What Are the Benefits and Risks of AI for Your Business in 2026?

AI is everywhere in 2026, powering tools, driving decisions, and reshaping how we work. But while it promises big rewards, it also raises hard questions. This guide of MOR Software will break down the benefits and risks of AI for your business and show how to make smarter, safer choices as you adopt this fast-moving tech.
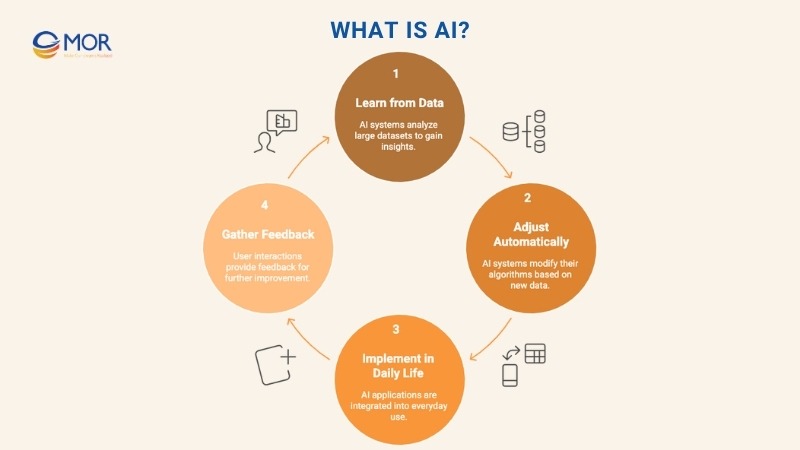
What Is AI?
Artificial intelligence is the science of building machines that can think and act like people. These systems learn from patterns in large amounts of data, then adjust how they respond over time. No manual updates needed.
We already use AI in ways that feel ordinary. Smart assistants answer questions, suggest music, and even manage reminders. In business, AI powers everything from customer support chatbots to supply chain forecasts. It helps flag risks, predict trends, and keep machines running before something breaks.
The rise of AI technology means we’re no longer asking if we should use it. We’re asking how fast we can use it well.
What Are the Benefits and Risks of AI?
Every new tech brings good and bad. That’s especially true with AI. Conversations about the benefits and risks of AI are all over the place. Some are all hype. Others paint doom. But underneath it all, one thing’s clear: AI is already changing how we live and work.
The benefits and risk of AI go hand in hand. On the upside, it saves time, cuts down on human error, and handles the boring stuff. On the downside, AI systems can cost a lot, replace jobs, and lack common sense or creativity. So how do we balance it?
Benefits Of AI
For most businesses, AI is a tool to move faster and work smarter. In Appen’s 2021 AI report, companies said AI and ML are becoming must-haves. Not having them in your workflows could mean falling behind. Today, businesses use AI to sharpen their operations and speed up how they hit goals. Some even use it to power customer experiences.
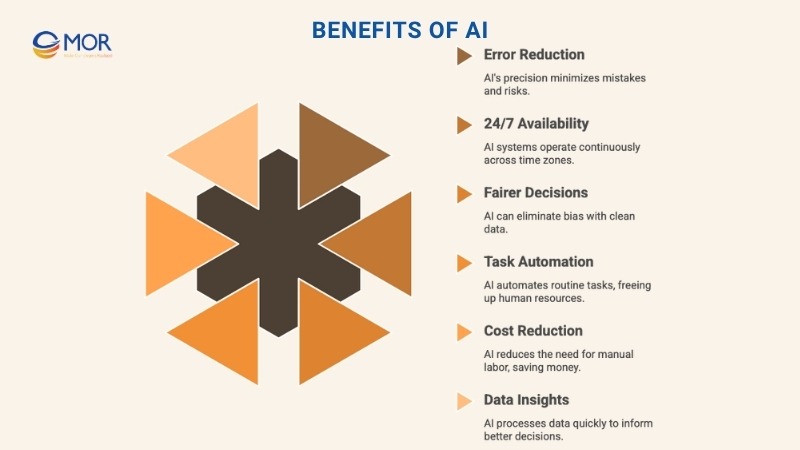
Cuts Down On Human Mistakes And Danger
One big advantage of AI is that it helps avoid human mistakes. Even the best people slip up. AI systems, once trained, can keep doing a job without distraction or fatigue.
It’s not just about accuracy. AI can take on risky tasks too. Think of robots inspecting places with high radiation. That kind of job could harm or even kill a person. A machine can do it without danger. And if it breaks? You just fix or replace it. People aren’t that easy to rebuild.
Works Around The Clock
Unlike people, machines don’t need rest. AI systems are always available. No shifts. No time zones. Whether it’s a smart chatbot answering late-night questions or a predictive engine running reports at 3 a.m., AI tools can stay active 24/7.
That nonstop output matters. It means your business can serve customers outside office hours, keep systems running smoothly overnight, and respond faster than teams working fixed schedules. Over time, that can lead to higher output and better service, without burning anyone out.
Makes Decisions Without Bias (When Built Correctly)
Let’s be honest, people have biases, even when they don’t realize it. These biases affect hiring, approvals, pricing, and more. AI can help, but only if it’s built with care.
When trained with clean, fair data, AI algorithms can support fairer decision-making. They don’t get tired, and they don’t ‘favor’ anyone. This makes AI useful in reviewing job applications or scoring loans without letting human emotion sway the results.
But bias can still creep in if the data behind the system is flawed. That’s why regular checks on your AI’s training inputs and outcomes are so important. If you’re serious about benefits and risks of AI, you can’t ignore how small errors in training can lead to big mistakes in real life.
Handles Repetitive, Time-Consuming Tasks
Every job has dull parts. Whether it’s checking invoices, labeling documents, or pulling weekly reports, repetitive tasks eat up hours that could be used elsewhere. AI is perfect for this kind of work.
By using automation to handle these tasks, teams stay focused on the creative and strategic parts of their job. That shift can raise morale, speed up output, and reduce burnout. It’s one of the key positives for AI in real business settings.
Helps Cut Operating Costs
AI doesn’t take breaks. It doesn’t need holidays or sick days either. That constant availability adds up, especially when AI replaces or supports routine tasks that used to require full-time staff.
Instead of hiring more for low-skill work, you can move current teams into higher-value roles. This shift creates long-term savings while also delivering more to your customers. It’s a major reason why leaders weigh the risks and benefits of AI before committing to major system changes.
Turns Massive Data Into Usable Insights
We’ve never had access to more data. But raw data is worthless unless you can make sense of it. That’s where AI comes in.
Trained AI systems can break down massive datasets in seconds, flag patterns, and even suggest actions. It turns overwhelming information into something your team can actually use. The result? Better decisions, faster reaction times, and a stronger view of what’s really happening across the business.
Risks Of AI
After seeing the upsides, jumping into AI might feel like the obvious move. But there are trade-offs. Before making big shifts, leaders need to understand the benefits and risks of AI in full. It’s not just about what you gain, it’s also about what it may cost or disrupt along the way.
Even though there are many artificial intelligence benefits and risks, overlooking the downside can lead to poor implementation, wasted money, or long-term inefficiencies.
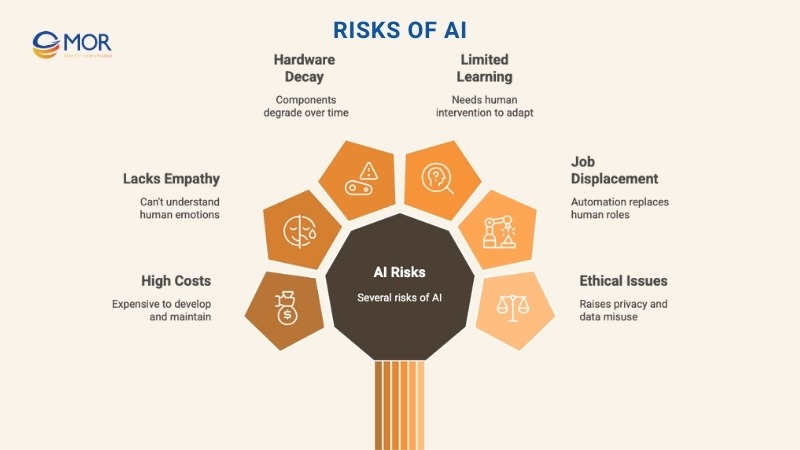
High Upfront Costs
One of the first hurdles is price. Building or buying AI systems isn’t cheap. What you spend depends on what you need, but a complete solution can cost anywhere from $20,000 to several million dollars.
That’s not counting the time it takes to train the system, manage data, or test for errors. Over time, AI may improve workflows and lower your cost per task, but the initial investment often keeps small and mid-sized businesses on the fence.
No Emotional Intelligence Or Creativity
Another limitation of AI is that it can’t think creatively or feel anything. It runs on logic, patterns, and data, not instinct, empathy, or imagination.
Even though AI can generate ‘new’ ideas based on existing inputs, it still lacks true originality. A research paper argued that current AI models can only remix what they’ve seen, not create something unexpected. That limits how useful they are when solving novel problems or working in fields that depend on original thought. If your business needs innovation or fresh perspective, human minds are still the best source.
Emotion is another gap. People consider how decisions affect others. AI doesn’t. It simply picks what’s most efficient, based on how it’s been trained. And when trained on flawed emotional data, it can misread people badly.
One study found that AI systems reading facial expressions assigned negative emotions more often to non-white individuals, reinforcing bias in decisions.
Kindness, empathy, and social understanding still live firmly in the human camp.
Systems Wear Down Or Become Outdated
It’s easy to forget that machines break. But over time, they do. AI-powered systems aren’t immune. If you’ve got AI running in a physical environment, say, on a factory line, it’s tied to hardware that wears out. Unless you build in self-checks or repair routines, the system will eventually fail.
The software side can wear down too. AI that doesn’t keep learning falls behind. Trends shift. Data changes. If you don’t retrain the model or monitor performance regularly, it becomes less useful. This is one of the benefits and risks of artificial intelligence, you gain speed and scale, but staying current takes constant effort.
Doesn’t Learn Unless Programmed To
Humans learn from failure. We make mistakes, adjust, and try again. Most AI doesn’t do that. Unless built with learning abilities, it simply repeats what it knows.
Creating AI that can improve without help is possible, but hard. And expensive. AlphaGo, developed by Google, is a standout case. It learned to master the game of Go in just a few days, inventing new strategies on its own. But that level of learning isn’t common.
For most companies, AI still needs humans in the loop, people who can update the system, refine the logic, and feed it better data. That’s another reason why understanding the what are the risk and benefits of AI equation is so important when planning your investment.
Potential Job Displacement
It’s a familiar concern, and one that’s not going away. As AI takes over more repetitive or rules-based tasks, many worry about losing jobs to automation. And for good reason. Machines don’t call in sick, don’t need breaks, and can work at scale.
Still, reports like the World Economic Forum’s suggest that AI may end up creating as many jobs as it replaces, maybe more. But that shift comes with friction. People need training to take on new roles. Without support, workers risk being left behind while companies adopt new tech.
That tension highlights a core question when weighing the benefits and risks of AI: who gains, and who gets displaced?
Raises Tough Ethical And Privacy Concerns
With speed comes risk. AI has moved so fast that big questions about how we use it are still unanswered. Privacy is at the top of the list.
AI can learn a lot about people from what they do online. Even without direct access to personal data, AI tools can predict behavior and preferences. That makes it harder to control who sees what, and when. It also raises the issue of consent. If someone never gave permission, but the system still figures them out, is that okay?
These ethical concerns are part of a wider debate. Questions about data use, bias, responsibility, and job loss all fall under the same umbrella: is using AI bad when the consequences are unclear?
Real-World Use Cases For AI
We’ve already seen how AI can take over repetitive work and speed things up. But that’s just scratching the surface. In real business environments, the benefits and risks of AI play out in dozens of ways, some simple, some highly technical. Here are a few common examples where AI is already making a difference:
- In healthcare, AI helps detect disease early by analyzing test results, scans, and patient data to predict potential issues before they become serious.
- In customer service, AI-powered chatbots answer basic questions, resolve common problems, and escalate issues to real people when needed. They work after hours, too.
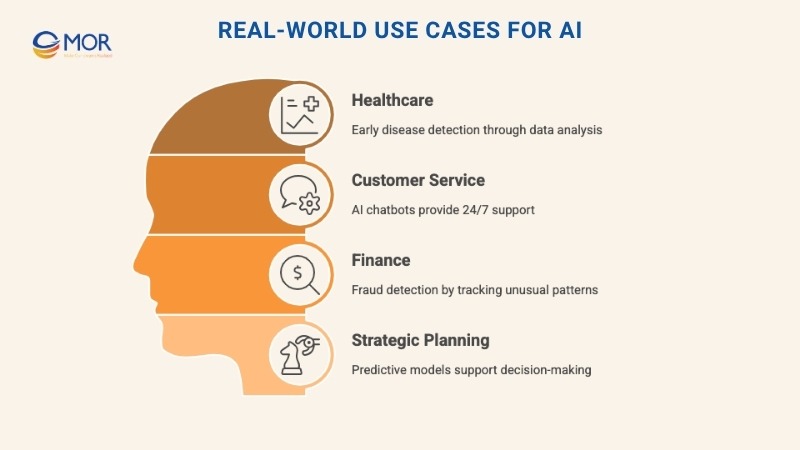
- In finance, AI helps spot fraud. It tracks unusual behavior across accounts and flags risks early, stopping suspicious transactions before damage is done.
- In strategy and planning, AI systems generate predictive models. They show businesses where trends are headed, helping leaders avoid bad bets and make smarter calls.
These examples show the practical side of benefits of AI technology, when used right, it’s not just helpful, it’s proactive.
Managing The Benefits And Risks Of AI Safely
AI can help your business grow, but only if it’s handled with care. To see the upside without getting burned, you need to manage risk, pick smart tools, and set guardrails early. This is where planning matters just as much as the tech itself.
Have A Plan For AI Risk Management
Managing AI well means building a strategy from the start. Just like companies created policies around cloud storage a decade ago, businesses today need a framework for how AI is used, reviewed, and secured.
That includes following data privacy laws and security best practices. If you're using AI tools that handle customer or employee information, you're responsible for keeping that data safe. Treat this as seriously as you would any financial or legal risk, because it is. Whether you’re weighing the benefits and risks of AI or the long-term cost of getting things wrong, a structured plan gives you control.
Pick The Right AI Tools For The Job
Not every AI tool is built with safety in mind. That’s why choosing reliable platforms, like Microsoft Copilot or other enterprise-grade software, can help reduce exposure. These tools come with security baked in: encryption, user permissions, audit logs, and more.
But tech alone isn’t enough. You still need to vet the vendor. Look beyond surface-level compliance. Assess how their systems handle risks and benefits of AI, especially in how they process data and adjust to user behavior. Good vendor evaluations include AI-specific questions and risk scoring. And since AI is everywhere (even in your phone), this process needs to become part of how you choose every tool going forward.
Set Clear AI Usage Guidelines
Even with great tools, people need to know the rules. That’s where policies come in. Define which platforms your team can use, what kinds of data they can feed into those systems, and how to work responsibly with AI.
Make those rules clear. Add them to onboarding, refresh them in regular training, and update them as your tools evolve. This keeps your team aligned and lowers the chance of mistakes.
Done right, policies don’t slow people down, they help you get the most out of AI while staying safe. It’s one more reason businesses need to understand what are the benefits and risks of AI, and create systems that bring the good while managing the bad.
How To Start Leveraging AI In Your Organization
Some companies try to block AI entirely to avoid trouble. But that’s rarely practical, or smart. Instead of banning the tech, it’s better to manage it. Set rules, define use cases, and start small. That way, teams can begin exploring the benefits and risks of AI with control and purpose.
The goal isn’t to dive in all at once. It’s to find where AI fits best in your current setup, then train your people to use it safely.
Start Small, Think Strategic
Begin with tasks that waste time or frustrate your team. That might be scheduling, data cleanup, report writing, or filtering messages. AI can take the pressure off and reduce mistakes. Focus on pain points first, things that drain time without much return.
This structured rollout lets you see early wins, while your team learns what AI can (and can’t) do. With each step, you’ll unlock more advantage of AI in daily operations.
Train Your Team To Work With AI
AI isn’t just a tool, it’s a skill. Teams need to learn how to use it properly. That means training on both the tech and the risks.
Employees should know how to use approved tools, stay compliant with policy, and understand when human oversight is needed. Training should also cover AI-driven scams, like deepfakes and smart phishing tactics. These threats are harder to spot and spreading fast.
The more your team knows, the better they can manage the benefits and risks of artificial intelligence across your operations.
Use AI For Cybersecurity And Fraud Prevention
AI can spot trouble early. In cybersecurity, that’s a big deal. Instead of reacting after a breach, AI systems track patterns and flag problems in real time.
From financial fraud to phishing emails, AI tools are now critical in threat detection. They not only help automate protection but also stay one step ahead of attackers. That’s where the true value of AI shines, in reducing damage before it even happens.
Prepare For AI-Powered Threats
Threats are getting smarter. So your defenses need to as well.
AI-powered attacks, whether through fake videos, cloned voices, or hyper-targeted scams, are rising fast. That means education and readiness are just as important as the tech.
Build a response plan. Run phishing drills. Train your staff to spot tricks and know what to do when something feels off. You’ll be protecting your team and your customers.
Being proactive with security is another way to handle the benefits and risk of AI without falling into the trap of overconfidence.
Supporting Smarter AI Adoption With MOR Software
At MOR Software, we help businesses unlock the benefits of AI without falling into common traps. That means going beyond flashy tech. We focus on practical, secure, and sustainable solutions.
Our teams build AI-powered systems that match your business goals and comply with data and security standards from day one. We don’t just write code. We guide you through smart integration, ethical use, and long-term support.
Whether it’s machine learning for analytics, automation in mobile apps, or AI-enhanced web platforms, we make sure it works for your users and your bottom line.
We also understand the risks. That’s why we bake in transparency, testing, and clear governance into every project. With MOR Software, you don’t just adopt AI. You do it responsibly, and with confidence.
Conclusion
AI can speed up processes, cut costs, and uncover insights, but it also brings risks that can’t be ignored. From data privacy to job shifts, the trade-offs are real. Understanding the benefits and risks of AI is the first step to using it wisely.
At MOR Software, we help businesses move forward with confidence. Whether you're exploring automation, improving security, or building custom AI tools, we guide you every step of the way. Want to apply AI the right way? Contact us today.
MOR SOFTWARE
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the benefits and risks of AI?
AI brings many advantages like minimizing human errors, saving time, offering constant support, and making objective decisions. However, it also has drawbacks such as lacking emotional awareness, promoting passivity, and replacing certain jobs. AI can analyze, learn, and simulate human-like reasoning.
What are 5 disadvantages of AI?
Key disadvantages include overdependence on technology, reduced critical thinking, less face-to-face interaction, concerns about data security, and the potential for technical failures. These issues are particularly noticeable in educational and work settings.
What are the risks of AI?
AI poses risks in real-world applications, including threats to user privacy, algorithmic bias, harm to humans in certain contexts, and the lack of proper legal regulations. These problems highlight the need for responsible development.
What are the benefits of artificial intelligence?
AI improves operational efficiency, automates repetitive tasks, and drives innovation. Still, challenges like job replacement, ethical concerns, and data misuse require careful planning and oversight.
What are the pros and cons of AI?
The pros include automating routine work, increasing productivity, offering personalized experiences, and providing easy access to information. The cons involve ethical dilemmas, dependence on data, and the absence of human empathy or intuition.
Is AI good or bad for society?
AI has the potential to improve access to healthcare, education, and environmental solutions. But without proper regulation, it can cause unintended harm. Its success depends on ethical development and responsible use.
Is AI good or bad for students?
AI can make learning more efficient, but overreliance may hinder creativity, emotional development, and social interaction. Students benefit most when AI is balanced with human-led learning.
What is the biggest problem with AI?
The biggest issue is determining accountability when AI causes harm. Questions about legal responsibility, intellectual property, and ethical use remain complex and unresolved.
Rate this article
0
over 5.0 based on 0 reviews
Your rating on this news:
Name
*Email
*Write your comment
*Send your comment
1