Waterfall vs Agile Development: What’s the Real Difference?

Choosing the right delivery model can shape your product’s speed, cost, and long-term success. The debate around waterfall vs agile development often comes down to change, control, and real-world risk in modern software projects. This guide from MOR Software will clarify the difference, help you spot the right fit, and avoid costly mistakes before development starts.
What Is Agile Methodology?
Agile is a project management approach created to handle changing requirements while helping teams deliver results faster. It focuses on close collaboration, steady improvement, and customer satisfaction through small, regular releases of a working product.
At its core, Agile seeks to make software development more flexible and open to change. This mindset often stands out in discussions around waterfall vs agile development, especially when teams face shifting priorities, frequent feedback, or uncertain requirements, which is common in software development agile vs waterfall scenarios.
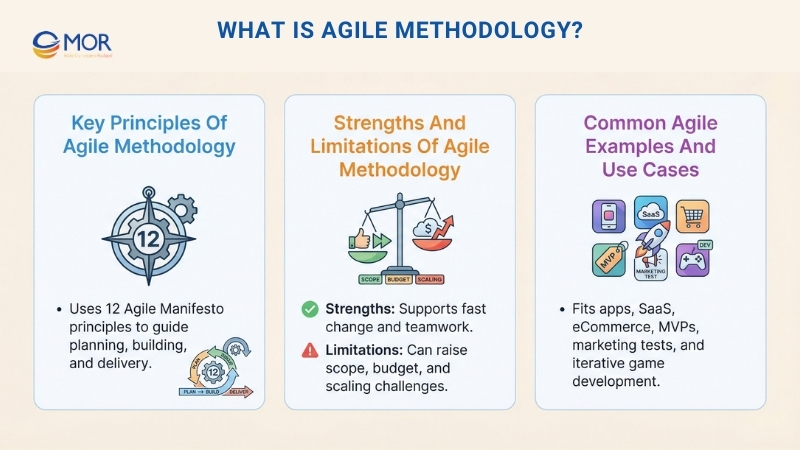
Key Principles Of Agile Methodology
Agile methodology follows 12 core principles outlined in the Agile Manifesto, which guide how teams plan, build, and deliver products:
- Focus on customer satisfaction through early and continuous delivery
- Accept changing requirements, even during later stages of development
- Release working software on a regular basis
- Encourage daily cooperation between business teams and development teams
- Create projects around motivated people and trust them to do the work
- Treat face-to-face communication as the most effective way to share information
- Measure progress primarily through working software
- Support sustainable development that teams can maintain over time
- Give consistent attention to technical quality and thoughtful design
- Value simplicity by reducing unnecessary work
- Allow teams to organize themselves to achieve better outcomes
- Review team performance often and make adjustments when needed
Strengths And Limitations Of Agile Methodology
Agile methodology is a flexible, iterative way of building software that supports close collaboration and quick adaptation. At the same time, teams need to be aware of several limitations and manage them carefully.
Pros | Cons |
Adaptive Response To Change: Teams can respond quickly to change based on real feedback. | Risk Of Expanding Scope: Ongoing changes may push the project beyond its original scope. |
Quicker Delivery Cycles: Small releases help teams deliver usable software sooner. | Reduced Formal Documentation: Strong focus on working solutions can result in lighter documentation. |
Enhanced Team Collaboration: Frequent communication supports teamwork and stakeholder engagement. | Frequent Client Participation Needed: Continuous input is needed, which is not always possible. |
Higher Overall Quality: Regular testing and repeated improvements raise overall quality. | Challenging Cost Predictions: Shifting requirements can complicate budgeting and forecasts. |
Early Risk Reduction: Early problem detection lowers the chance of major setbacks. | Difficult To Scale For Large Groups: Scaling this approach across large organizations can be difficult. |
Agile works well for projects that rely on constant user input and frequent change. When teams compare it in a waterfall vs agile development discussion, many find that its flexibility, gradual delivery, and risk handling stand out, especially when agile compared to waterfall in fast-moving environments.
Common Agile Examples And Use Cases
Agile’s iterative structure and ability to adapt make it a strong fit for fast-changing environments. This approach is often favored in agile development vs waterfall situations where speed, teamwork, and customer input matter most. Below are common cases where teams apply Agile successfully.
- Digital Product Creation: Teams building mobile apps, SaaS software development, or eCommerce platforms rely on Agile to gather user feedback early and adjust features quickly.
- Early-Stage Companies: Early-stage companies use this approach to react to market changes, prioritize app development for startups and release Minimum Viable Products (MVPs) in short cycles.
- Adaptive Marketing Workflows: Agile supports testing ideas, refining messages, and improving campaigns based on live performance data.
- Interactive Game Production: Game teams apply Agile to design, test, and release new features step by step while collecting player feedback.
What Is Waterfall Methodology?
Waterfall Methodology is a traditional, linear approach used in project management and software development. This model follows a strict sequence where each stage must be finished before the next one starts. These stages usually include requirement analysis, design, implementation, testing, deployment, and maintenance.
This approach places strong emphasis on structure, upfront planning, and detailed documentation, which makes it a dependable choice for projects with fixed schedules and clearly defined outcomes. Still, its rigid flow leaves little room for change when new needs appear, which often becomes a key discussion point in waterfall vs agile development, especially when comparing waterfall development vs agile in projects that face uncertainty.
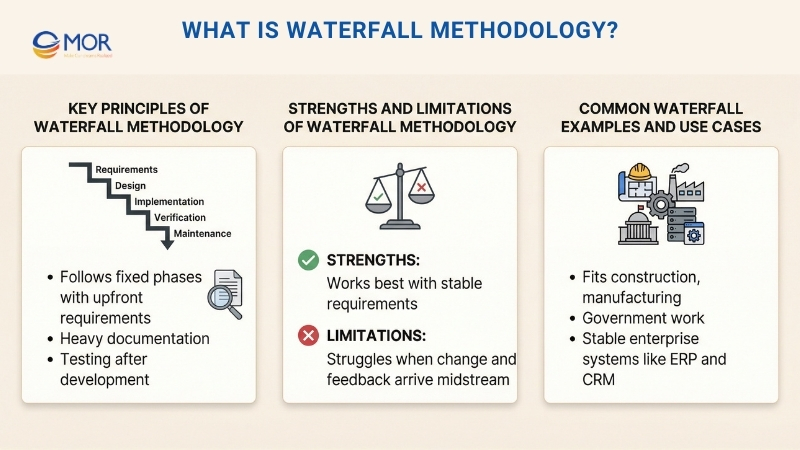
Key Principles Of Waterfall Methodology
Waterfall methodology is built on six core principles that support a structured and step-by-step way of delivering projects.
- Step-By-Step Workflow: Each stage must be finished completely before the next stage begins.
- Upfront Requirement Approval: All project requirements are collected and approved at the start.
- Comprehensive Documentation: Clear and thorough documentation is produced for every phase.
- Strictly Separated Phases: Each phase is separate and runs without overlap.
- Final Output Delivery: The full solution is released only after every phase is completed.
- Testing Performed Last: Quality checks and testing take place after development is finished.
Strengths And Limitations Of Waterfall Methodology
Waterfall methodology is a structured, linear way to manage projects and is most suitable when requirements are clear from the start. The table below outlines its main strengths and weaknesses.
Pros | Cons |
Structured Workflow: Each phase follows a fixed order, which makes planning and execution easier to manage. | Low Change Tolerance: Changes are hard to apply once the project moves into the next phase. |
Thorough Documentation: Detailed documentation supports clarity and smooth knowledge transfer. | Slow Response To Change: This approach does not fit projects that need frequent updates or revisions. |
Predictable Time And Budget: A fixed scope allows more accurate estimates for time and cost. | Testing Happens Late: Issues found near the end can be expensive and slow to resolve. |
Straightforward Tracking: Clear milestones help managers follow progress closely. | Poor Fit For Evolving Projects: It can struggle when requirements change or feedback evolves. |
Best For Stable Requirements: It works best when uncertainty is low and goals are stable. | Limited Client Participation: Feedback usually comes late, which can lead to unmet expectations. |
Although this model provides predictability and order, its limits become clear in waterfall vs agile development discussions. The rigidity of this method often highlights the difference between waterfall model and agile, especially in fast-moving or customer-focused projects where change is expected.
Common Waterfall Examples And Use Cases
The structured design of Waterfall works well for projects where requirements are stable and clearly defined from the beginning. When flexibility or frequent change is required, many teams lean toward Agile instead. Still, the following scenarios show where this method remains effective, especially when comparing waterfall development vs agile development in real-world settings.
- Construction And Infrastructure Work: When designs and requirements are fixed, this approach suits projects like roads, bridges, and large buildings.
- Manufacturing And Production Systems: Assembly lines and production workflows benefit from strict processes that follow predefined specifications.
- Public Sector And Government Initiatives: Compliance-focused projects often rely on this model due to heavy documentation needs and fixed delivery schedules.
- Large-Scale Enterprise Software Systems: Platforms such as Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems or CRM dashboard often use this method when requirements remain stable throughout development.
Waterfall Vs Agile Development: Key Differences Explained
Here are 5 core differences that clearly show how these two approaches work in practice and where each one fits best within waterfall vs agile development.
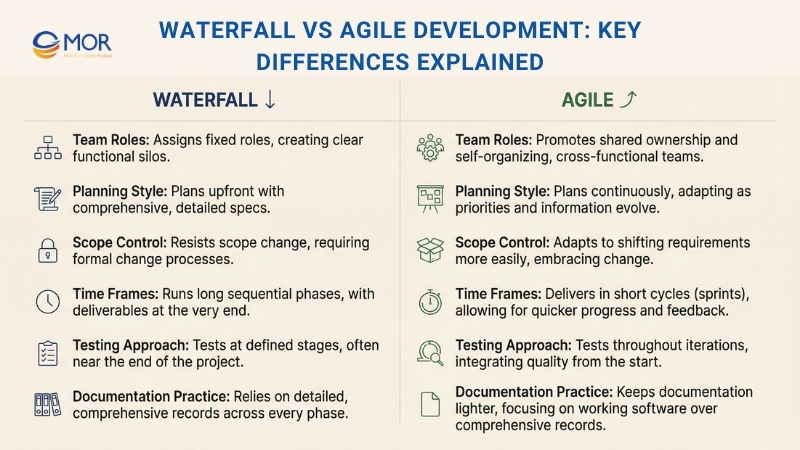
- Team Roles And Ownership: Waterfall assigns clear, fixed roles to each team member, with duties and responsibilities defined from the start. In contrast, Agile encourages shared ownership, where team members collaborate across tasks and gradually form a more self-organizing team structure.
- Planning Style: In Waterfall, planning follows a linear path and happens at the beginning of the project, with requirements and goals defined in detail upfront. Agile treats planning as an ongoing activity throughout the project life cycle, allowing teams to adjust direction as new information or needs appear.
- Scope Control: The Waterfall approach generally avoids changes to project scope, even when formal change requests are handled correctly. This is due to the heavy planning effort at the start, which makes later changes more expensive. Agile, on the other hand, adapts more easily, as teams can respond quickly when requirements shift.
- Project Time Frames: Waterfall is designed for long-term projects with fixed timelines, where each phase depends on the completion of the previous one. Agile works in short cycles, helping teams deliver value faster and adjust plans over time to reach results sooner.
- Delivery Speed: Waterfall projects often move slower because all requirements must be approved before development begins. Agile projects usually move faster, since iterative cycles allow teams to release working outputs earlier and improve them over time.
- Delivery Model: Agile supports faster releases with shorter cycles, since each iteration produces a usable result. Waterfall waits until every task is finished before any part of the product is delivered.
- Flexibility Level: Agile encourages teams to react quickly and adjust when changes arise during development. Waterfall offers limited flexibility and resists change once the scope is locked in.
- Testing Approach: Testing plays an important role in both methodologies, but the execution differs. Agile applies testing in small steps throughout development to catch issues early. In Waterfall, testing usually happens at defined stages, often near the end of the project.
- Documentation Practice: Agile keeps documentation light and focuses on teamwork and shared understanding. Waterfall depends on detailed records at every stage so everyone follows the same plan.
- Communication Style: Agile favors informal communication with frequent check-ins among individuals or small stakeholder groups. Waterfall relies on formal communication, using detailed communication plans and regular progress reports shared across larger teams.
Waterfall Versus Agile: Quick Comparison
This side-by-side view highlights how the two development models differ in daily execution, planning style, and team dynamics. It helps you quickly assess which approach aligns better with your project goals and working environment.
Aspect | Waterfall | Agile |
Team Roles And Responsibilities | Roles are clearly defined, with fixed duties assigned to each team member. | Team members work across tasks and share responsibility within a self-organizing setup. |
Planning Approach | Planning takes place once at the beginning, with detailed requirements set upfront. | Planning continues throughout the project and adjusts as new needs appear. |
Scope Management | Scope changes are discouraged and often expensive after the project starts. | Scope changes are expected and handled with flexibility during development. |
Project Time Frames | Built for long-term initiatives with fixed, sequential schedules. | Uses short cycles that allow frequent updates and faster progress. |
Delivery Speed | Slower progress since all requirements must be finalized before development begins. | Faster progress through repeated cycles and early delivery of value. |
Release Method | The full product is released only after every phase is complete. | Each cycle delivers a usable or working output. |
Flexibility Level | Limited flexibility once plans and scope are approved. | High flexibility with quick responses to change. |
Testing Strategy | Testing occurs at defined stages, often near the end. | Testing runs continuously as part of each cycle. |
Documentation Focus | Detailed documentation is required at every step. | Documentation stays light, with emphasis on teamwork and working results. |
| Communication Style | Communication is formal, supported by structured plans and reports. | Communication is informal and frequent among teams and stakeholders. |
Agile Vs Waterfall Software Development: A Detailed Cost Comparison
Cost is often a deciding factor when teams compare delivery models. Looking closely at how budgets are spent helps you understand the tradeoffs in waterfall vs agile development and plan more realistically for time, change, and risk.
Cost Category | Agile Development | Waterfall Development |
Upfront Planning Expenses | 5–10% of the total budget, with lighter planning at the start | 15–20% of the total budget, driven by heavy upfront planning |
Build And Testing Effort | 60–70%, with repeated cycles and testing done continuously | 60–70%, with work split into stages and testing done at the end |
Change Handling Costs | 5–10%, since changes are expected and easier to absorb | 15–25%, as changes tend to be disruptive and expensive |
Rework And Fixes | 5–8%, reduced through early feedback and regular checks | 15–25%, with a higher chance of late fixes |
Time To Market | 20–30% faster releases through small, incremental deliveries | Slower delivery, with the product released only at the end |
Total Project Spending | Often 10–20% lower thanks to flexibility and adjustment over time | Usually higher due to rigidity and the cost of late changes |
When your product relies heavily on cloud services, the cost of cloud computing can influence whether frequent iterations are affordable.
How To Choose Between Agile Vs Waterfall Development?
Choosing the right project management method is not about selecting the better option, but about picking the one that fits your situation best. The right decision depends on how well you assess your project needs, team setup, and company environment within waterfall vs agile development.
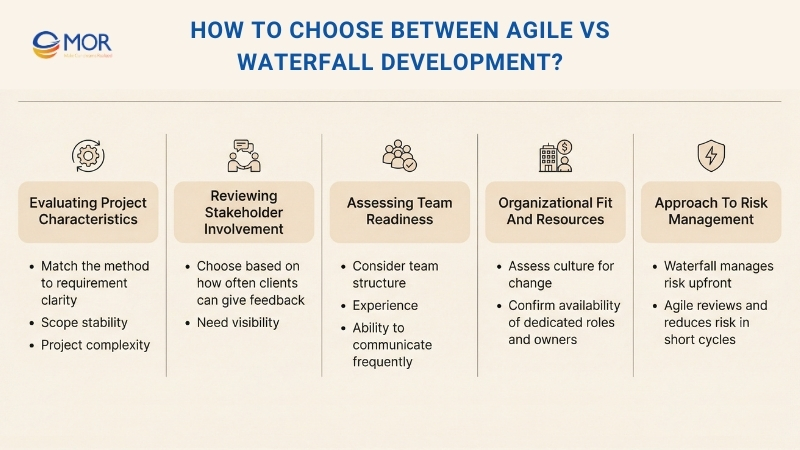
Evaluating Project Characteristics
Clarity And Stability Of Requirements:
- Select Waterfall when your project requirements are clear, detailed, and unlikely to change. This approach works well when you already know exactly what needs to be delivered from the beginning.
- Select Agile when requirements may shift, start unclear, or change as the project moves forward. Its iterative structure supports regular adjustment and improvement.
Project Scope Definition:
- Waterfall fits projects with a fixed and well-defined scope.
- Agile suits projects where scope can change, evolve, or be refined over time through ongoing feedback.
Project Scale And Complexity: Waterfall can handle large initiatives when requirements remain stable. Agile often works better for complex efforts, as it breaks work into smaller cycles that help lower risk and support steady learning.
Reviewing Stakeholder Involvement
Client Collaboration Approach:
- Waterfall usually brings clients in at the beginning to confirm requirements and again at the end for final approval.
- Agile depends on steady client and stakeholder involvement, with frequent feedback built into every cycle so the product can adjust as needs change. This difference is often discussed in agile vs waterfall project management decisions.
Project Visibility Needs: If you need regular access to working results and early chances to adjust direction, Agile is often the better fit. Waterfall tracks progress against a fixed plan, while usable outputs usually appear much later in development.
Assessing Team Readiness
Team Structure And Experience Level:
- Waterfall fits teams that prefer clear hierarchies, defined roles, and a step-by-step workflow.
- Agile works best for self-organizing, cross-functional teams that value collaboration, fast feedback, and ongoing improvement. This contrast is common in agile development vs waterfall model discussions.
Team Location And Distribution: Even with modern tools, Agile’s frequent communication, such as daily check-ins, can be difficult for teams spread across many locations without strong communication practices in place.
Organizational Fit And Resources
Organizational Flexibility Level:
- Waterfall fits organizations that operate with rigid structures, clear processes, and a cautious approach to risk.
- Agile needs a culture that supports change, gives teams more ownership, and values learning over sticking strictly to an early plan. This contrast often appears in discussions around agile software development vs waterfall model.
Resource Availability: Agile requires steady access to dedicated team members and active product owners throughout every iteration.
Whichever model you choose, your software development contract should define how change requests, acceptance criteria, and delivery checkpoints will be handled.
Approach To Risk Management
Upfront Versus Iterative Risk Handling:
- Waterfall focuses on finding and reducing all possible risks at the very beginning of the project, with the goal of avoiding costly problems later.
- Agile treats risk as a continuous factor, reviewing and addressing it in short cycles so teams can respond faster to new challenges. This difference is a key factor when deciding between waterfall vs agile development.
For vendor-based builds or distributed teams, outsourcing risk management helps reduce misalignment, delays, and quality gaps.
Combining Agile And Waterfall In Hybrid Development Models
Agile and Waterfall each have clear strengths, and many teams achieve better results by combining elements of both into a hybrid delivery model. This setup helps organizations use the structure of one approach while reducing the limits of the other, which is often discussed in waterfall vs agile development decisions.
A common way to mix these methods is to apply different techniques at different levels of a project. A project manager may follow a Waterfall structure for high-level planning and fixed requirements at the start. At the same time, individual delivery teams can work in Agile sprints for day-to-day tasks, gaining value from short cycles and continuous feedback. This balance reflects how agile software development vs waterfall can coexist within the same program.
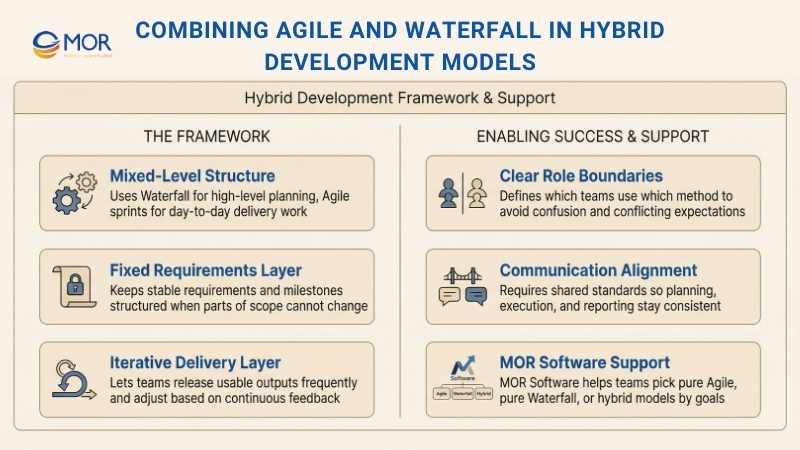
The success of a hybrid setup depends on clear communication and shared expectations. When teams understand which approach fits their responsibilities best, organizations can combine the flexibility of Agile with the order of Waterfall. This practical blend of waterfall and agile methodologies often suits complex projects with mixed needs.
At MOR Software, we help businesses design delivery models that match their goals, timelines, and risk profile. Whether you need a pure Agile setup, a structured Waterfall plan, or a hybrid approach, our teams guide you through the right choice. Contact us to discuss how we can support your next project.
Conclusion
Understanding waterfall vs agile development helps you choose a practical path that fits your project goals and resources. Each method has clear strengths, and the right choice depends on your scope, team, and timeline. If you want expert support to plan or build your next digital product, MOR Software is ready to help you move forward with confidence. Contact MOR Software to start your project today.
MOR SOFTWARE
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the main difference between Waterfall and Agile development?
Waterfall follows a fixed, step-by-step process where each phase is completed once. Agile works in short cycles, allowing teams to adjust plans based on feedback and changing needs.
Which development approach works better when requirements are unclear?
Agile is better suited for unclear or changing requirements. It allows teams to refine features as they learn more during development, instead of locking decisions early.
Is Waterfall development still relevant today?
Yes. Waterfall still fits projects with stable requirements, strict regulations, or fixed budgets. Industries like construction, government systems, and compliance software often rely on it.
How does testing differ in Waterfall vs Agile development?
In Waterfall, testing usually happens near the end of the project. Agile integrates testing into every iteration, helping teams find and fix issues earlier.
Which model delivers results faster, Agile or Waterfall?
Agile typically delivers usable features faster through frequent releases. Waterfall delivers the full product only after all phases are completed.
How do Agile and Waterfall handle changes during development?
Agile expects changes and adapts continuously. Waterfall limits changes once development starts, making late adjustments more expensive and complex.
Which approach is easier to estimate costs upfront?
Waterfall is easier to estimate early because scope and requirements are fixed. Agile cost estimates evolve over time as the product takes shape.
Does Agile require more client involvement than Waterfall?
Yes. Agile depends on regular feedback and decision-making from stakeholders. Waterfall usually involves clients mainly at the beginning and final delivery stages.
Can Agile and Waterfall be used together?
Yes. Many teams use a hybrid approach, applying Waterfall for planning and governance, while using Agile methods for development and delivery.
Rate this article
0
over 5.0 based on 0 reviews
Your rating on this news:
Name
*Email
*Write your comment
*Send your comment
1