How to Code AI? Complete Guide for 2026
Learning how to code AI can feel overwhelming at first, especially with so many tools, languages, and frameworks to choose from. Yet, understanding the process step-by-step makes it easier to build smart, practical solutions. This MOR Software’s guide will help you master the fundamentals, from data preparation to deploying intelligent models with real-world impact.
Understanding AI And Machine Learning: Key Concepts To Know
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) often appear together, but they mean different things. AI focuses on developing programs that can think, reason, or act like humans. If you’ve ever wondered how to code an AI, it starts here, understanding how machines can simulate human intelligence in simple or complex ways. Some systems only follow clear rules, while others learn and make choices on their own.
ML is one of the core methods inside AI. It helps computers recognize patterns, study data, and get smarter over time without written instructions for each task. The global machine-learning market is projected to reach $105.45 billion by 2025. This shows how rapidly this technique has moved from the “research lab” into everyday applications. You can picture AI as the overall goal, creating intelligent behavior, and ML as one of the main techniques that make it possible.
Not every AI relies on ML, and not every ML project leads to a full AI product. Still, knowing this difference makes it easier to grasp how to code AI in practice. It also helps you see how modern tools, like smart AI coding assistant and predictive models, are built. Today, AI is becoming common in software work, with about 75% of enterprise engineers expected to use AI code assistants by 2028. Once you understand these basics, the rest of your AI journey feels a lot clearer.
The Basics of AI
Artificial Intelligence focuses on creating programs that can perform tasks that usually need human thinking. It uses data and algorithms to copy mental actions like learning, reasoning, and solving problems. Understanding these ideas is key when you start exploring how to code AI and build systems that act with logic and awareness.
Machine Learning is a central branch of AI that helps computers learn through experience instead of strict instructions. It improves performance each time the system processes new data. The main learning approaches include:
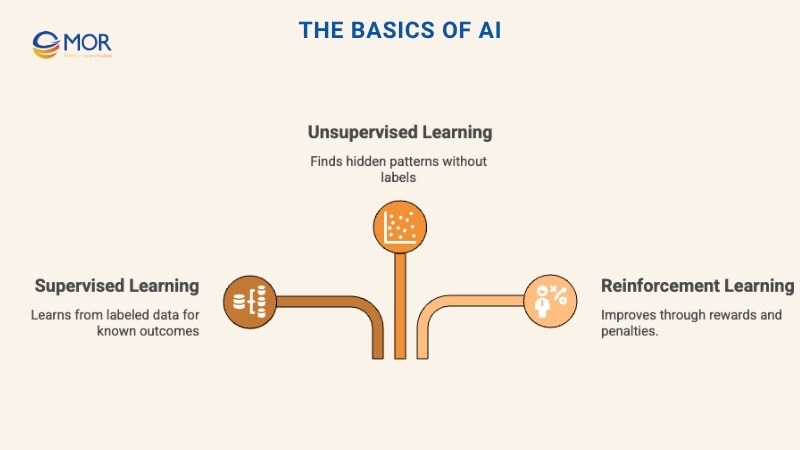
- Supervised learning: The model studies labeled data where the right answers are already known.
- Unsupervised learning: The model searches for hidden patterns without needing labeled results.
- Reinforcement learning: The model learns from its own choices, earning rewards or facing penalties.
Modern AI platforms, such as ChatGPT, combine several of these methods during training. A model might begin with self-supervised learning on large text sets, then get refined through supervised learning and reinforcement learning with human feedback. This layered process shows how to code AI that continues to adapt, discover new insights, and make decisions faster than humans could alone.
Types of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence is grouped into three main categories based on how capable the system is. Understanding these types gives a clear view of how to code AI for different levels of intelligence and control.
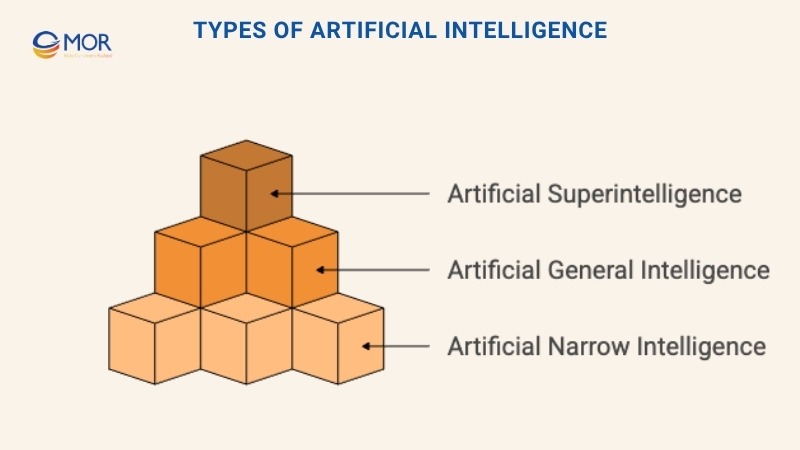
- Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI): This form is the most common today. It performs one task extremely well but cannot operate beyond what it was trained for. Voice assistants, spam filters, and chatbots all fall under this type.
- Artificial General Intelligence (AGI): AGI represents the idea of a machine that can think, learn, and understand across many subjects like a human. It is still a concept in research and has not yet been achieved.
- Artificial Superintelligence (ASI): ASI would go beyond human intelligence in every area. It remains a theory and often sparks debate about safety and ethics.
Most existing systems use ANI. These models complete specific tasks accurately but cannot adapt like humans. As you study how to code AI, recognizing these levels helps define what kind of intelligence your project aims to build.
Preparation Steps Before You Learn How To Code AI
Learning how to code AI starts with a solid setup. Every project needs the right data, tools, and people before any code is written. Careful preparation makes a huge difference when you start testing and training models.
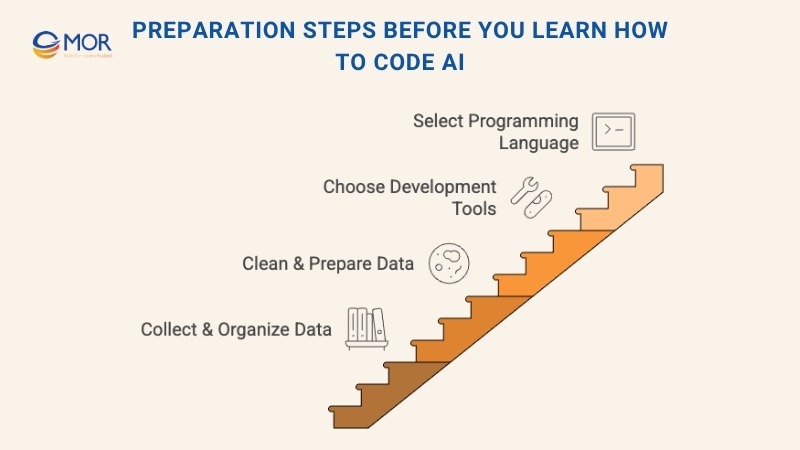
Collecting and Organizing Data
Strong data is the foundation for every machine learning model. Before developers think about how to code an AI, they need to collect information that matches the project’s goal. This can include text, photos, videos, or even sensor signals.
High-quality data always shares a few traits:
- It connects closely to the problem you are solving.
- It includes enough examples to show different situations.
- It stays diverse so the model doesn’t learn from only one pattern.
- It is labeled clearly if the project uses supervised learning.
Teams can collect data from open databases, APIs, or their own recordings. The amount you need depends on how complex the model is. A small AI might need only thousands of entries, while deep learning models often need millions. Understanding this step early helps you plan smarter and move faster once you begin to code AI.
Cleaning and Preparing Data
Raw data often comes messy and inconsistent, which makes it hard to use right away. Before you move further in learning how to code AI, the data must be cleaned and prepared so the model can learn from it effectively.
Typical preparation steps include:
- Removing repeated or irrelevant records
- Correcting mistakes and formatting errors
- Filling or managing missing data points
- Adjusting numeric values to stay on the same scale
- Turning text or categories into readable numbers
Well-prepared data helps the AI model train faster and make more accurate predictions. It also reduces the risk of hidden problems later. Many AI coder teams spend a large part of their time on this stage because clean data builds stronger results.
Picking the Right Development Tools
Selecting the right AI automation tools is one of the most practical steps when learning how to code AI. The choice depends on the project’s goal, the team’s experience, and the kind of system you plan to build. The right setup can cut development time and simplify testing. This is also where an AI tool maker approach becomes useful, combining the best frameworks and cloud services.
For deep learning, the most used tools include:
- TensorFlow – Google’s open-source library that supports building and training deep neural networks.
- PyTorch – A flexible and widely used framework created by Facebook for research and production.
- Keras – A simple, high-level API built on TensorFlow that helps prototype faster.
For traditional machine learning projects that use algorithms like linear regression, decision trees, or SVM, developers often choose:
- Scikit-learn – A Python library tailored for classical ML techniques.
Cloud platforms like AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure also support teams through built-in AI automation environments and scalable infrastructure. They help businesses test ideas faster and bring AI coded projects to life without heavy setup costs.
Selecting a Programming Language
Choosing a language is a key step when learning how to code AI. Among all options, Python stands out as the most popular and practical choice. It powers most AI and ML frameworks like TensorFlow, PyTorch, Keras, and Scikit-learn, making it the standard language for modern development. Alternatives like TensorFlow.js exist but are less common and harder to scale. For most projects, Python remains the most efficient path.
Other languages still have their place in AI-related work:
- R – Ideal for data science and statistics but not widely used to build AI systems.
- Java – Common in enterprise solutions that integrate AI into large applications.
- C++ – Often used behind the scenes to handle complex computations and improve performance, especially in robotics or embedded devices.
For newcomers exploring how to code AI, Python offers an easy start. Its simple syntax, active community, and tools like Jupyter Notebook make it a friendly environment for learning, testing, and experimenting with new ideas in artificial intelligence.
Designing Algorithms To Learn How To Code AI
Designing smart algorithms is at the heart of learning how to code AI. Every model depends on the logic behind it, and choosing the right approach shapes how well it performs. A clear plan and good optimization often make the difference between an average and a powerful solution. Understanding how to code a AI begins with knowing the main types of learning methods.
Main Learning Approaches
Supervised learning uses labeled data to train models for tasks like detecting spam or recognizing images. It studies pairs of inputs and correct outputs until it learns the right mapping.
Unsupervised learning works with raw, unlabeled data. It identifies hidden patterns, relationships, or groups within the data, making it ideal for clustering or feature discovery.
Reinforcement learning trains a system through rewards and penalties. It fits well in robotics, strategy games, or any setting where the model must make sequential decisions through trial and feedback.
Each learning type supports different AI marketing use cases, and knowing when to apply them helps developers build smarter, faster, and more reliable AI systems. This understanding lays the groundwork for anyone exploring how to code AI effectively.
Improving Algorithm Accuracy
Once developers understand how to code AI, the next focus is making those models smarter and faster. This process, known as optimization, helps fine-tune algorithms for better results. Building a custom AI assistant or any intelligent system depends heavily on how well this step is done.
One common method is adjusting the model’s hyperparameters, which control how it learns. Finding the right balance often leads to more accurate predictions. Another key step is feature selection, where developers choose the most meaningful data for the model to study. This allows the system to focus on patterns that truly matter.
A popular optimization method called gradient descent works in the background, giving the model small adjustments after each round of training. Developers also use cross-validation to test performance on new data, making sure it can handle real-world cases instead of just memorizing examples.
Sometimes, training stops early if the results start to decline, a practice known as early stopping. These fine-tuning steps may seem complex, but they are what separate an average AI from one that performs with precision and reliability.
How To Code AI Models And Train Them Effectively
Training is the stage where an idea turns into a working model. It involves setting up clear processes, testing results, and refining performance until the system learns correctly. Anyone learning how to code AI needs to understand how these steps connect to real-world outcomes.
Building and Configuring the Training Process
The first step in model training is preparing quality data that matches the goal of the project. Clean and structured datasets make it easier for the model to recognize patterns. Developers who aim to create your own artificial intelligence always begin here, ensuring that the input data is accurate and consistent.
Next, select the right machine learning algorithm for the problem. Neural networks, decision trees, or support vector machines are common choices, depending on data type and size. Then, configure the training environment, whether on local machines, GPUs, or cloud platforms that handle heavy workloads.
Finally, define important hyperparameters such as batch size and learning rate. These control how fast and how well the model learns. Testing different settings helps find the perfect balance for reliable results. With careful setup, the training process becomes the foundation for mastering how to code AI successfully.
Measuring Model Success
Evaluating results is one of the most important steps when learning how to code AI. Tracking the right metrics helps developers understand if their model is learning properly and performing as expected.
For classification tasks, focus on accuracy, precision, and recall to measure how well the model predicts categories. For regression problems, metrics like mean squared error or R-squared show how close predictions are to real values. Time-series models often rely on mean absolute error to assess prediction quality.
Monitoring these metrics during training helps detect problems early, such as overfitting or underfitting. Developers can then fine-tune settings or adjust the algorithm to improve results. Testing the final model on fresh data that wasn’t part of the training phase ensures a realistic view of how it performs. Comparing results with baseline models or accepted benchmarks gives a clear measure of success in how to code AI effectively.
Implementing Neural Networks In AI Coding
Neural networks are the foundation of most modern AI systems. They handle large amounts of data, recognize patterns, and make predictions based on learned relationships. Understanding how they work is a major step when learning how to code AI.
Core Network Structure
A neural network is built from layers of connected nodes called neurons. The input layer receives the data, hidden layers process it, and the output layer generates the final result. Each neuron connects to others through weighted paths that determine how information flows.
Activation functions, such as ReLU, sigmoid, or tanh, decide when a neuron activates. These functions make the system capable of solving complex, non-linear problems. The process of building an AI coded neural network includes:
- Designing the architecture
- Setting up weights and biases
- Running forward propagation
- Calculating loss
- Adjusting through backpropagation
Frameworks like TensorFlow and PyTorch make it easier to build and train neural networks. They provide pre-built tools that help developers experiment, refine, and scale their AI projects with greater speed and accuracy.
Deep Learning Essentials
Deep learning builds on neural networks that include many connected layers, allowing the system to learn complex features from raw data. It plays a major role in projects where understanding how to code AI involves handling images, language, or sequences of information.
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) are designed for image analysis and recognition. They use filters to identify details such as edges, shapes, and patterns, crucial for tasks like detecting an AI assistant photo or recognizing objects in pictures.
Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) are better suited for sequential data since they can retain information across time steps. They’re often used in speech, translation, or text-based AI applications.
Another key method, transfer learning, lets developers reuse existing pre-trained networks to shorten training time and reduce data requirements.
To successfully implement deep learning, teams need:
- Large, well-prepared datasets
- High-performance GPUs or cloud hardware
- Tuned hyperparameters for balance and accuracy
- Regularization methods that help avoid overfitting
These techniques make deep learning one of the most advanced and rewarding areas for anyone mastering how to code AI.
Specialized Areas To Explore When Learning How To Code AI
AI can be shaped for very specific tasks through specialized methods. These techniques help systems understand speech, interpret visuals, and respond naturally to human language. Learning how to code AI in these areas opens the door to building smarter, real-world applications.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Natural Language Processing helps machines read, understand, and generate human language. It powers tools like chatbots, translators, and writing assistants. For developers exploring how to create AI chatbot, NLP is the foundation that allows systems to communicate clearly and contextually.
NLP models begin by breaking sentences into smaller parts through tokenization, then convert these words into numbers using word embeddings so the computer can interpret them.
Common NLP tasks include:
- Sentiment analysis
- Named entity recognition
- Text classification
Modern large language models, such as GPT, rely on transformer architectures that make it possible to write text, answer questions, or even assist with programming. NLP also deals with harder challenges like sarcasm and context understanding. Researchers continue improving these systems to make them more accurate and unbiased in real-world language use.
Computer Vision
Computer Vision helps machines understand and analyze visual input such as images or videos, much like humans process sight. It supports many everyday applications, from self-driving cars to healthcare diagnostics and facial recognition. Developers studying how to code AI often explore this field early because it connects directly to real-world perception.
AI models in computer vision are trained to handle different tasks, including:
- Object detection – Finding and marking specific items within an image.
- Image classification – Identifying what the image contains and assigning the right label.
- Image segmentation – Separating parts of an image to understand its structure, such as background and foreground.
- Text recognition (OCR) – Extracting printed or handwritten text from pictures.
These processes rely heavily on Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), which use filters to capture details like edges, patterns, and textures. CNNs also handle feature extraction, breaking down visuals into meaningful data points to help the system learn.
Training these models requires large sets of labeled images. The more examples the system sees, the more accurate it becomes at analyzing pictures, whether for detecting an AI assistant photo, reading documents, or interpreting complex scenes.
Speech Recognition
Speech recognition allows AI systems to understand spoken words and convert them into text. It powers tools like virtual assistants, voice search, and transcription apps. Anyone exploring how to code AI for conversational technology will find this field essential for creating interactive, voice-driven systems.
The process starts with breaking an audio signal into small fragments. Each segment is analyzed for sound features like pitch, volume, and frequency. These are then mapped to phonemes, the smallest sound units of language, which the model uses to build complete words and sentences.
Older systems used a mix of Hidden Markov Models (HMMs) and neural networks. The HMMs handled time-based changes in speech, while neural networks helped predict which sounds were most likely. Although still used in some settings, this structure is being replaced with more advanced deep learning models.
Today’s speech recognition tools often rely on Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) and their stronger variants, like LSTMs. These can process continuous audio data and recognize long speech patterns with high accuracy. Newer end-to-end models go a step further, directly converting raw audio into text for faster and cleaner results.
While there are still challenges, like dealing with noise or regional accents, advances in deep learning continue to improve how personal AI systems listen, process, and respond to natural speech.
>>> Explore MOR Blog right here!
Testing And Tuning Your AI Code
Every AI system must go through a careful testing and adjustment process. This step helps confirm whether the model is accurate, reliable, and ready for real-world use. Learning how to code AI also means knowing how to measure and refine its performance to avoid common mistakes like overfitting or bias.
Model Validation Techniques
Cross-validation is a widely used way to test how well an AI model performs. It divides the available data into several groups so that the system can train on some and test on others. This method helps developers see how their model reacts to new information.
The k-fold cross-validation method splits the data into k sections. The model trains on k-1 sections, then tests on the remaining one, repeating the cycle k times to check overall consistency.
Another option, leave-one-out cross-validation (LOOCV), trains the model on all data points except one and tests on the excluded point. This process repeats until each data sample is tested once.
Both approaches reveal whether the model can generalize or if it’s too dependent on training data. Developers who understand these testing methods take an important step toward mastering how to code AI that performs well across different situations.
Optimization and Continuous Updates
Fine-tuning is an essential part of learning how to code AI effectively. It focuses on adjusting the model’s hyperparameters, which influence how the system learns and reacts to data. Proper tuning helps strike a balance between accuracy, speed, and stability.
There are several popular tuning techniques. Grid search tests many combinations of settings to find the best mix. Random search tries random combinations instead, which can sometimes reach strong results faster. A more advanced method, Bayesian optimization, uses feedback from previous tests to predict which settings are worth exploring next, saving time and computing power.
Good tuning can make an multimodal AI model smarter or more efficient depending on the task. Developers often retrain their systems when new data appears to maintain reliability and adapt to change. This mindset keeps AI models learning continuously, helping every AI coder deliver consistent and up-to-date performance.
How To Deploy Your AI Models
Deployment is the final stage of learning how to code AI, where a trained model becomes part of a working application. This step brings your AI to life, allowing users and systems to interact with it in real time.
Deployment Methods
Cloud services are one of the easiest ways to launch AI models. Platforms like AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure provide scalable infrastructure, monitoring tools, and version control for updates. They’re especially useful for teams looking to expand quickly without managing physical hardware.
On-premises deployment offers complete control over setup and data but requires more resources and technical maintenance. It’s often chosen when handling confidential or regulated information.
Containers such as Docker make deployment smoother by packaging the model with all its dependencies, ensuring it runs consistently across environments.
Edge deployment places the model directly on devices like smartphones or IoT sensors. This reduces delay and allows offline performance, though it’s limited by device power.
Serverless deployment runs models using cloud functions that scale automatically. It’s fast and efficient but can experience short delays during startup. Knowing how to code with AI and deploy it across these options helps teams choose the best balance between speed, control, and scalability.
Using APIs for Integration
APIs make it easy for applications to connect with trained AI models. They act as a bridge between the model and users, allowing data to move smoothly in both directions. Anyone mastering how to code AI needs to understand how these interfaces bring AI functionality into real-world systems.
RESTful APIs are the most common choice for web or mobile apps because they’re simple and widely supported. gRPC offers faster performance for high-traffic or internal service communication. GraphQL allows clients to request exactly the data they need, making it flexible for custom integrations.
WebSockets support continuous, real-time interactions, which are perfect for applications that need live predictions or data streaming.
To simplify integration, developers can use Software Development Kits (SDKs) that handle authentication, data formatting, and connectivity in specific programming languages. Mobile SDKs also allow models to run directly on iOS or Android devices, supporting on-device inference and improving responsiveness for AI coded applications.
Maintaining And Updating AI Systems After Coding
Keeping an AI model accurate and reliable requires ongoing attention. Once you’ve learned how to code AI, regular maintenance becomes just as important as the initial development. These updates help your system adapt to new data, changing environments, and security needs.
Keeping AI Models Healthy
Strong AI model maintenance begins with constant performance monitoring. Teams should track outputs closely and use automated tools to detect any drop in accuracy or unexpected behavior in real time.
Clean and updated data is another key factor. When information becomes outdated or contains errors, it can mislead the model. Adding new and relevant data keeps predictions reliable and improves results over time.
Frequent testing helps verify that the AI continues to perform well under new conditions. If performance weakens, retraining may be necessary. Security is equally critical, every AI coder should apply timely patches and upgrades to defend against new vulnerabilities.
With these habits, AI systems stay effective, secure, and ready for future challenges.
Iterating for Improvement
AI systems should evolve just like the data they learn from. After understanding how to code AI, developers need to keep refining models so they remain accurate and valuable over time.
Retraining with new data is one of the most effective ways to strengthen a model. It helps the system stay updated with real-world changes and new patterns. Many teams schedule regular retraining sessions to keep performance consistent.
User feedback also plays a big role. Listening to how people interact with the AI provides insights that guide improvements and new features.
Sometimes, machine learning developers may adjust the model’s structure, test new algorithms, or connect additional data sources. These ongoing updates help every AI coder build smarter, more responsive systems that continue to deliver value long after deployment.
Helpful Resources For Learning How To Code AI
Mastering how to code AI takes continuous learning and collaboration. Joining active communities and using trusted tools helps developers grow their skills and stay current with new techniques.
GitHub is one of the best places to explore real AI projects, share your own work, and collaborate with others. Developers can study open-source examples or contribute to community-driven repositories to learn faster.
Stack Overflow remains the go-to platform for troubleshooting. Its AI and machine learning tags connect you with experts who can answer technical questions and offer practical advice.
Reddit communities like r/MachineLearning feature ongoing discussions about new tools, research, and breakthroughs in AI.
Finally, Discord and Slack groups centered on AI development let you chat directly with peers and professionals. Many of these channels host live Q&A sessions, giving anyone interested in how to code AI a chance to learn from industry experts in real time.
Common Mistakes Beginners Make When Learning How To Code AI
Starting to learn how to code AI can be exciting, but it also comes with a few common challenges. Many new developers face issues that affect model performance, yet most can be avoided with careful attention and practice.
Ignoring Data Quality
Low-quality data is one of the biggest reasons AI models fail. Missing or inaccurate values often lead to unreliable predictions. In Python, tools like Pandas help fix these problems through methods such as .fillna() to replace missing numbers or .dropna() to remove incomplete records.
The right solution depends on the situation. Filling gaps with the average or median works well for numeric data, while dropping missing rows may be safer when dealing with critical information. Clean data ensures that anyone learning how to code AI builds models that stay accurate and consistent.
Overfitting the Model
Overfitting happens when a model learns training data too well but fails to handle new information. It’s one of the most common issues beginners face when exploring how to code AI. The model seems accurate during training but performs poorly in real-world tests.
A proven way to reduce overfitting in deep learning is to add dropout layers in frameworks like TensorFlow. Dropout temporarily turns off a portion of neurons during training, helping the system focus on general patterns instead of memorizing specific details.
This can be done easily with one line of code:
tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.5)
Here, 0.5 means that half of the neurons are disabled at random. Adjusting this number lets you control how much the model generalizes versus how deeply it learns from the data. Understanding how to apply dropout effectively is a key skill for any beginner learning how to code AI successfully.
Slow Training Times
Long training times can slow down progress for anyone learning how to code AI, especially when working with deep learning models. These systems process massive datasets and require strong computing power to train effectively.
Using the right hardware can significantly speed up this process. GPUs (Graphics Processing Units) are the most popular choice because they perform many calculations at once, which is ideal for the matrix operations inside neural networks.
TPUs (Tensor Processing Units) were created specifically for deep learning tasks, but they are mostly limited to platforms like Google Cloud. For most developers, GPUs remain the most accessible and efficient option.
Cloud services such as Google Colab, AWS, and Azure make it easy to access high-performance GPUs without buying expensive equipment. These platforms give both beginners and professionals the chance to experiment with large-scale models and gain hands-on experience in how to code AI effectively.
Trends Shaping The Future Of AI Coding
Artificial Intelligence continues to evolve at high speed, transforming how technology learns, interacts, and makes decisions. Understanding these changes helps developers master how to code AI with the latest tools and responsible practices.
New Trends in AI Development
In 2025, breakthroughs are happening across multiple areas of AI research and development. One major shift is the growth of multimodal large language models, such as OpenAI’s GPT-4o, which can understand and generate text, images, and audio together. These systems make communication with machines more natural and dynamic. Competing models like Google’s Gemini and Meta’s LLaMA 4 show how fast this field is expanding.
Another growing area is autonomous and agentic AI vs generative AI, where systems can reason, plan, and act without constant human input. These intelligent digital coworkers can complete tasks, manage processes, and collaborate with other systems independently, an exciting step for anyone learning how to code AI for automation.
Edge AI is also advancing. Thanks to more efficient chips and smaller models, intelligent features now run directly on phones, wearables, and IoT devices. This reduces latency, strengthens privacy, and cuts reliance on cloud computing.
At the hardware level, companies are building custom AI hardware like advanced chips and processors to handle the huge demands of modern neural networks. Open-source models such as LLaMA and DeepSeek are also making innovation more accessible for developers around the world.
As AI technology grows, responsible coding and regulation become just as important. The industry is developing new standards for data use, system accountability, and collaboration between autonomous platforms. These steps ensure a safer and more transparent future for everyone exploring how to code AI.
Responsible AI Coding
As developers continue learning how to code AI, responsibility becomes just as important as innovation. Modern systems are being used in sensitive areas like healthcare, finance, and security, making transparency essential. Teams are now creating explainable AI tools that clarify how decisions are made, helping users trust what the system produces.
Bias remains one of the biggest challenges in AI. Since models learn from real-world data, they can easily repeat or even magnify human bias. Researchers are building better techniques to identify and reduce unfair patterns before they affect outcomes.
There’s also concern about how automation changes the job market. While AI can open new opportunities, it may replace certain tasks or roles. Developers, educators, and policymakers will need to work together to help people adapt to these shifts. Responsible innovation ensures that learning how to code AI not only advances technology but also benefits society as a whole.
MOR Software: Your Trusted Partner In AI Development
At MOR Software, we turn ideas into intelligent solutions. With years of experience in software outsourcing and custom AI development services for businesses, our team helps businesses design, train, and deploy AI systems that actually work.
We combine technical expertise with practical problem-solving, guiding clients through every step, from building data pipelines to fine-tuning machine learning models. Whether you’re developing a chatbot, automating workflows, or integrating AI into existing software, we tailor each solution to your goals.
Our approach focuses on collaboration, transparency, and long-term results. By staying updated with the latest technologies in Python, TensorFlow, and cloud-based AI outsourcing, we help companies unlock smarter ways to operate and grow.
If you’re ready to bring your AI vision to life, contact MOR Software to start building your next breakthrough.
Conclusion
Mastering how to code AI opens endless opportunities to innovate, automate, and make smarter decisions. With the right data, tools, and mindset, anyone can build systems that learn and adapt. Whether you’re creating your first model or scaling enterprise-level AI, success comes from continuous learning and experimentation. MOR Software is here to guide you through every step, from strategy to deployment. Contact us today to start developing AI solutions that truly make an impact.
MOR SOFTWARE
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How to start coding for AI?
Start by learning Python, since it’s beginner-friendly and has rich AI libraries like TensorFlow, PyTorch, and Scikit-learn. Once you understand programming basics, study data handling, algorithms, and core math concepts such as statistics and linear algebra. Then, try small AI projects like image recognition or chatbots to practice.
Is it easy to code AI?
Not at first. AI coding involves math, data science, and logic, which can be challenging. But with the right learning path, starting small, following tutorials, and experimenting, you’ll find it easier over time. The key is consistency and hands-on practice.
What coding language is best for AI?
Python is the most popular choice for AI because of its simplicity and extensive ecosystem. It’s used with major frameworks like TensorFlow, Keras, and Scikit-learn. R is useful for data analysis, while C++ is chosen for performance-critical applications.
Should I learn C++ or Python for AI?
For beginners, Python is usually better. It’s easier to read and has thousands of pre-built AI tools. C++ is ideal for projects needing high speed and hardware control, like robotics or real-time systems. Many developers learn both over time.
Is AI coded in C++?
Yes, many AI systems use C++ because it offers speed and precision. Although high-level development often happens in Python, core AI engines and libraries are frequently written in C++ to handle complex computations efficiently.
Can AI code itself?
To some extent, yes. AI can now generate small code snippets, automate testing, or suggest fixes using tools like GitHub Copilot or ChatGPT. However, it still needs human oversight for logic, structure, and debugging, especially in large-scale applications.
How to check if code is AI generated?
You can look for patterns like repetitive logic, inconsistent comments, or similar phrasing across files. Online AI-detection tools such as GPTZero or CodeCarbon can help flag machine-written sections. Manual review by an experienced coder also helps confirm authenticity.
How to tell if code was written by AI?
AI-generated code often lacks creativity and optimization. It may use generic variable names, miss detailed comments, or rely on redundant steps. Comparing it to known AI model outputs or running a plagiarism scan for code can provide more evidence.
Why do most AI projects fail?
Many AI projects fail because teams focus too heavily on technology instead of solving real business problems. Success depends on clear goals, good data, and collaboration between developers, analysts, and stakeholders, not just advanced algorithms.
How to make an AI assistant?
Building an AI assistant involves collecting voice or text data, training a language model, and connecting it with APIs for speech recognition and task handling. Tools like Dialogflow or OpenAI APIs make it easier to design conversational workflows.
How long does it take to learn how to code AI?
If you already know basic programming, you can start building small AI projects within a few months. Mastering complex systems like deep learning can take one to two years of steady study and practice.
Do I need math skills to code AI?
Yes, math is fundamental. You should understand linear algebra, calculus, probability, and statistics. These concepts help you tune algorithms, analyze data, and improve model performance.
What software do I need to code AI?
You’ll need a code editor like VS Code or Jupyter Notebook, Python installed on your system, and libraries such as TensorFlow, NumPy, or Scikit-learn. For bigger models, consider cloud platforms like Google Colab or AWS.
Can I learn how to code AI without a computer science degree?
Absolutely. Many successful AI developers are self-taught. With free online courses, tutorials, and open-source tools, you can learn everything from data preprocessing to neural networks at your own pace.
What are the first projects to try when learning how to code AI?
Start with simple tasks like image classification, chatbot creation, or sentiment analysis. These projects teach you data collection, model training, and prediction, all core AI development skills.
Rate this article
0
over 5.0 based on 0 reviews
Your rating on this news:
Name
*Email
*Write your comment
*Send your comment
1