences.
Security is also a concern. Because dApps development happens on open networks without centralized oversight, rushed or poorly written code can expose vulnerabilities. Hackers can exploit these flaws, leading to lost funds or data breaches. Regular auditing and community reviews are critical, yet not all projects follow these practices.
Once deployed, updating a dApp is difficult because blockchain code is immutable. Fixing bugs or improving features often requires complex governance votes or new smart contract versions, which slows innovation.
Summary table of pros and cons of Decentralized Apps
Pros | Cons |
Protects user privacy | Limited scalability and potential network congestion |
Censorship-resistant structure | Harder to deliver a polished, user-friendly interface |
Encourages innovation through a flexible, open platform | Challenging to modify or update code once deployed |
| Security risks from unaudited or rushed programming |
Regulatory And Compliance Issues Facing Dappsps
Regulating dApp examples is complex because of their decentralized and borderless structure. Traditional laws rely on location-based oversight, but dApps operate on distributed networks that aren’t tied to a single country or governing authority. This lack of jurisdiction creates uncertainty for governments trying to monitor financial activity, protect users, or enforce compliance standards.
Centralization Trends Within Decentralized Platforms
A good illustration of this challenge is the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union. Even decentralized platforms must comply with GDPR when serving EU users, regardless of where their developers or servers are located. In late 2023, a European subnet of the Internet Computer Protocol (ICP) introduced blockchain infrastructure to help developers build GDPR-compliant dApps.
However, this approach introduces a paradox. Because ICP nodes are approved by a governing DAO and restricted to EU locations, it creates a form of centralization. If such frameworks become the norm, dApps risk losing some of the autonomy that defines them.
Financial and token-based platforms face additional scrutiny. Some dApps development projects raise funds through token sales, which regulators may classify as unregistered securities offerings. Likewise, decentralized exchanges and lending protocols must navigate know-your-client (KYC) requirements to prevent fraud and ensure investor protection.
Protecting End Users
Beyond financial regulation, dApps raise concerns about personal data, privacy, and digital safety. Every on-chain transaction is permanent, and signing a transaction through a dApp wallet carries risk if the user doesn’t fully understand what they’re approving. Wallets like MetaMask consistently remind users to verify every signature, as one wrong confirmation could expose assets to loss.
These regulatory and consumer protection challenges highlight a growing tension: preserving decentralization while ensuring accountability. Balancing innovation with oversight will shape the future of how the best dApps operate in global markets.
MOR Software Helps Businesses Build Real-World dApps
MOR Software plays a key role in helping businesses transform blockchain ideas into real decentralized applications that deliver measurable value. As a trusted software development company in Vietnam, we design and build dApp solutions that combine blockchain innovation with business practicality. Our teams specialize in developing secure, scalable, and high-performance applications using technologies like Ethereum, Polygon, and Solana, along with smart contracts written in Solidity or Rust.
We’ve supported clients across finance, healthcare, and eCommerce to create decentralized systems that enhance transparency, automate workflows, and improve data security. From consulting and UI/UX design to blockchain integration and deployment, we manage every stage of the development process with precision.
With a strong foundation in Agile practices, certified blockchain engineers, and a proven delivery record, MOR Software provides end-to-end support for companies exploring decentralized technologies. Our approach focuses on long-term value, helping businesses move from experimentation to production-ready dApp ecosystems.
Contact us to explore how we can help you build your next decentralized application.
Conclusion
Decentralized applications are reshaping industries by making systems more transparent, secure, and user-driven. From finance to gaming and beyond, these dApp examples show how blockchain is unlocking new ways to build trust and efficiency. As the technology matures, more businesses will explore its real potential. MOR Software stands ready to guide that journey, turning bold blockchain ideas into impactful decentralized solutions. Contact us today to start building your next-generation dApp.
MOR SOFTWARE
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a dApp in blockchain?
A dApp, or decentralized application, is software that runs on a blockchain rather than a centralized server. It uses smart contracts to manage its logic and operations automatically without a single authority controlling it. Unlike traditional apps that rely on intermediaries, dApps are maintained by a distributed network of users and enable direct peer-to-peer interaction through crypto wallets.
What is an example of DApps?
Decentralized applications, or dApps, remove the need for intermediaries by running on blockchain networks. Examples include automated financial contracts, online multiplayer games, and decentralized social platforms.
What is the most popular DApp?
As of recent rankings, KAI-CHING NEAR leads with over 2 million unique active wallets, followed by World of Dypians, HOT Protocol, and Pixudi on DappRadar.
Is Binance a DApp?
The Binance Smart Chain (BSC) enables developers to create decentralized applications and smart contracts. While Binance itself is centralized, many DApps are built on its blockchain infrastructure.
Is Bitcoin a DApp?
Yes. Bitcoin is often regarded as the first decentralized application, operating on a peer-to-peer network without intermediaries. It follows open-source principles, though later DApps expanded on its concept.
Is Trust Wallet a DApp?
Trust Wallet is a decentralized, non-custodial crypto wallet that supports multiple blockchains. It provides features like token swaps, staking, and built-in DApp browsing, suitable for both new and experienced users.
Is MetaMask a DApp?
MetaMask is primarily a Web3 wallet, but it also acts as a gateway to decentralized applications. It evolved from a simple browser extension into a multi-functional tool for DeFi and NFT interaction.
Is PancakeSwap a DApp?
Yes. PancakeSwap is a decentralized application and automated market maker (AMM) that allows users to trade digital assets, earn liquidity rewards, and participate in staking on the Binance Smart Chain.
Can you make money with dApps?
Yes. Developers and investors can earn through gaming DApps, transaction fees, token sales, or sponsorships. Players may also gain rewards or tokens based on gameplay performance or contributions.
Which blockchain is best for dApps?
Chainlink is often considered the top choice for DApps due to its wide data provider network. It ensures reliable, real-world data for industries like finance, gaming, insurance, and logistics.
How to build a dApp?
To build a DApp, start by defining its purpose, then design smart contracts, set up the framework, ensure data backups, and implement strong security practices before deployment.
What are dApps in crypto?
In cryptocurrency, a dApp is a decentralized software application that runs on a blockchain or peer-to-peer network, eliminating centralized servers and ensuring transparency.
What is the dApps rule?
The DAPPS rule is a goal-setting framework that stands for Dated, Achievable, Personal, Positive, and Specific, helping individuals set clear and motivating objectives.
What are the risks of using dApps?
Major risks include smart contract bugs, wallet or private key theft, malicious permissions, and vulnerabilities in cross-chain bridges that can lead to loss of funds.
What is a Web3 dApp?
A Web3 dApp is a decentralized application that runs on blockchain technology. All dApps are Web3 apps, but not every Web3 app is fully decentralized. Users connect through crypto wallets to interact securely.
Rate this article
0
over 5.0 based on 0 reviews
Your rating on this news:
Name
*Email
*Write your comment
*Send your comment
1