Blockchain Hybrid: Next-gen Combined Technology For Your Business
Is your business struggling to balance transparency, security, and scalability in its digital operations? Blockchain hybrid technology provides a powerful solution by combining the strengths of public and private blockchains. In this article, MOR Software highlights how hybrid blockchain can transform enterprise operations, improve efficiency, and create a secure, transparent ecosystem for business-critical processes.
What Is Blockchain Hybrid?
A blockchain hybrid is a model that combines the strengths of both public and private blockchains, giving businesses the flexibility to decide what information should remain private and what can be shared publicly. In this system, part of the data and transactions are open for transparency, while sensitive information is securely stored in a private chain.
The definition of a hybrid blockchain can be explained as a “best of both worlds” solution. For example, in healthcare, hospitals may store patient medical records on the private layer for security and compliance, while publishing anonymized research data on the public chain to ensure transparency and collaboration.
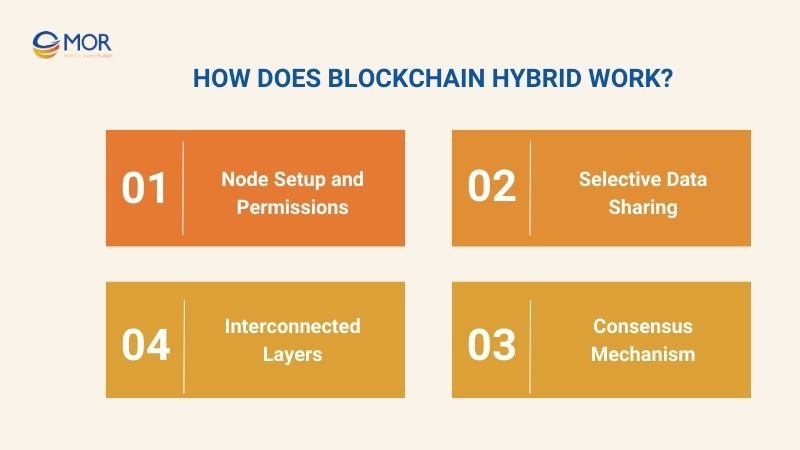
How Does Blockchain Hybrid Work?
To better understand how a blockchain hybrid operates, we need to examine the core factors that determine its functionality. Below are the key components:
Node Setup and Permissions
In a blockchain hybrid, the system is organized into two main types of nodes: public nodes and private nodes.
- Public nodes: responsible for validating transactions recorded on the public layer, ensuring transparency and decentralization. All transactions on this layer can be independently verified by other public nodes.
- Private nodes: handle sensitive information and are accessible only to authorized participants. These nodes are usually deployed within the enterprise network, with strict access controls to protect critical data.
Access levels are clearly defined:
- Viewer: can only read and monitor data, cannot validate or add new blocks.
- Validator: authorized to confirm transactions and append new blocks to the chain.
- Admin: manages node setup, assigns permissions, and controls the data flow between public and private layers.
Implementing such a complex node structure requires the expertise of a hybrid blockchain developer, who designs the network architecture, defines access rights, and optimizes data flow between public and private nodes to ensure both stability and security.
Selective Data Sharing
A key feature of a blockchain hybrid is its ability to enable selective data sharing. Data is categorized into two types:
- Public data: transactions or information that need to be transparent for partners, customers, or the community, stored on the public blockchain layer.
- Private data: sensitive information such as contracts, client records, or internal data, stored on the private blockchain and accessible only by authorized nodes.
This selective sharing mechanism relies on data layering and encryption. Each transaction can be tagged with access permissions, allowing only nodes with the correct cryptographic keys to decrypt the data. This enables a single system to handle multiple data flows securely while maintaining transparency where needed.
Consensus Mechanism
In a blockchain hybrid, consensus mechanisms ensure that transactions are accurately validated across both public and private layers. The system can adopt popular algorithms such as Proof of Authority (PoA) or Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT).
Instead of using a single fixed mechanism, hybrid blockchains can combine consensus algorithms: the private layer prioritizes speed and internal security using PoA. In contrast, the public layer applies BFT to prevent fraudulent activity. This combination ensures that the entire system remains both stable and flexible, striking a balance between efficiency and data integrity.
Interconnected Layers
A blockchain hybrid operates efficiently through interconnected public and private layers. This connection is usually achieved through:
- APIs (Application Programming Interfaces): allow external applications and systems to access or exchange data with both blockchain layers.
- Bridges: secure pathways for transferring data between the public and private layers without exposing sensitive information.
For example, in supply chain management, detailed product and shipment data may reside on the private layer, while origin and certification information is published on the public layer.
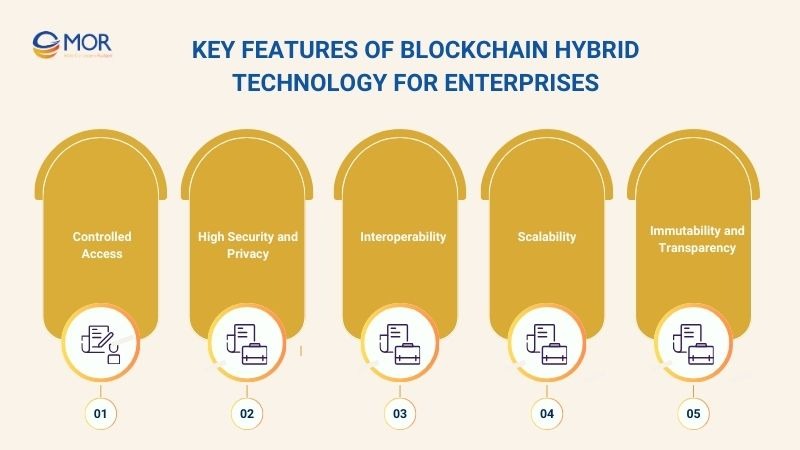
Key Features Of Blockchain Hybrid Technology For Enterprises
Nowadays, businesses are turning to flexible blockchain solutions, and a blockchain hybrid offers key features that meet enterprise requirements. Below are the core characteristics that drive efficiency, security, and transparency across business operations.
Controlled Access
One of the most important features of a blockchain hybrid is the ability to implement detailed access control (controlled access) for all participants. Enterprises can precisely define who is allowed to view data, who can update information, and who has the authority to approve or validate transactions.
This ensures unauthorized access is prevented, sensitive information is protected, and errors or fraudulent activities are minimized during operations. Implementing controlled access often requires hiring a hybrid blockchain developer to design the access rules and manage participant permissions efficiently.
High Security and Privacy
Another key feature of a hybrid blockchain is its high security and privacy capabilities. The system uses a private chain logic to store and process sensitive data while integrating a public layer to record essential transactions without exposing confidential information.
The layered structure allows critical data to be encrypted and accessible only to authorized nodes. Additional security measures, such as digital signatures, multi-factor authentication, and role-based access controls, can also be integrated to ensure data is not accessed improperly.
Interoperability
A blockchain hybrid provides interoperability with other blockchains and systems. This feature enables enterprises to connect with external networks or internal systems, facilitating linked and synchronized data flows.
Through APIs and bridges, data can be transferred and exchanged between blockchains while maintaining its structure and security.
Scalability
A critical technical feature of a blockchain hybrid is scalability. The system is designed to handle large volumes of transactions, with efficient block distribution and consensus mechanisms, enabling high transaction throughput without reducing processing speed.
The hybrid architecture separates public and private layers, optimizing performance based on specific enterprise requirements. Additionally, the system can scale by adding nodes or partitioning data without affecting the overall network, ensuring stability during expansion.
Immutability and Transparency
Blockchain hybrid ensures immutability and transparency of data. Once information is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted, maintaining data integrity.
The public layer allows verification and auditing of transactions that require transparency, while the private layer protects sensitive data. The recording mechanism guarantees reliable records, preserving integrity and transparency throughout the system.
Key Benefits Of Blockchain Hybrid Technology For Your Business
Blockchain hybrid provides numerous advantages for enterprises, enhancing security, efficiency, access control, regulatory compliance, and data transparency. Below are the key benefits that businesses can leverage to optimize operations and protect sensitive information.
Enhanced Privacy and Security
By using a blockchain hybrid, enterprises can ensure that sensitive data remains protected and private. This helps prevent information leaks, safeguard customer privacy, and avoid data compliance violations.
Without this feature, sensitive data could be accessed or leaked by unauthorized parties, leading to reputation loss, financial damage, and legal risks.
According to a study, 91% of organizations believe investing in blockchain will deliver verifiable returns within five years.
Efficient and Scalable
A blockchain hybrid allows enterprises to process transactions quickly and scale operations flexibly. This ensures high-volume transaction processing without slowing down, even in industries with heavy data requirements such as logistics, finance, or e-commerce.
Without this capability, systems may experience bottlenecks during peak loads, causing delays, data loss, or operational disruption.
Real-world example: In the supply chain industry, hundreds of thousands of shipment transactions are recorded daily. With a private layer handling internal processing and a public layer recording transparent data, companies can maintain speed and accuracy while expanding their partner network or distribution areas.
Flexible Access and Control
Blockchain hybrid enables customizable access permissions, allowing enterprises to assign rights to individual users or groups, ensuring each participant accesses only the data relevant to their role.
Without this feature, businesses may struggle to manage access, increasing risks of data leaks, errors in data processing, or conflicts of interest among departments and partners.
Improved Compliance with Regulations
Using a blockchain hybrid, enterprises can comply with legal regulations such as GDPR, financial controls, and industry-specific standards through rule-based data sharing. Without this feature, businesses risk legal penalties and reputational damage due to uncontrolled or improper sharing of sensitive data.
A study found that 83% of multinational companies consider regulatory compliance the biggest challenge when using blockchain for cross-border payments. Another survey showed that 95% of organizations using private or hybrid blockchain reported compliance as a key motivation.
Enhanced Transparency
Blockchain hybrid enables public transaction verification when needed, allowing stakeholders to access accurate and reliable information. The public layer ensures transparency, while the private layer protects sensitive data.
Without this feature, businesses may struggle to build trust with partners, customers, and regulators, as transactions or data cannot be independently verified, potentially leading to disputes or a lack of transparency.
Example: In real estate, property sale transactions are recorded publicly on the public layer, while detailed contracts and client information are stored on the private layer. This allows stakeholders to verify transaction histories accurately while keeping sensitive data secure.
Real-World Business Use Cases Of Blockchain Hybrid Technology
Blockchain hybrid is widely applied across industries, helping businesses optimize processes, secure data, enhance transaction transparency, and improve management efficiency. Below are detailed real-world use cases:
Financial Services
In the financial sector, banks and international payment companies often face challenges in securing customer data.
A blockchain hybrid allows a private layer to store sensitive information such as balances, transaction history, and personal data. While a public layer records transaction summaries for verification by partners and regulators, speeding up processing and reduces fraud risks.
Real-World Example: An international bank in the U.S. is implementing a blockchain hybrid to optimize cross-border payments. The bank has a large enterprise client base, with thousands of cross-border transactions daily, requiring compliance with international regulations and protection of sensitive data.
Flow:
- Private layer stores all detailed customer transaction data, securing sensitive information.
- Public layer records transaction summaries, ensuring transparency for regulators and payment partners.
- Hybrid consensus system validates transactions quickly, reducing fraud risk and manual processing errors.
- Stakeholders can access transparent data without exposing sensitive customer information.
Healthcare
In healthcare, data privacy and controlled sharing are major concerns. Blockchain hybrid enables secure storage of patient records and controlled data sharing between hospitals, clinics, and insurance companies, while the public layer records aggregated data for research or reporting without violating privacy.
Real-World Example: A large European healthcare system is deploying a blockchain hybrid to manage patient records. The system handles millions of patient files, and hospitals and insurers require access while complying with GDPR.
Flow:
- Private layer stores personal records, test results, and treatment history.
- Public layer records aggregated data for medical research and regulatory reporting.
- Tiered access ensures only authorized doctors and staff view detailed records, while insurers access only data needed for claims.
- Audit logs track all access to prevent misuse and ensure accountability.
Supply Chain Management
In supply chain management, a blockchain hybrid helps track product origin, ensure quality, and prevent counterfeiting. The private layer stores internal supplier, warehouse, and production data, while the public layer records certifications and inspection checkpoints for partners and customers.
Real-World Example: A global cosmetics company is deploying blockchain hybrid to improve supply chain transparency. The company works with dozens of suppliers worldwide and needs to ensure consistent product quality while protecting trade secrets.
Flow:
- Private layer stores supplier information, production process, and shipping details.
- Public layer records product safety certifications and inspection results at intermediate warehouses.
- Data is automatically synchronized between shipping partners and suppliers via APIs and bridges.
- Customers and partners can verify product origin and quality through the public layer without accessing trade secrets.
Real Estate
In real estate, a blockchain hybrid enables smart contract automation and transparent property ownership recording, reducing fraud and errors. Private layer protects customer information and loan details, while public layer records ownership and transaction history.
Real-World Example: A real estate company in Singapore implements a blockchain hybrid to manage thousands of property transactions annually, ensuring transparent ownership and protecting client information.
Flow:
- Private layer stores detailed contracts, client information, and loan data.
- Public layer records all public property transactions.
- Smart contracts automatically execute payments and transfer ownership when conditions are met.
- Stakeholders and regulators can access the public layer to verify transaction history without accessing sensitive data.
Government and Public Sector
In government and public services, blockchain hybrid supports citizen data management and transparent services such as e-voting or asset registration. Private layer stores sensitive citizen information, while public layer records ownership and verification results.
Real-World Example: A city in Canada deploys a blockchain hybrid to manage property registration and electronic voting. The city has hundreds of thousands of citizens, needing to reduce election fraud and ensure asset management transparency.
Flow:
- Private layer stores detailed citizen and asset information.
- Public layer records ownership and public transactions.
- E-voting uses smart contracts on the hybrid blockchain to record votes while protecting voter privacy.
- Regulators and citizens can verify public data transparently without accessing personal information.
Key Differences Between Blockchain Hybrid and Public & Private Blockchains
Understanding the differences between blockchain hybrid, public, and private blockchains is essential for enterprises seeking the right solution for their business needs. Each type of blockchain offers unique strengths and limitations in terms of access control, security, transparency, scalability, and practical use cases.
Feature / Type | Public Blockchain | Private Blockchain | Hybrid Blockchain |
Access Control | Open to anyone; anyone can read/write | Restricted to authorized participants | Fine-grained control; public layer for transparency, private layer for sensitive data |
Security Level | High due to decentralized consensus, but public exposure can be risky | High within private network; controlled environment reduces external threats | Combines private chain security with public layer verification for optimal protection |
Transparency | Fully transparent; all transactions visible to everyone | Limited transparency; only authorized participants can view data | Selective transparency; public transactions are visible while sensitive data stays private |
Scalability | Limited by network size and consensus mechanism | High scalability due to controlled nodes and network | Scalable by separating public and private layers and optimizing consensus mechanisms |
Practical Use Cases | Cryptocurrencies, decentralized apps, voting | Enterprise internal systems, financial institutions, confidential data management | Cross-border payments, supply chain, healthcare, real estate, government services |
Major Challenges of Blockchain Hybrid Technology To Consider
While a blockchain hybrid offers numerous advantages, enterprises must be aware of several challenges before implementation. Understanding these obstacles can help organizations plan resources, reduce risks, and ensure successful deployment.
Complex Setup and Maintenance
Implementing a hybrid blockchain requires advanced technical expertise to configure both the public and private layers. Without specialized technical personnel, companies may encounter delays, misconfigurations, or security vulnerabilities.
Maintenance costs can also be substantial due to system updates, node monitoring, and infrastructure scaling. The company faced difficulties integrating internal warehouse data with the public verification layer, requiring them to hire dedicated hybrid blockchain developers and increase the budget for system operation and maintenance.
Regulatory Compliance
Combining public and private blockchain models introduces various legal and regulatory challenges. Especially when data crosses countries with different privacy laws, such as GDPR or HIPAA. Non-compliance can lead to hefty fines, legal disputes, or operational disruptions.
Furthermore, the lack of global standards makes governance, auditing, and cross-border data sharing more complex. Enterprises must carefully design compliance protocols to meet both local and international regulations when implementing hybrid blockchain systems.
Interoperability
Another critical challenge of hybrid blockchain is ensuring interoperability between private and public layers, as well as integration with external systems. Poor integration can lead to data fragmentation, transaction errors, or data duplication.
According to a study by Webpuppies, fragmented data can reduce 20–30% of an enterprise’s potential revenue. Addressing this challenge requires strong standardization and effective API management to ensure smooth system operation.

MOR Software: Offshore Blockchain Hybrid Development Company
When implementing a hybrid blockchain, many enterprises face challenges related to technical expertise, costs, and security management. Instead of building everything in-house, hiring hybrid blockchain developer can help businesses save time, optimize expenses, and ensure high-quality deployment.
MOR Software is a trusted provider in this space, offering global experience and a team of skilled blockchain experts.
Reasons to choose MOR Software for your hybrid blockchain implementation:
- Proven reputation in global software development: Successfully delivered numerous blockchain projects for international clients, ensuring reliable and high-quality solutions.
- Team of professional blockchain experts: MOR’s developers possess extensive experience in both public and private blockchain layers and hybrid mechanisms.
- Customized hybrid blockchain solutions: Tailored solutions to meet the specific needs of your enterprise, optimizing performance, security, and scalability.
- Cost-effective services: Offshore development reduces implementation costs compared to in-house builds without compromising quality.
- Strong commitment to security and compliance: MOR ensures all blockchain solutions comply with legal regulations, protect sensitive data, and minimize security risks.
In Conclusion
In today’s competitive landscape, adopting a hybrid blockchain can transform how your business manages data, transactions, and collaboration across partners. With proven expertise and customized solutions, MOR Software helps enterprises harness the full potential of hybrid blockchain technology. Contact MOR Software today to implement a blockchain hybrid solution tailored to your business needs.
Rate this article
0
over 5.0 based on 0 reviews
Your rating on this news:
Name
*Email
*Write your comment
*Send your comment
1