Best Autonomous AI Agents by Category - 2026’s Top Picks

Autonomous systems are no longer experiments. They are reshaping how teams build, decide, and scale. As interest in the best autonomous AI agents grows, many businesses struggle to choose tools that truly fit real workloads and long-term goals. This MOR Software’s guide will highlight leading options, key categories, and practical insights to help you move forward with clarity and confidence.
What Are Autonomous AI Agents?
The key difference between traditional AI tools and autonomous ones comes down to how much human guidance is needed to set goals and carry them out.
Think about a customer support chatbot that works from fixed rules and sends harder cases to a human team. It adds value, but it stays inside the limits you define.
Now picture a system asked to “increase customer retention by 15%.” One of the best autonomous AI agents would review customer behavior on its own, spot users likely to leave, plan retention actions, and run those actions across channels without checking in at every step. This is how modern autonomous AI agents behave in practice.
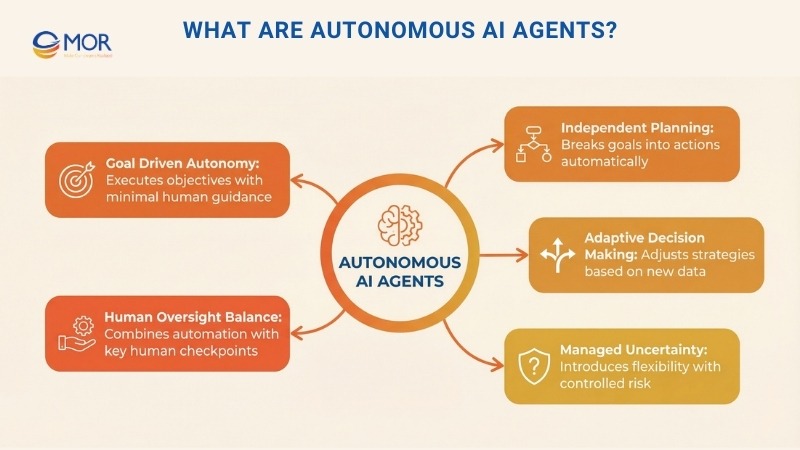
That level of freedom can drive strong outcomes, but it also introduces uncertainty. An autonomous AI agent may select approaches you did not expect, reach for data sources you did not plan for, or judge success in a way that differs from your original goal. This reflects how an agent in artificial intelligence can reason beyond simple instructions.
Most real-world deployments today sit in the middle. They rely on advanced automation for complex, multi-step work, yet still keep humans involved at key decision moments. This balance is common across autonomous agents in AI automation used in business settings.
Best Autonomous AI Agents Categorized List For 2026
We are at a stage where selecting an AI agent framework matters as much as choosing a core stack. The options below go beyond simple libraries. They act as the foundation for building systems that can plan, reason, and act with limited human input. Some give teams deep control. Others hide complexity so the focus stays on results. Together, they reflect where the best autonomous AI agents are heading, especially as the autonomous AI and autonomous agents market continues to expand across enterprise use cases.
These solutions are grouped by focus areas such as LLM-centric design, task execution, conversational systems, multi-agent coordination, and visual builders. This structure helps teams match tools to real goals. Whether you are testing ideas, expanding usage, or moving into production, this category includes AI autonomous agents that can change how products are built and maintained.
LLM-Centric Frameworks For Autonomous Reasoning
This category centers on reasoning-first design. These frameworks support agents that plan steps, manage state, and adapt decisions over time. They form the backbone of many autonomous agents in AI that rely on language models as their core engine.
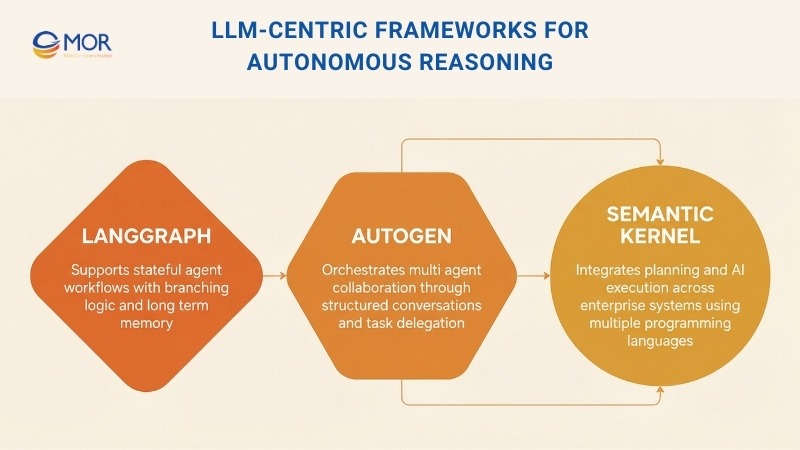
1. LangGraph
LangGraph is a programming language for AI created for stateful, multi-agent, and workflow-driven LLM applications. It suits agent flows that need branching logic, retrieval-based systems, chat interfaces, and advanced automation where conditions and decisions matter.
Core Capabilities:
- Stateful workflow control with long-term memory support
- Flexible branching logic for complex decision paths
- Direct connections with multiple LLM services and APIs
Typical Applications: Create tailored invoices from templates, direct IT support requests, and review supplier agreements.
2. AutoGen
AutoGen is an open source framework from Microsoft that focuses on orchestrating multiple agents in shared workflows. It allows modular agents to communicate, use tools, and divide tasks through structured conversations and dynamic delegation.
Core Capabilities:
- Coordinated multi-agent dialogue and collaboration handling
- Structured control over chat flows and task sequencing
- Broad tool and function support for extended behavior
Typical Applications: Condense legal files, prepare marketing messages, and assemble internal compliance lists.
3. Semantic Kernel
Semantic Kernel is a cross-language framework from Microsoft that works with some of fastest programming languages like Python, C#, and Java for enterprise orchestration. It connects planning, language understanding, and AI execution inside existing systems, making it useful for agentic AI autonomous systems tied to business workflows.
Core Capabilities:
- Multi-language support across common enterprise environments
- Enterprise-focused orchestration with built-in security options
- Tight links with Microsoft services and external platforms
Typical Applications: Log sales calls into CRM software, prepare investor briefings, and monitor staff review cycles.
Autonomous Task Agents
This group focuses on systems built to plan, act, and finish work on their own. These tools power many of the best autonomous AI agents used for long-running tasks where constant human input slows progress.
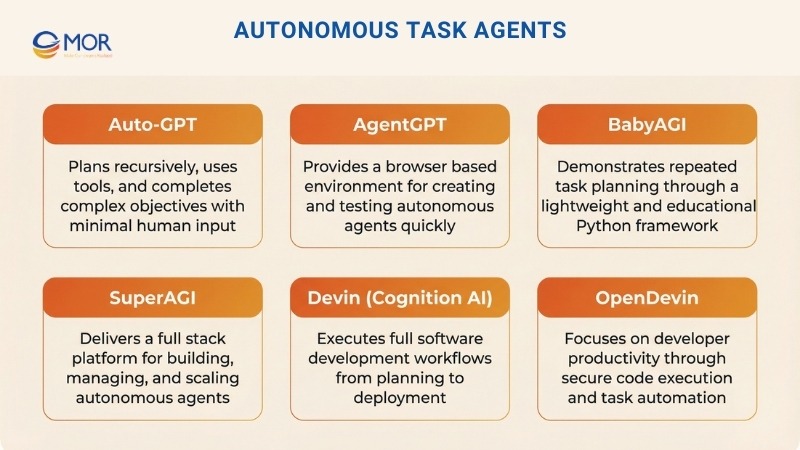
4. Auto-GPT
Auto-GPT is a framework designed for agents that can plan recursively, act dynamically, and store long-term context. It allows an autonomous AI agent to split large objectives into smaller steps, use external tools, and complete work with very limited human involvement.
Core Capabilities:
- Recursive planning logic with smart task breakdown
- Long-term memory to preserve context across runs
- Broad tool access for handling many execution needs
Typical Applications: Create full marketing strategies, organize event operations, and study churn patterns.
5. AgentGPT
AgentGPT delivers a no-code, browser-based environment for creating and running autonomous AI agents without technical setup. The interface makes it easy to define goals, test ideas, and observe how these systems behave in real time.
Core Capabilities:
- Visual browser interface for quick agent setup
- Independent task execution with light configuration
- Built-in testing tools for trials and validation
Typical Applications: Generate ad ideas, outline recruitment plans, and prepare monthly KPI summaries.
6. BabyAGI
BabyAGI is a lightweight Python framework built around repeated task planning and execution. It uses a function-driven design that cycles through task creation, action, and prioritization, making it useful for learning how AI autonomous agents operate.
Core Capabilities:
- Simple structure with readable and compact code
- Repeating task loops that adjust over time
- Strong learning focus with clear guides and samples
Typical Applications: Experiment with campaign concepts, plan internal training sessions, and draft process notes.
7. SuperAGI
SuperAGI delivers a full-stack platform for developing and running autonomous agents at scale. It includes a visual interface and an extensive plugin system, with features aimed at enterprise teams that need visibility and control.
Core Capabilities:
- End-to-end tooling for building and deploying agents
- Scalable design for memory, tools, and extensions
- Visual dashboard for monitoring behavior and output
Typical Applications: Track support quality, prepare investor reports, and handle internal audit tasks.
8. Devin (Cognition AI)
Devin is an autonomous software engineering system built to write, test, and ship code across full development pipelines. It shows how AI coding assistant agents write code autonomously across planning, debugging, and deployment with minimal supervision.
Core Capabilities:
- End-to-end software development support
- Cross-language execution and debugging functions
- Coverage across frontend, backend, and infrastructure
9. OpenDevin
OpenDevin is an open source option created as an alternative to closed agent solutions. It focuses on developer efficiency through code execution, command automation, and structured task handling inside safe environments.
Core Capabilities:
- Developer-centered tools with smart coding support
- Secure execution spaces for running code
- Command automation to speed up daily workflows
Typical Applications: Create HR reporting dashboards, sort emails automatically, and generate routine operations reports.
>>> Let's walk through the best AI tools for DevOps, how they work, and how your team can use them with confidence.
Conversational Autonomous AI Agents And Chat Frameworks
This category focuses on dialogue-first systems built to interact with users in natural language. These tools support many of the best autonomous AI agents used in customer service, internal support, and guided workflows where conversation drives action.
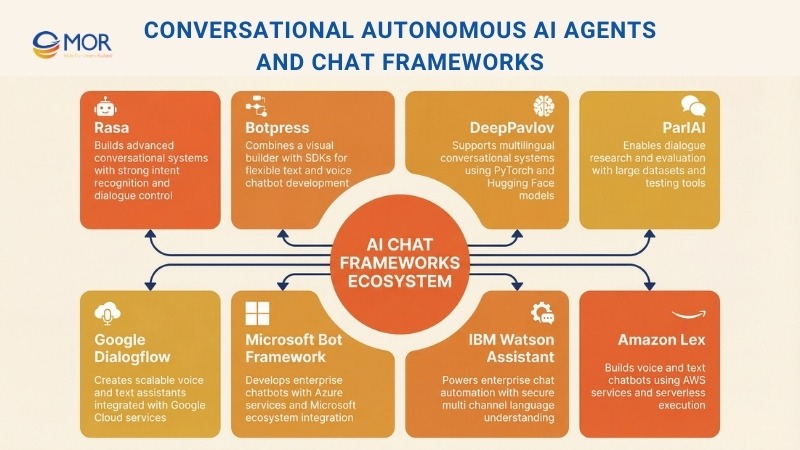
10. Rasa
Rasa is an open source framework designed for building advanced conversational systems. It provides natural language understanding, custom dialogue control, and context tracking. The framework supports multi-step conversations, multiple channels, and smooth connections with enterprise software.
Core Capabilities:
- Strong NLU for intent detection and entity extraction
- Flexible dialogue control with clear conversation flows
- Deployment across web, mobile, and voice environments
Typical Applications: Schedule appointments, respond to support requests, and suggest subscription options.
11. Botpress
Botpress is a modular open source platform that blends a visual builder with developer-focused SDKs. It supports text and voice interactions and connects well with enterprise systems, making it suitable for both technical teams and business users working with autonomous AI agents.
Core Capabilities:
- Modular structure with adaptable UI and SDK elements
- Support for text and voice conversations across channels
- Enterprise-ready integrations with security and compliance support
Typical Applications: Handle delivery questions, support employee onboarding software, and promote related products.
12. DeepPavlov
DeepPavlov is an open source conversational framework built on PyTorch and Hugging Face. It supports multilingual dialogue and full conversation lifecycle development. The platform includes ready-made models, adjustable pipelines, and advanced language processing tools.
Core Capabilities:
- Integration with modern PyTorch and Hugging Face models
- Broad language coverage with localization support
- Complete dialogue systems from input to response handling
Typical Applications: Translate live chat sessions, run policy questionnaires, and onboard new partners.
13. ParlAI
ParlAI is an open source framework from Facebook AI created for dialogue research and testing. It gives access to large datasets, trained models, and evaluation tools used to study and compare conversational behavior across tasks.
Core Capabilities:
- Research-focused toolkit for dialogue system development
- Large datasets and ready-to-use conversational models
- Tools designed for testing and academic experimentation
Typical Applications: Evaluate online store chatbots, assess language quality, and test healthcare conversation flows.
14. Google Dialogflow
Google Dialogflow is a cloud-based orchestration platform built for creating conversational interfaces with strong language understanding. It handles voice and text interactions, connects closely with Google Cloud services, and supports deployment at enterprise scale.
Core Capabilities:
- Cloud-based language understanding using Google’s processing models
- Full support for voice and text conversations across devices
- Enterprise connections with Google Cloud and external services
Typical Applications: Gather customer feedback, direct technical support calls, and respond to event questions.
15. Microsoft Bot Framework
Microsoft Bot Framework provides a robust SDK for building conversational bots. It connects smoothly with Azure Cognitive Services, Microsoft Teams, and other Microsoft tools. The platform supports complex conversations, multiple languages, and large-scale enterprise use.
Core Capabilities:
- Full SDK with tools for multi-language bot development
- Direct access to Azure Cognitive Services for added intelligence
- Tight links with Office 365, Teams, and the wider Microsoft stack
Typical Applications: Support IT help desks, monitor open support tickets, and screen incoming sales leads.
16. IBM Watson Assistant
IBM Watson Assistant is an enterprise-focused chatbot platform built with advanced language understanding and broad business system support. It allows secure deployment across channels and fits organizations running large conversational automation programs.
Core Capabilities:
- Enterprise AI chatbot development solutions with strong language understanding
- Integration options across internal systems and workflows
- Multi-channel delivery across voice, text, and web interfaces
Typical Applications: Manage service requests, suggest related offerings, and report service interruptions.
17. Amazon Lex
Amazon Lex is AWS’s native chatbot builder designed for voice and text conversations. It integrates with AWS Lambda for serverless execution, making it suitable for scalable conversational solutions inside the AWS environment.
Core Capabilities:
- Chatbot builder with support for voice and text input
- Language understanding for intent detection and entity capture
- Serverless execution through Lambda with automatic scaling
Typical Applications: Follow return requests, help users find nearby stores, and collect order details through voice input.
Multi-Agent Systems For Autonomous Collaboration
This group focuses on coordination rather than single-agent execution. These frameworks support teams of autonomous AI agents that share roles, exchange information, and complete work together with limited human input.
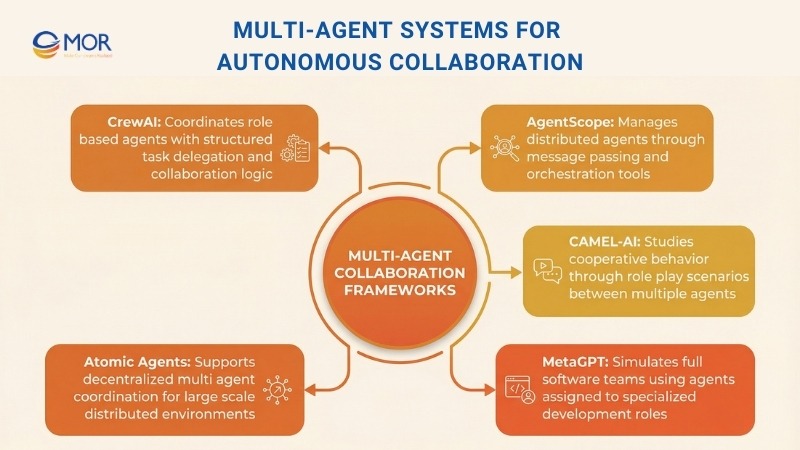
18. CrewAI
CrewAI is built around role-based collaboration between multiple agents, with clear task delegation and coordination logic. It allows groups of AI systems to work together on complex projects through structured workflows and shared responsibilities.
Core Capabilities:
- Role-based collaboration with defined duties and reporting lines
- Smart task delegation that balances workload across agents
- Workflow management with tracking and coordination controls
Typical Applications: Draft press releases, conduct content reviews, and automate SaaS pricing studies.
19. AgentScope
AgentScope uses a message-passing model to support orchestration and distributed execution across many agents. It provides a scalable base for building advanced multi-agent systems that rely on fast communication and coordinated task handling.
Core Capabilities:
- Message-based communication between agents with reliable protocols
- Orchestration tools for managing complex processes
- Distributed execution support for large multi-agent setups
Typical Applications: Send renewal alerts, handle form processing, and prepare legal summaries.
20. CAMEL-AI
CAMEL-AI supports role-play scenarios between multiple agents and helps teams study emerging behaviors. It is often used to explore how agents cooperate, align, and adapt inside controlled environments.
Core Capabilities:
- Role-play systems with detailed interaction modeling
- Tools for observing and analyzing emergent behavior
- Support for alignment studies related to AI safety and cooperation
Typical Applications: Simulate investor meetings, train interview agents, and demonstrate procurement workflows.
21. MetaGPT
MetaGPT recreates full software teams by assigning roles like product managers, developers, and QA engineers to separate agents. It automates the software lifecycle through coordinated collaboration, helping teams manage complex builds with less manual oversight.
Core Capabilities:
- Realistic team simulation with clearly defined roles
- Automation across planning, development, testing, and release stages
- Structured collaboration with communication between agent roles
Typical Applications: Plan product roadmaps, prepare internal policies, and review interface design flows.
22. Atomic Agents
Atomic Agents is an open source framework created for multi-agent systems that follow a decentralized design. It supports distributed execution and coordination across independent agents, making it suitable for large and fast-changing environments within the autonomous agents ecosystem.
Core Capabilities:
- Multi-agent coordination supported by clear communication rules
- Decentralized setup for independent execution and teamwork
- Distributed task handling with balanced workload management
Typical Applications: Route incoming support tickets, track vendor service levels, and speed up hiring reviews.
Low Code And No Code Platforms For Autonomous AI Agents
These platforms focus on speed and accessibility. They help teams create autonomous AI agent platforms without heavy engineering effort, making them a practical option for fast testing and business-led automation.
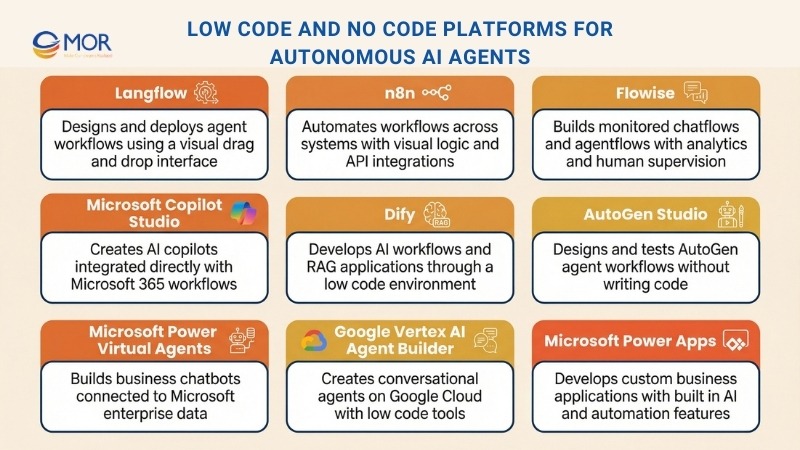
23. Langflow
Langflow provides a visual drag-and-drop environment for designing agent workflows and deploying them through APIs. It reduces entry barriers by allowing users with limited coding experience to build, adjust, and release intelligent agent solutions.
Core Capabilities:
- Visual drag-and-drop interface for clear workflow design
- Full agent workflow builder with reusable components
- API deployment with support for scaling and monitoring
Typical Applications: Create a hiring chatbot, test a sales assistant concept, and map decision logic.
24. n8n
n8n is a visual automation platform that links multiple APIs and automates complex workflows. It connects with AI and language model services, supports custom logic, and suits teams that need flexible automation across systems.
Core Capabilities:
- Visual automation flows with broad API connectivity
- Integration with AI automation services and language model services
- Custom logic using scripts and conditional rules
Typical Applications: Send leads into CRM systems, clean data files, and trigger Slack alerts when churn signals appear.
25. Flowise
Flowise delivers a graphical builder for chatflows and agentflows, with analytics and supervised control built in. It supports monitored interactions, helping teams refine conversational behavior and improve outcomes over time.
Core Capabilities:
- Visual builder for chatflow and agentflow creation
- Integrated analytics for performance tracking
- Human-in-the-loop support for supervision and quality checks
Typical Applications: Design chatbot logic, create support surveys, and notify managers when escalation is needed.
26. Microsoft Copilot Studio
Microsoft Copilot Studio is a visual low code platform built for creating, adjusting, and launching AI copilots and chatbots. It connects deeply with Microsoft 365 applications, allowing automation and task support inside tools teams already use.
Core Capabilities:
- Visual low code environment with an easy design interface
- Customization options for AI copilots and chat experiences
- Direct integration with Microsoft 365 data and workflows
Typical Applications: Summarize leadership emails, create performance dashboards, and support compliance reviews.
27. Dify
Dify provides a low code environment for building AI workflow automation, Retrieval Augmented Generation solutions, and coordinating autonomous agents. It simplifies development and deployment, making advanced AI agent software easier to apply in business scenarios.
Core Capabilities:
- User-friendly low code interface for rapid development
- Support for AI workflows and RAG-based applications
- Orchestration tools for managing and coordinating agents
Typical Applications: Manage client onboarding flows, handle support questions, and generate content idea pipelines.
28. AutoGen Studio
AutoGen Studio delivers a no code workspace for designing, testing, and visualizing agent workflows inside the AutoGen ecosystem. It supports quick trials and iteration of multi-agent setups, helping teams explore custom AI agents without heavy setup.
Core Capabilities:
- No code tools for designing and testing agent workflows
- Native integration with AutoGen orchestration features
- Fast prototyping for validating agent interaction logic
Typical Applications: Trial sales assistant agents, simulate product research tasks, and review meeting summaries.
29. Microsoft Power Virtual Agents
Microsoft Power Virtual Agents is a low code chatbot platform that helps business teams build conversational solutions without deep technical work. It connects with Microsoft 365, Azure, and Dataverse, supporting scalable rollout and automation across enterprise setups.
Core Capabilities:
- Low code chatbot builder with a clear visual design experience
- Microsoft 365 connection for direct access to business data
- Azure service integration for cloud-based AI functions
Typical Applications: Respond to HR policy questions, guide users through ticket submission, and suggest learning resources.
30. Google Vertex AI Agent Builder
Google Vertex AI Agent Builder delivers a low code workspace for creating conversational agents on Google Cloud. It combines advanced automation development services with strong integration and scale, supporting context-aware assistants across multiple channels.
Core Capabilities:
- Low code tools for designing conversational agents
- Google Cloud integration with AI and machine learning services
- Scalability for large deployments and ongoing management
31. Microsoft Power Apps
Power Apps is Microsoft’s low code platform for building custom business applications. It blends built-in AI features, workflow automation, and broad integration with Microsoft and external services, forming a flexible AI agent platform for business teams.
Core Capabilities:
- Low code tools for custom application development
- AI support for automated decisions and workflows
- Wide connectivity across Microsoft and third-party systems
Typical Applications: Produce live sales reports, manage time-off requests, and automate invoice approval flows.
Hybrid And Emerging Autonomous AI Agent Frameworks
This category covers flexible frameworks that blend multiple approaches. They often sit between experimentation and production, supporting teams that need adaptable tools inside a growing autonomous agents ecosystem.
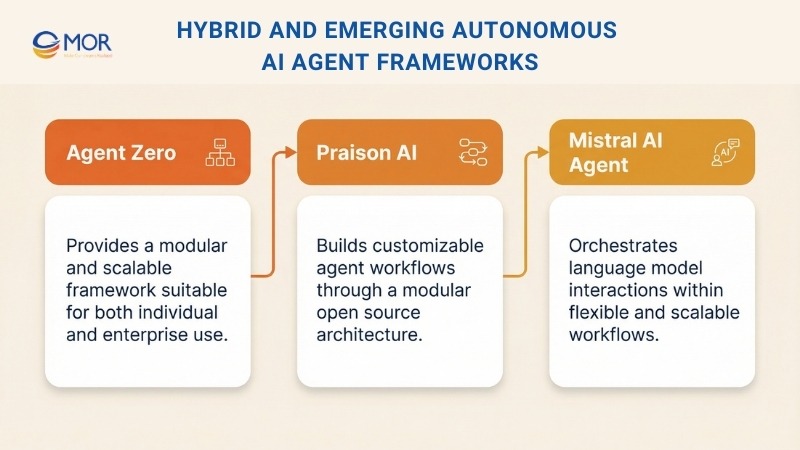
32. Agent Zero
Agent Zero is a modular and scalable framework created for building AI agents with different levels of complexity. It offers a flexible structure, strong API access, and active community support, making it suitable for individual developers and enterprise teams alike.
Core Capabilities:
- Modular structure with scalable design for varied deployment needs
- API-rich foundation with broad integration and developer tooling
- Community-led development supporting personal and enterprise projects
33. Praison AI
Praison AI is a modular open source platform built for creating complex agent workflows. It focuses on flexibility and customization, allowing developers to shape agent systems that match specific operational needs.
Core Capabilities:
- Modular open source setup with adaptable architecture
- Workflow-focused agent design with orchestration support
- High customization for different use cases and environments
Typical Applications: Build comparison engines, manage customer surveys, and automate internal reminder tasks.
34. Mistral AI Agent
Mistral AI Agent centers on orchestration of large language models through a modular structure. It gives developers tools to manage, coordinate, and scale language model interactions, fitting well into custom workflows and multi-agent systems.
Core Capabilities:
- Language model orchestration with focused management tools
- Modular design that supports flexible integration
- Coordination features for handling complex model workflows
Typical Applications: Pull insights from reports, create product visuals, and automate preparation for sales meetings.
Comparison Of The Best Autonomous AI Agents (2026)
The table below provides a side-by-side view of leading frameworks across categories. It helps teams compare the best autonomous AI agents based on strengths, collaboration support, and typical use cases without digging into documentation for each option.
Tool | Type | Category | Primary Strength | Multi-Agent | Voice | Best For |
LangGraph | Open source | LLM-Oriented | Stateful workflows | Yes | No | Complex agent workflows, RAG |
AutoGen | Open source | LLM-Oriented | Multi-agent collaboration | Yes | No | Team simulation, collaborative tasks |
Semantic Kernel | Open source | LLM-Oriented | Cross-platform integration | Limited | No | Enterprise integration |
Auto-GPT | Open source | Autonomous Task | Autonomous execution | No | No | R&D, prototyping |
AgentGPT | Open source | Autonomous Task | Browser-based simplicity | No | No | Experimentation, demos |
BabyAGI | Open source | Autonomous Task | Educational simplicity | No | No | Learning, proof-of-concept |
SuperAGI | Open source | Autonomous Task | Full-stack platform | Yes | No | Enterprise agent deployment |
Devin | Proprietary | Autonomous Task | Code execution | No | No | Software development |
OpenDevin | Open source | Autonomous Task | Developer productivity | No | No | Development assistance |
Rasa | Open source | Conversational AI | NLU capabilities | Limited | Yes | Enterprise chatbots |
Botpress | Open source | Conversational AI | Modular architecture | No | Yes | Business automation |
DeepPavlov | Open source | Conversational AI | Multilingual support | No | Yes | Research, multilingual bots |
ParlAI | Open source | Conversational AI | Research datasets | No | Limited | Dialogue research |
Google Dialogflow | Proprietary | Conversational AI | Cloud NLU | No | Yes | Voice assistants |
Microsoft Bot Framework | Proprietary | Conversational AI | Azure integration | No | Yes | Enterprise chatbots |
IBM Watson Assistant | Proprietary | Conversational AI | Enterprise features | No | Yes | Enterprise customer service |
Amazon Lex | Proprietary | Conversational AI | AWS integration | No | Yes | AWS ecosystem |
CrewAI | Open source | Multi-Agent | Role-based agents | Yes | No | Task delegation |
AgentScope | Open source | Multi-Agent | Message-passing | Yes | No | Distributed execution |
CAMEL-AI | Open source | Multi-Agent | Role-play research | Yes | No | AI research |
MetaGPT | Open source | Multi-Agent | SDLC simulation | Yes | No | Software development |
Atomic Agents | Open source | Multi-Agent | Decentralized systems | Yes | No | Distributed computing |
Langflow | Open source | Low-Code | Visual interface | Yes | No | Rapid prototyping |
n8n | Open source | Low-Code | Workflow automation | Limited | No | Business automation |
Flowise | Open source | Low-Code | Graphical builder | Limited | No | Chatbot development |
Microsoft Copilot Studio | Proprietary | Low-Code | Microsoft 365 integration | Limited | Yes | Business productivity |
Dify | Open source | Low-Code | RAG applications | Yes | No | Knowledge management |
AutoGen Studio | Open source | Low-Code | No-code interface | Yes | No | Agent prototyping |
Microsoft Power Virtual Agents | Proprietary | Low-Code | Low-code chatbots | No | Yes | Business chatbots |
Google Vertex AI Agent Builder | Proprietary | Low-Code | Google Cloud integration | Limited | Yes | Google ecosystem |
Microsoft Power Apps | Proprietary | Low-Code | Custom business apps | Limited | Limited | Business applications |
Agent Zero | Open source | Hybrid | Modular design | Yes | No | Flexible development |
Praison AI | Open source | Hybrid | Agent workflows | Yes | No | Custom workflows |
Mistral AI Agent | Open source | Hybrid | LLM orchestration | Limited | No | LLM management |
How We Evaluated The Best Autonomous AI Agents In 2026
Our review process for identifying leading frameworks followed a structured approach with several evaluation stages. Each option was reviewed across multiple dimensions to reflect how best autonomous AI agents perform in real business environments.
We combined measurable data with hands-on review to confirm that our selections reflect actual performance and adoption, not just feature lists or marketing claims.
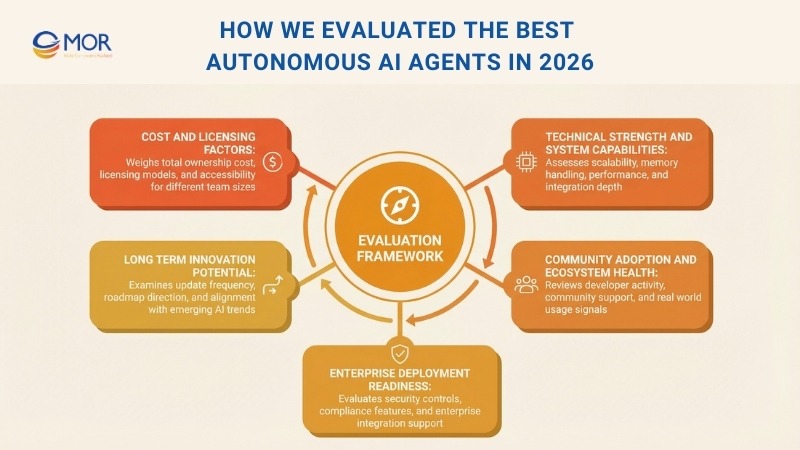
Technical Strength And System Capabilities
Each framework was assessed against core technical factors, including response speed, ability to scale, memory handling, and integration range. We tested these systems across different setups, from single-agent use to complex multi-agent coordination, to confirm they can support enterprise-level demands.
Community Adoption And Ecosystem Health
We reviewed developer engagement using public data from GitHub, including stars, forks, contributor activity, and issue resolution speed. Active communities often signal long-term stability and faster problem solving. We also reviewed Stack Overflow discussions and developer surveys to understand how these platforms are used in real projects.
Enterprise Deployment Readiness
For business use, we reviewed security controls, compliance support, audit logs, role-based access, and enterprise integration options. Platforms that support SSO, LDAP connections, and SOC 2 standards received extra weight for large organization needs, especially where AI autonomous systems run across teams.
Long Term Innovation Potential
We favored frameworks that show steady development, frequent updates, and clear movement with new AI software development trends. This included support for recent language models, links to modern AI services, and roadmaps that align with where autonomous agents in AI are headed.
Cost And Licensing Factors
Our review also covered total ownership cost, including licensing, infrastructure needs, build time, and ongoing upkeep. We weighed feature depth against ease of access so both small teams and large enterprises can adopt suitable AI agent software without strain.
How To Choose The Best Autonomous AI Agents For Your Use Case?
Selecting the right framework is not about following trends. It comes down to fit. Fit with your product goals. Fit with your team’s skills. Fit with the problem you need to solve.
These platforms differ in more than feature sets. They reflect different design mindsets. Some focus on deep control and flexibility. Others simplify complexity so teams can move faster. Some target engineers. Others support business users. A clear choice starts with the right evaluation questions.
The sections below help guide that decision.
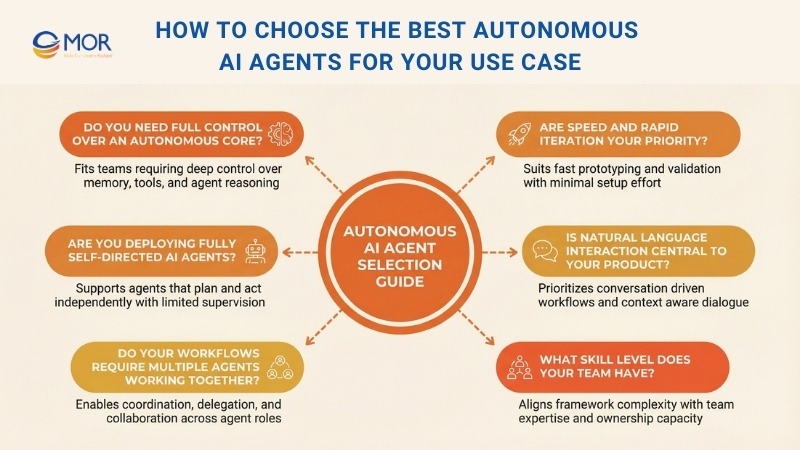
1. Do You Need Full Control Over An Autonomous Core?
When agents sit at the heart of your product, control matters. You may need direct influence over memory, tool access, orchestration logic, and reasoning behavior. In this case, the framework should act more like a development environment than a ready-made utility.
Key questions to consider:
- Does your team have the skills to build and support agent systems over time?
- Do you need fine control over how agents plan actions and make decisions?
- Will the system connect deeply with internal services or external APIs?
If the answer is yes, a flexible and developer-focused option makes sense. These solutions provide full access to the codebase, but they also place responsibility for system design and upkeep on your team.
Representative platforms: LangGraph, AutoGen, Semantic Kernel
2. Are Speed And Rapid Iteration Your Priority?
You may be testing ideas, running internal pilots, or trying to show progress without waiting on heavy infrastructure. In these cases, fast execution often matters more than deep technical control.
Key questions to consider:
- Is the goal to validate an idea or prototype an agent in a short time?
- Does your team lack dedicated backend engineers?
- Do visual builders or low code tools fit your workflow better?
If these points apply, focus on platforms that reduce setup effort and limit coding needs. Many options provide visual editors and ready components that help teams move quickly, even if some flexibility is reduced.
Representative platforms: Langflow, Dify, AutoGen Studio, n8n
3. Are You Deploying Fully Self-Directed AI Agents?
Some systems are built to accept high-level goals and turn them into plans, actions, and results with little human input. This approach can unlock scale, but it also brings added complexity and risk.
Key questions to consider:
- Do you want agents that plan and act on their own, not just reply to prompts?
- Are your use cases open-ended, like research, exploration, or large-scale automation?
- Can your team define limits, checks, or oversight rules?
If these points align with your needs, autonomy should sit at the core of the framework. These solutions often rely on task loops, memory layers, and planning logic. Careful design is important to keep outcomes predictable.
Representative platforms: Auto-GPT, SuperAGI, Devin, OpenDevin
4. Is Natural Language Interaction Central To Your Product?
When agents communicate directly with customers, staff, or end users, conversation design becomes a core concern. Chat assistants, voice tools, and copilots all depend on systems that manage context, understand intent, and handle smooth handoffs.
Key questions to consider:
- Are you building chat-based assistants or voice-driven interactions?
- Do you require multilingual or omnichannel reach across web, mobile, and voice?
- Does your use case depend on multi-turn conversations with context retention?
If so, the framework should prioritize language understanding, dialogue state control, and connections with messaging channels and platforms.
Representative platforms: Rasa, Botpress, Microsoft Bot Framework, Dialogflow
5. Do Your Workflows Require Multiple Agents Working Together?
Some processes cannot be handled by a single agent. You may need a setup where different agents act as planners, researchers, or builders, then pass work between one another. These frameworks focus on collaboration rather than isolated execution.
Key questions to consider:
- Does the workflow require several agent roles working in sequence or at the same time?
- Are you aiming to mirror how a real team divides and completes work?
- Do you need clear visibility into task delegation and progress reporting?
If this matches your situation, choose platforms that support agent-to-agent communication, coordination rules, and structured handoffs. These systems often reflect real organizational flows and depend on clear task breakdowns.
Representative platforms: CrewAI, MetaGPT, CAMEL-AI, AgentScope
6. What Skill Level Does Your Team Have?
A framework may look strong on paper, but it fails if your team cannot use it well. Some options target ML engineers. Others are built for product teams or business users. A clear choice starts with knowing who will build and run these systems day to day.
Key questions to consider:
- Who will own development and upkeep, engineers, analysts, or business teams?
- Do you prefer building through code, a visual interface, or a mixed approach?
- Will your team rely on documentation, support channels, or community help?
The right option is the one your team can deliver and maintain with confidence.
Representative platforms:
- For technical teams: LangGraph, Semantic Kernel, OpenDevin
- For cross-functional or non-technical teams: Langflow, Dify, Microsoft Copilot Studio
Partner With MOR Software For Autonomous AI Agents Built For Enterprise Use
We work with teams that need autonomous AI outsourcing agents to run inside real systems, not isolated demos. Our focus stays on reliability, control, and long-term use across enterprise environments.
We help define how agents plan tasks, store memory, and act within clear boundaries. Goals stay measurable. Decisions stay auditable. Human oversight remains in place where it matters.
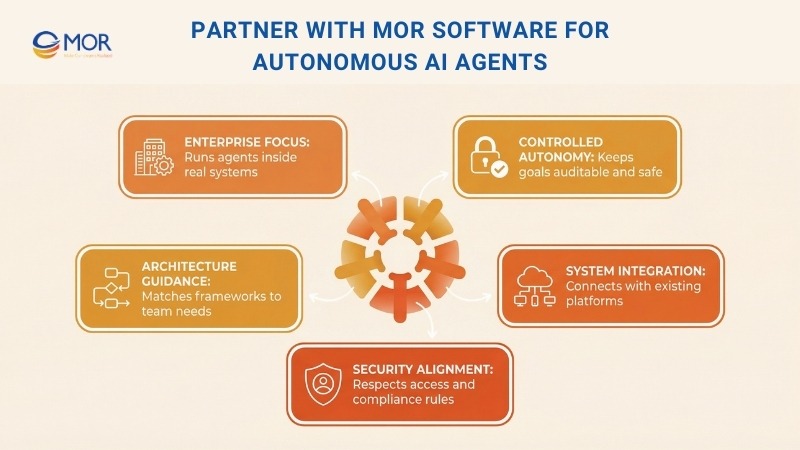
Our teams integrate autonomous AI agents with existing platforms like CRMs, internal tools, and data pipelines. Agents operate within your security rules, access controls, and compliance needs. Nothing runs outside approved workflows.
We also guide framework selection based on team skills and system complexity. Some teams need deep engineering control. Others need faster iteration with visual tools. We align the architecture with how your organization actually works.
If you want autonomous AI project management that scale safely across departments and systems, contact us to discuss how MOR Software supports enterprise-ready implementation.
Conclusion
Autonomous systems are moving fast, but success depends on choosing and building them the right way. The best autonomous AI agents balance independence with control, scale with safety, and automation with human oversight. When designed well, they become long-term assets, not short-term experiments. MOR Software helps teams turn these systems into reliable, enterprise-ready solutions that fit real operations. Contact us to discuss how autonomous AI agents can work inside your organization with confidence.
MOR SOFTWARE
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are autonomous AI agents?
Autonomous AI agents are systems that can plan, decide, and act toward a goal with limited human input. They break goals into tasks, choose actions, and adapt based on results.
How are autonomous AI agents different from chatbots?
Chatbots mainly respond to prompts. Autonomous AI agents go further by setting sub-tasks, using tools, and executing multi-step workflows without constant guidance.
What are the best autonomous AI agents used for today?
They are used for software development, research automation, customer operations, data analysis, internal reporting, and complex workflow orchestration.
Do autonomous AI agents work without any human oversight?
Not completely. Most production systems include guardrails, monitoring, and approval points to keep decisions aligned with business rules and safety requirements.
What skills are needed to build autonomous AI agents?
It depends on the framework. Some require strong engineering skills in Python or APIs. Others support low-code or no-code setups for faster experimentation.
Are autonomous AI agents safe to use in enterprise environments?
They can be, if designed correctly. Safety depends on access control, logging, memory limits, and clear constraints on what actions agents are allowed to take.
Can autonomous AI agents work with existing business systems?
Yes. Many frameworks integrate with CRMs, databases, internal tools, cloud services, and APIs to operate within existing workflows.
What are the main risks of using autonomous AI agents?
Common risks include unexpected behavior, unclear decision logic, data access issues, and cost overruns if agents run without proper limits.
How do teams choose the best autonomous AI agents for their needs?
Teams usually evaluate autonomy level, technical complexity, integration needs, team skills, and how much control or speed they require.
Are autonomous AI agents suitable for small teams or startups?
Yes. Lightweight frameworks and low-code platforms allow small teams to test and deploy autonomous agents without large infrastructure or headcount.
Rate this article
0
over 5.0 based on 0 reviews
Your rating on this news:
Name
*Email
*Write your comment
*Send your comment
1