Generative AI in Cybersecurity Explained: How To Use It?

As cyber threats grow smarter and faster, businesses are turning to generative AI in cybersecurity to stay ahead. This technology not only detects risks but also predicts and prevents them before they strike. In this guide, MOR Software explores how generative AI transforms digital defence, revealing its real-world benefits, challenges, and future possibilities for every organization.
What Is Generative AI In Cybersecurity?
Generative AI in cybersecurity refers to advanced models that can create new content, including code, text, or simulated data, by learning from existing datasets. These systems use large-scale machine learning to identify and reproduce complex patterns that resemble human-generated work.
Through this ability, AI in cybersecurity opens up opportunities for faster threat detection, better automation, and more predictive analysis in digital protection systems. In the U.S. alone, the FBI logged 859,532 internet crime complaints in 2024 with reported losses exceeding 16 billion dollars, a 33% jump from 2023. This shows how urgent faster detection and response have become.
Yet, cyber security and AI together form a complicated relationship. While this technology helps organizations anticipate and counter evolving attacks, it also gives hackers new tools to design malicious code, fake identities, or phishing content that appears authentic.
As a result, experts describe generative AI in cybersecurity as both a powerful defence mechanism and a potential attack surface, depending on how it’s applied. In short, this innovation has redefined how we approach cyber security and artificial intelligence, forcing security teams to balance the benefits of automation with the growing risks of AI-driven threats.
Defensive Roles Of Generative AI In Cybersecurity
From a defensive standpoint, generative AI in cybersecurity helps organizations strengthen protection, increase response speed, and improve analytical precision across their systems. This approach reshapes the role of AI in cybersecurity, allowing automated models to take over repetitive and time-consuming security tasks while assisting experts with complex threat analysis.
- Synthetic data generation: Creates secure, realistic datasets for model training without risking exposure of confidential business or customer information.
- Attack simulation: Produces virtual scenarios that mirror real-world intrusions, enabling teams to test their defences and refine incident response plans.
- Advanced threat detection: Evaluates massive volumes of network data and system logs, and when organizations used security AI and automation extensively their average breach costs were 1.88 million dollars lower and they identified and contained breaches nearly 100 days faster compared with no AI use.
- Automated incident response: Summarizes event details, provides remediation guidance, and supports informed decision-making to limit damage and downtime. The need for this is clear since about 59% of security teams say they face too many alerts, and around 55% struggle with too many false positives.
These applications show how generative AI can be used in cybersecurity to streamline daily operations and identify risks before they escalate. Combining AI for cyber security with human expertise, companies can reduce alert fatigue, improve visibility, and focus their teams on strategy and innovation instead of manual data review.
Offensive Risks Of Generative AI In Cybersecurity
While generative AI in cybersecurity brings clear defensive benefits, it also creates new avenues for exploitation. Cybercriminals now use these same tools to design sophisticated attacks that are faster, smarter, and harder to trace. As a result, AI cyber threats have become more unpredictable and damaging than ever.
- Phishing and social engineering: Malicious actors can craft highly convincing emails, messages, or websites that imitate trusted sources, making scams almost indistinguishable from legitimate communication. By early 2025, around 80% of social engineering attacks worldwide were already using AI-powered phishing.
- Deepfakes: AI-driven voice and video generators can clone real people’s likenesses, enabling fraud, identity theft, and large-scale misinformation campaigns. A 2025 industry study found that 85% of cybersecurity and IT leaders faced at least one deepfake attack in the prior year with average damages reaching 280,000 dollars.
- Adaptive malware: Attackers can use AI to write and rewrite malicious code that evolves on its own, bypassing traditional security measures and detection systems. Ransomware was linked to 75% of system intrusion breaches in the 2025 Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report.
These evolving risks highlight the disadvantages of AI in cybersecurity, as automation can now work against defenders just as effectively as it supports them. For this reason, organizations must stay alert and develop proactive strategies to detect and neutralize threats before they take advantage of generative models.
Key Benefits Of Generative AI In Cybersecurity
Generative AI in cybersecurity strengthens how organizations detect, analyze, and respond to complex digital threats. Through applying advanced deep learning models, it can simulate realistic attack scenarios that expose system weaknesses and help teams reinforce their defences. These simulations prepare companies to handle both existing and emerging forms of cyberattacks, offering measurable improvements in prevention and response.
Beyond testing, this technology automates repetitive tasks in security workflows, such as log analysis or alert classification. That automation enables professionals to dedicate more time to strategic planning and risk assessment. It also enhances staff development by creating dynamic, hands-on environments for cybersecurity training, ensuring professionals are ready for real-world incidents.
As attackers evolve their methods, the adaptive learning capabilities of AI-driven systems become invaluable. Their ability to anticipate risks and react in real time underscores the growing impact of AI in cybersecurity, helping enterprises maintain operational continuity and confidence in their defences.

Enhancing Threat Detection and Response
Through predictive algorithms and behavioral analysis, generative models can detect anomalies that traditional rule-based systems overlook. This precision-driven benefits of AI in cybersecurity allows faster detection and smarter incident response, minimizing downtime and potential losses.
Because these models continuously learn from fresh data, they adapt to new attack patterns and maintain high accuracy even as threats evolve. The combination of automation, prediction, and contextual awareness creates an agile system that can identify breaches early, coordinate mitigation steps, and deliver actionable intelligence. This approach keeps security frameworks agile, empowering teams to outpace emerging cyber security AI challenges with accuracy and speed.
Automating Security Operations
In modern defence strategies, generative AI in cybersecurity plays a key role in automating core protection processes. It handles repetitive yet essential activities like configuring firewalls, scanning for vulnerabilities, and monitoring network traffic in real time. Doing so, it reduces manual workload and allows teams to focus on threat analysis, compliance, and strategy development.
This intelligent automation adapts to each system’s unique environment, identifying patterns in large datasets to predict and enforce the most suitable defences. With this approach, companies can deploy flexible, data-driven safeguards that scale easily as their infrastructure grows. The result is a more responsive system that minimizes cyber security and AI errors caused by human oversight, enhances performance, and maintains stronger overall protection.
Scenario-Based Cybersecurity Training
Generative AI transforms traditional cybersecurity education into an immersive, simulation-driven experience. Recreating realistic attack scenarios, it enables trainees to face evolving threats as they unfold, rather than in static test conditions. These simulations adjust in real time, helping professionals practice strategic decision-making and sharpen their responses to complex digital intrusions.
This hands-on training model encourages critical thinking and collaboration among IT specialists. It strengthens their ability to identify weaknesses, contain incidents, and act confidently under pressure. Over time, organizations using AI in cybersecurity examples like scenario-driven simulations see noticeable improvements in preparedness, coordination, and resilience across their teams.
6 Practical Applications Of Generative AI In Cybersecurity
Generative AI in cybersecurity is transforming how organizations protect their systems by enhancing detection accuracy, supporting continuous learning, and streamlining defence operations. It equips security teams with advanced tools that automate analysis, interpret complex data, and anticipate new threats before they arise. With practical deployment across multiple domains, this technology strengthens the foundation of digital protection strategies.
Threat Intelligence and Adaptive Detection
One of the most effective ways generative AI can be used in cybersecurity is through intelligent threat analysis. Scanning and interpreting massive volumes of network logs, user behaviors, and global attack data, AI models identify unusual activities and rank potential risks based on relevance to an organization’s infrastructure. This capability filters out noise from non-critical alerts, allowing teams to focus on the most pressing incidents.
As models continue to learn from evolving data, they refine their ability to recognize subtle anomalies that signal new forms of attack. This adaptive approach keeps systems responsive and predictive, rather than purely reactive. A prime example is Google’s Gemini system, which processes extensive datasets, integrating information from Mandiant and VirusTotal, to summarize, prioritize, and report emerging threats in real time. Its generative summaries simplify decision-making for analysts and demonstrate how cyber security AI solutions can transform traditional risk management into a proactive, insight-driven practice.
Predictive Security and Vulnerability Analysis
Another crucial function of generative AI in cybersecurity lies in its predictive and diagnostic capabilities. Through studying historical data, past attack trends, and existing system configurations, it forecasts potential weaknesses before they can be exploited. This allows organizations to strengthen defences in advance rather than react after an incident.
Through continuous learning, AI models detect correlations between known vulnerabilities and new attack techniques, making it easier to anticipate risks with higher precision. This proactive analysis helps teams focus their attention and resources on the most critical systems, reducing exposure to large-scale breaches.
A strong example is Tenable.io, which integrates cyber security and AI technologies to evaluate past vulnerability records and forecast likely future threats. The platform prioritizes weak points based on potential impact and exploitation probability, giving enterprises a smarter, data-backed way to manage risks and reinforce their overall resilience.
Malware Simulation and Biometric Protection
In research and testing, generative AI in cybersecurity provides a controlled environment for studying how malicious software behaves without endangering live systems. By generating synthetic malware samples, analysts can observe infection patterns, test defensive tools, and refine detection algorithms with zero risk of real-world compromise. This controlled simulation approach accelerates innovation in malware analysis while maintaining complete system safety.
The same principle applies to identity verification. In biometric protection, generative models can create artificial fingerprints, facial scans, or voice patterns that closely resemble real data. These realistic datasets help evaluate and improve authentication mechanisms against spoofing and deepfake attempts.
Companies such as Syntheticus demonstrate how cyber security and artificial intelligence can combine to produce privacy-compliant, statistically accurate datasets. Their technology supports safer testing for both malware and biometric systems, empowering enterprises to enhance authentication reliability and safeguard sensitive user information.
Secure Coding and Development Support
Within software engineering, generative AI in cybersecurity acts as an intelligent coding assistant that helps developers build safer applications from the start. It reviews code in real time, identifies risky patterns, and provides guidance based on proven security standards. Learning from millions of existing code samples, these systems recommend cleaner syntax, suggest preventive measures, and flag potential vulnerabilities long before deployment.
This support reduces the likelihood of human error and ensures security remains an integral part of the development lifecycle rather than an afterthought. Developers benefit from faster reviews, clearer documentation, and immediate insights into potential threats within their code.
One prominent example is GitHub Copilot, whose Autofix feature uses using AI in cyber security to automatically detect and repair weaknesses. It not only highlights the source of an issue but also explains the risk behind it, offering instant, context-aware fixes that strengthen the security of applications before they go live.
Incident Management and Alert Summarization
In cybersecurity operations, generative AI in cybersecurity streamlines how teams manage alerts, reports, and post-incident documentation. It interprets complex system data, condenses lengthy technical logs, and produces clear, structured summaries that help analysts grasp the situation quickly. This efficiency allows teams to act faster, assign priorities accurately, and focus on high-impact mitigation steps instead of being overwhelmed by raw data.
The technology also provides context-aware recommendations for follow-up actions, turning information into practical strategies for reducing risks. By automating much of the reporting process, it ensures that key insights, such as incident type, origin, and corrective actions, are captured and communicated effectively.
Platforms like ServiceNow Security Operations show how AI in cybersecurity infographic systems can translate technical incident data into concise, accessible summaries. Through automated alert generation and detailed reporting, such tools improve visibility, reduce response time, and empower teams to handle complex threats with precision and confidence.
Employee Training and Awareness
Employee education remains one of the most impactful applications of generative AI in cybersecurity. Through adaptive, interactive modules, this technology teaches staff how to recognize phishing attempts, manage data safely, and follow internal security guidelines. It turns traditional awareness programs into engaging experiences that evolve with each learner’s progress and knowledge gaps.
Tailoring content to specific behaviors and risk levels, AI-driven training minimizes human error, the most common weakness in digital security frameworks. Real-time simulations, quizzes, and scenario-based exercises keep employees alert to emerging threats and reinforce consistent cyber hygiene across departments.
Platforms like CybSafe illustrate how AI in cybersecurity market innovation is reshaping training. Using generative models, CybSafe evaluates user behavior, designs customized lessons, and simulates phishing attempts with instant feedback. This personalized approach boosts engagement, strengthens long-term retention, and empowers teams to play an active role in defending their organizations.
Generative AI Cybersecurity Risks
As valuable as generative AI in cybersecurity has become for defenders, it also poses growing challenges when misused. The same tools that enhance detection and automate protection can be exploited by attackers to identify weaknesses, create new threats, and scale cyberattacks faster than ever before. This dual nature makes AI cyber threats one of the most pressing concerns in today’s security landscape.
Malicious actors are now using AI’s ability to analyze complex data to uncover vulnerabilities in enterprise systems. As these models advance, adversaries may even reverse-engineer them to manipulate security algorithms or bypass authentication processes. In short, the disadvantages of AI in cybersecurity extend far beyond automation errors, they include the potential for large-scale, AI-driven exploitation.
How Adversaries Exploit Generative AI
Cybercriminals are quickly adopting generative tools to enhance precision, automate attacks, and mimic legitimate communication. Their methods have become faster, smarter, and more deceptive, turning AI into a major weapon against digital defences. Some of the most common uses include:
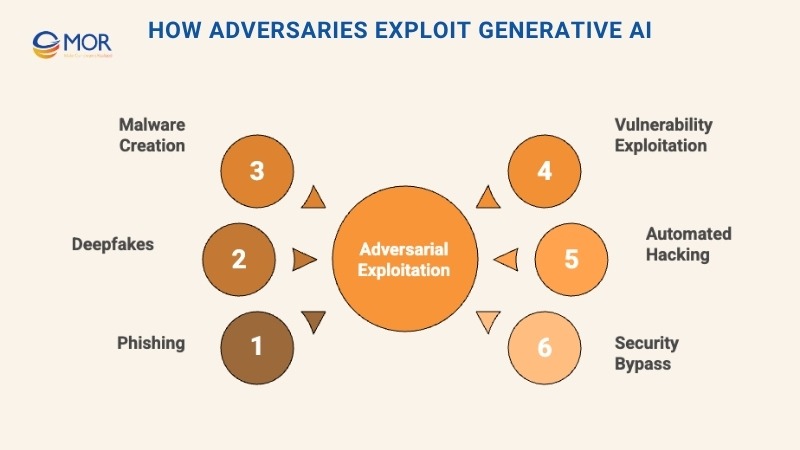
Phishing and Social Engineering
Generative models can produce personalized, convincing messages that replicate trusted sources, tricking recipients into sharing confidential data or installing malicious files.
Deepfakes
AI-generated voice and video can impersonate executives, employees, or public figures, making it easier to manipulate opinions or execute targeted cyber security AI scams.
Malware Creation
Attackers can build adaptive malware that rewrites its code to avoid signature-based detection, challenging even advanced security tools.
Exploiting Vulnerabilities
By scanning systems, software, and user behavior, AI can pinpoint weak spots and enable precision-targeted breaches.
Automated Hacking
Generative systems can automate key stages of intrusion, allowing criminals to launch complex, large-scale attacks at unprecedented speed.
Bypassing Security Measures
Adversarial AI can mimic legitimate user behavior or produce fake biometric inputs to trick systems like CAPTCHAs or facial recognition, revealing the darker potential of cyber security and AI convergence.
Securing the AI Development Pipeline
Protecting the AI development lifecycle is now a key focus within generative AI in cybersecurity. This process covers every stage, from data collection and model training to deployment, monitoring, and maintenance. It ensures that the data feeding AI models remains untampered, the algorithms retain integrity, and system access stays tightly controlled against unauthorized interference.
Maintaining a secure pipeline is essential for several reasons. First, safeguarding sensitive datasets is crucial, especially when models handle personal or confidential business information. Second, preserving the reliability and transparency of AI-driven systems builds user trust and encourages responsible adoption. Finally, preventing manipulation or poisoning of AI models helps avoid serious consequences, such as misinformation, data breaches, or even operational disruptions in AI-controlled systems.
To achieve strong protection, organizations must apply best practices like data governance, end-to-end encryption, multi-factor authentication, secure coding, and real-time system monitoring. Together, these safeguards create a layered defence that minimizes risks and reinforces confidence in deploying cyber security and artificial intelligence responsibly.
Best Practices For Using Generative AI In Cybersecurity
While generative AI in cybersecurity offers new opportunities for speed, accuracy, and automation, it also introduces unique vulnerabilities. To use these technologies effectively, organizations must apply disciplined security measures that balance innovation with protection. Following structured guidelines helps minimize exposure and ensures AI systems remain safe, compliant, and aligned with company policies.
Strong using AI in cyber security practices include reviewing vendor security frameworks, protecting sensitive data, updating AI models regularly, deploying advanced monitoring tools, defining responsible-use policies, and providing continuous employee training. These steps help teams gain the benefits of automation while staying resilient against evolving risks.
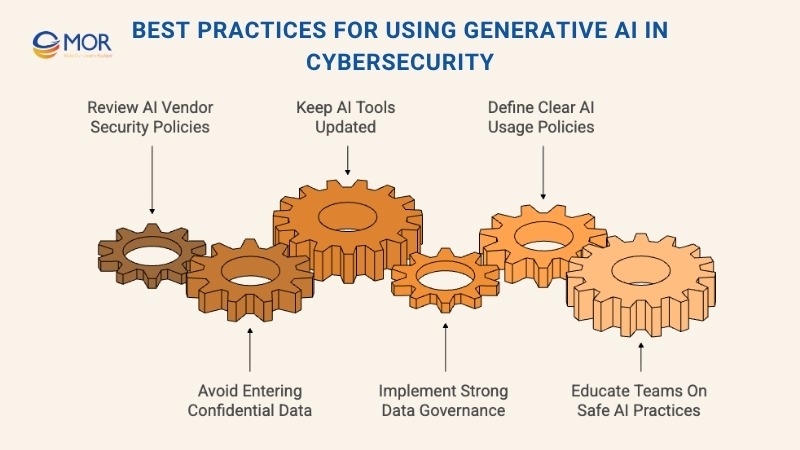
Review AI Vendor Security Policies
Before adopting any AI-powered platform, carefully assess the vendor’s security documentation and data-handling policies. Understand how your information is stored, processed, and retained, as well as the vendor’s compliance with relevant industry standards. Transparency about encryption, access control, and data sharing practices is crucial for identifying potential risks early. Only partner with providers who demonstrate clear accountability and offer consistent visibility into their security operations.
Avoid Entering Confidential or Sensitive Data
When using generative AI in cybersecurity, remember that its security depends on the data it processes. Never input confidential business details, financial information, or proprietary material into public or unverified AI systems. Many tools retain and reuse data to refine their models, which could inadvertently expose sensitive information. Keeping data entry limited to non-confidential content helps lower the risk of leaks or unauthorized access, strengthening your organization’s overall data protection posture.
Keep Generative AI Tools Regularly Updated
Maintaining the latest version of your AI tools is one of the simplest yet most effective ways to protect against emerging threats. Frequent updates ensure vulnerabilities are patched, performance is optimized, and defences remain aligned with current security standards. Work closely with AI in cybersecurity providers that issue consistent updates, notify users about security improvements, and maintain transparent communication regarding system changes. Regular maintenance helps close potential gaps and keeps your generative models secure and reliable.
Implement Strong Data Governance and Security Tools
To use generative AI in cybersecurity safely, organizations need solid data governance and monitoring systems in place. Encryption, strict access controls, and regular audits protect sensitive information from exposure or manipulation. Integrating data governance frameworks with advanced tools like Data Loss Prevention (DLP) and Identity and Access Management (IAM) helps prevent unauthorized data use or sharing. These safeguards ensure that AI models operate securely while maintaining compliance with internal and external security standards.
Define Clear AI Usage Policies
Establish transparent policies outlining how AI tools should be applied within your organization. Your internal AI policy should detail which systems are approved, how employees may use them, and what actions are prohibited. By defining expectations and accountability measures early, teams maintain consistency in applying AI for cyber security technologies while reducing potential misuse. A clear policy also supports regulatory compliance and reinforces a culture of security awareness across departments.
Educate Teams on Safe AI Practices
Human error remains one of the biggest weaknesses in cybersecurity. Regular training ensures that employees understand what data they can safely input into AI platforms and how to spot malicious outputs or phishing attempts. Encourage continuous learning on security protocols and proper AI usage. When staff are well-informed, they’re more likely to apply tools responsibly, minimizing the risk of data loss or accidental exposure while maximizing the benefits of cyber security and AI innovation.
Generative AI In Cybersecurity: The Future Ahead
The future of AI in cybersecurity will be shaped by both innovation and risk. As these systems grow more advanced, they will revolutionize digital protection while simultaneously creating new attack surfaces. According to industry forecasts, several key trends will define how this technology evolves:
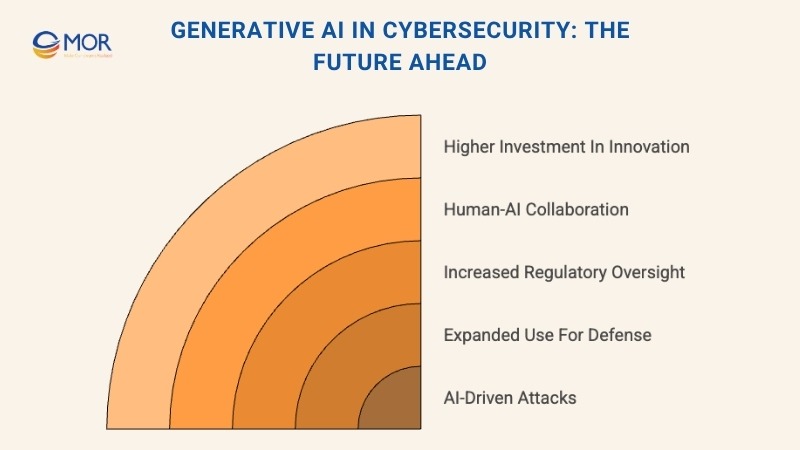
- Rise of AI-driven attacks: Threat actors will continue developing more precise and adaptive strikes that evade conventional defences, pushing organizations to modernize their security infrastructure.
- Expanded use of AI for defence: Enterprises will rely more heavily on automation for threat detection, analysis, and rapid incident response, allowing teams to act faster with greater accuracy.
- Increased regulatory oversight: Governments and agencies are expected to introduce stricter standards to govern the ethical and secure use of AI systems across industries.
- Human-AI collaboration: Despite automation’s growth, human oversight will remain crucial. Analysts and engineers will guide AI tools to make informed, responsible decisions and prevent misuse.
- Higher investment in AI innovation: As the impact of AI in cybersecurity continues to rise, organizations will dedicate more resources to developing secure, scalable, and trustworthy AI-powered protection systems.
Ultimately, the AI in cybersecurity market will depend on how effectively security leaders harness generative technologies for prevention, detection, and recovery. The goal is not just to use AI for automation, but to build resilient, proactive defences that safeguard every digital environment for the long term.
Partner With MOR Software For AI-Driven Cybersecurity Solutions
As cyber threats become more sophisticated, businesses need partners who can merge innovation with protection. At MOR Software, we integrate AI development and cybersecurity engineering to help organizations predict risks, respond faster, and safeguard their digital infrastructure. With years of experience across finance, healthcare, manufacturing, and enterprise systems, we deliver practical, data-driven security that evolves with your business.
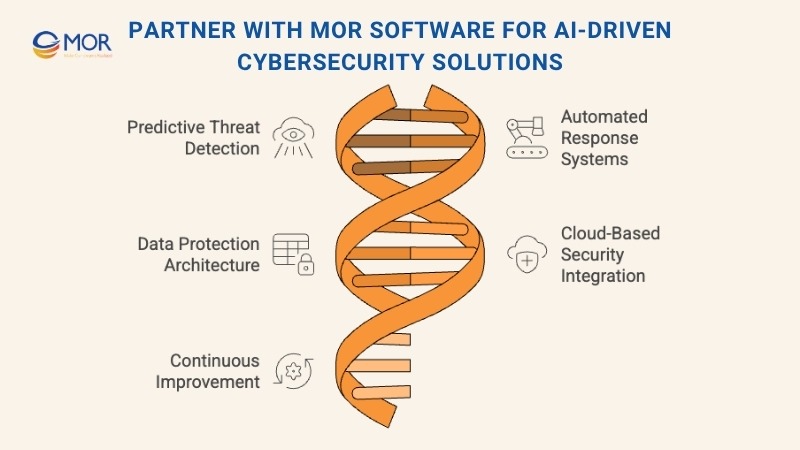
Our AI-driven cybersecurity capabilities include:
- Predictive threat detection: Using machine learning to identify abnormal behavior before breaches occur.
- Automated response systems: Building smart workflows that contain threats instantly and minimize downtime.
- Data protection architecture: Applying encryption, access control, and anomaly monitoring for secure operations.
- Cloud-based security integration: Combining AI and cloud computing for scalable, real-time protection.
- Continuous improvement: Leveraging analytics and feedback loops to adapt defenses to new attack patterns.
Through blending innovation with reliability, we help companies create safer digital environments and maintain business continuity.
Contact MOR Software today to explore how AI can strengthen your cybersecurity strategy.
Conclusion
The rise of generative AI in cybersecurity marks a turning point for modern defense strategies. It enables faster detection, smarter automation, and stronger prevention against evolving threats. Yet, true protection requires the right expertise to deploy it safely and effectively. MOR Software specializes in creating AI-driven cybersecurity solutions tailored to your business needs. Contact us today to build a proactive, intelligent defense system that secures your data and strengthens your digital future.
Rate this article
0
over 5.0 based on 0 reviews
Your rating on this news:
Name
*Email
*Write your comment
*Send your comment
1