How Does AI Work? Complete Guide For Businesses 2025 [Detailed]
Evolving alongside the digital age, AI is no longer a futuristic concept but a practical tool that supports businesses across multiple areas. For companies aiming to maximize technology’s benefits, understanding “How does AI work?” is the first step to unlocking its full potential. Let’s explore with MOR Software how AI operates, the different types of AI, and how applying this technology can help your business thrive in the digital era.
A Closer Look At Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI (Artificial Intelligence) is a field of computer science focused on developing systems capable of simulating human intelligence. These systems can learn from data, make decisions, recognize images, understand natural language, and even generate new content capabilities that were once unique to humans.

Put simply, AI is technology that enables machines to think, learn, and act intelligently. Unlike traditional software that follows predefined rules, AI works by using data and machine learning algorithms, allowing systems to continuously improve over time.
In today’s fast-paced digital world, learning about AI is no longer optional. It’s essential for both individuals and businesses. Understanding what AI is and how it works can give your business a significant edge in leveraging it for automation, analytics, personalization, and more.
How Does AI Work?
Now that we’ve understood what AI is, the next big question is: “How does AI work?” To answer this, we need to explore each stage in the operational process of an artificial intelligence system. In the sections below, you’ll learn about the complete AI workflow, broken down into five essential phases.
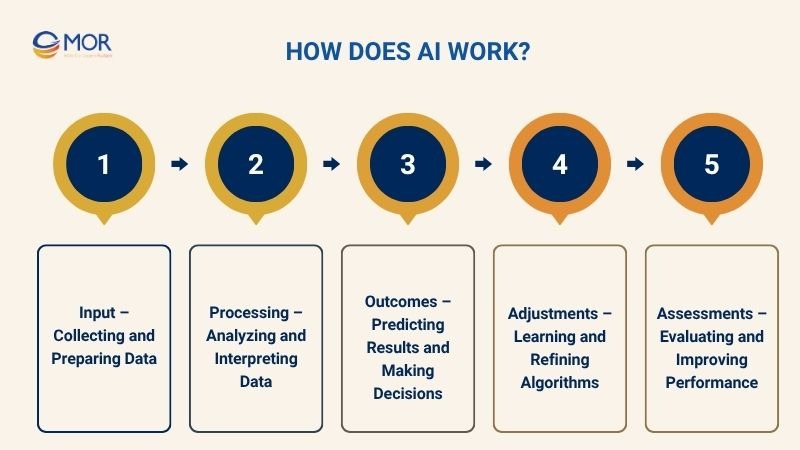
Input – Collecting and Preparing Data
To understand how does AI work, the first and most fundamental step is collecting and preparing input data. This is where AI machine learning systems begin interacting with information from various sources: text, audio, images, video, or sensor data.
However, not all data is ready for use. Raw data is often messy, incomplete, or inconsistent. Therefore, the system must perform tasks such as cleaning the data, removing duplicates, standardizing formats, and categorizing the information according to criteria that match the model’s objectives.
At this stage, AI does not perform any analysis or action; it is simply “learning to understand the data.”
Processing – Analyzing and Interpreting Data
AI uses machine learning algorithms to detect patterns, identify relationships between variables, and extract valuable insights from data. These algorithms are not hard-coded like traditional software. Instead, they are adaptive and can handle a wide range of data types.
Example: In the banking sector, AI analyzes thousands of daily transactions to identify unusual patterns. It learns what normal spending behavior looks like for each customer and can detect subtle anomalies that may signal fraudulent activity.
Outcomes – Predicting Results and Making Decisions
At this stage of the AI workflow, all collected, processed, and analyzed data is transformed into concrete predictions or actions. To answer the question: “How does AI detection work?” in this phase, let’s take the example of a bank transaction fraud detection system:
- Applying the trained model: The AI scans new transaction data, looking for unusual patterns compared to the customer’s normal spending behavior.
- Predicting risk: Based on historical data, the AI forecasts the likelihood that the transaction is fraudulent, assigning a specific probability score.
- Classifying the input: The system labels the transaction as “normal” or “suspicious” depending on a predefined risk threshold.
- Making the decision: If the transaction is flagged as suspicious, the AI automatically places it on hold and sends an alert to the security team or the customer for verification.
Adjustments – Learning and Refining Algorithms
AI doesn’t stop at producing results. It continues to learn from its own mistakes to become smarter. This self-adjustment phase highlights AI’s ability to continuously improve performance, which is a key differentiator from traditional software.
Example: The fraud detection system becomes more accurate over time by learning from every confirmed or dismissed alert. When a flagged transaction turns out to be legitimate, the AI updates its model to reduce false positives in the future. This ongoing learning helps the system adapt to new fraud tactics and maintain strong detection accuracy.
Assessments – Evaluating and Improving Performance
The final step in the AI workflow is evaluating performance and improving the overall model. AI reviews its predictions, measures the accuracy and effectiveness of the applied algorithms, and if needed, recommends changes or re-trains the model with new data.
Popular Types Of AI You Should Know
Artificial Intelligence can be classified in several ways. The most common categories are based on capability, functionality, and underlying technology. Each offers a different perspective on how AI systems operate and evolve.
1. Types of AI Based on Capability
This classification focuses on how intelligent or autonomous an AI system can be.
Narrow AI (Weak AI)
Narrow AI, or Weak AI, is the most common type of artificial intelligence today. These systems are built to perform a specific task with exceptional accuracy, often surpassing human ability in that single domain.
Typical examples include Siri, Google Translate, and fraud detection systems in banking. They process language, recognize images, and analyze data, but they lack true understanding or general reasoning abilities.
General AI (Strong AI)
General AI, also known as Strong AI, represents the theoretical stage where machines could perform any intellectual task a human can do. This level of AI would have full cognitive understanding, adaptability, and emotional intelligence.
Although it doesn’t yet exist, General AI remains the long-term goal of AI research, shaping how scientists imagine the future of human-machine collaboration.
Superintelligent AI
Superintelligent AI is a hypothetical form that would surpass human intelligence across every field such as science, creativity, and social skills included. It could make decisions and learn at speeds far beyond human capacity.
This level is purely speculative for now, often discussed in ethical and philosophical debates about the future of AI.
2. Types of AI Based on Functionality
This classification looks at how AI systems behave and respond to the environment.
Reactive Machines
These are the most basic AI systems. They react to specific inputs without storing past experiences. A classic example is IBM’s Deep Blue, the chess-playing computer that defeated Garry Kasparov.
Limited Memory AI
Limited Memory AI systems can learn from past data for a short time. Most modern applications, such as self-driving cars or fraud detection tools, fall into this group. They analyze recent patterns but cannot store long-term memory.
Theory of Mind AI
This type of AI would be capable of understanding emotions, beliefs, and intentions, essentially grasping human psychology. It’s still under development and remains largely theoretical.
Self-Aware AI
The most advanced and still hypothetical form, self-aware AI would possess consciousness and self-reflection. It would understand its existence, goals, and emotions. While this concept drives much of AI ethics research, it’s far from becoming reality.
3. Technology-Based Classifications of AI
AI can also be categorized by the technologies and methods used to build and train it.
Machine Learning AI
These systems use algorithms that allow them to learn from data and improve automatically. Machine learning AI is used in areas like market forecasting, medical diagnostics, and recommendation systems.
Generative AI
Generative AI is a newer branch that can create new content like text, images, audio, video, and even code. It powers tools like ChatGPT, DALL·E, and Midjourney, enabling machines to produce original, human-like output.
Deep Learning AI
Deep Learning AI relies on artificial neural networks inspired by the human brain. It’s behind advanced image recognition, speech processing, and natural language understanding models.
Type of AI | Description | Real-World Examples | Intelligence Level | Learning Capability |
Narrow AI (Weak AI) | Performs a specific task with high accuracy within a limited scope | Siri, Google Translate, fraud detection systems | Low (task-specific) | Learns from predefined datasets |
General AI (Strong AI) | Can perform any intellectual task a human can do (still theoretical) | None yet (research phase) | Human-level (in theory) | Capable of adaptation and reasoning |
Superintelligent AI | Surpasses human intelligence in all aspects | None yet (theoretical concept) | Beyond human level | Self-improving through recursive learning |
Reactive Machines | Responds to inputs without memory | IBM Deep Blue | Basic | No learning capability |
Limited Memory AI | Learns from recent data and patterns | Self-driving cars, fraud detection | Moderate | Learns from short-term data |
Generative AI | Creates new content (text, images, video, code) | ChatGPT, DALL·E, Midjourney | Medium to High | Learns from large datasets |
Machine Learning AI | Analyzes and predicts patterns from data | Market forecasting, diagnostics | High (task-specific) | Improves with new data |
Key Training Models Used In Artificial Intelligence
AI systems rely on several core training models, each shaping how machines learn and make decisions.
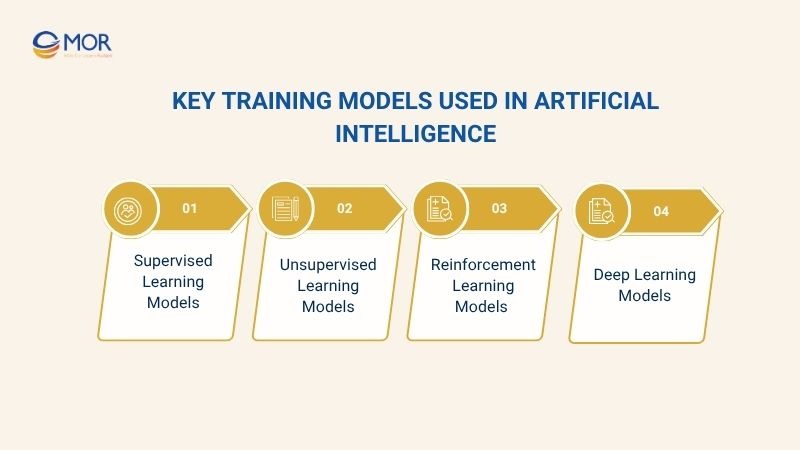
- Supervised Learning: The model learns from labeled data, where inputs already have known outputs. It’s widely used in image recognition, spam filtering, and fraud detection because it delivers precise, predictable results.
- Unsupervised Learning: This model works with unlabeled data to find hidden structures or natural groupings. It’s common in clustering, market segmentation, and anomaly detection, helping businesses discover insights they didn’t know existed.
- Reinforcement Learning: The AI learns through interaction and feedback, improving decisions based on rewards or penalties. It’s ideal for robotics, autonomous vehicles, and any system that adapts to changing environments.
- Deep Learning: Built on multi-layer neural networks, deep learning handles complex data like images, speech, and text. It powers modern applications in computer vision, natural language processing, and voice recognition.
Learn The Process Of AI With Real-world Applications
To better understand how AI works in real life, we need to look at the artificial intelligence applications that have been transforming our daily lives. Below are the most notable AI applications that are helping enhance user experience, improve efficiency, and increase safety across various industries.
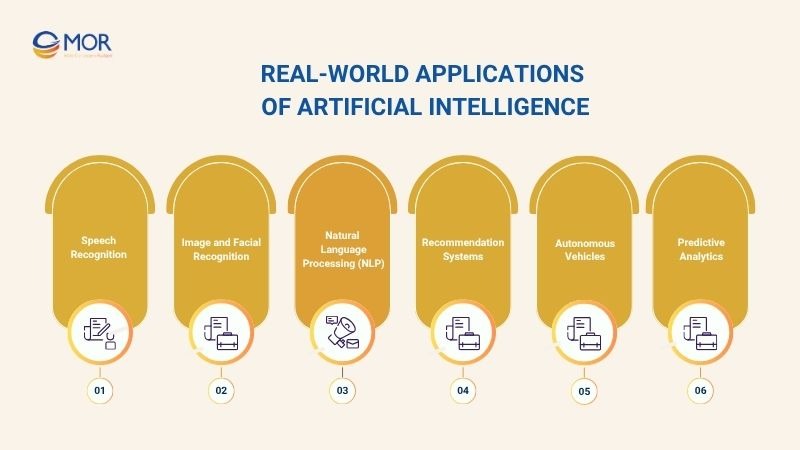
Speech Recognition
Speech recognition is a common example of “How does AI work” to understand and respond to human voice commands. This AI-powered technology is integrated into virtual assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant.
Real-world example: A user tells Siri, “Play relaxing jazz music.” The AI processes this command through the following steps:
- Audio capture: The microphone records the user’s voice and applies noise cancellation to remove background sounds.
- Analog-to-digital conversion: AI encodes the sound waves into digital signals for analysis.
- Speech-to-text conversion: Deep learning models (e.g., RNN, Transformer) transcribe the voice into the text “Play relaxing jazz music” with high accuracy.
- Context understanding (Natural Language Processing – NLP): AI analyzes the intent and determines that the request is to “play jazz music.”
- Service integration: AI sends the request to the connected music app (Apple Music or Spotify).
- Response: Siri plays the jazz playlist and replies via text-to-speech: “Playing your relaxing jazz playlist.”
Image and Facial Recognition
Image and facial recognition use AI to analyze visual content from photos or videos to identify objects, people, or actions.
Real-world example: Unlocking an iPhone using Face ID:
- Image capture: The TrueDepth camera scans the user’s face and collects both 3D and 2D data.
- Image preprocessing: AI adjusts lighting, removes noise, and aligns the image for optimal input quality.
- Feature extraction: Deep neural networks detect unique facial features, such as the distance between eyes, nose shape, and bone structure.
- Data matching: AI compares these features with the stored facial template in the Secure Enclave.
- Authentication decision: If matched, the phone unlocks; if not, it requests a passcode.
- Action: The device grants access to the home screen.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is an AI technology that enables computers to understand, analyze, and respond to human language almost in real time. Thanks to NLP, systems like chatbots or translation tools can interpret user intent and provide accurate responses.
Real-world example: Customer service chatbot:
- User query: The customer types or says, “I want to reset my account password.”
- Text preprocessing: AI removes extra characters, normalizes vocabulary (lemmatization), and detects the language.
- Intent recognition: The NLP model identifies the request as “password reset.”
- Entity extraction: AI detects key information such as account name or linked email.
- System query: The chatbot calls internal APIs to generate a password reset link.
- User response: The chatbot sends reset instructions or a link, along with an email confirmation.
Recommendation Systems
Recommendation systems use AI to analyze user behavior and suggest relevant content or products.
Real-world example: Netflix recommending new movies:
- Behavior data collection: AI records watch history, ratings, and viewing time.
- Data preprocessing: Personal information is anonymized and standardized.
- Pattern recognition: Algorithms like collaborative filtering or deep learning find similar user profiles.
- Recommendation generation: AI selects movies that match the user’s interests or trends among similar viewers.
- Display: Suggestions appear on the Netflix homepage with posters and trailers.
- Continuous learning: AI updates recommendations as users watch or skip titles.
Autonomous Vehicles
Autonomous vehicles are among the most complex AI applications, combining computer vision, reinforcement learning, and path planning. These systems detect surroundings, predict traffic situations, and control the vehicle without human intervention.
Real-world example: Tesla autopilot on the highway:
- Data collection: Cameras, radar, and lidar capture images and measure object distances.
- Data preprocessing: AI filters noise and synchronizes data from multiple sensors.
- Object detection (Computer Vision): AI recognizes vehicles, lanes, traffic lights, and pedestrians.
- Behavior prediction: AI anticipates the movement of surrounding vehicles and traffic scenarios.
- Decision-making: Reinforcement learning algorithms choose safe actions such as lane-keeping, slowing down, or overtaking.
- Vehicle control: AI sends commands to steering, braking, and acceleration systems.
- Continuous monitoring: The car adjusts in real time to environmental changes.
Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics is an AI discipline that uses historical data and machine learning models to forecast trends, events, or risks. It helps organizations seize opportunities and prevent losses by issuing early warnings.
Real-world example: Predictive maintenance in a factory:
- Sensor data collection: Machines send data on temperature, vibration, and operating speed.
- Data preprocessing: Outliers are removed, and timestamps are synchronized.
- Pattern analysis: AI detects abnormal patterns that indicate potential issues.
- Failure prediction: AI estimates that a machine may fail within two weeks.
- Recommendation: The system alerts the maintenance team to schedule repairs before breakdowns occur.
- Performance tracking: AI updates its predictive model based on actual maintenance results.
Top Benefits Of Artificial Intelligence In Everyday Life
Not just a future technology, artificial intelligence (AI) has now become an essential part of modern life. Below are the top benefits of AI in everyday life for your work, productivity, and daily experience.
Increased Efficiency Through Artificial Intelligence
One of the most visible benefits of artificial intelligence in daily life is its ability to improve efficiency through automation. AI can handle large volumes of repetitive tasks without constant human intervention.
According to a survey by Atlassian, 68% of developers saved more than 10 hours per week using generative AI coding tools, up from 46% the previous year. This demonstrates AI’s growing impact in reducing workload and enhancing productivity across various roles.
Improved Accuracy With AI Systems
AI significantly reduces errors in data processing and decision-making due to its speed, consistency, and ability to analyze massive datasets. In high-precision industries like healthcare, finance, or manufacturing, AI systems can detect anomalies and provide insights faster than traditional methods.
For example, AI tools deployed across 20,000 clinical consultations helped reduce diagnostic errors by 16% and treatment errors by 13% compared to conventional approaches. This proves that artificial intelligence improves accuracy in critical decision-making environments.
Enhanced Personalization Powered
One of the most prominent everyday applications of artificial intelligence is user experience personalization. AI systems can analyze browsing habits, purchase history, or interaction patterns to deliver highly relevant suggestions tailored to each individual.
For instance, e-commerce platforms like Amazon and streaming services like Netflix use AI to recommend products or content based on user behavior.
Better Decision-Making Supported
Artificial intelligence doesn't just process data; it enables data-driven decision-making by providing deep insights and actionable recommendations. In business, AI can analyze market trends, consumer behavior, and financial risks to help managers make faster, smarter, and more strategic decisions.
By leveraging AI-powered analytics tools, companies can stay ahead of the competition, optimize resource allocation, and minimize decision-making errors, turning data into a competitive advantage.
In Conclusion
Mastering “How does AI work” is the key to harnessing the transformative power of this technology, driving sustainable growth and continuous innovation. MOR Software is always ready to partner with you in designing and implementing AI solutions tailored to your business objectives. Contact us today to turn AI into a catalyst for your business success.
MOR SOFTWARE
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the 4 types of AI?
The four main categories of AI are: reactive machines, limited memory systems, theory of mind, and self-aware AI. Each type reflects a different level of capability, from basic task performance to advanced reasoning and consciousness.
How does AI work step by step?
AI works in five main steps:
- Data collection
- Data preprocessing
- Model training
- Prediction and decision-making
- Evaluation and improvement
How does artificial intelligence work?
Artificial intelligence works by using algorithms and models to analyze data, recognize patterns, make predictions, and adapt over time through machine learning.
How do you explain AI to beginners?
AI is technology that enables machines to simulate human intelligence, learning, reasoning, and making decisions using data and algorithms.
Who created AI?
AI was pioneered by computer scientists like John McCarthy, Alan Turing, and Marvin Minsky in the mid-20th century.
Does AI learn by itself?
AI can learn by itself in reinforcement learning and unsupervised learning models, where it improves without explicit human programming.
What can AI do that humans can't?
AI can process massive datasets, detect complex patterns instantly, and operate continuously without fatigue, surpassing human speed and scale.
Rate this article
0
over 5.0 based on 0 reviews
Your rating on this news:
Name
*Email
*Write your comment
*Send your comment
1